Features of dental x-rays for children
Previously (about 10-15 years ago), x-rays of baby teeth were not a common procedure. Some parents even believed in the myth that baby teeth have neither a root nor a nerve, so the causes of toothache must lie somewhere on the surface, that is, on the crown. This is absolutely not true, and childhood toothache can be caused by the same reasons as in an adult (more on this below).
When asked whether children undergo dental x-rays, we can confidently answer that yes, they do. Moreover, to accurately diagnose the problem and build the correct treatment plan, this is necessary. Another thing is that preference should be given to relatively safe types of x-ray examination, for example, digital.
There are several recommendations for parents to listen to when going for an x-ray with their child:
- You need to come to the clinic in advance so that you have time to psychologically prepare your child for the procedure. You need to tell him that the x-ray will not cause any pain, so you shouldn’t be afraid of it.
- The child's clothing should be loose, easily removable and without complex metal decorations.
- As for girls, you need to give them a simple hairstyle, without using metal pins, bobby pins, etc.
What is a targeted dental photograph?
Another name for the procedure is targeted intraoral contact radiography - this is a simple and fast method of X-ray diagnostics in dental practice. Research is carried out in clinics using analog X-ray machines or digital radiovisiographs. The doctor gets the opportunity to examine both the condition of the tooth being examined and those located nearby.
- Carry out diagnostics. For example, detect the development of an inflammatory process.
- Evaluate the results of the therapy. This is necessary not only in the treatment of pulpitis, caries or other dental diseases, but also in preparation for prosthetics.
When using analog X-ray equipment, an image is created on film and then transferred to special paper. A digital device allows you to obtain an electronic photograph. If necessary, any area of the image can be enlarged on the monitor for a more thorough examination.
- Interproximal. Allows you to diagnose pathologies of the crown part of the tooth, detect the presence of carious cavities, as well as defects that can form under fillings and crowns.
- Periapical, allowing to assess the condition of bone tissue. This type of imaging helps monitor the quality of therapy provided.
The radiation dose for a dental x-ray is 2-3 μSv, which is very small. For comparison, with fluorography we receive a radiation dose of 500-800 μSv.
Types of X-rays for children
Like adults, children may be prescribed different types of x-rays.
Sight radiograph
A targeted radiograph is performed using a special digital visiograph. A specific problematic tooth or several adjacent ones (maximum 4) are removed.
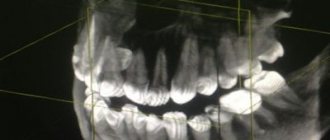
Panoramic radiograph
The panoramic image shows the entire oral cavity: the upper and lower dentition, teeth that have not yet erupted, and the jaws. It also affects the sinuses. An orthopantomogram (this is what a panoramic image is called) is often prescribed to young patients when it becomes noticeable that their teeth are erupting incorrectly: with an inclination, rotation, and so on. In this case, X-rays help to understand whether there is an anomaly in the development of the jaw bone. There are cases when, after the loss of baby teeth, permanent teeth do not appear for a long time. An x-ray will help identify the cause of this deviation.
Operating principle
The technique is based on X-ray radiation, which is combined with special programs and equipment. X-rays are a special type of radiation that can pass through the tissues of our body. These rays pass through some tissues (for example, abdominal organs) very easily, but through others (for example, muscles, ligaments or bone tissue) - worse, since they are partially or completely absorbed.
When taking a panoramic photo, the body receives a certain amount of radiation. Some of the rays are retained by tissues, while the rest passes through them. All information is sent to a special computer, which analyzes the received data and forms a contour image of the organs located in the path of radiation. As a result, the most accurate image of the oral cavity is obtained, on which the roots of all teeth, periodontal tissue, etc. are clearly visible.
Indications for testing
To determine the extent of caries damage
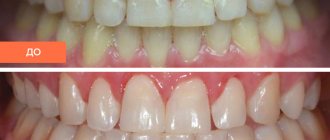
Children's teeth are susceptible to caries. We cannot assume that caries of baby teeth is not dangerous, since they will fall out anyway. Pathology can spread to permanent teeth even before they erupt. Therefore, it is very important to identify caries and carry out effective treatment.
To identify periodontitis and pulpitis
Periodontitis (tooth root pathology, pulpitis) is an inflammation of the pulp where the nerve is located. It is clear that such diseases cannot be detected during the initial examination, because they are hidden in the tooth itself or inside the gums. The child’s main complaint is pain in his baby teeth, and the ability to identify its cause is through an X-ray photo.
When planning endodontic treatment
Endodontic treatment is a set of procedures aimed at preserving a tooth. When emerging caries causes complications, such as pulpitis or periodontitis, the doctor needs to perform therapeutic manipulations inside the tooth. To understand how much pathology has affected the tooth, what percentage of it is destroyed, you need to take an x-ray.
To assess the condition of the permanent tooth buds
An assessment of the condition of the permanent tooth buds is also required before endodontic treatment. It is necessary in order to understand whether the permanent teeth have been affected by pathology and how close they have already descended to the milk teeth.
To diagnose and determine treatment regimens for pathologies of occlusion or teething
At an early age, it is still relatively easy to correct an incorrectly formed bite or correct the position of erupted teeth. This can be done using braces or other special systems. However, to begin orthodontic intervention, you need to understand how serious the pathology is. X-rays help with this.
