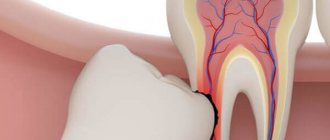
Tooth extraction is carried out plannedly, as well as for emergency indications.
The main indications for planned tooth extraction: complete or severe destruction of the tooth crown and the inability to use it for prosthetics, chronic periodontitis that is not amenable to conservative treatment, grade III tooth mobility in periodontal diseases, and others.
Urgent tooth extraction is indicated for purulent periodontitis, acute osteomyelitis, periostitis, sinusitis, lymphadenitis (if the source is a diseased tooth), fracture of the tooth crown exposing the pulp and some other diseases and conditions.
Removing various teeth has some of its own characteristics, for example, removing teeth with a crown is somewhat simpler than removing tooth roots. The extraction technique for the teeth of the upper and lower jaws, incisors and molars is also slightly different.
When is molar tooth extraction indicated?
Only an experienced doctor can make an adequate decision about whether it is necessary or not to remove a molar tooth after a thorough examination. For detailed diagnostics, not only a visual examination is used, but also an analysis of the results of radiography or visiography. Indications for the removal of permanent teeth can be divided into absolute (in which the tooth requires mandatory removal) and relative (in these cases, the opinions of doctors may be divided).
Mandatory removal of a molar tooth is indicated in the following cases:
- there is a high probability that odontogenic osteomyelitis will develop;
- there is a risk of developing phlegmon or abscess.
- tooth root fracture.
Among the relative indications for the removal of molars are the following:
- if due to a dental disease, inflammation has developed in the area of a specific tooth (sinusitis);
- with longitudinal fractures of the tooth root;
- if the root and coronal part are so badly destroyed that therapeutic treatment is fraught with serious difficulties;
- if during the treatment of root canals their walls were damaged;
- tooth mobility is in the third or fourth degree;
- a fracture of the alveolar process, on the line of which the tooth is located, was diagnosed;
- in the oral cavity there are pathologies occurring around dystopic or impacted teeth;
- if orthopedic treatment is being carried out and certain molars cannot be used as support;
- if an orthopedic dentist or orthodontist has prescribed removal of molars and premolars.
As for the relative indications for molar tooth extraction, if you disagree with the opinion of one specialist, you should consult with another. This will help you choose the most gentle treatment and, possibly, save teeth that are at risk of removal.
Atraumatic removal
If the tooth is severely damaged and it is difficult for the surgeon to pull it out, atraumatic extraction is recommended. It is also indicated in cases of high crowding, large suppuration, or when too twisted roots interfere with normal removal. But the most common reason for such manipulation is preparation for implantation. For implantation and successful implantation, it is extremely important to carefully remove the tooth so as not to harm the bone tissue.
Therefore, it is better that all extraction procedures are carried out by the same specialist who will place the implant. Atraumatic removal is characterized by a set of advantages:
- Saves bone tissue for implantation;
- Accelerated healing;
- Suitable for difficult cases.
During the procedure, the doctor divides the tooth and removes it piece by piece. At the same time, it gently peels off the surrounding tissues without damaging them. The entire procedure takes 20 minutes (usual removal takes 10 minutes).
You can find out how much tooth extraction costs in our clinic by leaving a request on the website (a manager will call you back at a time convenient for you) or by calling the administrator.
Is it painful to remove molars?
Modern dentistry uses the latest drugs for local anesthesia when removing molars. Therefore, the patient should not be afraid of pain or serious discomfort during the process of tooth extraction. The thinnest needles are used to administer anesthetic injections into the gum area, so the injection is virtually painless.
Preparation
Before the procedure, the doctor conducts a consultation, a detailed examination and an x-ray of the tooth to be extracted: the degree of damage to the dental crown and the presence of anomalies are revealed. Based on the diagnostic results and radiographs, a clinical picture is formed, the number, size, shape of the roots, their relationship with the mandibular canal and maxillary sinus, and the size of bone resorption are established.
When removing 8 units, be sure to take into account its position, the width of the retromolar space, and the depth of immersion. Based on these data, the doctor draws up a surgical procedure and selects surgical instruments.
If the patient has an inflammatory focus in the periodontium, antibiotics are prescribed 24 hours before the planned surgery. Patients who are terrified of the dental chair are given sedative preparation.
Stages of molar removal
Before deciding to remove a molar tooth, the dentist conducts an examination using radiography or visiography. Based on the results of image analysis, the choice of surgical intervention technique is made. The procedure is then carried out in the following steps:
- An anesthetic drug is injected into the gum area, which leads to numbness in the patient’s mouth; Ultracain and Septanest are used in the Optimal Choice clinics.
