When we eat a dish, our taste buds on the tongue are stimulated and allow us to appreciate various nuances - spiciness, sweetness, acidity. The sense of taste is one of the five basic senses of a person, allowing him to live comfortably and safely in our difficult world. Initially, the perception of taste was protective - it made it possible to identify dangerous or spoiled products due to their different tastes. But today it helps us enjoy and enjoy food. And if the food seems tasteless or “no good” - this is a problem.
A taste disorder is a condition that alters your normal sense of taste. The change in your taste, which is closely related to your sense of smell, can be temporary or permanent.
More than 2 million Russians suffer from a permanent disorder of taste and smell, the degree of severity varies from a slightly reduced sensation to the complete disappearance of taste and smell. Most often, these disorders are not caused by other, more serious problems. However, a sudden loss of these senses could be a sign of a serious problem, such as a brain tumor, and in today's times, a sign of coronavirus infection. Although such serious problems are rare, you should report any changes in taste or smell to your doctor.
The medical term for loss of taste is ageus. If you haven't lost your sense of taste, but it has changed, it's called dysgeusia.
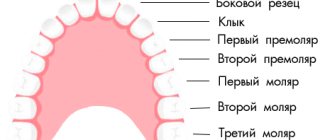
Taste buds are special structures that detect the taste of chemicals responsible for flavors when food or drink dissolves in saliva. Most of the taste buds are located on your tongue. There are several receptors in the back of the mouth. The sense of taste is not as well developed as the sense of smell. Taste buds can only distinguish between salty, sweet, sour and bitter tastes.
Fragrances can be perceived more broadly because the sense of taste works closely with the sense of smell. Losing your sense of smell almost always greatly impacts your ability to taste. Your sense of taste is most developed between the ages of 30 and 60. Around age 60, you begin to lose your ability to taste, especially sour and bitter tastes. Because older people can still taste salty and sweet foods, they sometimes add more sugar or salt to food to improve its taste.
Food allergies
List of foods that most often cause allergies
Causes of loss of taste
Besides normal aging, the most common causes of loss of taste are:
- nasal airway problems, especially nasal congestion caused by allergies or colds;
- upper respiratory tract infections, sinus infections (sinusitis), tonsillitis or sore throat.
Other reasons:
- dry mouth;
- gum or dental disease;
- nasal polyps;
- seasonal allergies;
- damage to the sensory nerves that conduct impulses from the tongue and pharynx;
- exposure to chemicals;
- taking certain medications;
- smoking;
- radiation therapy.
An increase in taste is also possible, but little is known about the reasons for this phenomenon.
Loss of taste can also be caused by other conditions, including:
- glossitis (a condition in which the tongue swells and changes color);
- oral candidiasis (infection of the oral mucosa);
- vitamin B12 deficiency;
- zinc deficiency.
In some cases, loss of taste may be a sign of a serious or life-threatening condition that should be immediately assessed in an emergency situation. These include:
- a brain tumor;
- head injury;
- oral cancer;
- stroke;
- transient ischemic attack (temporary stroke-like symptoms that may be a warning sign of an impending stroke).
When you have ageusia or dysgeusia, food and drink taste different than before. Some foods may taste strange or have a metallic taste. Your sense of taste may be better or worse, or you may not be able to taste at all. If your sense of taste is lost or diminished, you may lose interest in your favorite foods. Then the body does not receive all the necessary nutrients. This may cause additional problems.
Gum inflammation
Problems with gums can cause loss of taste, so how to relieve gum inflammation?
What is dysgeusia and what causes its occurrence?
Dysgeusia (distortion of taste) is a disease in which the sense of taste is partially or completely absent. There are many reasons for this disease. Using the sense of taste, we can determine the taste of food and other elements entering the body. The sense organs that are responsible for this function are called taste buds.
