In the twenty-first century, the world has seen an increase in the number of people suffering from tumors and swellings in the neck area. This problem occurs mainly in adults aged twenty-five years and older. Children get this disease less often, and the forms of pathologies that develop in them are milder.
Tumors and swellings in the neck area
In this article we will look at what tumors and swellings in the neck are, the reasons for their formation, symptoms, diagnosis and their treatment.
About tumors in the neck area
The neck is an important part of the human body because it connects the head to the torso. Therefore, new growths on it should at least give cause for concern.
Tumors and lumps are unnatural formations. They are divided into two types:
- benign;
- malignant.
Tumors prevent a person from living a normal life
Benign tumors do not appear for a long time and are easy to get rid of. Malignant ones, on the contrary, manifest themselves sharply, develop rapidly and over time become more difficult to get rid of.
The tumor can appear in any part of the neck.
Tumor classifications
Tumors in the neck vary depending on where they originate.
Table No. 1. Types of tumors
| View | Description |
| Organ tumors | They keep the elements of the organ structure intact. There are benign and malignant. Appear from organs that are located in the neck. |
| Extraorgan tumors | Do not come into contact with organs located in the neck area. They can be either benign or malignant. Affects muscle and nerve tissue. |
| Tumor lesions | The lymph nodes located in the neck are affected. May be primary or secondary. |
Causes of pathology
If the lymph node in the neck under the jaw is inflamed, then the possible causes are:
- diseases of infectious origin that affect the ENT organs and the upper parts of the respiratory system (tonsillitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, otitis media);
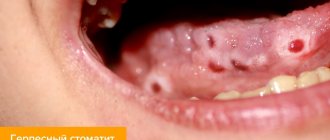
- diseases developing in the oral cavity (caries, periodontal disease, periodontitis, periostitis, or gumboil, pulpitis, gingivitis, alveolitis, stomatitis);
- systemic infections (measles, whooping cough, mumps, popularly called mumps, chicken pox);
- pathologies affecting the immune system (lymphomas, leukemia, lupus, HIV);
- neoplasms (benign or malignant) of various origins (atheromas, granulomas, lipomas, cysts);
- infections caused by parasitic microflora (lymphoreticulosis, toxoplasmosis);
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system.
You should know that the above ailments are not always accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes. Quite often, the nodes remain in a normal state even if the disease is acute.
If the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed, then in 60% of cases the pathology is caused by dental problems, in 30% by diseases of the respiratory system. In 20% of cases, the reason why the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed and hurts is advanced caries, leading to the development of a purulent abscess. After tooth extraction or conservative treatment of caries, pathological processes in the lymph nodes stop.
But sometimes it is tooth extraction that can become a provoking factor and cause an enlarged lymph node. A similar situation is possible if an infection enters the hole.
Causes
How the tumor develops depends on the cause of its appearance.
There are several reasons for the development of tumors
The most common reasons are listed below.
- Injuries, blows, bruises of the cervical vertebrae and/or muscles. Such incidents can cause swelling and lead to breathing problems.
- Neck cyst. This problem most often occurs in children. If you do not get rid of it in time, purulent inflammation may develop, and subsequently a tumor.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes. It is common in children and adults. An experienced doctor can easily determine it by palpation.
- Problems with the thyroid gland. In this case, the tumor most often develops in the front of the neck.
Prices for massagers
Why does my neck swell?
Traumatic injuries
Soft tissue bruises are accompanied by moderate local swelling and pain that intensifies during neck movements.
The swelling disappears within a few days. Subluxation of the cervical vertebra occurs as a result of a sharp turn of the head, and is more often detected in children. Asymmetrical swelling of the back of the neck is complemented by a forced position of the head, pain, and muscle tension. In case of fractures, local swelling is determined in the projection of the spinous process of the damaged vertebra. In victims with laryngeal injuries, external swelling is usually minor. Severe swelling can be a consequence of severe complications: internal bleeding into soft tissues, subcutaneous emphysema that occurs against the background of a rupture or penetrating wound of the larynx. Difficulty breathing, aphonia, and pain are noted. Hemoptysis and asphyxia are possible.
