What to do if a child or adult has bitten their tongue, cheek, or lip. First aid and treatment.
Children, like adults, can accidentally bite their lip or cheek. A minor and non-dangerous injury can cause a lot of discomfort, and in the case of children, tears. The mucous membrane tightens and heals much longer than the rest of the skin, and this is associated with prolonged pain, and sometimes possible inflammation. After all, an infection can get through an open wound at any time, especially when children are still small and constantly put their dirty hands in their mouths.
In this article we will look at the causes of lip and cheek biting, as well as help and treatment. We will also touch on the topic in which cases it is urgently necessary to visit a doctor.
What it is
Damage to the oral mucosa can be caused in a variety of ways. In a healthy person, minor injuries disappear quite quickly and without leaving a trace. In the presence of chronic diseases that reduce the level of immunity, any infection or dirt that gets into the wound provokes the development of inflammation.
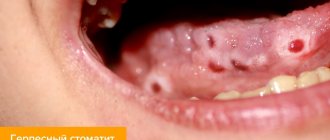
Traumatic stomatitis is the result of a single or long-term impact on soft tissues, as a result of which painful formations appear in places of damage that are not characteristic of the normal state of the mucous membrane. These may be small blisters, ulcers, erosions, ulcers or wounds covered with a grayish or white coating.
Most often, with a single exposure and the absence of infectious contamination, such consequences of injury disappear quickly and without drug treatment. If soft tissue injury occurs over a long period of time (by braces, a sharp tooth fragment, tartar, dentures, etc.), gum inflammation and stomatitis can develop into a chronic form.
Biting your lip is not a folk sign, but a signal for the doctor
Are there diseases that are specific only to smokers?
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures while smoking tobacco causes a mucosal disease called nicotine stomatitis. People with this disease are familiar with the following symptoms: a burning sensation or tightness, dry mouth. In general, people who smoke need to pay special attention to their oral cavity. Any changes in the oral cavity should be taken seriously and if abrasions, roughness, bleeding ulcers, lumps appear, as well as areas of red, white or any uncharacteristic color appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. I can say that already during the first year of my work on this problem, 20 of my patients gave up the bad habit of smoking.
Can a person not notice the development of any disease?
Erythroplakia is such a disease. The whole danger lies in the fact that the person does not complain of any discomfort. You can notice changes only visually. Usually, erythroplakia does not manifest itself in any way until it becomes a malignant tumor. In the place where the mucous membrane is affected, swelling appears. Some areas become crusty and begin to resemble small erosions. Unreasonable bleeding in the oral cavity, numbness, and loss of sensitivity in a particular area may begin.
Aksinya Alexandrovna, let’s once again name the main symptoms of oncological diseases of the oral cavity.
So, nonspecific symptoms include weakness, a rise in body temperature to 37-38 degrees, loss of weight and appetite, and fatigue. Further symptoms depend on the nature of the affected organ:
- with tumors of the oropharynx, a “foreign body sensation”, difficulty swallowing,
- with tumors of the tongue, swelling and impaired mobility occur, difficulties in pronouncing sounds, speech, difficult painful swallowing,
- with tumors of the upper palate, nasal breathing is impaired and the voice timbre changes (nasality),
- with advanced, disintegrating tumors, profuse salivation with an admixture of blood, pus and pieces of the tumor appears, and the presence of foul odor from the mouth.
I would like to remind patients that all the achievements of modern dentistry are aimed primarily at helping a person overcome mental anxiety and make the treatment process as painless and comfortable as possible. On your part, you only need to promptly seek help from a doctor in order to remain healthy and smiling for as long as possible.
Natalya Orobets, public relations manager t.: 39-06-68
Causes
The causes of traumatic stomatitis may be the following:
- In children, this phenomenon is most often associated with active games and damage to the tooth or soft tissue as a result of a blow (for example, with a ball) or an unsuccessful landing on a hard object. However, this disease can also occur in infants as a result of injury to the gums by a protruding tooth.
- In the everyday life of an adult, the main cause of the onset of stomatitis can be a simple burn from hot tea. And if a person consumes very hot food and drinks systematically, such a burn and, accordingly, stomatitis, become chronic. By the way, you can get burned not only by hot food, but also by chemicals and medications used not according to instructions, acids, alkalis, and even electric shock and fire. In addition to a burn, stomatitis can also be caused by frostbite.
- Constant friction against the sharp edge of a chipped or broken tooth, poorly ground metal of braces, or poorly fitting dentures can also cause traumatic stomatitis. It is for this reason that you should not endure discomfort and pain due to the problems described above. The only correct solution would be to contact a dentist to eliminate the interference.
Another reason for the occurrence of this disease is bad habits, as a result of which the mucous membrane is injured:
- biting lips and inner cheeks;
- frequent consumption of seeds, which injures the tongue;
- haste in eating with frequent biting of the cheeks and tongue;
- the habit of holding sharp objects in the mouth and much more.
All these mechanical effects lead not only to permanent injuries to soft tissues, but also to the formation of swelling, inflammation and even ulcers.
What to do if a child bites through his tongue, how to stop the bleeding?
When chewing food, as a result of a fall, or simply stumbling, a child can bite his tongue until it bleeds, and sometimes even bite through. At the first second, every parent may be confused and not know what to do, but here, as in the case of other injuries, the main thing is to quickly pull yourself together and help the child.
Even if the bite is minor and only redness is visible, be sure to treat and disinfect the wound. Today it may seem that the injury to the tongue is insignificant, but in a day or two a completely different result may appear.
Please note that the tongue can be bitten on the top, bottom and side. Examine the entire tongue before making a final decision.
