A jaw bruise is a common injury in which the facial skin is not broken. Also, the jaw bone tissue remains intact. For comparison, with bruises a person is able to close his jaw, but with fractures this is almost impossible to do. In both cases, the condition is accompanied by pain and discomfort. Only an experienced doctor can diagnose a bruise and distinguish it from a fracture. For bruises of various origins, the prognosis in most cases is favorable, but it is very important to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis to exclude complications and follow medical recommendations.
Causes of bruises of the lower and upper jaw
- collisions with surfaces;
- various types of blows (during road accidents, collisions with other people, domestic fights, contact sports, accidental blows with objects, etc.);
- falling onto a hard surface.
Most often, signs of a bruise and fracture of the jaw occur in people against the background of road accidents, domestic conflicts, or industrial emergencies. In most cases, it is the lower jaw that is susceptible to bruises.
The severity and nature of the injury also depend on the following factors:
- collision zones;
- the type (and sharpness) of the object that had a detrimental effect on the bone;
- speed of collision or approach with an object;
- condition of facial tissues and bones during mechanical trauma.
Diagnostic methods
To identify existing damage and refute more severe injuries, the doctor performs the following diagnostic procedures:
- Visual inspection of the area that has been subjected to increased mechanical stress;
- Palpation of injured areas;
- X-ray of the skull;
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography, ultrasound (in rare cases).
Based on the results of the study, the doctor describes in detail the method of caring for the injury and prescribes medications that speed up the process of treating the bruise.
The main symptoms of a jaw bruise
- pain in the bruised area, which becomes especially severe with pressure and movement;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- difficulties in speaking;
- it becomes painful for a person to chew;
- there is a loss of strength;
- a lump may form on the jaw;
- temperature rises;
- the jaw goes numb;
- swelling, redness, swelling, and hematomas are noticeable in the area of contact with an object or hard surface.
Unlike the symptoms of fractures, with bruises the jaw connects to the skull. Violation of the connection, as a rule, occurs in fractures (open and closed), dislocation, fracture, etc.
First aid
Before proceeding with the treatment of the emerging pathology, the victim should be given first aid and taken for examination to a traumatologist in order to refute more serious damage to the bones of the skull (fracture, dislocation, displacement).
First of all, it is necessary, using available auxiliary items, to ensure cooling of the injured area. If the injury occurred at home, it is recommended to apply ice, frozen meat, vegetables or fruits to the bruised area of skin.
It is worth remembering that direct contact of the cold compress with the skin is not allowed. It is better to wrap ice products with a towel, rag or bag.
If the injury occurred on the street or in another place where it is not possible to get ice from the refrigerator, doctors recommend using snow, rags (pieces of things) soaked in cold water, bottles of cold water or iron tools. In such situations, it is also very important to avoid direct contact of the object with the skin, because you can introduce an unfavorable infection into the resulting wound area.
To eliminate excessively intense pain, you can take a non-steroidal painkiller.
Under no circumstances should heating the damaged area be allowed. Such manipulations do not improve, but only worsen the situation.
The jaws, the field of a cold compress, should be kept at rest (wrap with a bandage or other material at hand) and go for examination to the hospital, where the doctor will tell you in more detail about the treatment of the bruise.
What to do if your jaw hurts?
If your jaw hurts, it hurts to chew, and the above symptoms are also observed, you should urgently contact a jaw surgeon-traumatologist.
First aid for such injuries looks like this:
- apply a bandage;
- use cold (applications made of ice, snow, frozen objects wrapped in fabric or polyethylene);
- rest until examined by a doctor;
- if your jaw hurts badly on the right or left, you can take a painkiller.
Until the doctor examines you, you should never heat the bone or place it in direct sunlight, so as not to provoke a deterioration in the patient’s condition.
Tooth pain after being hit in the face
Despite their strong structure, our teeth are susceptible to damage due to mechanical stress. A hit to the face can immediately provoke a number of problems with them. Perhaps the most unpleasant of them is tooth pain - a symptom indicating the seriousness of damage to the injured area. How can you quickly get rid of this problem?
Causes
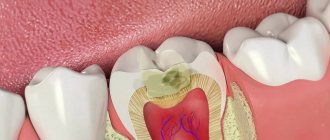
The blow to the face itself may occur on some other part of the head, but pain in the tooth will still most likely occur. By all indicators, this injury is a typical bruise - a closed injury without violating the integrity of the damaged object in anatomical terms. With it, the tooth remains in place, without changing its position relative to the jaw and other teeth, but some parts of it are affected. The mechanism of a bruise is simple: damage occurs to the dental ligaments, which fix the tooth in place and attach it to the jaw bone. With a strong impact, there is even a serious risk of their complete rupture. A severe tooth bruise can lead to tangible consequences. First, there is the possibility of damage to the dental nerve, which can lead to loss of sensitivity. Secondly, a blow to the face can also cause destruction of the dental pulp, which can lead to tooth loss. In this case, pain becomes a signal that dental problems require an immediate solution.