With uncomplicated laryngeal foreign bodies, there is no symptom. Against the background of inflammation in the area where a foreign object is located, swelling of varying severity occurs, combined with pain, hyperthermia, and symptoms of intoxication. A life-threatening condition is perforation of the larynx by a sharp foreign body with the development of subcutaneous emphysema.
Diseases of the lymphatic system
Swelling of the neck is often associated with inflammation of the regional lymph nodes. The following diseases can cause lymphadenitis:
- Purulent lesions of soft tissues
: infected wounds, boils, carbuncles, abscesses, phlegmon of the face, head and neck. - Dental problems
: caries, pulpitis, gumboil, stomatitis, purulent mumps, maxillary abscess, abscesses of the tongue, oral cavity, osteomyelitis of the jaw. - ENT pathologies
: tonsillitis, chronic tonsillitis, paratonsillar, parapharyngeal, intratonsilal abscesses, otitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis. - Children's infectious diseases
: diphtheria, scarlet fever, mumps. - Dangerous infections
: plague, anthrax.
In children with chronic skin diseases, lymphadenitis of the cervical, submandibular, and occipital lymph nodes occurs with the development of Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis. Enlarged lymph nodes also become a consequence of the lymphogenous spread of malignant tumors: cancer of the tongue, lower and upper jaw, larynx, pharynx, nose, paranasal sinuses.
Swelling of the neck due to thyroiditis
Endocrine pathologies
The most pronounced diffuse swelling of the neck is observed with myxedema. Not only the neck, but also the face swells; in severe cases, the swelling spreads throughout the body. Distinctive features are the absence of redness, pallor, pitting when pressing on the skin, shortness of breath, lethargy, lethargy, and increased sensitivity to cold. Changes in the anterior surface of the neck are determined in all forms of goiter:
- Diffuse euthyroid goiter.
The general condition has not changed, sometimes weakness and headaches are observed. In mild cases, swelling is noticeable only when palpating, tilting the head back, in severe cases it reaches the level of a pronounced cosmetic defect. - Diffuse toxic goiter.
Detailed symptoms of thyrotoxicosis are detected. The thyroid gland is uniformly enlarged, the degree of swelling does not always correlate with the severity of the disease. - Nodular goiter.
The function of the gland is often preserved; some patients show signs of hypo- or hyperthyroidism. The swelling of the neck is uneven, one side is larger than the other.
In acute thyroiditis, swelling is combined with pain, local hyperthermia, hyperthermia. The onset of the purulent form of thyroiditis is marked by increased pain, severe fever, and lymphadenitis. In patients with subacute thyroiditis, the body temperature is subfebrile, there is swelling, moderate pain in the projection of the thyroid gland, in half of the cases symptoms of thyrotoxicosis are detected. Chronic thyroiditis develops gradually. The affected area is lumpy and painless.
Maxillofacial pathology
The cause of swelling is often diseases of the salivary glands and soft tissues. Swelling is observed in the following pathological conditions:
- Sialadenitis.
The parotid salivary gland most often suffers; a one-sided painful swelling is located on the border of the neck and lower jaw, next to the earlobe. Less commonly affected are the submandibular salivary glands, which are localized in the submandibular triangle of the neck. - Purulent parotitis.
With purulent inflammation, swelling spreads to the neck, cheek, and submandibular area on the affected side. A pronounced deformation occurs. Pain, general hyperthermia, severe weakness, weakness are noted. - Salivary gland abscess.
Along with the parotid, other salivary glands may be affected. In 50% of cases, inflammation affects the paired organ. The area of swelling corresponds to the location of the affected gland. There is severe pain, febrile body temperature, and severe intoxication syndrome. - Perimaxillary abscess.
Formed as a complication of tonsillitis, furunculosis, infected abrasions of the skin and oral mucosa. Unilateral swelling is detected in the area of the submandibular triangle. When the abscess ruptures, swelling spreads down the neck. - Cellulitis of the neck.
It is provoked by odontogenic or tonsillogenic infection, foreign bodies of the laryngopharynx. Swelling appears on one side, grows quickly, and diffusely covers a significant part of the neck. The skin over the area of swelling is red, hot, and tense. The general condition is serious.
