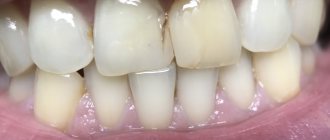
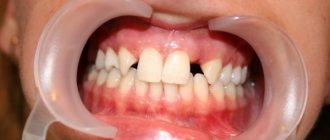
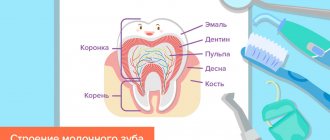
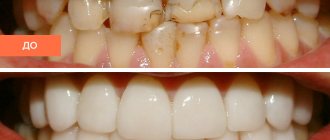
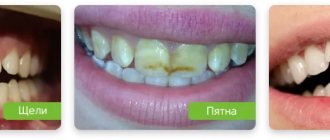
Why do adults' teeth crumble?
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of the destruction and increased fragility of dental tissues, so you should immediately contact a dentist as soon as such a problem has been identified. However, there are common reasons for its occurrence:
- Metabolic disorders leading to changes in the acid-base balance in the oral cavity (enzymopathies, inflammatory bowel diseases that lead to metabolic problems, etc.).
- Hormonal imbalances are most often observed in women during pregnancy and menopause, in adolescents during puberty, as well as in people with diseases of the thyroid gland or other organs of the endocrine system.
- Lack of minerals and vitamins. It is often associated with dietary habits, but may also depend on the region of residence (for example, people living in northern regions have more problems with the oral cavity due to a lack of a number of microelements).
- Insufficient or irregular oral hygiene. Poor cleaning of plaque and food debris creates a favorable background for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms that cause caries and gradually destroy dental tissue.
- Malocclusion. Very often, the destruction of tooth enamel is caused by an incorrect bite, due to which the dentition does not close as nature intended, and the dental tissues are therefore injured and destroyed.
- Bad habits. Smoking, the habit of chewing hard objects, cracking nuts and seeds, as well as the habit of consuming foods that contrast in temperature at the same time (for example, ice cream and hot coffee) often lead to crumbling of tooth enamel.
- Genetic predisposition.
If an adult’s teeth are crumbling, the cause of this pathology is one of the listed factors. However, only a doctor can determine exactly what affected the dental tissues.
If children's teeth are crumbling...
Teeth change color and become extremely sensitive to hot and cold: as soon as children have permanent teeth, many already suffer from so-called molar hypomineralization (MIH).
This is a special form of disruption of the formation of tooth enamel. First of all, this disease affects the chewing teeth. But incisors can also suffer from this disease.
A lack of minerals makes teeth porous. Teeth affected by MIH have fewer minerals present than are present in healthy teeth. First of all, they have a lower concentration of calcium and phosphates. As a result, teeth become porous, and this, in turn, leads to very rapid development of caries.
When affected molars erupt in schoolchildren, molar hypomineralization is now diagnosed quite simply. But just a few years ago the situation was completely different, since this form of diagnosis simply did not exist yet.
The picture of the disease has only recently been described. It was not until 2001 that this phenomenon was brought together under the term Molar Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH), that is, “mineral deficiency in the molars and incisors.”
This approach has significantly improved the diagnosis of children's and adolescent teeth. After all, before this, it was very difficult for the dentist to determine whether the tooth was porous even before the onset of the disease or whether it was a matter of ordinary caries.
Every tenth child has problems with the formation of tooth enamel. Doctors say that the problem of MIH affects ten percent of children, and in five percent it manifests itself in a severe form, accompanied by significantly increased sensitivity and loss of substance.
In adults, it is much more difficult to assess the extent of molar hypomineralization. Even if they had manifestations of MIH, the teeth affected by this disease in most cases have already undergone treatment and restoration, for which reason an appropriate diagnosis is no longer possible.
The causes of MIH should probably be sought in pregnancy. It has not yet been possible to determine where MIH originates from. Doctors admit that they can only guess about the causes of this disease. For example, problems during pregnancy are considered, which could theoretically have a negative impact on dental development.
In addition, events that occur in early childhood, such as high fever infections, antibiotic use and respiratory diseases, as well as dioxin in breast milk, are also suspected. It is possible that the cause of MIH is a combination of several different factors.
Doctors use different methods to treat molar hypomineralization. If MIH is detected in the early stages, the teeth are usually “sealed,” meaning they are coated with a special compound. In more complex cases, fillers and even crowns are used.
