Bitterness in the mouth may indicate problems with the digestive system. Severe or persistent bitterness in the mouth is a reason to consult a doctor.
From time to time you may experience an unpleasant bitter taste in your mouth. As a rule, this is due to a sudden release of bile into the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, some bile may enter the esophagus and cause a bitter sensation in the mouth.
. Often a bitter taste in the mouth is felt in the morning, since bile can enter the stomach during sleep (especially if you sleep on your left side and dinner included fatty foods).
Bile is a secretion produced by the liver and is necessary for digesting food. The bile duct carries bile from the liver to the gallbladder, which acts as a storage reservoir. During the active digestive phase, bile from the gallbladder enters the duodenum. Some substances have choleretic properties, that is, they increase the production of bile. Eating foods with choleretic properties (for example, pine nuts) can provoke a sharp increase in the flow of bile into the intestines and, as a result, the appearance of bitterness in the mouth. Some medications have the same effect - both medical preparations and traditional medicine (St. John's wort, sea buckthorn oil, etc.).
However, bitterness in the mouth should not be ignored
. Its appearance indicates that not everything is in order with the digestive system. For example, a bitter taste may appear after eating fatty (heavy) foods. Fatty foods stimulate bile secretion. Normally, the secreted bile should not enter the stomach and esophagus, but should be released exactly as much as is necessary for the digestive process in the intestines. The appearance of bitterness indicates that this is not the case. And we need to figure out what caused this. If bitterness in the mouth occurs frequently or persists for a long time, then it is better not to delay a visit to the doctor.
How does a bitter taste in the mouth occur?
The taste in your mouth doesn't have to be overtly bitter; it can feel metallic, sour, or just plain unpleasant. Usually its appearance is associated with certain conditions:
- immediately after eating (if you overeat or eat certain foods);
- after taking medications, especially if a person takes them on an empty stomach;
- after physical activity;
- immediately after waking up.
Bitterness is felt as a foreign, strong, unpleasant taste that comes from the oropharynx or has no obvious source. It may be part of a symptom complex. Along with a bitter taste, the following may appear:
- heaviness in the side;
- abdominal pain;
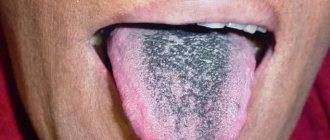
- white coating on the tongue;
- nausea, vomiting;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- dry mouth or, on the contrary, excessive salivation;
- dizziness;
- bloating;
- bleeding gums;
- cold symptoms (sore throat, cough, fever, weakness);
- decreased appetite;
- deterioration of smell and other symptoms.
By exactly when bitterness appears and what other symptoms arise, one can judge the causes of the condition. To make a diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and describe to him in detail how you feel.
Why is water with excess iron harmful?
The normal level of iron content in well water is 0.3 mg/liter. If the iron content in water is higher than normal, it becomes dark, cloudy and begins to taste bitter. However, the presence of an excess of iron is detected only during its oxidation - when water comes into contact with air - the color of the water gradually begins to acquire an orange tint.
Alkaline earth metals get into well water because they are washed out of gypsum and chalk soils. The softest water is obtained from underground aquifers that run through granite soil rocks.
The danger of using drinking water with an excess of iron.
If, in addition to iron, nitrites, nitrates and ammonia, organic and mechanical impurities (residues of fertilizers and synthetic detergents) are detected in well water, it becomes clear that the water has been polluted by wastewater from household pipeline systems.
If you choose the wrong material for equipping a well, the water at the source may turn out to be bitter. In this case, the taste of the water is not affected by the depth of the well and the number of aquifers passed through. If a well frame is built from aspen, this tree can give the water a putrid smell and a bitter taste. Therefore, when deciding to build a wooden well, choose the wood carefully. If you do not understand the characteristics of tree species, consult with specialists so as not to risk your health.
Causes of bitter taste in mouth
Bitterness in the mouth can appear due to diseases of the digestive system, teeth and gums, due to changes in hormonal levels, taking certain medications and for other reasons (Fig. 1). At the same time, the accompanying symptoms and conditions under which a person feels a bitter taste in the mouth will be different.
