What can inflammation of the salivary gland ?
Read the answer to this question in this article. The human body is a complex mechanism consisting of a huge number of organs and systems. Several structures are responsible for performing the same function, constantly complementing each other. For example, different organs take part in the digestion process.
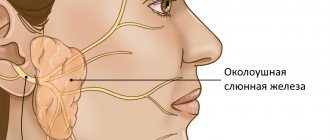
In the human body during normal development there are three pairs of salivary glands
The parotid gland is most often affected by various diseases. There are a number of diseases in which the sublingual and submandibular salivary glands become inflamed. If you do not start treatment on time or undergo inappropriate therapy, then serious complications may occur after such diseases, such as encephalitis, orchitis, meningitis, nephritis, neuritis and pancreatitis. However, do not worry, treatment often gives positive results. To avoid inflammation of the salivary glands, you just need to follow a few recommendations.
University
→ Home → University → University in the media → Stone “thresholds” of the salivary duct
My husband was diagnosed with salivary stone disease. Tell us about her. Anastasia, Minsk.
Factors contributing to the development of salivary stone disease disorder in the body
- disturbance of mineral metabolism (primarily phosphorus-calcium);
- hypo- and vitamin deficiency A, due to which the epithelium of the excretory ducts is severely desquamated and the acidic state of saliva changes;
- disturbance of mineral metabolism in the gland itself;
- disturbance of the electrolyte composition of saliva (against the background of deterioration of metabolism in diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis of the liver);
- hereditary disorders of enzymatic activity;
- decreased secretory activity of the salivary gland, which is accompanied by thickening of saliva with the formation of a gel;
- disruption of saliva formation with a decrease in the rate of its secretion (at the same time, elements of the “core” of the future salivary stone are retained);
- congenital changes in the anatomical structure of the ductal system of the salivary glands - areas of uneven narrowing and expansion of the ducts;
- special structure of the excretory duct of the gland in the form of a broken line with sharp bends, inversion of the excretory duct of the gland;
- chronic inflammatory process in the glandular tissue or excretory ducts (chronic sialadenitis and sialodochitis) of the salivary glands; their insufficient blood supply.
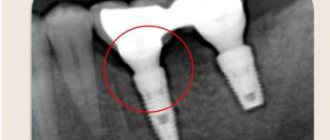
With salivary stone disease, stones (calculi) form in the salivary glands and their excretory ducts. Usually (91–95.4% of cases) the submandibular glands are affected. Among all pathologies of the salivary glands, this disease accounts for 20–60%. The incidence of development in men and women is approximately the same; People at any age are susceptible (even in early childhood).
As a rule, patients suffering from salivary stone disease complain of “formation, swelling” under the lower jaw while eating (after some time everything disappears). In the early stages, there is either no pain, or typical “salivary colic” occurs (when the duct is blocked by a salivary stone).
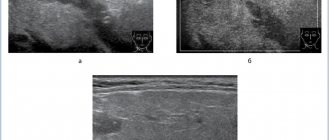
Salivary stone disease of the submandibular gland in 70–80% of patients can be successfully diagnosed on the basis of characteristic complaints, features of the development of the disease, the results of general clinical examination methods and radiographic data. Radiation methods (radiographic, including computed tomography, ultrasound) are key; they make it possible to distinguish the disease from other diseases and choose an adequate treatment method. Despite this, the frequency of diagnostic errors in salivary stone disease is 30–40%.
Treatment of salivary stone disease of the submandibular gland
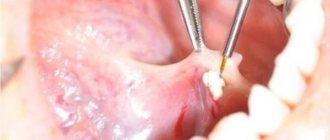
Non-surgical and low-traumatic methods for removing salivary stones involve exposure to a physical factor (ultrasound, laser radiation), then fragments of the stone along with saliva are released into the oral cavity, or the use of special devices that allow the removal of salivary stones in a “closed” way (the effectiveness of such methods reaches 88%) .
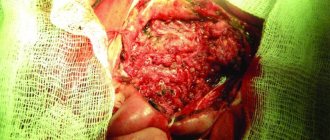
The surgical method gives the best result; Now it is the main one in the treatment of salivary stone disease of the submandibular glands. The salivary stone is removed during surgery.
With salivary stone disease, stones (calculi) form in the salivary glands and their excretory ducts. Usually (91–95.4% of cases) the submandibular glands are affected. Among all pathologies of the salivary glands, this disease accounts for 20–60%. The incidence of development in men and women is approximately the same; People at any age are susceptible (even in early childhood).
As a rule, patients suffering from salivary stone disease complain of “formation, swelling” under the lower jaw while eating (after some time everything disappears). In the early stages, there is either no pain, or typical “salivary colic” occurs (when the duct is blocked by a salivary stone).
Salivary stone disease of the submandibular gland in 70–80% of patients can be successfully diagnosed on the basis of characteristic complaints, features of the development of the disease, the results of general clinical examination methods and radiographic data. Radiation methods (radiographic, including computed tomography, ultrasound) are key; they make it possible to distinguish the disease from other diseases and choose an adequate treatment method. Despite this, the frequency of diagnostic errors in salivary stone disease is 30–40%.
Treatment of salivary stone disease of the submandibular gland
Non-surgical and low-traumatic methods for removing salivary stones involve exposure to a physical factor (ultrasound, laser radiation), then fragments of the stone along with saliva are released into the oral cavity, or the use of special devices that allow the removal of salivary stones in a “closed” way (the effectiveness of such methods reaches 88%) .
