Afty Bednar
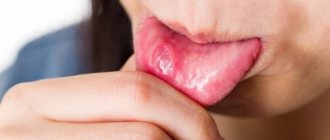
This disease affects children. The disease manifests itself as ulcers, which are covered with a plaque with a clear yellow tint. The main reason that causes the disease is insufficient oral hygiene. Erosions of traumatic origin can form due to rough mechanical rubbing of the soft tissues of the mouth. Therefore, from early childhood, parents should teach their children to properly brush their teeth and rinse their mouths. The selection of toothpaste and brush is important. Hard bristles often damage delicate tissues. It is better to use a brush with soft bristles.
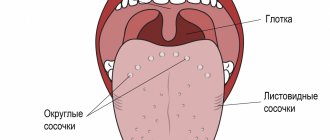
Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivostomatitis
A white sore appeared on the tongue, then an abscess appeared? The erosive area could have formed during a period of weak immunity. If you ignore this problem, a complication may develop in the form of gingivostomatitis. This disease is very unpleasant.
- With systematic hypothermia and damage to the body by viral infections and allergic stomatitis, a necrotic form of the disease often appears.
- Ulcers are diagnosed in the oral cavity, a sharply unpleasant odor appears from the mouth, the temperature rises, saliva is released, and a gray-yellow coating is visible on the muscle organ.
- Ulcers with uneven edges have a noticeable greenish coating and bleed.
The disease usually affects young people, more often men. Patients note pain while eating, swelling of soft tissues. The epithelium becomes cloudy. Treatment is prescribed taking into account the severity of the lesion. Antibiotics, anti-allergy medications, vitamins P and C are prescribed. In severe cases, necrotic tissue is removed.
Tuberculosis
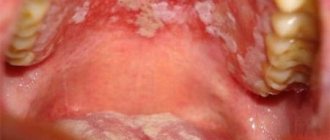
If tuberculosis of the airways is diagnosed, this negatively affects the condition of the oral cavity. Patients notice a dense white coating on the tongue that cannot be removed by brushing. The disease is due to the fact that tuberculosis bacteria have penetrated into the soft tissues of the muscular organ. Pathological tubercles develop on the mucous membrane, then ulcers. Their size is gradually increasing. Ulcerations are loose, shallow, bleeding. Their edges are uneven. In such patients, the temperature rises, weakness appears, and the ulcers are sharply painful. Increased sweating and weight loss are noted. In addition to general therapy, local treatment is recommended, and oral sanitation is prescribed when remission occurs. Pathological soft tissues are treated with antiseptic agents.
Syphilis
When an ulcer under the tongue does not heal for a long time, one can assume an infectious disease caused by Treponema pallidum. After an incubation period (three weeks), ulcerations appear in the mouth. They are diagnosed throughout all phases of the pathology. At first, mucosal lesions are painless. Discomfort and mild pain gradually appear. Ulcers can take 120-150 days to heal. Scars form at the site of the lesion.
When examining the ulcer, it has an oval or round shape. Their edges are smooth, raised, the infiltrate is similar to cartilaginous tissue. The bottom of the ulceration is bright red, the top is most often covered with a dark gray coating in the form of a roller. General therapy for sexually transmitted diseases is carried out in a hospital. Local procedures include sanitation of the oral cavity during remission.
HIV
In a third of patients suffering from immunodeficiency, the oral cavity is covered with ulcerations. Gum tissues, cheeks, palate, lips are affected. An ulcer appears under the tongue in the frenulum area. For this disease, specific treatment is prescribed. It is carried out by infectious disease specialists. Dentists provide care to such patients in all clinics, carefully observing safety precautions.
Content:
- Why does 1.1 occur? Infectious lesions of mucous membranes 1.2. Injuries as a provocateur of illness 1.3. Poor oral hygiene is a contributing factor to problem 1.4. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are the culprits of stomatitis 1.5. Stomatitis as a symptom of helminthic infestation 1.6. Allergy is the cause of illness 1.7. Intoxication causes illness
- Classification
- Symptoms
- How to treat 4.1. Features of treatment of stomatitis
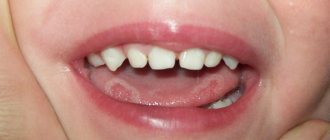
Tongue stomatitis is a dental disease in which the mucous membranes become inflamed. It is dangerous because it is prone to recurrence and sometimes becomes chronic. Children most often suffer from the pathology, but in 20% of cases it is diagnosed in adults.
