From this article you will learn:
- reviews on Ultracain, release forms,
- pros and cons of the drug,
- How much does Ultracaine anesthesia cost?
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
The anesthetic Ultracaine is a drug in the form of an injection solution that has a very high analgesic effect when administered locally into tissues. The main active component of ultracaine is the substance “articaine hydrochloride” (Articaine), which makes it possible to classify this drug as an anesthetic of the articaine series. Ultracaine is most often used in dentistry, which is explained by its high efficiency.
There are several forms of release of this drug, which differ from each other in the concentration of the vasoconstrictor component (epinephrine) included in ultracaine. It is added to articaine to locally reduce blood supply in the anesthesia zone and reduce the leaching of the anesthetic from the tissues. Those. Epinephrine increases the duration and depth (strength) of anesthesia.
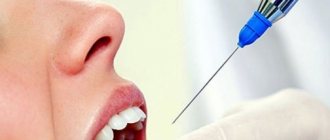
Anesthetic Ultracaine and carpule syringe –
For dentistry, the anesthetic is available both in the form of regular injection ampoules and special cartridges called carpules (these are most often used). The anesthetic carpule is inserted inside a special carpule syringe, which has a piston in the form of a handle, and a special double-edged needle is inserted into it from the side of the syringe nose. When pressing on the syringe piston, the latter presses on the movable rubber liner inside the carpule, which leads to an increase in pressure inside the carpule and the release of the anesthetic solution through the needle.
Ultracaine release forms –
- ultracaine DS-forte (epinephrine concentration 1:100,000),
- ultracaine DS (epinephrine concentration 1:200,000),
- ultracaine D (without epinephrine).
The presence of three forms of drugs is explained by the possible side effects of epinephrine, which can increase the patient's blood pressure. For completely healthy people who do not have cardiovascular or other diseases, Ultracain DS Forte is used. For moderately high blood pressure, Ultracaine DS with a reduced concentration of epinephrine can be used. However, the instructions for use for Ultracain indicate that any of the listed forms can be used from the age of 4 years. We will tell you more about the indications for use of each form below.
How anesthesia is performed in dentistry: video
Ultracaine: price of anesthesia
The cost of 1 carpule of Ultracaine is from 90 rubles (this is the price at which dental clinics purchase it). But in a dental clinic using Ultracain, the price for anesthesia will be approximately 400 to 500 rubles. Unfortunately, you won’t be able to buy a carpule of anesthetic at a pharmacy and bring it with you. This is strictly prohibited by law, because... In this case, the dentist cannot guarantee that the anesthetic is not counterfeit or that it was stored correctly. As a result, the dentist will in any case be to blame for the complications and will be held responsible for it.
Forms of release of the anesthetic Ultracaine -
Ultracaine: the composition, regardless of the release form, 1 carpool of anesthetic contains the anesthetic articaine 40 mg, and the volume of anesthetic solution in the carpul will be 1.7 ml. As for the content of epinephrine, as we said above, each of the three forms will have its own concentration of this vasoconstrictor component (vasoconstrictor). It should also be noted that ultracaine anesthetic contains the preservative sodium disulfite, which is designed to stabilize epinephrine in the drug. Moreover, since Ultracain D is produced without epinephrine, it will not contain preservatives.
Ultracaine DS forte (epinephrine 1:100.000) –
An excellent anesthetic for achieving a pronounced and long-lasting analgesic effect during surgical interventions in the oral cavity, for depulping teeth, etc. However, this form cannot be used for high blood pressure, severe cardiovascular diseases, thyroid disease and bronchial asthma.
For detailed instructions from the manufacturer, read: → Ultracain DS forte – instructions for use (PDF)
Ultracaine DS (epinephrine 1:200.000) –
The best option for use in patients at risk - pregnant and lactating women, patients with compensated cardiovascular diseases. It is undesirable to use for bronchial asthma. Cannot be used for thyroid diseases.
For detailed instructions from the manufacturer, read: → Ultracain DS – instructions for use (PDF)
Ultracaine D (without epinephrine) –
The optimal choice if there is a high risk of allergic reactions, because... This anesthetic is completely free of any preservatives that are necessary to stabilize anesthetics containing adrenaline. In this regard, it is a good choice also for patients with bronchial asthma. Due to the absence of adrenaline, it can be used for diseases of the thyroid gland. The absence of adrenaline allows its use in patients with severe cardiovascular disorders, but it must be taken into account that the duration of action of the anesthetic without epinephrine/adrenaline will be no more than 20 minutes.