The surgical method gives the best result; Now it is the main one in the treatment of salivary stone disease of the submandibular glands. The salivary stone is removed during surgery.
In the early stages of the development of the disease, preference should be given to methods that allow maintaining the functioning of the salivary gland (premature removal of it can lead to an imbalance in the activity of some body systems). The submandibular salivary gland is completely removed only in cases where there are pronounced irreversible structural and functional changes in the gland itself and its excretory ducts (this usually happens with a long course of the disease, repeated exacerbations of the inflammatory process and persistent re-formation of stones).
At the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery of the Belarusian State Medical University, original organ-preserving microsurgical techniques for the removal of salivary stones of the submandibular salivary gland were developed. They have been successfully used in practice for more than 12 years and give good results.
Prevention of re-formation of salivary stones:
- taking medications prescribed by a doctor that increase saliva secretion;
- salivary diet;
- massage of the salivary gland after eating;
- avoiding colds and hypothermia.
Alexander Lastovka, Head of the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, Belarusian State Medical University (BSMU), Doctor of Medicine. sciences, professor; Leonid Tesevich, Associate Professor of the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery of the Belarusian State Medical University, Candidate of Medical Sciences. sciences; Elena Rudaya, Head of the Department of Purulent Maxillofacial Surgery No. 2 of the 11th City Clinical Hospital of Minsk Medical Bulletin , April 9, 2013
Share
Three types of inflammation of the salivary gland
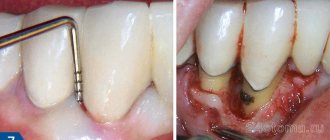
Depending on the disease, there are three types of inflammation, namely catarrhal, purulent and gangrenous. First of all, a swelling forms in the area of the salivary gland, which is often accompanied by pain. The inflamed area becomes red, and the skin there is tense and shiny. The exit site of the gland duct has a limited area of edema and inflammation.
In most cases, a specific liquid is released from it, similar to saliva or pus. Body temperature rises sharply to 39 degrees. Opening your mouth becomes more and more difficult and painful. If treatment is not started on time, the disease will develop into a more severe form with serious consequences.
Treatment
Therapy for sialadenitis is carried out in a hospital. Most often, signs of pathology are eliminated with the help of medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. Less commonly, doctors resort to surgery to cleanse or remove the gland. The operation is indicated for purulent or gangrenous type of problem.
For mumps, patients are prescribed antiviral drugs. Symptomatic treatment is also carried out, aimed at reducing the temperature and relieving pain in the affected area.
Acute blockage of the salivary gland requires complex therapy. To normalize the function of the gland, patients are prescribed a special salivary diet. The diet includes crackers, sour fruits and vegetables, and berries. Drink a 1% solution of pilocarpine hydrochloride orally. The substance promotes contraction of the muscles located next to the salivary gland. All measures are aimed at accelerating the removal of foreign objects and pathogenic particles by enhancing the secretory function of the gland.
If the disease is infectious, the use of antibacterial agents is required. Penicillin antibiotics and antiseptic solutions are injected into the ducts to disinfect the affected area (Miramistin, Dioxidin)
To relieve swelling and inflammation, compresses with Dimexide are applied to the problem area. The procedure is carried out twice a day for 30 minutes. The drug also reduces the intensity of pain.
Additionally, the inflamed glands are heated using UHF. If the situation worsens, a novocaine-penicillin blockade is performed. The procedure is necessary to prevent infection of neighboring tissues.
Chronic sialadenitis is treated according to a different scheme:
- The inflamed ducts are massaged daily with the introduction of antibacterial drugs. The procedure acts as a prevention of purulent complications of sialadenitis.
- Injections with novocaine are made into the subcutaneous fat to improve the secretory function of the glands.
- For 10 days they undergo daily treatment with electric currents.
- To prevent exacerbation of the pathology, iodolipol is injected into the problem area once every 3 months.
It is very difficult to diagnose this disease in the early stages.
In most cases, patients notice that something is wrong when the stone prevents the complete drainage of fluid. All this is accompanied by sharp pain, similar to salivary colic. At the site of inflammation, the tissues swell and become swollen. These symptoms are not constant, the pain either increases or disappears. During treatment, the stone is removed; if the situation is too advanced, sometimes the entire gland is removed.
The salivary glands under the tongue extremely rarely. But at the same time, the disease develops at a rapid pace and can have adverse consequences.
In order to maintain your health, first of all, you must adhere to the rules of hygiene and if you experience the slightest discomfort, immediately consult a doctor.
Inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue
Prevention of violation
There are no vaccines or specially developed drugs against sialadenitis. The only exception is mumps. To prevent the development of the disease, the child is offered an inactivated vaccine against measles, mumps and rubella. All children over 1 year of age are vaccinated against the disease. After the vaccine, stable immunity to the pathogen remains in 96% of vaccinated people.
There are also nonspecific measures to protect against sialoadenitis, including:
- regular oral hygiene;
- timely treatment of wounds and mouth ulcers;
- elimination of chronic foci of infection;
- prevention of saliva stagnation in infectious diseases.
Treatment of salivary gland blockage should be carried out promptly. Otherwise, the disease threatens infection of the soft tissues of the face and further infection of the body. The consequences of sialadenitis require resuscitation measures to preserve the life and health of the patient. The list of dangerous consequences of pathology also includes: rapid destruction of enamel, disruption of oral microflora, chronic inflammation of the gums. For this reason, it is important not to bring your health condition to a critical level.