Some children experience the period of teething baby teeth and their replacement with permanent molars painlessly and calmly, while others, on the contrary, are forced to feel excruciating pain. In the latter case, only special medications can alleviate the child’s condition, for example, pain-relieving gels during teething.
Comparison of the effectiveness of Cholisal and Dentinox
Dentinox is more effective than Cholisal - this means that the ability of the drug substance to provide the maximum possible effect is different.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Dentinox is more pronounced, then with Cholisal it is impossible to achieve this effect even in large doses.
Also, the speed of therapy is an indicator of the speed of the therapeutic action; Dentinox and Cholisal are also different, as is bioavailability - the amount of the drug reaching the place of its action in the body. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
Drugs for the treatment of inflammation of the gum mucosa
They must be prescribed strictly by a dentist after identifying the causes of the disorder and making a diagnosis. Self-medication is unacceptable!
Below are some of the most accessible and effective remedies.
Solutions
Soda solution - 1 teaspoon per glass of warm water, rinse 3-5 times a day.
Furacilin - ready-made solution or tablets for preparation (dissolve in warm water), rinse 3-5 times a day.
Chlorhexidine is a solution, rinsing must be done 3 times a day, has a bitter aftertaste.
Miramistin is a solution that additionally has an antifungal effect, rinse 3 times a day.
Gels and balms
Metrogil-denta is an antimicrobial agent, applied to the gums for 30 minutes with a cotton swab, and has a pleasant taste.
Asepta gel is an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agent, effective for the treatment of gingivitis.
Cholisal – relieves inflammation, pain, disinfects. Apply to the affected area 2-3 times a day.
Solcoseryl - has a wound-healing effect and is prescribed for the treatment of dental diseases accompanied by the formation of ulcers and wounds.
Comparison of safety of Cholisal and Dentinox
The safety of a drug includes many factors.
At the same time, it is higher for Cholisal than for Dentinox. It is important where the drug is metabolized: drugs are excreted from the body either unchanged or in the form of products of their biochemical transformations. Metabolism occurs spontaneously, but most often involves major organs such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, skin, brain and others. When assessing the metabolism of Cholisal, as well as Dentinox, we look at which organ is the metabolizing organ and how critical the effect on it is.
The risk-benefit ratio is when the prescription of a drug is undesirable, but justified under certain conditions and circumstances, with the obligatory observance of caution in use. At the same time, Cholisal has fewer risks when used than Dentinox.
Also, when calculating safety, it is taken into account whether only allergic reactions occur or possible dysfunction of the main organs. In other matters, as well as the reversibility of the consequences of using Cholisal and Dentinox.
Popular dental gels for teething
At the moment, gels for teeth and gums are presented by many companies. To make your choice easier, let's look at the most popular ones.
Dentinox
It is a transparent gel with a yellow tint and a distinct scent of mint and chamomile. Using Dentinox gel for preventive purposes allows you to achieve painless and normal formation of the first incisors, primary and subsequent molars. This drug also prevents inflammation of the oral mucosa (stomatitis), irritation of the gums and any painful sensations.
- Composition 1 g of the drug . Active ingredients - tincture based on chamomile flowers (150 mg), polidocanol 600 (3.2 mg), lidocaine hydrochloride (3.4 mg); excipients - xylitol, carbomer (974 P), sorbitol, propylene glycol, polysorbate 20, levomenthol, purified water, sodium edetate, saccharin and hydroxide.
- Side effects . The appearance of a slight burning sensation, redness and irritation. In some cases, allergies may develop, including contact allergic reactions, itching, skin rashes and angioedema. If any of the side effects occur, stop using the product and consult a doctor.
- Contraindications . Hypersensitivity to the substances of the drug, the presence of open wounds on the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. Due to the sorbitol content, Dentinox is not recommended for the treatment of children with congenital fructose hypersensitivity.
Cholisal-Gel
Compared to cooling gels based on lidocaine, Cholisal has a pathogenetic effect aimed at getting rid of the cause of pain in this process - swelling and inflammation.
After application to the surface of the gums, the active substance of the drug, choline salicylate, is absorbed by the mucous membrane and relieves local inflammation: compression and swelling of nearby tissues are reduced, due to which the pain effect disappears. The adhesive base of the gel ensures a rapid onset of the effect (after 2-3 minutes), as well as its long-term retention, which allows Cholisal to eliminate unpleasant sensations during teething in children for up to 8 hours in one application.