Treatment: special dental care, in some cases – removal. In some severe cases of violations of the formation of tooth enamel, the decision remains with the doctors: does a particular tooth have the prospect of long-term preservation? But if a tooth still has to be removed, it should be taken into account that the issue of filling the vacated space must be resolved as soon as possible, since in this case, due to the increased load, neighboring teeth will also suffer.
And you should remember: if children suffer from problems with the formation of tooth enamel, they should brush their teeth only with soft toothbrushes, using fluoride-containing toothpastes.
A child’s teeth are crumbling: what is the reason?
When a child’s teeth crumble, especially in young children in the first years of life, the reasons will be somewhat different than in adults:
- The child’s weak immune system, which reduces the body’s resistance to bacterial infections.
- Malocclusion.
- Intrauterine development disorders - usually the causes lie in poor nutrition or bad habits of the mother during pregnancy.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Poor nutrition, consumption of excessive amounts of sweet foods (including juices, sweet teas), night feeding.
- Poor hygiene. Unfortunately, not all parents take care to start brushing their children’s baby teeth on time and do not always teach their child to take care of the oral cavity from an early age.
- Long-term use of pacifiers and pacifiers. Very often, a child’s teeth crumble due to the fact that even with milk teeth already formed, the baby continues to regularly suck nipples and pacifiers, which spoils the bite and leads to the gradual destruction of the enamel.
What are the treatment methods for caries in children?
Treatment methods depend on the stage of caries development. The more serious the problem, the longer it will take to fix it.
Preventive
At the initial stage, a delicate intervention is sufficient, which can stop or reverse the process of destruction that has begun. In this case, for example, remineralization (treatment of teeth with a solution of calcium and fluoride) or deep fluoridation (treatment with fluoride) is used. Such procedures are carried out in courses until the condition of the teeth is stabilized.
There is also a treatment method without drilling, which allows you to quickly and completely painlessly prevent the development of inflammation. The procedure is suitable for children from 4–5 years of age and causes them minimal discomfort.
Medicinal
For medium and deep caries, classical filling with preliminary preparation of teeth for the procedure is already necessary. To ensure that the treatment is calm and painless, the most modern and effective anesthesia is used. Your baby doesn’t even have to endure the pain of the needle because the injection site is first numbed. The drill is used to a minimum in the treatment of childhood caries - if something can be done manually, then the doctor will do so.
If a child has a complex case of caries, or is very restless in the dentist's chair, treatment is carried out under anesthesia. After consulting with an anesthesiologist and passing all the necessary tests, the baby will be selected the appropriate drug and dose, he will be put into deep sleep, during which the doctor will carefully monitor the condition of the body. Time will fly by in a dream - the child will wake up with healthy teeth, a clear head and an unspoiled mood.
What to do if your teeth are crumbling?
The first and main thing to do if teeth are crumbling in adults and children is to consult a dentist for an examination and professional consultation. The doctor will advise how to strengthen the teeth so that they do not crumble, if necessary, he will carry out therapeutic procedures (remineralization, fluoridation), and if the process is advanced, restoration. In addition, this problem often requires concomitant treatment of the gums, since sometimes dental tissues suffer due to inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the oral cavity, and vice versa, dental diseases lead to problems with the gums.
You also need to pay attention to the following points:
- Normalization of nutrition with the development of a certain food regimen and revision of the diet in the direction of increasing “healthy” foods in it (fermented milk products, eggs, sea fish, herbs, legumes).
- Thorough oral hygiene includes not only mandatory brushing twice daily, but also rinsing your mouth after meals, using dental floss and toothpicks.
- Timely treatment of diseases of the endocrine and digestive system, adherence to the diet indicated in such cases.
- Consultations with an endocrinologist and therapist to identify possible causes of tooth enamel destruction.
- Rejection of bad habits.
Causes
Although enamel hypoplasia is more common in permanent teeth, it is also observed in children. The main factors that increase the risk of its occurrence include malocclusion, periodontal disease and the formation of irregularly shaped teeth. In addition, hypoplasia of primary teeth can be the result of:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which the absorption of vitamins and microelements is reduced,
- long-term diet low in vitamins A, D and K, as well as calcium, magnesium, fluorine and phosphorus,
- endocrine disorders (thyroid gland, pancreas, thymus),
- childhood diseases (smallpox, measles, rubella).
Some researchers have found that dental hypoplasia in children may be caused by prenatal abnormalities such as lead exposure or maternal tetracycline use.