Diseases of the ENT organs
Swelling of the neck in otolaryngological diseases is often caused by lymphadenitis. Diseases accompanied by swelling of the neck, not associated with enlarged lymph nodes, include:
- Chondroperichondritis of the larynx.
A limited area of swelling is located in the front of the lower or middle third of the neck. Combined with chills, weakness, hyperthermia, pain, aggravated by talking, coughing, swallowing. - Neck cyst.
The tumor-like formation is localized on the lateral or anterior surface, and is more clearly contoured when the head is turned in the opposite direction. In the absence of inflammation, it is asymptomatic. When infected, the skin turns red, the cyst enlarges, becomes painful, and swelling spreads beyond the affected area. - Retropharyngeal abscess.
Swelling of the neck behind the angle of the lower jaw, sore throat, breathing problems aggravated in an upright position, severe impairment of the general condition, and hyperthermia are detected. - Lemierre's syndrome.
Postanginal anaerobic sepsis is manifested by swelling of the lower part of the lateral surface of the neck (in the projection of the jugular vein), pain, progressive deterioration of the condition up to impairment of consciousness and speech, the development of pneumonia, arthritis, and osteomyelitis. - Ludwig's sore throat.
The disease is characterized by a rapid onset and severe course with fever, intoxication, severe sore throat, and diffuse swelling of the soft tissues of the neck. On palpation, the tissues are painful, dense, and “woody.”
Allergy
With angioedema, swelling of the neck, face, lips, eyelids, ears, limbs, and genital area is observed. The swelling is painless, accompanied by a feeling of tension and fullness, and pale skin. It is provoked by contact with allergens: drugs, food, insect poison. Sometimes it occurs due to pseudo-allergy. In addition, severe swelling of the face, neck, feet, and hands is found in the edematous type of allergy to salicylates.
Infectious diseases
The most common infectious cause of neck swelling is mumps. Swelling is detected in the area of the salivary glands, often bilateral, sometimes asymmetrical. Due to the enlargement of the upper parts of the neck, the face becomes pear-shaped. Severe swelling of the anterior parts of the neck is detected in the toxic form of diphtheria. 1st degree is characterized by swelling reaching the middle of the neck, 2nd – to the collarbones, 3rd – spreading to the face, chest, back, back of the neck.
In patients with typhus, redness and swelling of the face and neck are accompanied by injection of the conjunctiva, the appearance of a thick rash on the torso and limbs, hepatosplenomegaly, oliguria, neurological disorders, and severe intoxication.
Neoplasms
Local swelling of the neck may be due to the development of neoplasia, which includes:
- lipomas, fibromas;
- cancer of the pharynx and larynx;
- thyroid tumors.
Benign neoplasms are limited, painless swellings that do not increase or increase very slowly in size. Malignant neoplasia rapidly progresses, causes enlargement of lymph nodes, invades neighboring organs, and is accompanied by breathing and swallowing disorders, and voice changes.
Other reasons
The list of other causes of neck swelling includes a number of diseases of various etiologies:
- Rheumatology, orthopedics
: cervical myositis, Shulman's disease, scleroderma, dermatomyositis. - Cardiology, pulmonology
: exudative pericarditis, pleurisy, mediastinitis, superior vena cava syndrome. - Dermatology
: furunculosis, bullous dermatitis. - Neurology
: Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome. - Nephrology
: membranous glomerulonephritis. - Emergency conditions
: cytokine storm.
Symptoms
Symptoms of tumors and swellings in the neck:
- hoarseness of voice;
- swelling in the neck;
- aching pain;
- difficulty eating.
The symptoms of tumors and swellings in the neck are not very characteristic, and therefore it is not always possible to identify the disease in time
If symptoms get worse, the tumor is likely growing in size, which can be life-threatening. In this case, you must immediately undergo diagnostics and consult a specialist.
Secondary risk factors
Below are described the secondary signs that serve as the basis for the appearance of tumors and swellings.
Floor
Neck tumors are more common in men. On average, up to 80% of cases of complaints regarding this matter were made by men (according to statistics from WHO). However, the number of women suffering from neck tumors is rapidly changing, as more and more representatives of the fair sex are now abusing alcohol and cigarettes.