- Composition per 1 g of product . Cetalkonium chloride (100 mcg), choline salicylate (87.1 mcg); auxiliary components - anise seed oil (1.61 mg), methyl parahydroxybenzoate (1.5 mg), ethanol 96% (390 mg), hyaetellose (20 mg), glycerol (50 mg), propyl parahydroxybenzoate (0.8 mg), water (up to 1000 mg).
- Side effects . Allergy; A short-term burning sensation may occur in the area of application of the product, which can be eliminated independently.
- Contraindications . Hypersensitivity to salicylates, as well as other components of Cholisal. When treating a child under 1 year of age, caution should be exercised.
Kalgel
Designed to eliminate pain during teething in children aged 5 months and older. Calgelalidocaine, which is part of the product, helps block the excitability of the membranes of the most sensitive nerve endings, and cetylpyridinium chloride is responsible for suppressing harmful microorganisms.
- Compound . Cetylpyridinium chloride (10 mg), lidocaine hydrochloride (33 mg); auxiliary components - xylitol, sorbitol solution 70%, glycerin, PEG-40 castor oil, ethanol 96%, xylitol, hydroxyethylcellulose 5000, laureth-9, sodium saccharin, hydrogenated concentrate, macrogol 300, vegetable flavor, levomenthol, caramel E150, purified water .
- Side effects . Allergy, as well as local irritant effect with prolonged use.
- Contraindications . The presence of hypersensitivity to the main and auxiliary substances of the drug, liver or kidney failure, bradycardia, heart failure of the II or III degree, arterial hypotension, intraventricular conduction disturbance.
Pansoral “First teeth”
The most popular herbal gels to ease teething without anesthetics. At the same time, the plant extracts included in the composition have a softening and soothing effect on the gum mucosa.
- Compound . Extracts of marshmallow root (49.75 mg), saffron flowers (1 mg) and Roman chamomile (49.75 mg); excipients: sodium methylparaben, glycerol, sodium propylparaben, purified water, sodium saccharin, carbomer, sodium benzoate, Irish moss and triethanolamine.
- Side effects. Not identified.
- Contraindications . Newborns up to 4 months, hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Kamistad
Refers to the number of dental gels for small children, used at 3 months and later. Kamistad has a quick pain-relieving effect and allows you to temporarily normalize the child’s general well-being. Due to the high content of lidocaine, treatment of children under 12 years of age should be carried out only as prescribed by a pediatrician.
- Compound . Active ingredients: tincture of chamomile flowers (protects against inflammation), lidocaine hydrochloride (anesthetic for pain relief); excipients: purified water, sodium saccharin dihydrate, benzalkonium chloride, trometamol, carbomers.
- Side effects . If you follow the recommended dosage of the gel, there are no side effects. In rare cases, a burning sensation may occur in the area where the gel is applied, as well as transient hyperemia.
- Contraindications . Hypersensitivity. Not recommended for treating infants under 3 months.
Dentol
Indicated for quick relief of pain in children from 4 months during teething. After application, Dentol begins to act after 1 minute and provides an analgesic effect for 20 minutes.
- Gel composition .7.5%: per 1 g: benzocaine (75 mg); excipients - sodium saccharin, polyethylene glycol 8 and 75, glycerin, red dye, cherry flavor, ascorbic acid, purified water.
- Side effects . If the dosage is observed, no negative effects have been identified. There is a possibility of side effects due to individual intolerance. If swelling, itching, or hyperemia occurs in the area where the drug is applied, its further use should be discontinued.
- Contraindications . The presence of infection or multiple wounds at the site of application of the gel. Hypersensitivity to benzocaine.
Baby Doctor "First Teeth"
The product has a pinkish tint and is odorless and tasteless. Instantly eliminates inflammation and soothes gums. Regular use can significantly facilitate the process of teething without any complications, making it recommended for infants and older children.
- Compound . Calendula (5.8%), chamomile (5%), water (70%), echinacea (5%), methylparaben (0.2%), marshmallow root (5%), plantain (5%), methylcellulose (4 %).
- Side effects . When using the drug in recommended doses and according to indications, there are no side effects.
- Contraindications . Hypersensitivity to herbal components of the medicinal product.
Comparison of addiction between Cholisal and Dentinox
Like safety, addiction also involves many factors that must be considered when evaluating a drug.
