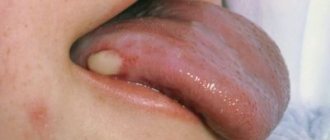
Tongue cancer is a fairly common pathology in the structure of malignant neoplasms of the head and neck organs (about 55% of cases), and in the general structure of malignant neoplasms it accounts for 0.45%. The average age of those affected is 60 years, men suffer from it 3 times more often than women. But the tumor can also occur in young people and even children.
- Causes of tongue cancer
- Symptoms of tongue cancer
- Methods for diagnosing tongue cancer
- Treatment of tongue cancer
- Prevention
Most often, cancer is localized on the lateral surface, a little less often on the root of the tongue, and very rarely in the area of its back and tip. [1,2]
Anatomical structure of the tongue
Kinds
In 70% of cases, cancer of the body of the tongue is detected, in 20% - damage to the root, and in 10% - to the lower surface of the organ. If we divide diseases according to cell characteristics, we can distinguish the following forms:
- Papillary. It looks like a dense growth with papillary outgrowths and plaque-like formations.
- Ulcerative. It is observed in approximately 50% of cases. Ulcers develop over time, can bleed, and often become infected, thereby masking the root cause of the disease.
- Infiltrative. Cancer grows inside the tongue and hardens its tissues. The form can be diffuse or spread throughout the entire organ.
If we talk about microscopic analysis, then in 95% of cases we are talking about a squamous cell form of tongue cancer, other options are much less common.
Symptoms
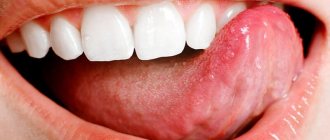
Often a person begins to notice symptoms of tongue cancer when a non-healing ulcer appears in his mouth or, conversely, some kind of lump (growth). If it is an ulcer, it does not heal and may bleed. When it comes to damage to the root of the tongue, there is pain when swallowing, a change in voice, and a feeling that something is blocking the throat.
If some kind of spot (white, red) or bump appears on the mucous membrane of the tongue, you should definitely go to the doctor. A sign may be a feeling of numbness, sometimes painful sensations radiate to the ear. The doctor must be chosen depending on the symptoms. If the symptoms of tongue cancer are localized to the tongue, you can start by visiting a dentist. When you experience a sore throat or a feeling of a lump, you should start a visit to the ENT specialist to rule out ENT diseases. A visit to a therapist is also possible. Any of these specialists, suspecting cancer, will redirect the patient to an oncologist.
Precancerous diseases
There are pathological processes that precede malignant formations. According to the medical classification, the following diseases pose a potential danger.
Bowen's disease
Modern scientists consider the disease as intraepithelial oncology
The pathology was described back in 1912 by Bowen and classified as a precancerous condition.
Modern scientists consider the disease as intraepithelial oncology, but in the International Histological Handbook it is identified as a risk factor.
Symptoms:
- rashes of a nodular-spotty nature;
- the location of the lesion is predominantly in the posterior parts of the oral cavity;
- the surface of the affected area of the mucosa is velvety;
- over time, atrophy of the oral mucosa appears;
- formation of erosions on the surface of the lesion.
When diagnosing, it is differentiated from red lichen and leukoplakia. The disease is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms.
The surgical method is chosen as the treatment method. Affected areas of mucous membrane and tissue are completely removed. If there is a large affected area, complex therapy is used.
Leukoplakia
One of the provoking reasons is frequent exposure to irritants on the oral mucosa
The disease is characterized by increased keratinization of the mucous tissue; lesions are localized on the inside of the cheeks, corners of the mouth, and tongue.
One of the provoking reasons is frequent exposure to irritants on the oral mucosa.
These can be either bad habits (tobacco, alcohol), or spicy or hot foods.
An improperly shaped denture can create favorable conditions for the development of leukoplakia.
Symptoms:
- slight burning sensation;
- tightening of the mucous membrane, which creates discomfort when talking and eating;
- itching;
- formation of white or gray plaques (diameter 2-4 mm).
The essence of treatment is to eliminate irritating factors, take a vitamin complex with a high content of vitamins A and E, treat the lesions with special solutions or undergo surgery.
The regimen is selected individually, depending on the form of leukoplakia.
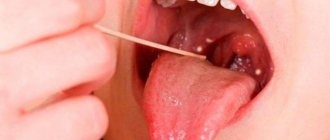
Papilloma
Both stressful situations and injuries can provoke active growth of papillomas.
The disease can be recognized simply by the intensive formation of papillomas on the oral mucosa.
Both stressful situations and injuries can provoke active growth.
Symptoms:
- formation on the oral mucosa of rounded pedunculated papillomas with a warty, granular or folded surface (size 0.2-2 cm);
- localization mainly on the hard and soft palate, tongue;
- pain, bleeding, deterioration in the person’s physical condition are not noted.
Treatment of papillomas includes surgery to cut off the formation from the mucosa, as well as antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy.