They are located on the surface of the tongue. Under some conditions, a person may lose the ability to taste foods. Experts distinguish four main types of such disorders, namely pargeusia, dysgeusia, ageusia or hypogeusia. The complete absence of all taste sensations is called ageusia, partial weakening is called hypogeusia . Sometimes, a person constantly feels an unpleasant taste, regardless of the product he consumes. Distorted taste, which has a metallic taste, is a sign of dysgeusia.
Treatment for loss of taste
To determine the cause of taste problems and eliminate them, you need to consult a dentist, ENT specialist or neurologist, depending on the suspected disease.
Diagnostics
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and medical history and examine you carefully. Your ability to taste is tested by applying weak solutions of salt, sugar and vinegar to your tongue. The specialist will check different parts of the tongue.
Smell and taste influence each other, so if you have problems with taste, your sense of smell should definitely be examined. The doctor will ask about any changes or problems with your sense of smell, then they will examine your nasal passages and evaluate your sense of smell.
Information to help your doctor make a diagnosis includes:
- what taste you distinguish and what you don’t;
- how long have you had the problem;
- is the taste constantly impaired or does it happen from time to time;
- What medications do you take.
Special tests with flavor combinations are rarely carried out. If there is a suspicion of possible sinus polyps or tumors, a CT scan may be done.
Modern methods of treatment
If the underlying cause of the taste disorder is identified, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment for the corresponding disease. For example, if the taste disorder is caused by medications, the doctor may suggest changing the dosage or stopping the medication. If your taste disorder is caused by dental problems, you will be referred to a dentist.
If your taste problem is caused by a problem with your nose, medications such as nasal sprays may help. First, try rinsing your nose with salt water (Salin, Aquamaris, Aqualor, Marimer, Morenazal), if that doesn’t help, you can use vasoconstrictor drops (Tizin, Nazivin, Nazol, SNUP, Ximelin).
show more
If these are allergy symptoms that continue to cause problems even though you are currently taking medications, talk to your doctor about steroid nasal sprays to relieve allergy symptoms (Avamys, Dezrinit, Tafen, Flixonase, Nasobek).
show more
Complications of ignoring taste
Ignoring the problem leads to the development of various complications:
- There is a loss of appetite. It seems to a person that his favorite dishes have a strange, unusual taste, so he stops enjoying eating.
- Against the background of sluggish infections, a decrease in immunity occurs.
- If you delay visiting a doctor, the disease enters the chronic phase.
- Transfer of infection from the oral cavity to vital organs.
- Insomnia, aggression, developing against a background of discomfort, irritation from the constant salty taste.
- Atherosclerosis resulting from dehydration, a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels.
Preventing loss of taste at home
For taste problems, there is not much that can be done in terms of prevention.
If you smoke, quit.
Make your food more flavorful and rich by adding additional herbs and spices. Avoid using too much sugar or salt.
Why does taste disappear during coronavirus?
There have already been several studies that link loss of taste and smell to COVID-19 infection. One of the largest studies, in which more than 2,000 people took part, shows that 68% had a loss of smell, and 71% had a loss of taste. For comparison, in the control group, where symptoms of a respiratory infection were noted, but the test for coronavirus was negative, 16% had impaired perception of smell, and 17% had impaired perception of taste.
Coronavirus symptoms
Loss of taste is one of the symptoms of coronavirus, but what are the others?
Although more research is needed, scientists note that the first symptoms of infection include fever, fatigue, and poor health. Loss of taste and smell should be considered as a probable early symptom, but its formation is still completely unnecessary. The study notes that such symptoms usually disappear within 10 to 14 days.
Is loss of taste always a sign of illness?
Complete or partial loss of taste, its distortion, the presence of a taste in the oral cavity is a symptom of diseases, pathological conditions, or it is a consequence of treatment or injury. In any case, this is a reason to visit a doctor and you need to start with a dentist or neurologist.
Depending on the suspected cause, consultation with other specialists and appropriate treatment will be necessary.
The effect of synthetic salt on the psyche
Unlike the use of heroin, cocaine and other hard drugs, which drug addicts use because of unbearable withdrawal symptoms and it seems to them that another minute without them and they will die, the dose acts on them like an anesthetic - they took it and released it, in a synthetic drug there is a different principle: drug addicts They get hooked on it, use it again and again because they like the sensations they experience: the feeling of weightlessness, invincibility.