Males are more likely to suffer from neck tumors
The ratio of men to women affected by this pathology is 3 to 1. According to studies that have been conducted over the past five years, this imbalance will continue.
Age
Most often, people over 50 years of age suffer from tumors in the neck area, but recently young people aged 25-35 years have increasingly begun to report this complaint.
The disease is getting younger - more and more young people are suffering from this disease
In addition, young people have problems diagnosing the disease due to the too long list of possible causes that must first be “weeded out.”
Climatic conditions
It is noteworthy that the risk of developing a tumor, for example, in India, is almost six times higher than in Scandinavia.
The climatic conditions in which a person lives directly affect the chance of a tumor appearing in the neck area
According to scientists, the high incidence rate in Asia is a consequence of common habits in the area, such as chewing betel nut and using smokeless tobacco. The high increase in the incidence of this pathology in Russia is caused by smoking and alcoholism.
Treatment of neck tumors
After final clarification of all the nuances of the disease and rendering a verdict, the doctor prescribes the patient a suitable course of treatment, the length and intensity of which depends on two points:
- degree of tumor development;
- her appearance.
Most types of tumors are treated with surgery. Conservative treatment acts as a secondary method that can be combined with surgical intervention.
Treating tumors is a top priority
However, it is possible to get rid of some types of tumors without it, but this is only possible if the patient consults a doctor in time.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
The list of therapeutic measures is determined by the nature of the pathology:
- Fractures of the lower jaw
. A linear fracture of the body without displacement is an indication for double-jaw wire splinting. The patient is recommended a gentle diet. In the first days, painkillers are prescribed; for open injuries, antibiotics are used. - Purulent processes
. The skin around the outbreak is treated with disinfectants and alcohol solutions. Antibacterial drugs are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen. The treatment regimen includes anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, immunostimulants, and vitamin complexes. - Neuralgia
. The basis of treatment is anticonvulsant medications, which, to increase effectiveness, are combined with medications to improve microcirculation, antispasmodics, antihistamines and therapeutic blockades. - Dental diseases
. Host local events. According to indications, it is recommended to take antibiotics and analgesics. - Atypical prosopalgia
. Tricyclic depressants and anticonvulsants (both separately and as part of complex therapy) provide good results. For intense pain, botulinum toxin is injected to temporarily reduce sensitivity. - Stylohyoid syndrome
. NSAIDs, sedatives, blockades with corticosteroids and local anesthetics, ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone are prescribed.
Conservative treatment
Treatment of early stages of tumors and swelling in the neck area is carried out conservatively. But it is worth remembering that this method may not give a positive result.
Conservative treatment includes the following procedures:
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy;
- drug treatment;
- folk remedies.
When choosing an appropriate course of treatment, the medical history, as well as the risk factors outlined earlier, must be taken into account by the attending physician.
Drug treatment
Medicines are used as a treatment for certain types of tumors and swellings in the neck area. In the process of choosing them, the doctor takes into account the type of tumor, its nature and progression.
In the treatment of this disease, medications are used that help reduce the intensity of pain and reduce the size of the tumor.
Medicines are the first assistants in the fight against tumors
The following medications are used to treat early stages of a tumor or swelling in the neck:
- "Cetuximab";
- "Fluorouracil";
- "Bleomycin sulfate";
- "Amifostin";
- "Temoprofin";
- "Methotrexate."
It is worth noting, however, that some people may initially have a positive response when taking these medications, but over time the effect may cease to be effective. It can be concluded that the medicine can only serve as a temporary way to cure neck cancer and get rid of a tumor or swelling.
"Bleomycin"
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is a method of treatment that is based on the use of decoctions, tinctures and other forms of herbal medicines.
Herbal medicines are an excellent assistant in the fight against neck tumors at an early stage of development. They help to “dissolve” tumors, reduce pain and discomfort.
Below are recipes for traditional medicines that can help treat this disease.
Recipe No. 1. Celandine compresses
What is needed:
- celandine – 2 pcs;
- gauze bandage – 1 pc.