Figure 1. Some causes of bitterness in the mouth. Source: MedPortal
Poor quality food
Foods cooked with a lot of oil, fat or burnt can cause a bitter taste in the mouth. Sometimes the bitter taste is associated with drinking black coffee or very strong tea. It can also appear if a person has eaten sunflower seeds or nuts. The bitterness will go away if you drink cool water, but a slight unpleasant aftertaste may persist for a while. If the bitter taste comes from food, there will be no other symptoms (pain, indigestion).
Age-related changes
With age, a person's taste perception gradually changes. Older people are less able to discern tastes, but may still experience bitterness. This is associated with a number of other health changes, for example, decreased saliva production, dry mucous membranes, and a gradual deterioration in oral health.
Smoking
If a person smokes frequently, they perceive the taste of food less well, and this can increase the bitter taste in the mouth. Also, bitterness in the mouth of smokers may be associated with the taste and smell of tobacco smoke. The resins contained in it linger on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and settle on the surface of the tooth enamel. This is the cause of bad breath, deteriorating dental health and the associated persistent bitter taste. You can beat it with chewing gum or mints, but it is better to quit smoking or at least reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke.
Pregnancy
In the first trimester, bitterness in the mouth may appear along with other symptoms of toxicosis. It usually worsens with nausea or after vomiting. Fluctuations in estrogen levels can affect the perception of tastes. Cholestasis of pregnancy can also cause bitterness. This is a relatively rare syndrome that develops in the third trimester and is characterized by pruritus and cholestatic jaundice. Cholestasis in pregnancy resolves after childbirth and is considered a relatively harmless condition, but if symptoms appear, you should inform your obstetrician-gynecologist.
Functional dyspepsia
Functional dyspepsia is a disorder in which a person does not have severe diseases of the digestive system, but experiences pain, early satiety and a feeling of fullness after eating, and a burning sensation in the upper abdomen. In this condition, the feeling of bitterness occurs due to slow digestion of food. It may be accompanied by abdominal cramps and other unpleasant sensations. Functional dyspepsia is associated with a number of factors, including stress, smoking, heredity, and recent infectious diseases. You can relieve the bitter taste in your mouth by drinking water with lemon juice. If the condition does not go away or the pain intensifies, diarrhea, vomiting or other severe symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Hepatitis
Bitterness in the mouth is the initial symptom of hepatitis and accompanies liver inflammation. In this case, the bitter taste appears in the morning, immediately after waking up or 30-60 minutes after eating. This is accompanied by heaviness in the right hypochondrium, pain, nausea and vomiting containing bile. With toxic hepatitis, symptoms appear for a short time and disappear after starting treatment. With viral hepatitis, bitterness in the mouth persists almost constantly.
Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract
If food digestion is impaired, an unpleasant taste appears in the mouth. The sensation of bitterness may occur due to a change in taste perception. It occurs, for example, with pancreatitis and may be accompanied by vomiting and the appearance of a yellow or grayish coating on the tongue. A common cause of bitterness in the mouth is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). In this disease, stomach contents (stomach juice and food particles) regularly back up into the esophagus, causing heartburn and a bitter taste in the mouth (video 1).
Video 1. Symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
If a person has chronic gastritis or duodenitis, a bitter taste appears when he violates the recommended diet. In diseases of the digestive system, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth is always associated with food intake (appears some time after it).
Biliary system damage
A bitter taste may appear in the mouth due to cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis and other diseases of the biliary system (gall bladder and bile ducts). At first, bitterness may appear only after drinking alcohol, fatty or fried foods.
“Burning in the mouth, tongue covered with a yellow coating, discomfort, and so on. In 95% of cases, this is due to the reflux of bile from the duodenum into the stomach. In the stomach, this bile is mixed with hydrochloric acid, thrown into the esophagus and then into the oral cavity.”