For detailed instructions from the manufacturer, read: → Ultracain D – instructions for use (PDF)
Instructions for use ARTICAINE + EPINEPHRINE
The drug is recommended for use in dentistry. Cannot be used to treat children under 4 years of age. The smallest amount of medication that will provide effective pain relief should be used.
Adults:
when removing upper teeth, in most cases 1.7 ml of the drug per tooth is sufficient;
- In most cases, there is no need to perform painful palatal injections. In cases of alternate removal of adjacent teeth, it is possible to reduce the number and volume of injections. If it is necessary to make an incision or suture in the palate, a palatal injection is indicated at the rate of 0.1 ml for each puncture. To remove premolars of the lower jaw, in most cases, infiltration anesthesia in a volume of 1.7 ml of the drug per tooth is sufficient;
- in some cases, repeated buccal injection in a volume of 1 to 1.7 ml is required. In rare cases, a mandibular nerve block may be indicated. To prepare a tooth cavity or tooth stump for a crown, drug injections are used in volumes of 0.5 to 1.7 ml per tooth.
When treating mandibular molars, a nerve block technique should be used. In surgery, the volume of the drug is selected individually depending on the severity and duration of the operation and the individual characteristics of the patient.
In elderly patients
Due to weakened metabolic processes and a lower volume of distribution, increased plasma levels of the drug may be observed. The risk of drug accumulation increases after repeated applications (eg, repeat injections). For this reason, for older people, as well as for adults with heart and liver diseases, it is recommended to use the drug in lower dosages compared to those recommended for adult patients (the minimum amount for a sufficient depth of pain relief).
In patients with liver failure
the active substance of the drug (Articaine) is metabolized in the liver. Due to its long duration of action and systemic accumulation, the anesthetic should be used in lower doses for patients with impaired liver function.
In patients with renal failure
Articaine and its metabolites are mainly excreted in the urine. Due to the long duration of action and systemic accumulation, lower doses of the anesthetic should be used in patients with severe renal impairment.
In patients with special genotypic characteristics:
in patients suffering from congenital or acquired deficiency of plasma cholinesterase activity, the use of the drug is contraindicated.
Other special populations:
patients with certain diseases (angina pectoris, atherosclerosis), as well as in patients who are simultaneously taking medications that may interact with aticaine and/or epinephrine, the dose is also reduced. For patients belonging to special groups, it is recommended to use a minimum amount of the drug to achieve a sufficient depth of anesthesia.
Children and teenagers:
The amount of drug to be administered is determined by the age and body weight of the patient and the extent of the surgical procedure.
Children over 4 years old and adolescents aged 13-18 years:
| Body weight, kg | Recommended dosage | |
| Articaine/mg/child | HP/ml/child | |
| 20 — <30 | 10-40 | 0.25 ml - 1 ml |
| 30 — <40 | 20-80 | 0.5 ml - 2 ml |
| 40 — <45 | ||
Since articaine is quickly distributed in tissues, and bone density in children is lower than in adults, conduction anesthesia can be used in children and adolescents instead of infiltration.
Children under 4 years old:
the drug is contraindicated in children under 4 years of age, as safety and effectiveness have not been established.
Maximum recommended dose:
- For adults:
for healthy adult patients, the maximum dose is 7 mg articaine per kg body weight (500 mg for a 70 kg patient), equivalent to 12.5 ml of drug. The maximum dose is 0.175 ml of solution per 1 kg.
For children:
The amount to be injected should be determined based on the age and weight of the child and the extent of the operation. Do not exceed the equivalent of 7 mg articaine per kg body weight (0.175 ml drug/kg).
| Body weight (kg) (respective age groups ± within the height chart) | Maximum permissible dose (equivalent to 7 mg/kg body weight) | |
| Articaine mg/child | HP/ml/child | |
| 20 — <30 | 140 | 3.5 |
| 30 — <40 | 210 | 5.25 |
| 40 — <45 | 280 | 7.0 |
| 45 — <50 | 315 | 7.9 |
| 50 — <60 | 350 | 8.7 |
| 60 — <70 | 420 | 10.5 |
| 70 — <80 | 490 | 2.12 |
All the above dosages are typical for Articaine + Epinephrine (40 mg/0.01 mg)/ml and (40 mg/0.005 mg)/ml. Articaine + Epinephrine (40 mg/0.005 mg)/ml is more suitable for routine operations and/or treatments in which stopping bleeding is of secondary importance.