Main symptoms of tooth bruise
Knowledge of the symptoms of a tooth bruise will help you in correctly recognizing the nature of the damage. As a rule, experts identify four main characteristics of a bruised tooth:
- Severe pain (especially in the first few hours after a blow to the face), problems with a correct and painless bite.
- A feeling that the tooth has changed its position relative to the jawbone and other teeth (the victim begins to feel as if the tooth is located a little higher or is bent to the side).
- When blood vessels and the dental nerve rupture, the tooth itself may change color to pink (due to the release of blood inside it). After a few days, the color may change from pink to dark brown (after blood clotting).
- A good indicator of a bruised tooth is the gum near it: if there is damage, it will be inflamed, and the tooth itself may be slightly mobile.
How to cure a bruised tooth?
First aid for a bruised tooth after a blow to the face is to reduce pain. The victim should apply a cold compress to the injury site to help relieve swelling. You should avoid eating solid food for three to five days after the injury. If the pain is too acute, then it is recommended to use such powerful painkillers as analgin, paracetamol or tempalgin. We remind you that in any case you will have to see a specialized doctor: as mentioned above, after a blow to the face there is a risk of rupture of the dental nerve or destruction of the pulp, and therefore in order to avoid complications you will definitely need the help of a professional.
Diagnosis and treatment of jaw bruises
For minor injuries, including cracks in the jaw, hospitalization of the patient is not necessary. The following steps are used for diagnostics:
- general examination by a dentist, maxillofacial surgeon, orthopedist-traumatologist. You may need to consult a neurologist (for example, in the case of a parallel concussion) or an otolaryngologist (if the ENT organs are affected);
- radiography of the maxillofacial area;
- computed tomogram (CT).
Based on the existing picture of the patient’s health condition, treatment will be prescribed. Main stages of therapy:
- creating maximum rest for the patient (bed rest);
- applying a pressure bandage;
- warming procedures for the regeneration of hematomas and restoration of damaged tissues (you can use dry heat, a lamp, ozokerite applications and other physiotherapy procedures);
- use of painkillers.
To avoid negative consequences, you need to provide competent and timely medical care to the victim, undergo diagnostics in a trusted clinic, and follow all the doctor’s recommendations and prescriptions.
Jaw fracture
This is perhaps one of the most obvious reasons for severe jaw pain. The cause-and-effect relationship between blow - jaw fracture - pain is clear to everyone. Among the first symptoms indicating a fracture rather than a bruise are: unbearable pain, difficulty opening the mouth, malocclusion, swelling, bruising. In this case, immediate contact with an ambulance and maxillofacial surgery is required.
If you feel that your jaw hurts, do not delay in seeing a doctor, as this symptom may be a sign of the onset of a dangerous disease.
You can also read the article “Surgical dentistry”.
What happens if you don’t seek help in time?
- post-traumatic periostitis or inflammation of the periosteum;
- jaw deformation;
- inflammatory process of bone tissue;
- contractures or weakening of joint mobility;
- development of tumor processes (oncology).
Thus, if any mechanical injuries occur in the relevant area, it is imperative to contact a medical facility. The sooner you visit an experienced doctor, the sooner you will eliminate complications and return to a normal lifestyle.
Therapy technique
Treatment of an injury to the upper or lower jaw can be done at home. Doctors recommend keeping the damaged area at rest by applying a regular fixing bandage. To accelerate the resolution of hematomas, bruises and bruises, you can use cold compresses created with ordinary ice from the refrigerator. If abrasions, scratches or wounds have formed on the skin as a result of traumatic exposure, it would be advisable to treat them with antiseptic agents (iodine, brilliant green, alcohol, hydrogen peroxide) several times a day. It is possible to treat a bruise in the jaw area with pharmaceutical drugs. The following ointments and gels have proven themselves to be effective:
- Troxevasin;
- Heparin ointment;
- Fastum gel;
- Dolobene;
- Diclofinac.
The above remedies have a calming, vasodilating and analgesic effect. It is recommended to consult a specialist for the use of any pharmacological drug, since they may contain components that cause adverse, individual reactions.
Trauma to the front teeth in a child
The front teeth in children are most often injured. And while injury to other teeth may go unnoticed, injury to a child’s front teeth quickly attracts the attention of parents. An ordinary bruise, in which only a barely noticeable crack in the enamel can be visually seen, may not bother the child in any way. In some cases, there may be discomfort or pain during chewing, or mechanical stress, and slight swelling of the soft tissues.
It’s another matter if, as a result of an injury, a subluxation, dislocation, or even fracture of a tooth occurs. Then the injury to the child’s front teeth is primarily visually noticeable. In the case of subluxation or dislocation, parents may notice an atypical position of the tooth, its slight displacement relative to other teeth. In addition, with this type of injury to the front teeth, bleeding, swelling of the soft tissues, inflammation, severe pain, and mobility of the injured tooth will be noted.