The main causes of sores on the tongue
The main reasons for the development of pathology are:
- Diseases of the oral cavity (various types of stomatitis, Bandar's ulcers).
- Injuries to the mucous tissue in the mouth.
- Severe diseases (necrotizing gingivostomatitis, tuberculosis, syphilis, HIV, cancer).
The mucous membrane can be damaged in the following cases:
- using a hard toothbrush;
- the presence of a pointed edge of a tooth or filling;
- accidental tongue biting;
- consumption of a food product or medicine that can provoke the development of irritation in the oral cavity;
- the presence of low-quality dentures or braces.
During pregnancy, stomatitis can occur as a result of hormonal imbalance.
Why does it occur
Stomatitis on the tongue is caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi that live in the oral cavity. These can be pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms that begin to actively multiply as a result of decreased immunity or jaw injuries.
Any person has a huge number of bacteria on the mucous membranes of the tongue. Under normal conditions, they do not cause harm and do not cause any complications. This is due to the fact that saliva contains a special antiseptic component - lysozyme, which does not allow bacteria to actively spread.
With a decrease in the body's defenses and trauma to the tissues of the tongue, infection occurs. Lysozyme ceases to cope with the function of suppressing bacterial and viral agents. Then wounds appear that do not heal for a long time.
Infectious lesions of the mucous membranes
The human tongue is an ideal place for bacteria and viruses to multiply. But saliva exhibits harmful activity and does not allow the latter to spread. If the salivary glands do not function at full capacity, the content of harmful organisms increases. This happens with diabetes, dysbiosis, and severe dehydration.
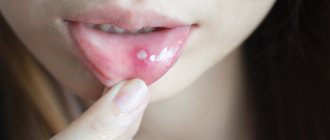
If there are too many bacteria, a white or yellowish coating forms on the tongue. Soon, ulcers of an infectious nature form. Bubbles can also form, which burst and merge with each other, turning into voluminous painful erosions.
Injuries as a provocateur of illness
In some people, stomatitis is a consequence of constant trauma to the membranes of the mouth from the braces. Damage can also be a consequence of an incorrect bite - for example, if, due to an anomaly, a person very often bites the tip of his tongue.
It has been noticed that the disease more often develops in people who eat solid foods that have sharp edges (lollipops, crackers, etc.). Injury to mucous membranes and broken crowns of teeth.
Poor oral hygiene is a contributing factor to the problem.
More often, people who do not pay due attention to oral hygiene need treatment. Typically, they rarely brush their teeth, do not undergo routine dental examinations, and do not use dental floss or mouthwash.
It is very bad if a person eats unwashed vegetables and fruits or has the bad habit of biting nails and foreign objects. All this aggravates the already imperfect hygiene and increases the risk of infection of microcracks on the surface of the tongue.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are the culprits of stomatitis
You can tell a lot about the features of the gastrointestinal tract by looking at the language. If the mucous membrane of an organ often becomes inflamed and becomes painful, doctors suspect the presence of ulcers, gastritis, colitis, etc.
In such a situation, self-medication is prohibited. The patient needs to consult both a dentist and a gastroenterologist.
Stomatitis as a symptom of helminthic infestation
The studies carried out made it possible to establish that tissue irritation is sometimes the result of the activity of worms living in the human body. The presence of worms can be suspected if the tissues of the oral cavity are covered with small ulcers at intervals of thirty to forty days.
Allergy is the cause of the disease
In allergy sufferers, inflammatory mouth disease is more common. Relapses occur after using certain foods, cosmetics, medications, toothpastes and various hygiene products.