Congenital enamel anomaly is a hereditary disorder of enamel development, leading to damage to both primary and permanent dentition. It may coexist with eruption pathology, congenital tooth loss, anterior open bite, pulp calcification, dentin dysplasia, crown and root resorption, root hypercementosis, root structural defects, and taurodontism. The defect is not associated with any systemic symptoms or defects in other organs and can be divided into subtypes:
- In the hypoplastic type, the enamel matrix is formed in smaller quantities, but is relatively well mineralized.
- In type 1 hypomineralization (hypocalcification), it is present in relatively normal amounts, but is not sufficiently mineralized.
- With the hypomaturation type, the last phases of the mineralization process are disrupted; this type is considered a milder form of the hypomineralizing type.
Each type of problem can be divided into different subtypes depending on the mechanism of inheritance, as well as clinical, radiological, histological and genetic characteristics. In all major types, both maturational and mineralization disorders are present to varying degrees. An anterior open bite can be observed in both the hypoplastic and hypomineralizing types. This variability in clinical manifestations makes differential diagnosis difficult.
Actions for wisdom tooth decay
Special attention should be paid to the “eights”. If we were talking, for example, about the second molar, then they would definitely try to save it. But regarding wisdom teeth, opinions differ. This is due to their characteristics. “Eights” do not have predecessors, so their eruption is often painful. There is no space in the oral cavity for these teeth, so they often bump into “neighbors,” partially erupt, or do not appear at all. Such teeth do not bear a functional load. The blood supply to the “eights” is weak, so they quickly become fragile.
The position of the third molars makes cleaning difficult. The accumulation of food debris (which is especially evident if the wisdom tooth has partially grown) creates a breeding ground for bacteria. Therefore, “eights” are highly susceptible to caries and inflammation.
What to do if a wisdom tooth crumbles? It seems that it causes more problems than it is worth. He does not take part in chewing. But if the destruction is not severe and it is possible to save the tooth, then many specialists still decide in favor of treatment. Firstly, it can take over the functions of the second molar if it is lost. Secondly, the “eight” can serve as a support for prosthetics of the “seven” and “six”. Thirdly, in case of adentia, including those associated with age-related changes, the wisdom tooth is an additional frame for the facial muscles.
The “eight” can be removed if the crown is severely or completely destroyed, if the tooth is impacted or if inflammatory processes, suppuration, or neoplasms on the root have developed, or with limited access for treatment.
Symptoms of tooth erosion in children
The severity of symptoms largely depends on the degree of destruction and activity of the process. With a shallow lesion, tissue changes are invisible; a specific yellowish coloration is visualized only in the dentist’s office after drying the surface and/or treating it with iodine.
As the process spreads, round or oval lesions resembling a bowl begin to appear on the surface of the teeth. Initially they are whitish in color, but as they approach dentin they acquire a yellowish or light brown tint.
Subjective complaints arise in the active phase of the process with moderate or deep damage. The child pays attention to the increased sensitivity of the teeth to hot, cold, sour foods, and discomfort when brushing the teeth.
How is diagnostics carried out?
Are your teeth starting to crumble? Don't hesitate to see a doctor. Only a specialist can correctly determine the cause of the pathology. The dentist will conduct a visual examination of the oral cavity, collect anamnesis, and assess the degree of damage. To perform a more accurate diagnosis, in some cases you may need:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- X-ray;
- blood test for hormone levels;
- allergy tests.
If the doctor suspects the presence of general diseases, the patient will be referred to other specialists. They will confirm or rule out diseases that cause tooth decay.
Types of injuries to baby teeth
To choose a method to restore a broken baby tooth, you first need to determine the type of injury.
Chip on a baby tooth
A chip can occur from minor damage: a child grinds his teeth in his sleep (a common sign of helminth infection), ate solid food (crackers) or chewed a pencil, or bit a spoon unsuccessfully. When examining the oral cavity, it is discovered that a piece of the child’s baby tooth has broken off, the lower edge of the crown has become uneven and scratches the tongue. In this case, it is important to determine the extent of the damage.
If a red dot is visible on the surface of the chip, then the injury is serious and affects the pulp (nerve). And although the child will complain of acute pain when eating cold/hot food, the broken tooth can be saved.
Horizontal crack
A crack indicates an incomplete fracture of the tooth. The baby tooth has not cracked, but the crown is loose, and when the teeth are closed and biting, a sharp pain appears. The most difficult case is when the child fell, the tooth did not break off, but a crack appeared on the crown along the edge of the gum. In this case, you will likely need to strengthen the tooth with a thin veneer.