How to prepare: take a gauze bandage and soak it in juice, decoction or tincture of celandine. Then it needs to be tightly applied to the neoplasm and secured with an adhesive plaster. In addition to celandine, it is allowed to use plants such as aloe vera, Kalanchoe or golden mustache. You can also simply apply a cut leaf from a plant to the tumor. Another option is to grind the plant with a meat grinder or blender to a pulp, which then needs to be placed on a bandage. This, in turn, is applied to the affected surface and also secured with an adhesive plaster. This type of compress is applied several times a day. Course – 3 weeks.
Recipe No. 2. Medicine from a mixture of onions and laundry soap
What is needed:
- large onion – 1 piece;
- laundry soap – 1 pc.
How to cook: first you need to leave the onion to bake in the oven for fifteen minutes. Then the onion is cooled and crushed to a paste using a meat grinder or blender. Meanwhile, the laundry soap needs to be grated on a fine grater. When both components are ready, they are added to the container in equal quantities and mixed thoroughly. The finished mixture is applied to the neoplasm. This procedure is carried out once a day for two to three weeks.
Folk remedies for the treatment of neck tumors are suitable for absolutely everyone
Recipe No. 3. Garlic medicine
What is needed:
- garlic – 2 cloves
- vegetable oil – 350 ml.
How to prepare: Garlic cloves are crushed and vegetable oil is added to them. The mixture is spread on the area of skin located above the tumor. Thanks to the medicine prepared according to this recipe, the tumor will begin to rapidly decrease in size. The procedure is carried out daily for 2-3 weeks.
Recipe No. 4. Miracle beets
What is needed:
- beets – 1 pc.
- vegetable oil – 350 ml.
How to prepare: grate the beets on a fine grater. Bring to a paste, mix with vegetable oil and apply to the site of the tumor. You need to use this product 1-2 times a day for 1-2 weeks.
Recipes for folk remedies
Before treating a benign tumor at home, you should find out exactly its nature and make sure that the tumor does not become malignant.
Benign tumors can be successfully treated with folk remedies. But there is one condition - the size of the tumors should be no more than five centimeters. If the tumor is larger than indicated or it has become malignant, then urgent surgical intervention is required.
Important! The indicated dosage should be observed, since if folk remedies are used incorrectly, organs located in the neck area may suffer.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a method of treating malignant tumors that uses all kinds of drugs against cancer.
If you want to learn in more detail how to treat a spinal cord tumor (cancer), as well as consider symptoms and alternative treatment methods, you can read an article about this on our portal.
This procedure is aimed at destroying cancer cells that are rapidly dividing. Unlike radiation therapy or surgery, which target specific areas, chemotherapy affects the entire body. But it greatly affects some healthy cells and organs, such as skin cells, hair cells, intestines and bone marrow. This influence is one of the side effects of treatment.
Chemotherapy helps get rid of cancer
In some cases, chemotherapy treatment destroys cancer cells completely. However, unfortunately, there is a high chance of relapse, so this method of treatment does not guarantee a cure for cancer.
There are some cases when therapy is not able to cure a disease, but only slow down its development and reduce pain.
Chemotherapy is rarely prescribed as the only method of treatment; more often it is used together with surgery (usually carried out after chemotherapy), radiation or biological therapy.
Radiation therapy
Physiotherapeutic devices
Radiation therapy is a procedure that uses penetrating radiation to shrink tumors and kill cells that cause cancer. This technique uses gamma radiation and x-rays.
There are two types of this procedure:
- external beam radiation therapy (rays come from a special medical device);
- close-focus radiation therapy, or brachytherapy (a radioactive substance is injected into the patient's body in a small amount). In this procedure, radioactive substances, such as radioactive iodine, are injected into the body and travel through the blood to contact and destroy cancer cells.
Radiation therapy is highly likely to destroy tumors
Approximately half of patients with neck cancer receive radiation therapy throughout their course of treatment.
How radiation therapy works: substances injected orally interact with cancer cells and damage their DNA.
Worth knowing! DNA is a macromolecule that ensures the storage and transfer of genetic information from generation to generation.
Either the direct injection of radioactive substances damages the DNA of cancer cells, or the charged particles created by the apparatus penetrate into the cells, which, again, leads to destabilization of the DNA.