To determine the reasons for the delay in the appearance of permanent teeth
If a child does not have baby teeth before one year of age, the doctor may order an X-ray to predict their appearance. Of course, such a developmental pathology as adentia (when there are simply no rudiments of baby teeth) is extremely rare, but it is still worth excluding it completely and understanding how soon the first tooth can appear.
Interpretation of a dental radiograph
Only a dentist or radiologist can decipher and describe a dental image. The image shows the tooth: its root, internal canals, shape, anatomical features.
- Examines the rigidity, density and uniformity of the bone structure. Evaluates the location of each element of the dentition.
- Determines the presence of signs of clearing or darkening, indicating the development of an inflammatory process, cysts, granulomas, neoplasms.
- Depending on what the dental x-ray shows, a diagnosis is made.
Carious formations in the picture look like light areas of various shapes with unclear boundaries. The development of pulpitis is characterized by bone damage. The image shows a violation of its homogeneity in the interroot space. With the development of periodontitis, a granuloma appears in the area of the tooth root in the form of a darkened round shape with clear contours. With periodontitis, the image shows a decrease in the density of the bone structure, a decrease in the height of the partitions between the elements of the dentition, and the formation of “pockets.”
How is research conducted?
Panoramic dental x-rays are done for children, just like for adults:
- The child stands inside the orthopantomograph.
- He clamps the plastic tube between his teeth and keeps his lips closed.
- The device blade is moved as close to the patient as possible.
- A picture is taken (while the device rotates around the child’s head). This takes no more than 20-30 seconds, during which you cannot move or breathe.
A targeted photograph is taken as follows: the child sits on a chair and approaches the device.
Next, he wraps his mouth around the digital sensor and clenches his teeth. A picture is taken (takes a few seconds); during this process you cannot move or breathe. To protect the body from exposure to x-rays, a special apron is worn.
Are there any risks?
Modern X-ray machines are characterized by a low dose of radiation, but since exposure to X-rays cannot be completely ruled out, it is recommended that X-rays be taken no more than 2 times a year for children with baby teeth and no more than once every 1.5 years for adolescents. The need for diagnosis is assessed by the attending physician. If the risk from x-rays is lower than the risk of complications from dental pathology, then the specialist may prescribe a study with a more frequent frequency.
There are no risks of side effects after radiography if all the rules of the procedure are followed. There are no contraindications to the study. The exception is the patient's serious condition or previous irradiation.
For children under the age of one year, an X-ray of the teeth/jaw is taken if other diagnostic methods have turned out to be uninformative or there are contraindications to their use. Thus, children are examined mainly only in case of mechanical injuries.
Contraindications
If there is bleeding
Bleeding in the mouth, caused, for example, by problem gums, can affect the quality of the X-ray image. First, the doctor must prescribe hygiene procedures that can stop the bleeding, and only then send for x-rays.
If you feel unwell
If your child is sick, has a fever, or simply feels unwell, you should not take him for an x-ray. It is better to postpone this procedure until complete recovery.
Pros and cons of the diagnostic method
The use of a dental visiograph has a number of advantages compared to analog X-ray machines. First of all, it is an opportunity to get a clear picture of the tooth and the tissues around it. It is convenient to store the resulting images on a computer or other electronic media, printing them if necessary. A digital image allows a more detailed assessment of the clinical picture, since the image can be enlarged several times. In addition, digital dental radiography is a safe procedure. If necessary, multiple procedures may be performed. For example, during implantation, control images are taken before and after each implant is installed. And also after complete completion of prosthetics. The equipment used is characterized by a reduced level of radiation exposure. The dose of radiation that the body of the person under study receives is so small that it does not cause any harm to health. Most often, it does not exceed the natural background recorded in some megacities. Despite the large number of advantages, this method has disadvantages. For example, the image can be performed only in 1 plane covering a small area of tissue. Therefore, the maximum effectiveness of the method is achieved at the stage of early diagnosis or to control the quality of therapy already carried out.
Where can I take a photo and how much does it cost?
Targeted radiography can be performed in any specialized medical institution. The average cost of the procedure is about 400-450 rubles. Some clinics include in the cost of conducting several studies at once, which involve monitoring the treatment being carried out.
All categories of patients, both adults and children, can take a targeted photograph of a tooth. The procedure is prescribed with caution to pregnant women and infants under 2 years of age.
A referral for a radiovisiographic image is given by a dentist. The resulting image makes it possible to determine the presence of a problem, confirm or refute the diagnosis, and prescribe treatment. To monitor the patient’s condition during treatment, the doctor may recommend taking a second photo of the tooth.
Causes and consequences of dental pathology
Abnormal two-row growth is possible for many reasons:
- heredity;
- chronic colds and decreased immunity;
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of soft foods and purees;
- lack of vitamins and useful elements;
- premature removal of milk units;
- disturbance in the location of tooth germs.
With timely treatment, the orthodontist will easily straighten the bite and place each tooth in its proper place. If you delay visiting a doctor, the consequences can be serious:
- malocclusion;
- problems with hygiene and the development of caries;
- facial deformation due to jaw imbalances;
- ugly smile.
A sign of a potential shark jaw is the absence of gaps between the teeth in a 4-6 year old child. Insufficient space is the first prerequisite for the appearance of a second row of teeth in children and a signal for an attentive parent.
It is easy to see an incorrectly growing tooth, especially in the lower jaw. During the period of change in bite, dentists recommend monitoring the process - periodically conducting home or professional examinations and listening carefully to the baby. Complaints of discomfort in the mouth, inconvenience of chewing and pain indicate the need to visit a dentist to assess the condition of the oral cavity.