Baby tooth broken at the root
Did the kid bring a broken tooth in his hand? Unfortunately, with such an injury, it will not be possible to restore the integrity of the dentition. However, you still need to go to the dentist in order to remove the remaining fragments from the gums.
Impacted tooth fracture
With such an injury, the tooth is partially immersed in the gum. The length of the tooth is reduced compared to other crowns, but its edge is not sharp and does not scratch. Characterized by diffuse pain in the jaw. Sometimes the injury is accompanied by heavy bleeding due to the many small vessels in the gums of children.
Fractures of the alveolar process and jaw due to impacted tooth trauma are extremely rare, since the roots of baby teeth are quite short. Damage to bone tissue is indicated by severe pain spreading throughout the entire jaw on one side, the inability to open the mouth wide and a change in the bite.
Displacement of a baby tooth
With a strong blow, damage to the coronal part may be accompanied by complete or incomplete dislocation. A child’s tooth (often a front one) breaks off and takes an unusual position in the socket: it moves to the side, moves forward or backward, and turns around its axis. In this case, the tooth becomes loose, causing pain, and the child refuses to eat. The gums swell a little. In case of such an injury, the tooth is saved, but treatment may last several weeks.
Important! A chip in a baby tooth allows bacteria access to the dentin. Caries appears on the damaged crown. This often leads to its destruction within a couple of months and tooth loss.
What are the dangers of dental injuries?
Tooth decay is associated with damage to internal tissues. If caries is not treated in time, damage to the pulp - the core of the tooth with the presence of nerves and blood vessels - will occur. And then – the inflammatory process. The child will begin to feel constant toothache and complain about his health. The inflammatory process will affect different areas. In children, pulp periodontitis develops due to inflammation. This is due to the fact that the roots of a child’s tooth develop and strengthen over a long period of time, so damage occurs faster.
Preventive actions
It is better to prevent any disease than to treat it. Therefore, in order to strengthen your teeth and prevent their fragility, you must follow these recommendations:
- Carefully and regularly care for your oral cavity using a properly selected toothbrush and toothpaste. Use dental floss, mouthwash, irrigator, and brush for hygiene procedures. Do not use a brush that is too hard, especially if you are prone to crumbling. After each meal, if possible, rinse your mouth with special solutions or at least water.
- Visit the dentist regularly: for adults - at least once every six months, for children - once every 3-4 months. This will allow diseases to be identified and eliminated in a timely manner. Periodic professional teeth cleaning will make it possible to get rid of plaque and tartar, which become a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microflora.
- Massage the gums to improve metabolism in dental tissues. It is useful to strengthen the gums by rinsing the mouth with infusions of herbs (sage, oak bark).
- Do not follow the rules of a strict diet without consulting a nutritionist.
- Eliminate bad habits (biting seeds, pistachios, nails, etc.), do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Keep your child's hands clean. Fruits and vegetables that are offered to him must be clean. It is imperative to maintain oral hygiene. You need to start caring for your teeth immediately after they erupt.
- Do not accustom your child to a pacifier. Otherwise, you should wean yourself off it as quickly as possible. It is also not recommended to feed your baby from a bottle with a nipple for a long time. It is important to ensure that the child does not fall asleep with it in his mouth. The remains of the sweet nutritional mixture provoke the development of so-called bottle caries, due to which the teeth turn black and crumble.
- Limit your consumption of sweets. The child must be introduced to complementary foods strictly according to the rules. You should consult your pediatrician on this issue.
For children, fissure sealing can be performed as a preventive measure. Often, caries develops in the grooves present on the surface of the chewing teeth. They are difficult to clean. In order to prevent caries, the doctor seals the cavities with a special material containing fluoride, therefore at the same time mineralizing the dental tissues.
Treatment for crumbling teeth
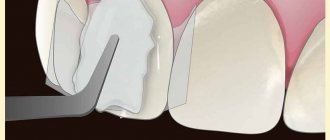
The method of treating tooth decay depends on the cause of this process. If it is caused by general somatic or chronic diseases, the dentist may involve specialized specialists in treatment. In addition, organizing a balanced diet and generally strengthening the immune system are of great importance. To restore damaged teeth, photopolymer filling materials are usually used, and in case of significant destruction, teeth are restored with artificial crowns.
At the ARTOX dental clinic, you can always get advice from a qualified dentist about crumbling teeth in patients of any age and carry out a course of treatment. The experience of our specialists and advanced technologies will allow you to eliminate problems effectively and safely.
Make an online appointment with a doctor or call: +7,.
View prices
Making an appointment with a dentist