Karasev Ivan Alexandrovich
expert
FSBI "N.N. Blokhin National Medical Research Center of Oncology", endoscopist
Without treatment, the condition will gradually worsen. The bitter taste will bother you more often and last longer. Along with it, nausea, pain in the hypochondrium on the right side, and stool disorders may occur. The feeling of bitterness becomes permanent if a severe inflammatory disease of the gallbladder or bile ducts develops (cholangitis, cholecystocholangitis, cholecystitis and others). Also among the possible causes are biliary dyskinesia, due to which the outflow of bile is disrupted, and cholelithiasis. Less commonly, the disorder is associated with parasitic liver disease (giardiasis, opisthorchiasis or echinococcosis).
Dental diseases
The feeling of bitterness can be caused by the presence of tartar, caries, gingivitis or other dental problems. There are usually other symptoms:
- toothache;
- enamel sensitivity (reaction to cold or hot, sweet, sour);
- bleeding gums;
- tooth mobility;
- gums look red or swollen;
- There is a noticeable plaque on the enamel that cannot be removed by regular teeth brushing.
Problems with the health of teeth and gums may be associated with xerostomia, a condition in which insufficient saliva is produced and the mouth constantly feels dry. This increases the risk of tooth decay and gum disease, and causes an unpleasant odor in the mouth, which is perceived as bitter. Xerostomia can occur due to smoking, mouth breathing, aging, diabetes, or autoimmune diseases. This condition requires consultation with a dentist.
Sometimes bitterness in the mouth appears after dental treatment. This may be due to the use of certain medications or materials, or the installation of dentures, braces and other structures in the mouth. If the bitter taste does not go away or persists for several days, you should contact your dentist.
Neurological disorders
The mouth may taste bitter due to damage to the brain structures that process taste information. In this case, taste perception is disrupted: for example, sour foods may seem sweet, salty foods may seem sour, and a person may not perceive some tastes. This can occur after a traumatic brain injury or stroke. Sometimes taste disturbances are associated with Alzheimer's disease and other age-related diseases in which neurodegenerative processes occur.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
There are more than 250 types of medications that can cause taste disturbances, including the appearance of bitterness in the mouth. This can happen if the drug affects the taste buds of the brain, if part of it remains in the saliva and changes its taste, if the drug suppresses the microflora, which is why fungal diseases develop. Among the drugs that can cause a bitter taste in the mouth:
- antibiotics;
- medications for arrhythmia, diuretics, statins and other drugs used for cardiovascular diseases;
- drugs used in chemotherapy;
- muscle relaxants, migraine medications and other neurological drugs;
- neuroleptics, sedatives, hypnotics, antidepressants;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- bronchodilators;
- antihistamines;
- antiviral drugs;
- nicotine replacement therapy products.
Rare causes
Sometimes bitterness in the mouth becomes a symptom of endocrine disorders: diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hypocortisolism and others. It can accompany some cancers and respiratory diseases. Rarely, the cause is an infection of the salivary glands. A bitter taste may occur in cases of poisoning due to accidental ingestion of a toxic substance. In all these cases, the appearance of bitterness is accompanied by other symptoms of the underlying disease.
Folk remedies
Bitterness in the mouth may be due to medication
In cases where no serious pathologies are found, folk recipes will help get rid of the feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
- Flax seed. To prepare the drink, take a quarter cup of ground flaxseed, add half a liter of boiled water and leave. Drink half a glass in the morning.
- Vegetable juices. Freshly squeezed juices from potatoes, carrots and celery increase the secretion of saliva and thereby help with bitterness in the mouth.
- Decoction of calendula flowers. For half a liter of boiling water you need to take 20 grams of calendula flowers, bring to a boil and leave. It is recommended to take 2 glasses per day for a month.
- Sunflower oil. Keep the slightly heated oil in your mouth for several minutes. The feeling of bitterness should disappear.
- Corn silk. A decoction of corn silk has choleretic properties, it contains fiber, B vitamins, and vitamin E. It helps cleanse the body, get rid of bad breath and stimulate the production of digestive enzymes.
- Rose hip decoction. Rosehip decoction is a choleretic agent and a real vitamin bomb. This drink not only relieves the feeling of bitterness in the mouth after eating, it also stimulates the immune system.