- the ligaments that hold the tooth in the socket and the gums are peeled off using a special tool in order to reduce the risk of rupture of the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- forceps are applied to the tooth or, in difficult cases, an elevator is used to loosen the damaged tooth, after which it is removed from the socket;
- the empty tooth socket is cleaned of tooth or bone fragments and checked for the presence of roots;
- if necessary, a hemostatic sponge is used or sutures are applied to stop bleeding.
After surgery, the doctor may prescribe analgesics to relieve pain after the anesthesia wears off.
Gentle removal
The Diamant dental clinic has set high standards for the quality of medical services. We not only provide multi-stage sterilization of instruments and comply with special requirements for office sterility. Our specialists use gentle technologies that reduce the consequences of surgery.
Our work includes:
- effective anesthesia (reliable pain relief, reduction in the amount of bleeding at the surgical site);
- atraumatic extraction (for complex cases);
- laying a self-absorbing antiseptic drug;
- suturing the hole.
You can have a tooth removed in Moscow in our clinic. Gentle intervention: quickly, without pain and with minimal healing time!
Prices for tooth extraction can be found in the “cost of services” section on our website, and can also be clarified by calling the administrator.
Possible complications
If the procedure for removing a molar tooth was carried out by a doctor without proper experience, sanitary and hygienic requirements were violated, or the patient violated medical recommendations, then there is a possibility of complications:
- heavy bleeding that cannot be stopped for a long time;
- inflammatory process in the socket caused by infection;
- jaw movements become limited due to problems with the masticatory muscles;
- the alveolus is exposed;
- sharp edges of the hole are formed;
- limited osteomyelitis is diagnosed in the socket from the extracted tooth.
Symptoms of developing pathologies can be severe pain, unpleasant odor from the mouth, purulent discharge from the socket, the appearance of white plaque on the alveoli and the onset of bleeding. In these cases, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Indications
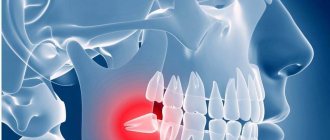
- impacted wisdom teeth. Retention is a delay in the eruption of a formed tooth due to lack of space in the row, pathology of the mucous membrane, diseases that inhibit the development of the skeletal system and prevent the tooth from erupting (tumors, local inflammation, jaw injuries). Difficult eruption of the “eighth” units provokes dangerous complications - phlegmon, abscess, pericoronitis;
- dystopic third molars on the upper/lower jaw. Anomalies in the position of the organ lead to damage to neighboring chewing units, crowding of row units, and the development of inflammatory processes;
- significant destruction/curvature of the root segment without the possibility of restoration;
- fusion of roots with bone tissue;
- presence of follicular cyst/fistula tracts on the anterior or lateral units.
Methods of complex tooth extraction
are divided according to the degree of impact (fragmentation of residues, alternate extraction of elements or extraction of residues completely), depending on the level of destruction of the walls of the hole.
Preventive measures
In order to avoid serious complications after molar tooth extraction, you need to follow a number of recommendations:
- 20 minutes after the end of medical procedures, the gauze swab should be removed from the socket of the extracted tooth;
- In order for healing to occur faster, you should not drink or eat for the first 2-3 hours after surgery;
- for several days you should avoid eating solid foods, as well as spicy and hot foods and drinks;
- hot water procedures and physical activity are contraindicated until the hole is completely healed;
- You cannot wash the hole yourself or try to clean it with foreign objects that have not been disinfected;
- During the first 24 hours after surgery, you should not rinse your mouth;
- A cold compress on the right side of the cheek will help prevent swelling and reduce the likelihood of bleeding.
If the hole does not heal for a long time or it seems that there are remains of a tooth in it, then you should contact your dentist again and under no circumstances try to solve these problems yourself.
Operation stages
- Pain relief
. General or local anesthesia is used, the anesthetic is selected depending on the health status, age, individual characteristics, and allergic status of the patient. - Impacted tooth
. Removing an impacted tooth is made difficult by limited access to the problem tooth - the crown part closed by mucous/bone tissue. After anesthesia, an incision is made into the mucous membrane, the unit is divided with a bur, and it is removed in fragments. - "Eight"
. The eruption of a wisdom tooth in 75-80% of cases occurs against the background of complications and pain, so it is better to remove it in order to avoid problems with the gums and healthy neighboring units in the future. The operation is performed under anesthesia: the doctor dissects the gum and extracts the tooth. The edges of the wound are connected and sutures are applied. - Root
. The complexity of the manipulation depends on the presence/absence of inflammation, the degree of neglect of the diseased tooth, the depth of the branches: the root is cut, the crown is destroyed into individual elements, and all tooth fragments are removed.
