No one doubts that every tooth in the mouth is important. The only exception is the “eight”. Their absence does not cause any functional disorders, does not affect the aesthetics of a smile or the ability to chew food. All other teeth are necessary so that the dentofacial apparatus can work as a single coherent mechanism.
With the help of incisors we bite off food, canines and premolars are used to grab food, molars are used to crush and grind food. The loss of any of these teeth inevitably leads initially to discomfort, various functional inconveniences, and later to deformation of the dentition.
Increased load on other teeth
In the absence of any teeth, their function is taken over by neighboring teeth, and accordingly, the load on tooth enamel, crowns and roots increases significantly. This leads to the fact that teeth begin to deteriorate many times faster. For example, when removing molars, the incisors have to take on a task not provided for by nature - grinding food. As a result, longitudinal and transverse cracks appear on the enamel, the edges of the teeth wear off and turn yellow.
Increased load over time turns out to be fatal for the roots, as it provokes their increased mobility. If you do not reduce the constant pressure, bone tissue will also begin to suffer from overload.
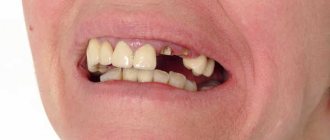
What is secondary edentia
Why, with partial edentia, teeth cannot fully perform the chewing function?
What does partial adentia lead to?
In dental practice, a situation often occurs when a patient is missing several teeth and one could say that this is partial adentia, BUT the remaining teeth are in such a deplorable condition that they cannot perform their natural functions, and in this case it would also be complete edentia, i.e. lack of teeth for chewing food.
On the picture
- partial edentia
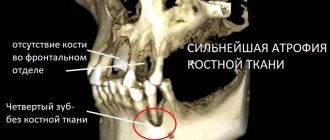
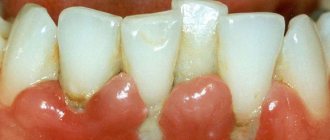
Bone loss
After a tooth is removed, the bone tissue begins to atrophy. Bone volume decreases by 25% per year, and the process is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. Bone atrophy can cause adjacent teeth to become loose and even fall out.
Bone loss also creates problems with subsequent prosthetics. If a tooth is missing for too long, doctors have to perform a bone grafting procedure before installing an implant. This significantly increases the overall treatment time and cost.
Why does bone tissue decrease when teeth are missing?
Very often, when planning dental restoration using implants, we are faced with a deficiency of bone tissue, which is accurately detected during computed tomography:
Let's figure out what it is and why it happens
Let's start with the fact that bone is a living tissue, with its own laws of life. In the case of implantation, we are talking about the alveolar bone, that is, the bone of the alveolar process - the bone where the roots of the teeth are located. And when we talk about bone deficiency, we are talking about a deficiency of the alveolar bone. This bone provides support and stability to teeth. Its entire structure is aimed at stabilization.
And when teeth are lost, the need for this bone disappears and its resorption or resorption occurs. Loss of alveolar bone can also occur with preserved teeth due to periodontitis. The loss of bone tissue increases many times over when using removable dentures, since the denture exerts unusual pressure on the gum and bone, pressure for which the bone was not “designed” to bear. As a result, we are faced with a situation where the bone - where the implants can be installed - is missing or insufficient.
An example of what can happen to the bone tissue of a patient who had a tooth removed more than 15 years ago and did not go to the doctor only because he was afraid of the sinus lift procedure is shown in detail in my article “He was afraid of the sinus lift and waited... 15 (!) years"
We will talk about methods of treating adentia in the next article.
What complications can there be?
The complete absence of teeth inevitably causes psychological problems, functional discomfort and quite dangerous consequences for the entire body:
- problems associated with eating: the inability to bite and chew food normally leads to serious diseases of the digestive tract,
- gingival subsidence and bone tissue atrophy, which causes difficulties in prosthetics,
- deformation of the shape of the face, the appearance of wrinkles, reduction of the lower third of the face, retraction of the lips into the oral cavity. If all teeth are missing, a person looks much older than his age.
Possible causes of complete edentia
There are quite a few reasons that cause the loss of all teeth. Basically, these are advanced diseases of the oral cavity, which lead to the need to remove mobile, diseased, and sometimes even rotting teeth. Often a provoking factor is also the patient’s health, which does not allow maintaining high-quality oral hygiene, as well as the good condition of the teeth and gums.
Other factors include the following:
- genetic predisposition: manifests itself in the weakening of the ligamentous apparatus, which ensures the retention of teeth, in the gradual destruction of bone tissue, etc. In such a situation, it is very difficult to prevent the process, and prosthetics on implants becomes the only option to solve the problem,
- age-related changes: tooth loss occurs due to changes in hormonal levels, lack of vitamins and minerals, destruction of the skeletal system, disruption of tissue nutrition,
- consequences of diseases: mainly associated with serious illnesses. Some drugs reduce immunity, reduce the amount of minimal substances in the body, which leads to weakening of the ligamentous apparatus, loss of bone tissue and, accordingly, the teeth themselves,
- mechanical impact: teeth may fall out due to injury or mechanical damage,
- Negligent attitude towards the condition of the oral cavity: this reason is manifested in the fact that the patient does not carry out high-quality oral hygiene and ignores diseases that lead to tooth loss. This may be due to either a fear of doctors or a reluctance to spend time, effort and money on solving the problem.
Important! The main reason for the loss of all teeth is considered to be inflammation of the periodontal tissues, namely periodontitis and periodontal disease. These are dangerous diseases that usually spread throughout the entire range. As a result of weakening of the ligamentous apparatus, mobility occurs, and over time, complete loss of all teeth.