For use in dental anesthesia only!
To avoid intravascular injection, careful aspiration control should always be ensured in at least two planes (rotating the needle 180°), although a negative aspiration result does not guarantee the complete exclusion of involuntary and undetected intravascular injection. The injection rate should not exceed 0.5 ml for 15 seconds, that is, 1 cartridge per minute.
In most cases, serious general reactions of the body as a result of accidental intravascular injection can be avoided by the following injection technique - after aspiration, slowly inject 0.1-0.2 ml of the drug, and use the rest no earlier than 20-30 seconds later.
Opened cartridges should not be used on other patients. Residues must be disposed of.
Ultracain: reviews from dentists
As a practicing physician, I try to use this particular anesthetic primarily, although its cost is 1.5-2 times more expensive than similar anesthetics based on articaine.
Thanks to the optimal composition, a minimum of preservatives in the composition (and the complete absence of preservatives in the form of Ultracaine D), this anesthetic can be used in all patients at risk (for cardiovascular, endocrine disorders, allergies, pregnancy and lactation). Ultracaine reviews from dentists are also as favorable as possible because this anesthetic will be a good choice if you have an allergic reaction to amide group anesthetics, for example Novocaine, Lidocaine and others. But in addition to the high safety profile, this anesthetic is also much stronger than its predecessors (see below). In addition, this anesthetic acts in inflamed tissues, but Novocain practically does not anesthetize in the presence of purulent inflammation.
The duration of action and depth of anesthesia will depend on the concentration of epinephrine in the composition of the product, for example, Ultracaine DS forte 1: 100,000 is the most powerful drug in the line. When conducting conduction anesthesia on the lower jaw, the duration of action averages from 2 to 3 hours. With infiltration anesthesia on the lower and upper jaws - a little more than an hour (24stoma.ru).
Ultracaine or lidocaine: which is better?
- Ultracaine is stronger than Novocaine - 5-6 times,
- more effective than lidocaine - 1.5-2 times.
Ultracaine during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The optimal form of this anesthetic during pregnancy is Ultracaine DS with an epinephrine concentration of 1:200,000. The use of anesthetics without epinephrine (or adrenaline) in pregnant and lactating women is generally not recommended. This is due to the fact that adrenaline, by constricting blood vessels at the injection site, slows down the absorption of the main component (articaine) into the blood, and accordingly this will reduce the peak concentrations of articaine in the blood, and therefore its possible side effects on the fetus.
Ultracaine during breastfeeding - after anesthesia with Ultracaine, the content of articaine in breast milk is possible, but the concentration is so low that it cannot cause any harm. Therefore, there is no need to give up breastfeeding. The epinephrine content in Ultracaine DS is also very small and cannot adversely affect either the mother or the child.
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a dentist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Local anesthesia in dentistry” (Baart J.), 5. https://dental.sanofi. de/.
Overdose
At the first manifestations of toxic effects, such as dizziness, motor agitation or stupor during drug administration, its administration should be stopped and the patient should be transferred to a horizontal position with the lower limbs raised. The airway should be maintained and hemodynamic parameters (heart rate and blood pressure) monitored. It is always recommended, even if the symptoms of intoxication seem mild, to install an intravenous catheter in order to be able to immediately administer the necessary medications intravenously, if necessary.
In case of breathing problems, depending on their severity, oxygen supply is recommended, and if there are indications for artificial respiration, endotracheal intubation and artificial ventilation of the lungs are recommended.
The administration of centrally acting analeptics is contraindicated.
Muscle twitching and generalized convulsions can be relieved by intravenous administration of short-acting or ultra-short-acting barbiturates. It is recommended to administer these drugs slowly, under constant medical supervision (risk of hemodynamic disorders and respiratory depression) and with simultaneous oxygen supply and monitoring of hemodynamic parameters.