If there is an assumption that the disease is a consequence of individual intolerance to any compound, the use of any formulations containing it should be excluded. During periods of exacerbation, it is necessary not only to relieve inflammation that appears in the mouth, but also to take antihistamine tablets prescribed by an allergist.
Intoxication causes illness
In some people, the disease appears in response to poisoning by some toxic elements. Sometimes one dose of a poisonous drug is enough to then suffer from relapses for a long time.
Intoxication occurs when inhaling fumes of paint, varnish, low-quality household chemicals, or after using a number of building materials. People who work with chemical fertilizers, dangerous cleaning solutions and gels are especially at risk of encountering it.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Classification
It is easy to understand why stomatitis develops by its classification. So, doctors distinguish the following types of pathology:
- viral;
- fungal;
- bacterial;
- allergic;
- autoimmune;
- traumatic.
When determining how to treat a disease, the doctor must take into account the provoking factor. Otherwise, it will not be possible to get positive dynamics quickly.
Which doctor treats glossitis and when should you contact him?
When suspicious ulcers are discovered on the tongue, many begin to ask a completely logical question regarding which doctor to turn to for help. In such a situation, you can, of course, immediately make an appointment with a dentist, but it is not a fact that the pathology was caused by a dental problem, and this specialist will be able to provide the necessary assistance. It is better to first consult with your attending physician - after a visual examination, he can send the patient for additional examination, the necessary tests, or immediately refer him to a highly specialized doctor: a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, immunologist, or again to a dentist.
The formation of strange suspicious spots, plaque and ulcers on the surface of the main speaking organ, the occurrence of obvious pain, burning and tingling sensations - all these are signs of tongue pathology. If we are talking about glossitis, then it can be an independent disease, since it is a secondary sign of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems. In any case, the problem requires an immediate solution, so in such a situation the only correct instruction for action is to urgently consult a doctor.
- Kharitonova, M. P. Burning tongue syndrome (Etiology, clinical picture, differential diagnosis, treatment), 2000.
Symptoms
The disease most often develops acutely. The patient's body temperature rises. He complains of weakness and decreased performance. Pain appears in the arms and legs. Your head may hurt a lot.
The skin of the tongue becomes very sensitive. Small lesions appear on its surface, and when touched, severe pain occurs. The ulcers are getting larger every day. It gets to the point where they merge with each other. Then the course of stomatitis worsens. The tissues swell.
A person cannot eat, smile, or talk normally. Bleeding gums may occur. The smell from the mouth becomes unpleasant and foul. No hygiene products intended for treating the oral cavity can help eliminate it. Salivation increases significantly.
Despite the fact that stomatitis affects only the tissues of the tongue and oral cavity, it negatively affects the well-being of a person as a whole. With a strong decrease in immunity, it often comes to the point that the patient develops severe intoxication.
How to treat
If the disease is not advanced, it is quite possible to cure it on your own by rinsing and using antiseptic pharmaceutical ointments. But if after two or three days of self-therapy the situation has not improved or, even worse, the disease has begun to progress even more actively, it is recommended to immediately consult a dentist. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis, determine the true cause of the pathology and select an effective treatment.
to monitor oral hygiene during therapy After every meal you need to rinse your mouth. For this purpose, it is allowed to use self-prepared decoctions and infusions of herbs, special dental solutions, or at least warm water.
Traditional recipes for getting rid of ulcers
How to treat wounds on the tongue if there are no necessary medications in your home medicine cabinet? Then you can use folk recipes that will help alleviate the condition at least a little. Among these are the following:
- Use of infusions of medicinal herbs. Among the gifts of nature, the following have powerful antiseptic properties: St. John's wort, sage, viburnum berries, and yarrow.
- Aloe and sea buckthorn oil have healing properties. They can be applied several times a day to wounds.
- The healing properties of oak bark, propolis, honey and onions have been proven.
- A decoction of coriander will help cope with sores on the tongue. To prepare it, you need to take a tablespoon of seeds, pour 200 ml of boiling water, and simmer over low heat for half an hour. After cooling, strain and can be used to rinse the mouth. Before the procedure, the broth must be diluted slightly with water.