Erosive-ulcerative form of lupus erythematosus and lichen planus
The course of the disease occurs in an acute form and with a benign clinical picture
Erosion formations are localized on the oral mucosa and lips.
The course of the disease occurs in an acute form and with a benign clinical picture.
The exact provoking factors have not been identified, but there is an opinion that ulcers and erosions appear as a result of sensitization to various infections, as well as due to malfunctions of the immune system.
Symptoms:
- the appearance of many red spots that transform into erosions and ulcers;
- sensations of dryness and roughness in the mouth;
- in the area of the lesions, the surface is covered with a fibrinous lesion.
The treatment regimen includes the use of antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and painkillers.
Sedatives, immunostimulating agents, and vitamins are also prescribed. If necessary, physiotherapeutic methods are used: phonophoresis, electrophoresis. In difficult cases, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Post-radiation stomatitis
Complications of radiation sickness lead to the development of post-radiation stomatitis
Formed after procedures using ionizing radiation, carried out with violations.
The disease can be triggered by careless handling of radioactive isotopes, resulting in burns on the oral mucosa.
A complication of radiation sickness leads to the development of post-radiation stomatitis.
Symptoms:
- dizziness, physical weakness;
- dullness of the face;
- dry mouth;
- pallor of the mucous membrane;
- formation of white spots in the mouth;
- loosening of teeth.
To diagnose the problem, anamnesis, a clinical picture of the disease, and a blood test are used.
The treatment regimen includes:
- development of a special diet;
- thorough sanitation of the oral cavity;
- treatment of the mucous membrane with an antiseptic solution.
Causes, risk factors
Possible causes of tongue cancer look like this:
- The influence of carcinogens in tobacco and other smoking mixtures.
- Constant exposure to alcohol on the tongue. Interesting fact: recent studies show that alcohol can enhance the effects of carcinogens found in tobacco.
- Contact with harmful substances: salts of heavy metals, asbestos, petroleum products - for example, when working in hazardous industries.
- Regular mechanical injuries to the tongue - biting, exposure to dentures, rubbing the tongue with a splintered tooth or poorly chosen filling, etc.
- The effect on the body of HPV - specifically strains that have a high oncogenic risk. People with HIV and other viruses are also at risk.
- Precancerous conditions of the tongue, which can later develop into cancer. These are chronic ulcers, papillomas, lichen planus, Bowen's disease, etc.
Obviously, not all reasons can cause tongue cancer (and not always) - we are only talking about a significant increase in risks.
Classification
Tumors in the oropharynx are divided into three types:
| Benign neoplasms | Not dangerous, but cause discomfort. Eliminated surgically | Osteochondroma |
| Leiomyoma | ||
| Eosinophilic granuloma | ||
| Condyloma acuminata | ||
| Fibroma | ||
| Odontogenic tumors | ||
| Verruciform xanthoma | ||
| Granular cell tumor | ||
| Pyogenic granuloma | ||
| Rhabdomyoma | ||
| Neurofibroma | ||
| Schwannoma | ||
| Keratoacanthoma | ||
| Papilloma | ||
| Lipoma | ||
| Precancerous conditions | There is a risk of malignancy, but sometimes dysplasia regresses on its own | Leukoplakia. Whitish or gray dots appear on the mucous membrane. They protrude above the surface or remain flat |
| Erythroplakia. Red spots form that bleed when touched lightly | ||
| Cancerous tumor arising from non-keratinizing epithelial cells | The doctor individually selects a treatment regimen | Carcinoma that grows only from the superficial layer of the epithelium. Diagnosed in 90% of cases, with 60% associated with the detection of HPV strain 16 or 18 |
| Polymorphic low-grade adenocarcinoma | ||
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | ||
| Mucoepidermal carcinoma | ||
| Lymphoma |
Figure 1. Leukoplakia
Figure 2.1. Erythroplakia
Figure 2.2. Erythroplakia
Stages
Cancer of the root of the tongue or its body is divided into four stages:
- 1st (initial). At this stage, oncology is often confused with glossitis, stomatitis and other diseases. The person himself may mistake unwanted stains for plaque. There are few symptoms.
- 2nd. Clinical manifestations begin: compactions, tumors, pain. The pain often radiates to neighboring organs (neck, ears). Suppuration and infection of the tumor may occur. The tongue often swells and becomes numb. Already at this stage, metastases from tongue cancer are possible - usually to nearby lymph nodes.
- 3rd. If you ignore the symptoms of the second stage, aggressive penetration of cancer into the thickness of the tongue and neighboring tissues begins. Tissue breakdown also begins.
- 4th. At this stage, metastases are observed in various organs: lungs, liver, bones. Treatment at the fourth stage, as a rule, is limited to palliative care; patients rarely survive more than a year.
It is important not to let the situation get worse and pay attention to the signs of tongue cancer in time - then there will be a much greater chance of recovery.