Often, bradycardia or a sharp decrease in blood pressure can be eliminated by simply moving the patient to a horizontal position with the lower limbs elevated.
In case of severe circulatory disorders and shock, regardless of their cause, the drug should be discontinued and the patient should be transferred to a horizontal position with the lower limbs elevated. Oxygen should be supplied, intravenous administration of electrolyte solutions, glucocorticosteroids (250-1000 mg methylprednisolone), if necessary, plasma substitutes, and albumin.
With the development of collapse and increased bradycardia, slow intravenous administration of a solution of epinephrine (0.0025-0.1 mg) under the control of heart rate and blood pressure is indicated. If it is necessary to administer doses exceeding 0.1 mg, epinephrine should be administered by infusion, adjusting the rate of administration under the control of heart rate and blood pressure.
Severe tachycardias and tachyarrhythmias can be stopped by the administration of antiarrhythmic drugs, with the exception of cardio-nonselective beta-blockers (see section “Contraindications”).
Increases in blood pressure in patients with arterial hypertension should be reduced with vasodilators if necessary.
Drug interactions
Contraindicated combinations
Concomitant use with non-selective beta-blockers, for example, propranolol, due to the risk of developing a hypertensive crisis and severe bradycardia.
Interactions to Consider
Concomitant use with tricyclic antidepressants or MAO inhibitors
The effect of vasoconstrictors that increase blood pressure, including adrenomimetics, such as epinephrine, can be enhanced by tricyclic antidepressants or MAO inhibitors. Similar observations have been reported for concentrations of norepinephrine 1:25,000 and epinephrine 1:80,000 when used as vasoconstrictors. The concentration of epinephrine in Articaine with adrenaline is lower - 1:200,000. However, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of such an increase in action.
Concomitant use with drugs that depress the central nervous system
Local anesthetics enhance the effect of drugs that depress the central nervous system. Narcotic analgesics enhance the effect of local anesthetics, but increase the risk of respiratory depression.
Simultaneous use with heparin, acetylsalicylic acid
When injecting Articaine with adrenaline to patients receiving heparin or acetylsalicylic acid, bleeding may develop at the injection site.
Concomitant use with muscle relaxants
It is possible to enhance and prolong the action of muscle relaxants.
Concomitant use with antimyasthenic drugs
The antagonistic effect on skeletal muscles, especially when used in high doses, requires additional adjustment in the treatment of myasthenia gravis.
Concomitant use with cholinesterase inhibitors
The metabolism of local anesthetic drugs may be slowed down.
Concomitant use with hypoglycemic agents for oral administration
Epinephrine may inhibit the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells and reduce the effects of oral hypoglycemic agents.
Simultaneous use with certain inhalation anesthetics (halothane)
Halothane may increase the sensitivity of the myocardium to catecholamines and therefore increase the risk of developing cardiac arrhythmias after injections of Articaine with epinephrine.
Simultaneous use with disinfectant solutions containing heavy metals
When treating the injection site of a local anesthetic with disinfectant solutions containing heavy metals, the risk of developing local reactions increases: swelling, pain.
special instructions
The drug cannot be administered intravenously!
Do not inject into an inflamed area!
To avoid intravascular injection, a double aspiration test should be performed before administering the drug.
Injection pressure should correspond to the sensitivity of the tissue.
To prevent the introduction of infections (including viral hepatitis), it is necessary to ensure that new sterile syringes and needles are always used when taking the solution from ampoules. Opened cartridges cannot be used again for other patients!
Do not use a damaged cartridge for injections.
In patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system (chronic heart failure, pathology of the coronary vessels, angina pectoris, heart rhythm disturbances, a history of myocardial infarction, arterial hypertension), cerebrovascular disorders, a history of stroke, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, and also in the presence of severe anxiety, it is advisable to use articaine without epinephrine.
You can eat food only after the local anesthesia has worn off (sensitivity has been restored).
Parents (guardians) of young children should ensure that they do not cause soft tissue damage to themselves when bitten during the period of anesthesia.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and perform work associated with increased danger
Based on the results of clinical studies, it was found that local anesthesia Articaine with adrenaline does not cause any noticeable impairment in the ability to drive vehicles. However, the doctor must decide when, after dental surgery, the patient can return to driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.