They are omnipotent, power prevails over them. Wild impulses during sex, superpowers that open up in them. These are a kind of stimulants that give a feeling of joy, brightness, everything that is not in real life. All these sensations seem to free a person from existence, the gray mass, ordinariness, as if they bring bright colors to life.
In addition, they increase the level of self-esteem so much that a person thinks that he is a hero. The drug addict seems to be instilled with self-confidence and courage. He begins to behave too greyhound, to speak in an orderly tone, because it seems to him that he owns the world. If we talk about sex life during consumption, the substance acts in such a way that it enhances this sexual desire. But in subsequent times, a person will not be able to get the same pleasure while in his normal state.
We suggest you read: The lymph node on the neck on the right under the jaw hurts: what is the reason
Popular questions and answers
Otolaryngologist Vera Polkanova answered our questions about loss of taste
When analyzing medical records of patients with COVID-19, it was found that one of the symptoms of infection was loss of taste and smell, which was recorded in 59% of patients. However, the scientists said more research is needed to confirm that sensory disturbances are among the first symptoms of infection.
What is loss of taste and how does it happen?
There are two main causes of impaired taste perception: ● neurological, associated with disruption of the sensory nerves or brain; ● organic, associated with impaired stimulation of taste buds or olfactory chemoreceptors.
Which doctor should I see?
This pathology may be encountered by: ● dentists;
● neurologists; ● otolaryngologists. Elimination of disturbances in the perception of taste is carried out by a specialist whose narrowly focused pathology caused these changes.
The main causes of disturbance and loss of taste?
Causes of deterioration in taste sensitivity may include dryness of the oral mucosa, caused, for example, by frequent smoking or dysfunction of the salivary glands, Sjögren's syndrome, radiation therapy to the head and neck, or peeling of the tongue, as well as the use of various medications (for example, drugs with anticholinergic properties and vincristine). Because different tastes are related to aromas, smell and taste are physiologically interdependent. Nasal breathing disorders can affect the perception of taste (from a simple runny nose to chronic recurrent diseases or formations of the paranasal sinuses).
Consequences
Excess salt in the body negatively affects the main organs that perform a number of vital functions - muscle tissue, heart, blood vessels, kidneys and the central nervous system:
- an excess of the compound leads to weakening and stretching of muscle fibers, affecting their contractile activity;
- The kidneys are under a lot of stress. Deposits can provoke kidney failure, inflammatory processes, nephritis;
- excess salt often causes blood thickening, which leads to increased blood pressure and increased heart rate. In these cases, the likelihood of arrhythmia, bradycardia, and stroke increases;
- in addition, compounds can affect the functioning of the brain and hypothalamus, disrupting the process of regulation and conduction of nerve impulses.
If the human body suffers from an overabundance of the substance for a long time, serious consequences can occur that affect all internal systems:
- Osteoporosis. Excessive salt accumulation leads to loss of calcium found in the bones, which provokes their thinning and the development of this disease.
- Stones in the kidneys. The kidneys are the main organ of the excretory system, which removes excess fluid from the body. If a person has a lot of salt in the body, the kidneys stop functioning normally, which often ends in the formation of calcium stones.
- Malignant tumor of the stomach. Excessive consumption of salty foods increases the likelihood of developing stomach cancer by about 10%.
We invite you to read why dental fluorosis occurs and how it develops: photos of the disease, symptoms and treatment rules
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RjCUcbkqzfw
Most often, this pathology occurs among the Japanese, where the most popular food is various pickled and salty dishes.
Dehydration
When the body loses too much fluid, such as after severe diarrhea or vomiting, saliva thickens and becomes salty due to the increased concentration of mineral salts in it.
What to do?
To prevent dehydration, doctors recommend drinking 1.5 to 2 liters of fluid per day. In case of severe dehydration, special solutions are prescribed to restore the water-salt balance.