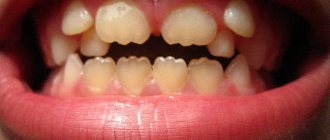
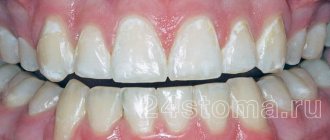
Gingival fibromatosis is an overgrowth of gum tissue. A typical manifestation of fibromatosis is hypertrophy of the gum edge or its entire surface. Gum tissue affected by fibromatosis is quite dense and has a pale pink tint combined with a roll-like shape. This pathology is most typical for young patients, as well as for children during the period of eruption of molars that replace milk teeth.
Fibromatosis is twice as common in women. Patients complain of enlargement and growth of gum tissue, as well as plaque accumulating on the teeth and under the gums. Minor bleeding is often observed during meals. Treatment for this type of pathology in most cases consists of surgical excision of the overgrown gums.
Reasons for appearance
Fibroids on the gums most often appear in children under 10 years of age and adolescents. In adults, the pathology is less common. The growth of a tumor can be provoked by the following factors:
- permanent tissue injury from fillings, artificial crowns, dentures, solid food,
- stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis,
- taking certain medications - estrogens, anticonvulsants, cyclosporine.
In children and adolescents, the growth of fibroids is usually due to a hereditary predisposition; in adults, it is caused by injuries to the mucous membranes.
General information
Single or multiple fibromas can affect the lungs, mammary glands, liver, skin, oral mucosa, etc. The proliferation of connective tissue occurs under the influence of various factors: unfavorable environmental conditions, severe injuries, bacterial or viral infections. When making a diagnosis and developing a treatment strategy for a patient, dermatologists, oncologists and surgeons take into account laboratory data. Information about the morphology of the tumor allows doctors to assess the risk of its malignant degeneration.
Symptoms
A benign tumor forms slowly and does not cause discomfort, so it may remain undetected for some time. If the fibroma reaches a large size and is constantly injured, the following may occur:
- swelling and redness of the gum tissue,
- discomfort and pain of varying intensity.
Constant trauma to the tumor can lead to the beginning of active growth and transition to a malignant form, infection, loosening and tooth loss. Therefore, at the first signs of fibroma, it is important to consult a doctor.
Types of diseases and their characteristics
The pathological process is more often diagnosed in adults, but this is also possible in childhood. There are two main types of hyperplasia:
- Limited. The second name is focal, it is diagnosed in the case of an increase in the volume of tissue in a small area (affects 1-2 teeth). The clinical picture develops slowly, the color of the mucous membrane does not change, and there is no pain. The gums can cover the tooth only 1/3 of its height.
- Generalized. It is characterized by the presence of several areas with a pathological process at the same time, often they merge together. There are no clear boundaries of the overgrown tissue; a large number of tubercles can form. The clinical picture is aggravated: the patient complains of a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the mouth, pain, discomfort during chewing, and a change in diction.
Gum growth occurs slowly, the clinical picture is often blurred. To carry out effective treatment, it is necessary to identify the problem in time. Often, a limited type of gum fibromatosis transforms into a generalized one over time.
Symptoms of hyperplasia in dentistry, stages of progression
Regardless of the type of disease, dentists identify 5 symptoms of fibromatosis:
- increase in gum volume, its visible growth;
- filling the interdental space;
- hiding the crown part of the tooth by lifting the gums;
- a denser structure in places where it increases;
- pale gum color.
The listed symptoms are not necessarily present at the same time; it all starts with a slight enlargement of the gums. Pain and discomfort bother you much later, when the process has already started. The severity of the clinical picture depends on the stage of severity of the disease:
- the first stage - the cushion between the teeth is visually determined, does not present any inconvenience;
- the second stage - the gum tissue grows by half of the tooth root, the increase in volume is determined visually;
- third stage – the tooth enamel is almost completely hidden behind the overgrown gum tissue, the structure becomes smoothed and dense, and bleeding develops.
It is highly advisable to seek dental help at the first stage of the disease so that treatment is quick, effective and without complications.
Treatment methods
Fibroids on the gums are usually removed with a laser or radio wave method. The operation lasts up to 40 minutes. If the neoplasm is large, to prevent deformation of the mucosa, the wound surface is covered with a flap formed from adjacent tissues.