Teeth become crooked
If one, or even more so, several teeth are missing, occlusion, the correct closure of the teeth of the upper and lower jaw, is disrupted. This is inevitable even if only one tooth is lost. The opposing tooth becomes unsupported and becomes loose. Teeth adjacent to the lost one converge in an effort to fill the empty space. The entire row of teeth gradually begins to move, the bite is disturbed, after which the impact on the jaw joint appears, causing headaches and neck and back pain.
If the teeth are not replaced with dentures, the gaps between them begin to increase, food will get stuck in these crevices, causing caries and other diseases.
Methods for restoring missing teeth
The modern level of development of dentistry in almost all cases of violation of the integrity of the dentition makes it possible to solve the problem taking into account all the wishes of the patient. Types of prosthetics:
- Removable dentures. They are necessary if most of the teeth are lost or all of them are missing.
- Fixed. Their use is possible if 1-2 teeth are missing or their main part is destroyed.
- Implantation. This method of prosthetics involves implanting an implant into the bone tissue, onto which a crown is subsequently placed. Implantation is considered the best method of prosthetics, as it returns the desired functionality to the dentition.
The type of prosthetics is selected together with the doctor, taking into account all indications and contraindications.
The link between dental and heart health
Dental disease and inflammation in the mouth increase the risk of bacterial infection in the bloodstream, and this, in turn, has a negative impact on the heart valves.
Atrial fibrillation, or atrial fibrillation, is considered the most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in the world, and the condition typically involves an abnormal heart rhythm (most commonly tachycardia, a rapid heartbeat). Possible consequences of atrial fibrillation include thromboembolic disease and heart failure. Scientific research has shown that various inflammatory processes in the body, including inflammation that occurs in the oral cavity, play an important role in how atrial fibrillation begins and progresses in patients.
Destruction of bone structures
The supporting alveolar bone contains a spongy substance that absorbs the chewing load. If at least one tooth is missing, this load changes. Remodeling begins in the bone: its structure, shape, and volume change. In order for it to remain dense and not deform, it needs a constant load that will stimulate it. With edentia, the bone becomes less dense. The alveolar process (or the alveolar part in edentulous lower dentition) becomes narrower. The next stage of destruction is when the bone gradually loses height. Without prosthetics, it decreases by 4 mm in just a year. The width is also reduced - by 25% of the original per year. This process does not stop: if implantation is not performed, destruction will continue. Installing a bridge can only partially solve this problem. This design transmits the chewing load, which is absorbed by the surface layer of bone tissue. The deeper layers remain without constant stimulation. Because of this, blood supply deteriorates and the volume of bone tissue decreases.
When even one tooth is lost, the alveolar bone is rebuilt and resorbed. In place of the hole, a narrow ridge is formed, running along its center. The formation of this ridge complicates prosthetics. When using a removable denture, it rests on the ridge and injures the overlying gum tissue.
Another consequence of bone loss is an increased risk of injury. It especially increases for the lower jaw. With a significant decrease in the volume of bone tissue, there is a possibility of a fracture in this area, even with minor injuries.
It is not only the alveolar bone that suffers from the lack of chewing load. Over time, destruction begins to occur in the main jaw bone. This process occurs faster in the posterior parts of the lower jaw, where destruction of up to 80% of the bone tissue volume is possible in the socket area.
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7
Bone resorption changes the characteristics of the dental system:
- oblique ridges are formed on the jaw in the sublingual area. May be accompanied by the formation of a local bedsore;
- changing the shape of the chin. In its anterior part there are two tubercles, which can protrude forward during the destruction of bone tissue;
- the muscles are attached near the top of the ridge, which can provoke pain and discomfort;
- thinning of the mucous membrane, causing discomfort even when eating or performing hygiene procedures;
- formation of functional bedsores.
Consequences of adentia or tooth loss
How are complete dentition and facial appearance related?
The loss of even one tooth already affects the patient’s appearance, let alone when teeth are completely missing. A person ages sharply, and the effect of the so-called “senile face” appears, when the distance from the tip of the nose to the top of the chin decreases greatly. This occurs due to a decrease in the height of the lower third of the face. Since there are no teeth, the support of the lower jaw by the teeth is lost, and the jaw moves backward in the joint area, and forward and upward in the chin area.
This displacement of the jaw leads to a decrease in the tone of the facial muscles, as a result of which the cheeks and chin sag, the corners of the lips go down, even the lips become smaller, as if falling inward. The face becomes more mature.
Dental restoration has a rejuvenating effect, as it allows you to return the lower jaw to its normal position, which provides the necessary support to the soft tissues and restores the smile. After treatment, patients regain confidence and quality of life improves.
How to improve your facial contour without going to a cosmetologist
The “senile face” effect can also occur with partial loss of teeth, especially the chewing group. Sometimes a woman goes to a cosmetologist to tighten her facial contour, and he refers her to a dentist to restore missing teeth. Good, responsible cosmetologists understand that any rejuvenation procedures will not give the expected effect if there are no teeth in place.
Missing part of teeth
If several teeth are lost, they can be replaced with dentures made of plastic or nylon, clasps and bridges. Dental prosthetics using implants installed in the jaw is considered extremely reliable. The latter method also provides the most aesthetic results. When implanting into the body of a bone, the validity period of the inserted implants is maximum; the adjacent teeth do not have to be ground down, which is necessary when using prosthetics with bridges. A dental prosthesis placed on an implant implanted into the bone is quite functional, and from an aesthetic point of view, it completely replaces the lost tooth.