- Juice from fresh cabbage will help eliminate the inflammatory process and reduce formations. Soak a cotton swab in the juice of the plant and treat the wounds.
- Propolis. For treatment you need to prepare a decoction. Pour boiling water over several pieces of propolis and keep in a water bath for 30-40 minutes. Cool to room temperature and use to rinse your mouth every hour.
- Potato. Peel raw potatoes. Cut into pieces to be applied to the wounds on the tongue. The starch in tubers relieves inflammation and reduces pain.
- Onion and garlic. Grind one of the vegetables into a paste and apply to damaged areas on the tongue. Phytoncides promote rapid relief of the inflammatory process and suppress the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
- You can also apply lemon juice directly to the wounds on your tongue.
Greater effectiveness can be achieved if you combine drug treatment with the use of traditional recipes. When using folk remedies, it is necessary to exclude the presence of allergies to some natural gifts.
Features of treatment of stomatitis
The therapeutic regimen is selected taking into account the cause of the disease. The approach must be comprehensive. To relieve pain symptoms, you need to use medications containing lidocaine. These can be gels, tablets, rinsing solutions.
If it turns out that the pathology is caused by herpes, you need to use antiviral drugs, including oxolin and acyclovir. In case of severe inflammation, medications with the addition of solcoseryl, vitamins, and oils help. If the culprit of the pathology is bacteria, the use of dental ointments based on chlorhexidine, miramistin, furatsilin, metronidazole, chlorophyllipt is indicated.
When a disease is of a fungal nature, antifungal compounds come to the rescue. Their active substances are nystatin, clotrimazole, miconazole. Rinsing your mouth with a weak soda solution helps with fungus.
If during the examination it is determined that the tongue is damaged as a result of the progression of an allergic reaction, general-spectrum antihistamines are prescribed. In the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the activity of the stomach and intestines is first of all normalized. Usually, after eliminating the underlying disease, cases of stomatitis also disappear.
In order for positive dynamics to emerge as quickly as possible, the patient must follow all medical prescriptions and not stop treatment ahead of time. Then the ulcers will heal within three to seven days, the pain will be a thing of the past.
Is the disease contagious?
Regarding the contagiousness of glossitis, it is quite difficult to give a definite answer, since the disease has many different forms, which mainly depend on the root cause of the problem.
“You say that the disease is rarely transmitted, but my son brought this infection from kindergarten! The diagnosis is herpetic glossitis. The tongue was swollen, covered with tiny sores, the child cried in pain. After the examination, the therapist prescribed us tablets and rinses and advised us to buy pharmaceutical chamomile. In principle, I won’t say that the treatment took a very long time, maybe a couple of weeks, but the unpleasant impressions remained. In my family, neither I nor my sisters had this, so I was generally in a panic...”
Lydia D., Nizhny Novgorod, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Some forms of the disease can be transmitted by contact
. If the provoking factor is not an infection, then there will be no risk of transmission from the carrier to a healthy person. If the whole point is infection and spread of the fungus, then the disease can be transmitted, but not by airborne droplets, but as a result of direct contact of another person with the affected organ.
Diagnostics
The initial examination of the oral cavity is carried out by the dentist.
In most cases, a visual examination is sufficient to establish a diagnosis. If a bacterial infection is suspected, a scraping is taken from the surface of the ulcers for bacterial culture. To identify viral diseases, a PCR test is carried out. If there are concomitant systemic pathologies, consultation with other specialized specialists is required. HIV and syphilis are diagnosed based on the results of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Tuberculous ulcers are identified from cancerous tumors, syphilomas using a biopsy of a tissue fragment.
Inflammation of the salivary glands
This disease is called sialadenitis. Any salivary glands can be affected by it, but painful sensations in the tongue, closer to the base, occur if the sublingual gland is affected. Pathology is caused by viruses or bacteria. Symptoms of sialadenitis include:
- pain at the base of the tongue;
- the formation of a compacted swelling underneath;
- decreased salivation.
How to treat the disease if the tongue hurts on the side precisely for this reason? Antibacterial and antiviral drugs.