What to do if a child bites through his tongue, how to stop the bleeding?
If you see that a child has bitten his tongue until it bleeds, immediately treat the surface of the tongue and stop the bleeding. The tongue consists of thousands of blood vessels, and carelessness can lead to a lot of difficulties in the future.
If the tongue is bitten through, go to the doctor immediately; the child may need immediate hospitalization.
So, if a child bites his tongue:
- We carefully examine the tongue, and even if we see the cause of the complaint, we continue to examine it to the end;
- Disinfect the wound;
- We numb the pain with a special antiseptic gel, which can be bought at the nearest pharmacy;
- Treat the wound every few hours until complete healing;
- If the wound increases, pus, swelling and lumps form, immediately go to the doctor.
Symptoms
Traumatic stomatitis can be distinguished from other types only by knowing the background of its occurrence, since the manifestations of symptoms of the disease are quite typical for all types:
- At the site of injury, a slight swelling or bruise first appears, the skin turns red, swells, and slight tissue hyperemia may appear;
- gradually the painful sensations increase, over time it becomes difficult to open the mouth and chew food;
- ulcers, wounds, ulcers, blisters, erosions appear;
- with severe lesions, irreversible soft tissue necrosis may occur;
- as a result of an acid burn, a dense film forms over the damage;
- until the cause of injury is eliminated, the manifestation of symptoms of stomatitis can be wave-like;
- Severe cases of traumatic stomatitis may be accompanied by suppuration or fungal infection.
Treatment
Like any serious disease, traumatic stomatitis requires immediate treatment. First of all, the doctor will have to eliminate the source of injury:
- In the case of a broken or chipped tooth, it is necessary to cure or remove this tooth, depending on the depth of the damage.
- Braces and dentures are improved or remade from higher quality material.
- Tartar is removed and the sharp edge of the tooth is ground down.
- If there are minor injuries, wounds and cracks are washed with antiseptics (peroxide, furacillin, infusions of calendula or chamomile).
- More serious injuries are numbed and treated with anti-inflammatory drugs.
- For quick healing of wounds, ulcers and erosions, your doctor may recommend applications with rosehip or sea buckthorn oils, vitamin A oil solution and other keratoplasties.
- In cases of thermal burns or frostbite, applications of an anesthetic drug may be necessary, but in case of a chemical burn, you must first thoroughly rinse the damaged area with a neutralizer. For an acid burn, use an alkali solution, and for an alkaline burn, accordingly, use an acid solution. And only after eliminating the traumatic substance is further treatment with antiseptics and anesthetic rinses possible.
Ulcerative stomatitis - symptoms and treatment
The main goal of therapy is to reduce pain and speed up healing. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate irritants that cause discomfort to the patient. The next step is to reduce symptoms as much as possible.
To treat stomatitis, rinsing with solutions of furatsilin, miramistin, chlorhexidine, and hydrogen peroxide is prescribed. Rinsing will reduce pain and itching, and cleanse the oral cavity of food debris that injures the damaged areas.
In case of severe pain, applications with painkillers are prescribed - “Kamistad”, “Lidocaine Asept”. Treatment for different forms of stomatitis will differ.
Infectious stomatitis. When treating, it is first necessary to understand what problem with the immune system caused this condition and to strengthen the body’s defenses. To do this, Prodigiosan is administered intramuscularly, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptics, proteolytic enzymes, and UV therapy is prescribed [11].
Vesicular stomatitis. To reduce symptoms, proper rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking antipyretic medications will be helpful. Also, the oral mucosa is treated with antiseptics (Suprastin, Hexetidine, Pipolfen) and antiviral ointments are used - rhiodoxol and tebrofen. Antiherpetic drugs are often prescribed - Famciclovir, Acyclovir, Valacyclovir. If you follow the doctor’s recommendations, the symptoms of the disease quickly go away and the patient recovers.
Vincent's ulcerative necrotic stomatitis. During treatment, dental plaque is carefully removed, the oral mucosa is treated with antiseptics, and multivitamins are prescribed (for example, Complivita).
Allergic stomatitis. Treatment consists of eliminating the cause of the allergy and taking oral antihistamines. In severe cases of allergic stomatitis, sodium thiosulfate solution is administered intravenously. During treatment in a hospital, drip infusions of hemodez, isotonic sodium chloride solution, polyglucin, and corticosteroids are prescribed.
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. With local treatment, traumatic factors are eliminated, the mouth is rinsed with tetracycline (250 mg per 5 ml of water 4 times a day for 5-7 days), applications are made with corticosteroids and antibiotics, and painkillers are prescribed. For deep ulcers, proteolytic enzymes are used.
General treatment includes taking medications:
- tetracycline, rifampicin (two capsules twice a day);
- “Tarivid” (one tablet twice a day for 20 days);
- sodium thiosulfate (10 ml of 30% solution intravenously once a day or 1.5-3 g orally);
- “Prodigiosan” (start with 15 mcg once every five days and increase the dose to 100 mcg);
- "Levamisole" (50 mg three times a day two days in a row a week or 150 mg once);
- "Delagil" (one tablet once a day);
- "Colchicine" (one tablet twice a day for two months);
- "Aevit" (1 ml once a day intramuscularly for 20 days);
- “Histaglobulin” (2 ml subcutaneously once every three days) [11].
Stomatitis due to intoxication with salts of heavy metals and chemical solutions. If a chemical gets on the mucous membrane, you must immediately wash it off with a neutralizing solution. Further treatment of patients with chemical burns is carried out with painkillers and antiseptics and drugs that accelerate the restoration of the epithelium. A high-calorie diet is also important. For extensive scars, surgical intervention is indicated [15].