So, the totality of the values of such parameters as “o syndrome” in Kholisal is quite similar to the similar values in Dentinox. Withdrawal syndrome is a pathological condition that occurs after the cessation of intake of addictive or dependent substances into the body. And resistance is understood as initial immunity to a drug; in this it differs from addiction, when immunity to a drug develops over a certain period of time. The presence of resistance can only be stated if an attempt has been made to increase the dose of the drug to the maximum possible. At the same time, Cholisal has a fairly low “syndrome” value, just like Dentinox.
Causes of gum inflammation in children and adults
Due to the differences between a child’s body and an adult’s and age-related changes during the growth period, the factors that cause inflammation also differ.
Gum inflammation in children
Most often it is caused by insufficient oral hygiene, which leads to the formation of plaque. Pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation quickly develop in it. Other reasons may be:
- eruption of baby teeth;
- increased vulnerability and sensitivity of periodontal tissues during the growth period;
- viral diseases that weaken the child’s body and reduce immunity;
- lack of vitamins, irregular, poor nutrition;
- hereditary predisposition;
- injuries to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity due to mechanical, thermal or chemical effects (bites, scratches, burns);
- adolescence, accompanied by a hormonal surge.
Gum inflammation in adults
It occurs due to insufficient hygiene, bad habits (smoking), hormonal disorders, hereditary predisposition, and general diseases. In addition to the above reasons, adults sometimes develop inflammation under a dental prosthesis. This occurs due to pulpitis, which begins as a result of:
- carious process;
- cracked or chipped tooth;
- chronic sinusitis;
- general infectious diseases of the body (the pathogen enters the pulp with the blood).
The main cause of pulpitis is caries in an advanced state, its deep form.
Comparison of side effects of Cholisal and Dentinox
Side effects or adverse events are any adverse medical event that occurs in a subject after administration of a drug.
Cholisal has almost the same level of adverse events as Dentinox. They both have few side effects. This implies that the frequency of their occurrence is low, that is, the indicator of how many cases of an undesirable effect of treatment are possible and registered is low. The undesirable effect on the body, the strength of influence and the toxic effect of Cholisal are similar to Dentinox: how quickly the body recovers after taking it and whether it recovers at all.
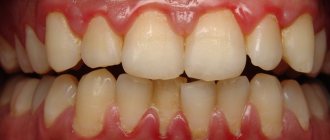
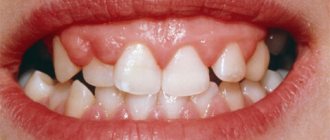
Types of gingivitis. Bleeding as a symptom of the disease
If you do not regularly examine and treat your teeth, the risk of developing complex dental diseases increases significantly.
Gingivitis
This is the name for inflammation of the gums, in which the integrity of the dentogingival junction is not compromised. It is characterized by excessive redness of the gums, swelling, and bleeding. When it becomes chronic, it is often discovered only during examination by a dentist, since there are no complaints of pain. An unpleasant odor appears from the oral cavity.
Advanced cases develop into more severe types of gingivitis:
- ulcerative - the patient complains of itching in the teeth, burning sensation, bleeding;
- atrophic – gum tissue decreases in volume, becomes thinner, and bleeds;
- desquamative – pronounced hyperemia (redness), intensive exfoliation of the gingival epithelium
- ulcerative-necrotic - the most severe form, necrosis (death) of the gingival tissue occurs.
Stomatitis
A very common disease manifested by swelling of the oral mucosa. The patient complains of pain, bleeding gums, increased salivation, ulcerative formations on the mucous membrane, and bad breath. Treatment should be prescribed by a dentist, since only he can determine the cause and choose the right medications.
Periostitis (flux)
It is a complication of periodontitis or pulpitis, or the result of infection through the circulatory system, lymph. There is swelling, swelling of the gums, and high temperature. As it progresses, a sharp, increasing pain appears, projecting to the temporal and ocular region. In severe cases, a fistula forms, through which purulent, bloody contents with an unpleasant odor are released. If the fistula is not treated immediately, the disease becomes chronic.
Depending on the complexity, conservative or surgical treatment is carried out. The first method is based on the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. In case of pronounced inflammation with acute pain, flux treatment is carried out by incision, disinfection and subsequent installation of drainage for the outflow of pus.