Staging
The stage of tongue cancer depends on the size of the tumor, its growth, the presence of malignant foci, and distant metastases.
Stage 1. Tumor up to 2 cm.
Stage 2. Tumor 2–4 cm.
Stage 3. One of the characteristics is present: the tumor is 4 cm, there is a focus in the regional lymph nodes.
Stage 4A. One of the signs is revealed:
- Tumor growth through the skin or inside the bone to the nerve, in the lymph nodes the lesion is up to 3 cm;
- The size of the tumor is any, but lesions no larger than 6 cm in regional lymph nodes are diagnosed;
- The tumor grows into the larynx, extending beyond the area of the muscles of the tongue, hard palate, lower jaw, and masticatory muscles.
Stage 4B. One of the signs is revealed:
- The size of the tumor is any, regional lymph nodes are affected, the lesion is more than 6 cm;
- The tumor has grown deeply into the surrounding tissues and organs.
4C stage. There are distant metastases.
Diagnostics
If tongue cancer is suspected, diagnostics include the following:
- a visit to the dentist, during which a specialist will examine the oral cavity and palpate it;
- examination of a smear from the oral cavity (bacterioscopy);
- CT or MRI - to detect metastases in the brain;
- biopsy - examination of a small piece of affected tissue;
- radiography - helps to detect changes in the bones, if any;
- Ultrasound.
List of sources
- Alieva. S.B., Alymov Yu.V., Kropotov M.A., Mudunov A.M., Podvyaznikov S.O. Cancer of the oral mucosa. Oncology. Clinical recommendations / Ed. M. I. Davydova. – M.: Publishing group RONC, 2015, pp. 27-37.
- Romanov, I.S. Features of regional metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, detected during preventive lymph node dissections. / Romanov, I.S., Yakovleva L.P., Udintsov D.B., Dzhumaev M.G., Tsiklauri V.T. // Dentistry. – 2012. – T.91, No. 4. — P. 28-31.
- Romanov I. S., Yakovleva L. P. Issues in the treatment of oral cancer. Farmateka 2013; (8):59–63.
- Paches A.I. Tumors of the head and neck. 5th ed., supplemented and revised M.: Practical Medicine, 2013. P. 119‒146.
- Romanov I. S. Prospects for the use of cetuximab in the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck / Oncology. Hematology. Chemotherapy. - 2015. - No. 17/1.
Treatment
If tongue cancer is detected, there are several types of treatment:
- Surgery. The operation is used most often and allows for recovery in 80% of situations. When the tumor is removed, the tongue may be partially or completely removed. In advanced cases, part of the jaw bone is also removed, then the jaw structures can be restored using special methods.
- Radiation therapy. When fighting tongue cancer it gives good results, also up to 80% effective. Can be used either alone or in combination with surgery.
- Chemotherapy. Prescribed if metastases are detected.
Both chemotherapy and radiation therapy can be palliative - that is, they are carried out in cases where the patient can no longer be cured, but his condition can be maintained and the quality of life can be improved.
Forecasts
With timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, the five-year survival rate for tongue cancer is about 90%. If the cases are advanced, but without metastases, this percentage drops to 60%. When metastases have spread, the five-year survival rate is less than 35%.
Prognosis for tongue cancer
After completing a treatment course at different stages of cancer, it is customary to take into account the average statistical prognosis based on five-year survival. Naturally, this process is strictly individual for each patient and depends on a number of objective and subjective factors.
Nowadays, when starting cancer treatment abroad, patients always consult their doctor about the prognosis for a particular case. For example, by the localization of the tumor process in the tongue, it is possible to predict the further development of the disease and find the most appropriate options for effective therapy. Timely diagnosis and combined treatment of tongue cancer make the patient’s recovery expected and predictable.
Prevention
The following are called preventive measures:
- Regular visits to the dentist - once every six months.
- Constant inspection of the tongue for strange formations.
- Elimination of traumatic factors. If there is an interfering filling in the mouth or the dentures do not fit well, this must be corrected.
- Quitting bad habits: alcohol, cigarettes.
- Timely treatment of all problems in the oral cavity.
- General strengthening of the immune system.
People who are attentive to oral hygiene, as a rule, notice the first signs of tongue cancer earlier than others and consult a dentist in time for initial diagnosis.
Observation
After treatment, you need to undergo regular examinations, their frequency depends on how many years have passed since entering remission.
- In the 1st year - every 1-3 months.
- In the 2nd year - every 2-6 months.
- In 3-5 years - every 4-8 months.
- In the 6th year and thereafter – annually.
The following manipulations and examinations are carried out as control tests:
- medical instrumental examination of the oral cavity, peripheral lymph nodes;
- examination by a dentist if radiation therapy was performed in the oral cavity;
- endoscopic examination of the pharynx and oral cavity;
- for patients who have previously smoked - MRI (CT) of the soft tissues of the neck with contrast, CT of the chest and abdominal cavity with contrast. If necessary, PET with glucose, osteoscintigraphy.