Cancer cells with damaged DNA strands die and are then eliminated by the body.
However, there is a danger that this therapy also affects healthy cells, which negatively affects the patient's health.
When agreeing on the course in which this therapy will be included, specialists do not exclude possible damage that will be caused to healthy cells of the body and warn the patient about this. They know well how much radiation healthy tissue can accept without harm. This knowledge helps them decide where best to direct the radiation during treatment.
Diagnostics
Therapists are involved in determining the cause of neck swelling. According to indications, patients are referred to otolaryngologists, endocrinologists, maxillofacial surgeons, and other specialists. The examination includes objective, instrumental, and laboratory techniques. The following diagnostic procedures are carried out:
- Questioning, general examination
. A basic study that allows you to establish a preliminary diagnosis and draw up a plan for further examination. Involves studying symptoms, medical history, and assessing external changes. - Sonography
. Ultrasound of the neck is informative when studying the condition of organs and soft tissues, it allows you to identify tumors, areas of inflammation, determine the localization and boundaries of pathological processes. An ultrasound of the thyroid gland is prescribed if an endocrine cause of neck swelling is suspected. Ultrasound of the lymph nodes is recommended for lymphadenitis and cancerous tumors. - Radiography
. To exclude subluxations and vertebral fractures, X-rays of C1 or the cervical spine are prescribed. If there are symptoms of damage to the ENT organs, an x-ray of the larynx is performed. - Other visualization techniques
. CT and MRI of the neck are performed to detail the information obtained during sonography or radiography and make it possible to clarify the location, volume, and nature of the pathological process. - Radioisotope scintigraphy.
Effective in studying the thyroid gland, visualizes nodes, confirms the presence of diffuse changes. - Endoscopic examination of the throat.
Direct and indirect laryngoscopy, microlaryngoscopy, fibrolaryngoscopy are prescribed for lesions of the larynx. According to indications, a biopsy is performed during the study. - Lab tests
. Depending on the existing symptoms, general and biochemical blood tests, examination of the level of thyroid hormones and antibodies to them, microbiological analysis of swabs, punctures, blood samples, cytological or histological examination of a biopsy specimen can be performed.
Neck palpation
Prevention
To prevent the recurrence of tumors or swelling in the neck area, the following preventive measures are recommended.
- You need to say “no” to bad habits. To eliminate any favorable conditions for the development of tumors and swellings in the neck area, you need to stop drinking alcohol and smoking. The disappearance of these two bad habits from a person’s life significantly reduces the chance of cancer recurrence, which can cause a tumor.
- Get vaccinated. Today, human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines help fight oropharyngeal and neck cancer.
- Sports activities. Everyone knows about the benefits of physical exercise for human health. Anyone who plays sports has a strong immune system and a well-developed body physically. This gives natural resistance to most diseases.
- Exposure to the sun should be done in moderation. Many people love to sunbathe, but not everyone benefits from the sun equally. After treatment for a tumor, it is better to be less exposed to direct sunlight and tightly cover the places where the tumor was once located. This will avoid a possible relapse.
Results
Tumors and swellings in the neck area are a serious problem that can affect every person. Even though some of them are considered benign, they are still dangerous because they can turn into malignant forms over time.
There are many reasons for the appearance of tumors, but mostly it is due to bad habits and viruses. They most often contribute to the occurrence of this type of problem in people.
A tumor in the neck is a dangerous disease that must be fought to the end
It is impossible to overestimate the need for prompt diagnosis of tumors in the neck and the work of qualified specialists, since early detection of the disease provides a greater chance of a full recovery.
Treatment of early symptoms of tumors and swellings in the neck area is possible without surgery, but if you do not consult a doctor in time, surgical removal of the tumor will be the only way out for a cure.
If you do not create favorable conditions for the development of malignant neoplasms, then tumors and swellings in the neck will never bother you.
Why does my chin hurt?
Traumatic injuries
The most common traumatic cause of the symptom is bruise.