Experts' opinion
Question: Is it possible to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction? If yes, then with what?
Answer : During the first 24 hours after a molar tooth has been removed, doctors at the Optimal Choice clinics do not recommend rinsing your mouth at all. Active rinsing of the mouth, even if its goal is to cleanse food debris, can lead to a number of negative consequences. The main danger is the destruction and washing out of the formed blood clot in the socket, which interferes with rapid healing. This can also lead to the development of alveolitis. In the first few days, instead of rinsing, it is better to use baths with a decoction of medicinal plants (sage, chamomile, oak bark), a weak solution of salt or baking soda (or a mixture of them in equal proportions), furatsilin, miramistin, chlorhexidine, if prescribed by a doctor.
Question: After tooth extraction, the gums hurt and swelling is noticeable. What to do?
Answer: Slight tissue swelling and pain are very often consequences of the removal of molars. For relatively tolerable pain, it is recommended to take analgesics prescribed by your doctor. If the pain is severe, then you urgently need to visit the dentist again for a check. A cold compress applied to the cheek on the side of the extracted tooth for 15-20 minutes will help relieve swelling.
Progress of the procedure
Before complex removal, the doctor must prescribe an x-ray to the patient. This is necessary in order to understand the configuration of the roots and know where to make the incisions and what to prepare for during the operation. After preparation, the actual removal begins:
- The patient is given anesthesia. Modern powerful anesthetics can completely eliminate pain during surgery. If the patient cannot tolerate anesthesia or is undergoing a very complex procedure, full anesthesia may be given instead of anesthesia. In this condition, sometimes even several teeth are removed at once.
- If the tooth is partially hidden by the gum, that is, it has not fully erupted, the gum is cut to gain access to it. The problematic tooth is removed using a special elevator.
- If the tooth is completely hidden by gum and bone tissue, it is necessary to cut most of the gum, cut the tooth into 2-3 parts and remove them one by one with an elevator.
- In the most difficult situations, when the lower teeth are close to the mandibular nerve, the operation becomes more complicated, since the roots sometimes completely surround the nerve. In this case, you must first cut down part of the tooth, gain access to the roots, and then divide and extract the roots one by one so as not to damage the nerve.
Features of wisdom teeth
The structure of the last molar is no different from other chewing teeth. It consists of an upper part - crown, neck and roots. The difficulty of removal is due to the location of the unit, as well as the presence of 4-5 roots in the gum cavity, which firmly hold the tooth in its place. In dentistry, there are cases where the root system developed as a single element. This option is rare, but occurs in patients.
Despite the external similarity, the tooth still has differences from other molars:
- It has no predecessors in the form of milk teeth;
- The shape of the root is often very tortuous, so during treatment it becomes difficult to clean the canals;
- Low blood supply, causing rapid aging of the tooth, thinning of the enamel, susceptibility to caries and other diseases leading to removal.
The functionality of wisdom teeth has not been proven according to recent studies. Scientists recognize this organ as a rudiment, so its removal according to indications will not cause any disturbances in the functioning of the entire oral apparatus and the body as a whole. Only 15% of the adult population does not have wisdom teeth.
The appearance of wisdom teeth can disrupt a normal bite. Often, even before the tooth erupts, the patient begins to feel it in the oral cavity. He speaks of his appearance by discomfort in the jaw, pain.
Contraindications
Removal surgery cannot be performed in the presence of oncology, acute infectious/viral diseases, mental disorders, renal failure, circulatory failure, pregnancy in the 1st and 3rd trimesters.
Relative contraindications to removal are:
- carrying out prosthetics with a bridge structure, for which the tooth is a supporting element;
- absence of 6-7 molars, in which case the wisdom tooth is necessary for chewing food;
- allergy to drugs used for anesthesia during removal.
It is not worth removing a wisdom tooth without indications for this intervention, since the procedure is quite painful and complicated, even despite the availability of modern means of pain relief and diagnostics.
Recovery period
On average, the recovery period after surgery lasts 6-10 days. The doctor prescribes complex therapy with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and painkillers and, as healing proceeds, conducts regular examinations of the surgical area.
Requirements for postoperative wound care:
- eating soft and warm foods without irritating ingredients;
- cavity hygiene using gentle means;
- regular gentle rinsing with soda solution or salted water;
- minimal load on the jaw from the removal side.
Lack of control and appropriate care can lead to alveolitis, pericoronitis and dry socket syndrome with subsequent complications in the form of abscesses.