The choice of treatment for bitterness in the mouth depends on the disease that caused this sensation. No matter how harmless this symptom may seem, the cause of its occurrence can be quite serious, so you should not neglect this signal from the body and listen to it: get examined and begin treatment.
Help before diagnosis
Even if a diagnosis has not yet been made, several measures can be taken to alleviate the condition:
- Adjust your diet, remove fatty and fried foods, eat more often and in small portions.
- Stop smoking or reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Drink more water.
Monitor the quality of oral hygiene. You should brush your teeth twice a day, as well as use mouthwash and floss. If you have problems with your teeth, you need to visit a dentist.
Photo: goffkein/freepik.com
Important!
You should not try to use folk remedies or treat yourself - this can be dangerous. If a bitter taste in your mouth appears regularly, you should consult a doctor and get recommendations for treatment.
To which authorities should well water be submitted for analysis?
You can only obtain a guarantee of high-quality testing of well water, as well as an accurate conclusion about the reasons for its bitterness, in an accredited independent laboratory that has all the necessary approvals, certifications and licenses. After conducting detailed analyses, chemists issue official certificates and protocols on the suitability of the well for drinking or using water for household purposes.
You can also contact the centers for hygiene and epidemiology, the laboratory of the regional branch of Vodokanal, or an organization that specializes in geological exploration and solves problems of water purification.
When to see a doctor?
If the appearance of bitterness in the mouth is not associated with drinking coffee, burnt or poor-quality food, if the bitter taste appears regularly or persists for a long time, if it is accompanied by other symptoms, you should consult a doctor. This could be a dentist, if the bitterness in the mouth is associated with diseases of the teeth and gums, a gastroenterologist, if the cause may be diseases of the digestive organs or biliary tract, a hepatologist, if there are symptoms of liver disease.
Important!
In some cases, you need to urgently seek medical help. If bitterness in the mouth is associated with accidental ingestion of poison, if it appears along with other severe symptoms (difficulty breathing, swelling of the tongue, lips, difficulty swallowing, paralysis, changes in consciousness), you should immediately call emergency medical help.
Filtration of well water
Thanks to the use of filters, you can make well water softer and eliminate the unpleasant taste. The following types of filtration systems exist:
Ion exchange. The most common use of filters is that they operate on an ion exchange resin. They adsorb magnesium and calcium salts, and the water is saturated with sodium compounds. The filters consist of a cylinder and a tank with tableted salt. An ion exchange resin is generated in the tank.
Reverse osmosis filter. Bitter water is supplied under strong pressure and passes through a filter membrane, which traps harmful impurities.
Carbon filter - these filters work using activated carbon as an active substance, which is capable of absorbing mechanical impurities and salts found in water.
Iron remover (manual or automatic). The principle of their operation is based on a backfill that catalyzes oxidation reactions, or on the principle of electrolysis. Oxidation occurs of iron and manganese contained in the water that passes through the iron remover. Harmful substances precipitate, the water becomes not bitter, but pleasant to the taste.
UV system. Such devices destroy harmful microflora and microfauna in water through a photochemical reaction. Such systems are used in combination with other types of filters and are the final stage of well water purification.
To correctly select an effective method for purifying well water with a bitter taste, the results of a laboratory analysis of the composition of the water are required. Therefore, the solution to this issue is individual. In this case, the seasonality and purpose of using the well, the types and extent of water pollution in it must be taken into account.
To ensure a safe water supply, the minimum requirement is to install an iron remover and a softener (ion filter).
If, after cleaning well water, its hardness has decreased to less than 0.2 mg/liter, corrosion may occur in metal pipes, so cleaning must be carried out competently and carefully.
It is good if the filtration system consists of several filters responsible for coarse, fine and disinfecting cleaning. Only with a comprehensive professional approach can you remove bitterness from well water and eliminate other risks that may arise when using it.
Diagnostics
You can start diagnosing with a consultation and examination with a doctor. To do this, you need to contact a therapist, gastroenterologist, hepatologist or dentist. The doctor will conduct a survey and refer the patient for examination.