Children often experience fractures of their front teeth. It will be characterized by a violation of the integrity of hard tissues, chipping of a part of the tooth, pain, bleeding, swelling of soft tissues, and hemorrhages in them.
Permanent fixation of fragments
Fragments of the lower jaw can be fixed using conservative and surgical methods.
Permanent fixation can be carried out using: steel standard tape splints (Vasiliev splints), Tigerstedt dental wire splints, dental dentogingival and supragingival plastic splints, which are made in dental laboratories (they are rarely used nowadays).
In recent years, some clinics have begun to use orthodontic screws, which are inserted through the mucosa into the alveolar processes of the jaws, 3 pieces on each side, after which a rubber rod is put on the heads of the screws, providing intermaxillary fixation. This avoids the time-consuming procedure of double-jaw splinting. On the other hand, when inserting screws, the roots of the teeth can be damaged; in addition, there are often situations when the screw, under the action of a rubber rod, becomes mobile, which leads to inadequate intermaxillary fixation and removal of the screw.
If conservative treatment methods do not produce an effect, osteosynthesis is used - this is a surgical method that, with the help of devices, allows you to fix the fragments and eliminate their mobility. Osteosynthesis is performed if the patient has comminuted fractures of the lower jaw, or the displacement of the fragments is so pronounced that they do not allow closed reduction. Osteosynthesis is also indicated in the absence or insufficient number of teeth in the patient.
Approximately 30% of patients with mandibular fractures require surgical treatment. Currently, osteosynthesis is one of the leading methods of surgical care, and is used much more often than in the past.
This is due both to an increase in the arsenal of technical means for performing surgery (the presence of physiodispensers, titanium miniplates), which leads to improved surgical techniques, greater predictability of results, and to the requests of patients, which are aimed at a more comfortable course of the post-traumatic period, reducing the time of intermaxillary fixation, and in some cases, complete abandonment of it.
Methods for treating fractures using surgical techniques make it possible to compare and fix mobile bone fragments in a normal anatomical position. This helps reduce treatment time and achieve early restoration of lower jaw function. However, according to various data from Russian and foreign clinics, there is also a negative aspect of using osteosynthesis - about 30% of patients experience complications after using this technique. This is due to the use of materials to hold fragments: steel, titanium, etc. Even the most bioinert alloys are not ideal. Being in bone tissue, they undergo corrosion and cause galvanosis, which negatively affects the recovery process and can cause purulent-inflammatory complications and pain reactions.
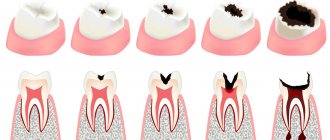
We divide all dental injuries of children
- Bruise - characterized by only minor damage, a crack in the enamel, hemorrhages in the pulp chamber, swelling, or bruising on the gums may be observed.
- Subluxation - a damaged tooth is displaced, its ligamentous apparatus and neurovascular bundle are partially damaged, and tooth mobility is noted.
- Luxation - incomplete and complete - the tooth protrudes significantly from the dentition, barely maintaining connection with the socket, or even falls out of it. The integrity of the neurovascular bundle and ligamentous apparatus of the tooth is compromised.
- Fracture of the crown of the tooth.
- Tooth root fracture
Further in the article we will tell you how acute injury to baby teeth in children is characterized by an impact, how to recognize an injury to the front teeth, and how to treat any tooth injury in a child.
Osteosynthesis methods
There are direct and indirect methods of osteosynthesis.
Direct methods:
— intraosseous osteosynthesis using knitting needles, rods, pins and screws,
— bone osteosynthesis using bone plates, staples, circular ligatures, frames,
— intraosseous osteosynthesis based on bone sutures or their combination with knitting needles and staples.
Indirect osteosynthesis is based on the use of various fixation devices, both extraosseous (bone clamps and clamps) and intraosseous (rods, pins, screws and knitting needles).
Osteosynthesis can be performed both under local anesthesia in combination with neuroleptanalgesia and ataralanalgesia, and under general anesthesia.
The nature of the access (extraoral or intraoral) is determined by the doctor.
If osteosynthesis is performed using an extraoral approach, then in case of a fracture in the area of the angle and body of the lower jaw, the doctor makes an incision in the submandibular region. If the fracture occurred in the frontal area, the incision will be in the submental area. For fractures in the area of the condylar process - in the retromandibular region. During the operation, the doctor exposes bone fragments, removes small fragments, and fixes large fragments and fragments in a normal anatomical position using the selected design.
If the doctor uses intraoral access to perform osteosynthesis, he makes an incision in the mucosa along with the periosteum, then compares the fragments and performs osteosynthesis.