If fibroma is formed due to tissue injury from a filling, crown or prosthesis, you can do without surgery. The tumor may shrink or disappear after the provoking factor is eliminated. In this case, treatment includes refilling or replacing the prosthesis.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of fibroids is performed by doctors of various specializations - dermatologists, oncologists, surgeons, gynecologists, etc. Methods for confirming the primary diagnosis are determined by the location of the benign neoplasm. At the first stage of the examination, patients receive a referral for radiography. Computed tomography allows you to determine the exact size of the tumor and identify signs of its invasion into adjacent organs.
Fibrous formations in bone and cartilage tissue are detected during scintigraphy. If necessary, the doctor can take a biopsy sample for laboratory tests. Microscopy of the obtained biomaterials will allow doctors to assess the morphological structure of tumor cells and the likelihood of their malignant degeneration.
Benign neoplasms of the female reproductive system are often detected during ultrasound examinations. The focus of the pathological process has less echogenicity compared to adjacent tissues.
Growth on the gum: how to treat
The treatment plan is developed by the doctor based on the nature of the growth, so in no case should you self-medicate. It is important to understand that if you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, serious complications can arise.
If the cause is an infection, then it must be removed. In case of periodontal inflammation, professional oral hygiene is performed. If the cause is periodontitis and complicated pulpitis, then first the lump is opened and pus is pumped out of it, and then conservative or surgical treatment is carried out.
If there is no pain, for example, with epulis or ecostosis, then the decision about surgical intervention is made together with the patient.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
Growth on the gum: why it appears and how to treat
A growth has appeared on the gum: what is the cause
Infectious diseases
Non-communicable diseases
Types of growth
Gum cancer
Lump after crown installation
Growth on the gum: how to treat
Which doctor should I contact if a growth appears on the gum?
Normally, the gums have a smooth, pale pink texture. Any change, be it a thickening or a growth, signals problems in the body that cannot be ignored, as they pose a health hazard. Why lumps appear on the gums and how to treat them, we will tell you in the article.
Classification of hypertrophic gingivitis by severity2
| DEGREE OF SEVERITY | A COMMENT | ||
| severity: | Lightweight | a comment: | The gum covers less than half the height of the tooth crown |
| severity: | Average | a comment: | The edge of the gum covers the crown up to half |
| severity: | Heavy | a comment: | The gum covers more than half of the crown |
Diagnostics
A visual examination alone will not be enough to make an accurate diagnosis. Fibromatosis is a benign tumor disease.
When diagnosing, it is important to differentiate it from other tumor diseases. A histological study of the structure will help to accurately determine the type of tumor. This study is carried out on material taken from a biopsy.
Differential diagnosis of fibromatosis is carried out with symmetric fibromas, osteomyelitis, periodontitis, hypertrophic gingivitis. This is done due to their clinical similarity of manifestations.
X-rays are used to evaluate the condition of the entire bone structure. Additionally, an orthopantomogram is prescribed, which will help clearly identify destructive areas of the alveolar process.
Forms
There are 2 forms of this pathology. They differ from each other only in the area of damage to the oral cavity.
Focal
The second name for this form of fibromatosis is limited. This is a fairly rare form of the disease that progresses slowly. With it, only those tissues that are localized in the area of the tubercle of the upper jaw grow.
In isolated cases, such growth appears on the lingual part of the (inner) gum near the lower jaw. They do not differ in color from healthy tissues and are painless.
Why is it so important to sanitize the oral cavity during pregnancy? We'll talk about this in our article. In the following review you can read about how to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction.
The areas that have increased in size have a rounded shape and a fairly smooth surface with a dense, uniform consistency. The formations are covered by a third of the crown of the teeth (less often completely).
They prevent the replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones. Pathology threatens the collapse of the partitions between the teeth and the development of osteoporosis.
Generalized
This form is characterized by the formation of several pathological areas at once. Gradually increasing in size, they unite into one large lesion. As a result, the crowns of the teeth are almost completely covered by overgrown tissue.
The generalized form is of 2 types:
- diffuse – tissue growth occurs uniformly;
- nodular - overgrown tissues have a large number of nodules.
The development of the disease occurs slowly. Having grown, the pathology becomes a serious obstacle to the correct implementation of oral hygiene procedures and interferes with normal nutrition, since these tissues interfere with biting and chewing food.
Over time, both forms of the disease turn into a serious cosmetic defect that affects the psychological state, developing depression.
Classification of hypertrophic gingivitis by location2
| DEGREE OF SEVERITY | A COMMENT | ||
| severity: | Localized form | a comment: | The gums are enlarged only in a certain group of teeth; it occurs due to trauma, crowded arrangement of a separate group of teeth |
| severity: | Generalized form | a comment: | The entire gum is affected and occurs when taking medications or diseases. |