Occurs as a result of a fight or fall. It manifests itself as moderate, gradually subsiding local pain and swelling. The formation of hemorrhages or hematomas is possible. Opening the mouth is not difficult or slightly limited, all manifestations disappear after 1-2 weeks. Hematomas, as a rule, resolve on their own; autopsy is very rarely required. Median, mental and lateral fractures of the body of the lower jaw are the result of intense traumatic effects: a frontal impact, an accident, the fall of heavy objects on the face. The pain is very sharp, intense, and decreases slightly over time. Hematomas and bruises form on the skin. Hemorrhages appear on the mucosa; with an open fracture, bleeding develops. Swelling increases quickly. Stepping of the dentition, mobility and, often, tooth dislocations are observed.
Purulent processes
Due to the characteristics of the skin, the increased oiliness of this area of the face, possible contamination and contact with mechanical irritants, the chin is a favorite location for superficial and deep pyoderma:
- Ostiofolliculitis.
Occurs most often. Initially, an area of redness and slight pain appear, which intensifies with pressure. The pain intensifies, a cone-shaped pustule with a yellow tip up to 0.5 cm in size is formed. Then a brownish crust forms on its own. - Folliculitis.
When inflammation spreads to the entire depth of the hair follicle, folliculitis develops. The symptoms are the same, but more pronounced than in the previous case. The pain at rest is insignificant, bursting, and when touched it is moderate. The pustule ruptures, leaving behind a small ulcer that heals to form a scar or area of hyperpigmentation. - Furuncle.
The purulent infiltrate increases and turns into a cone-shaped purple node. The pain is initially dull, bursting, quickly intensifies, becoming jerking and throbbing. There is extensive swelling. A fluctuation zone is formed. After the pus drains and the rod is rejected, the pain quickly decreases.
Adenophlegmon of the chin is not pyoderma; it develops as a result of suppuration of the submental lymph nodes after dental operations (for example, tooth extraction), with regional lymphadenitis of various origins. The pathology is manifested by a progressive pain syndrome of a bursting, tugging nature. A dense swelling forms on the chin, quickly spreading to nearby areas. Palpation is sharply painful. Severe intoxication is noted.
Osteomyelitis in this anatomical zone is post-traumatic in nature, affecting the body of the lower jaw with open fractures, deep wounds with subsequent suppuration, and the spread of local purulent processes to solid structures. With good drainage, pain is moderate. They intensify with bone involvement and are accompanied by an increase in edema and hyperemia of the wound edges. In the absence of a path for the outflow of pus, the pain quickly becomes unbearable and is complemented by a pronounced intoxication syndrome.
Chin pain
Trigeminal neuralgia
Pain in the chin appears when the third branch of the trigeminal nerve is involved and spreads to the lower lip, lower jaw, gums, and oral mucosa. Painful paroxysms are short-term, but extremely intense, reminiscent of electrical discharges, occur one after another, forcing patients to freeze without moving. Provoking factors for neuralgia include shaving, talking, laughing, chewing, and exposure to cold.
Dental pathologies
Referred odontogenic pain in the chin is detected when 1 premolar, canine and incisors are affected. They are caused by the spread of impulses along the autonomic nerve fibers to the corresponding Zakharyin-Ged zone. They can be aching, drilling, pulling, shooting. Sometimes they develop in the absence of pain in the affected area. They are provoked by tooth extraction, surgical operations, and pulpitis.
Atypical facial pain
The chin is one of the possible localizations of atypical prosopalgia. The pain is deep, aching, dull, debilitating. Sometimes it is painful, but more often it is of medium intensity. Wavy, disturbing often or constantly, intensifies under the influence of external stimuli, and in many patients disappears at night. It is often combined with facial pain in other locations, migraines, and back pain.
Other reasons
Radiating pain in the chin can be disturbing with myositis of the cervical muscles. They appear after hypothermia, are localized along the front surface of the neck, from where they spread upward to the chin and downward to the shoulder girdle. They can be dull or shooting, intensifying with physical activity. In patients with stylohyoid syndrome, the pain is one-sided, dull, occurs under the jaw, radiates to the chin, TMJ, ear, and root of the tongue. When turning the head, the cough becomes stabbing and sharp. Progresses gradually. Complemented by dysphagia, sensation of a foreign body in the throat.