Photo: okfoto / freepik.com
During the consultation, the doctor needs to describe in detail the existing symptoms, tell how often and under what circumstances bitterness appears. Information about lifestyle, diet, and existing diseases will be useful.
For diagnosis, the following studies are carried out:
- Duodenal sounding. If a malfunction of the biliary tract is suspected, portions of bile are taken using a probe for bacteriological examination, and the rate of excretion of bile into the duodenum is also assessed.
- Gastroscopy (EGDS, FGDS) is a study using a gastroscope. Allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the digestive organs and do a biopsy (take tissue samples for laboratory testing).
- Ultrasound of the liver, gall bladder and other organs. It is carried out to assess the size and presence of changes in internal organs.
- Lab tests. If diseases of the digestive organs or biliary tract are suspected, a stool test is prescribed. A biochemical blood test is performed if cholecystitis is suspected. A test for hCG and sex hormones, as well as a serological test if viral hepatitis is suspected, can also be performed.
Boiling and freezing well water
Boiling. It is the simplest and most accessible, as well as the least expensive way to remove hardness salts from water. When water boils, sulfates and chlorides settle on the walls and bottom of the vessel. However, it must be borne in mind that boiling hard water can prematurely damage the container, so boiling is contraindicated in heating boilers. It is a temporary solution.
Freezing. Purification by crystallization. It is necessary to place a vessel with bitter well water in the freezer. When it freezes, crystals of pure ice will begin to grow on the walls of the container, displacing the salts into the central area of the container. After a certain period of time (this is influenced by the degree of contamination of the liquid and the working volume), clean frozen water collects on the walls of the container, and the salt accumulations remain liquid in the center of the container, since their freezing rate is lower. They just merge.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed based on diagnostic results, taking into account the causes of bitterness in the mouth.
Conservative therapy
Photo: freepik.com
A doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Choleretics and cholekinetics. These are choleretic drugs that are prescribed for cholangitis and cholecystitis.
- Enzymes that stimulate digestion. They can be used not only for diseases of the digestive organs, but also for liver damage (in combination with hepatoprotectors).
- Antispasmodics. They are prescribed if bitterness in the mouth appears along with abdominal pain and is associated with gastritis or other diseases of the digestive system. Antispasmodic drugs relieve pain and relax the smooth muscles of the stomach.
If the appearance of bitterness is associated with viral hepatitis, the doctor will prescribe complex therapy for the underlying disease. In case of parasitic infection, anthelmintic drugs are prescribed. Additionally, it is recommended to follow a diet, frequent, small meals and control the drinking regime.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is carried out for gallstone disease to remove and remove stones - calculi. If the gallstones are small, the ESWL (extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy) technique is used, crushing the stones with a shock wave. In more severe cases, open or laparoscopic cholecystectomy is prescribed. It is carried out if neither diet nor ultrasound methods improve the condition. A cholecystectomy involves removing the gallbladder.
Stones extracted from the gallbladder. Photo: Alena1919 / Depositphotos
Gallbladder and liver problems
If bitterness causes you anxiety every day for a long time, it's time to get your liver and gallbladder checked. Perhaps, as a result of a malfunction or inflammation, the gallbladder does not have time to remove bile from the body on time, and it ends up in the esophagus. This is where the unpleasant taste comes from.
What to do
- A blood test is mandatory; it is advisable to do both a general and biochemical one, as well as an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- As a rule, the doctor recommends taking anti-inflammatory and choleretic drugs (prescription only).
- For patients with cholelithiasis and cholecystitis, a diet is prescribed: milk and light vegetable soups, low-fat cottage cheese and kefir, boiled fish, marmalade, and tea are allowed.
- It is recommended to drink about 2-3 liters of liquid per day
- Decoctions and infusions of chamomile and calendula are useful, for the preparation of which 1 tsp is used. dried inflorescences are brewed with a glass of boiling water for 15-20 minutes. Take the decoction 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. l. half an hour before meals.