The replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones usually takes place without any problems. However, many parents worry that some processes may go wrong. Therefore, they regularly monitor the condition of the baby’s teeth. Some people wonder how to distinguish a baby tooth from a permanent one, especially when it comes to molars. Indeed, when a child is 9-10 years old, this can become a problem - the incisors have already come out and there are no problems with them, but there is confusion with the distant teeth. How to learn to distinguish between them - let's figure it out together.
Content:
- Is there a difference? 2.1. Dairy 2.2. Indigenous
- How to tell the difference?
- Is there always a change?
- Are there baby wisdom teeth?
- Can milk root remain in the gums?
- When does radiography come to the rescue?
Children's milk and permanent teeth raise many questions from their parents.
The most attentive mothers and fathers try to clearly monitor the change in temporary bite. It happens that they do not understand whether the baby’s milk units remain in the baby’s mouth or are no longer there. How to determine whether a molar or baby tooth is? To do this you need to have certain information.
Number of baby and molar teeth in a person
There are ten baby teeth on each jaw: four incisors, two canines, four molars. By the time baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth, the child’s jaw reaches the size of an adult jaw and can already accommodate all 32 molars. On the upper and lower jaws there are two canines, four incisors, two premolars and three molars. To make it more convenient to describe the number of teeth in a patient’s oral cavity, dentistry uses a special dental formula, according to which each tooth is assigned its own number, according to its jaw location. Milk teeth are designated as follows:
- Incisors – I and II
- Fang - III
- Molars – IV and V.
- Molars are counted from the center to the sides:
- Incisors – 1 and 2
- Fang – 3
- Premolars – 4 and 5
- Molars – 6,7,8.
To understand on which jaw, as well as on the right or left, a tooth is located, another number is indicated before its number:
- Right side from top – 1
- Left side from above – 2
- Bottom left side – 3
- Bottom right side – 4.
That is, if, for example, a person is missing a lower wisdom tooth on the right side, it will be number 48 in the dental formula.
Is there a difference?
It happens that, trying to determine which children have milk teeth, mothers make a significant wave of their hand and say that there are no differences between the new and old units. In fact, they are.
Dairy
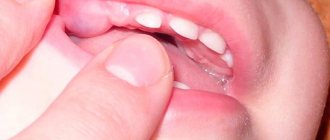
They take their places for closer to two to three years. The very first ones erupt when the baby is 6-12 months old. There are only twenty primary teeth (while there are 32 primary teeth). Therefore, they are arranged in a row quite freely. As the jaw grows, the spaces between them increase significantly. This can be seen with the naked eye.
At the age of 5-6 years, temporary teeth begin to loosen and fall out. This process is completed by the age of 10-12 years.
Indigenous
They appear at five or six years old or a little later. First, molars grow , which become “sixes”. After this, the incisors begin to wobble. They are pushed out by a constant shift.
Children with permanent dentition usually have 28 teeth. The four terminal units (which are popularly called “wise”) usually appear after 20 years. For many, it grows at 30-40 years old. And this is the norm.
Teething order
Typically, all children start teething at about the same time. Teeth emerge from the molar set at the age of 5, and it is the molars (large ones) that emerge. Then the diagram is as follows:
- Initially, the incisors on the lower jaw change, which are located in the center;
- then the central incisors appear on the upper jaw and the incisors on the sides on the lower jaw;
- at about 8-9 years old, the incisors on the top and sides change;
- up to 12 years of age, molars (small) grow;
- at the age of 13, the fangs change;
- after the child turns 14 years old, the second molars (large ones) come in. They were not included in the milk kit;
- and after another 1 year the third molars (large) appear. This is a wisdom tooth. But he may not appear at all.
How to tell the difference?
It is possible to determine which “generation” a tooth belongs to by its:
- Size and shape. Molars are larger, because they are designed for the jaw of an adult. Their edges and boundaries are clear and lumpy. Dairy ones have rounded, smooth edges.
- Blossom. Children's units are white with a bluish tint, adults are yellowish-gray. This is due to the fact that the latter has a higher percentage of mineralizing components. Over the years, they also turn white, but at first they don’t look very presentable.
- Position in the oral cavity. The molars face towards the lips and cheeks. They appear to be slightly tilted. Dairy plants grow evenly and straight.
If we talk about the differences in more detail :
- Six and seven are always radical. You need to count from the middle line of the row (located between the central incisors) towards the ear. In the milk row there are only fives, since there are ten teeth at the bottom and at the top.
- If you have questions regarding the fours and fives, then maximum attention should be paid to their form. Primary teeth have wide crowns and chewing cusps (usually four). If a change has already occurred, then there will be fewer tubercles and the crown will be narrow.
- Temporary fangs are smaller than permanent ones. By the time they fall out, their sharp tips become dull. Instead, units with clearly pointed apexes grow.
- When assessing the nature of the incisors, you need to look at the size. In dairy ones, the width is about 4 mm, the height is 5-6. Permanent ones are usually larger. During the period of change of bite, children's incisors have smooth, even edges, while adults' incisors are lumpy.
Sweet paste
Proper care will help preserve your baby's delicate teeth. It should be started immediately after teething. At first, this is done even without toothpaste and brush. In the morning and evening, or better yet, after each feeding, be sure to wipe your teeth with special napkins for oral hygiene. They carefully remove food particles, plaque and protect teeth from caries. Over time, you can use finger tips with silicone bristles.
When should you buy a toothbrush for your baby? As soon as he can brush his teeth and rinse his mouth with water on his own. When choosing a toothbrush, keep in mind that it should not be too hard so as not to wear away young, weakly mineralized enamel, and the width of the bristles should be no less than two and no more than three of the child’s teeth.
An equally important issue is the choice of toothpaste. One pasta for the whole family is excluded! The composition of children's pastes differs significantly from the composition of adult pastes. So, in children's pastes, there are different proportions and dosages of fluoride and calcium, which are necessary and harmless for the baby. Today, special pastes are produced for the little ones, for example, with natural plant extracts or various fruit and berry flavors.
The child’s nutrition also plays an important role in preserving and strengthening teeth. His diet should always include dairy products containing calcium, mineral water and sea fish - the main sources of fluoride. But sweets should be excluded if possible. From childhood, accustom your baby to healthy treats, for example, cut carrots, apples, turnips into cubes, and replace sweets and chocolate with figs, raisins, dried apricots or dates.
Is there always a change?
Not a single child's tooth should be preserved - they all fall out. Instead of each temporary one, a permanent one is cut through. But it also occurs in dental practice that the rudiment of the root unit is missing. This can be seen in the X-ray of the jaws.
In this case, the life of the baby tooth is extended to the maximum - after all, nothing will grow in its place. When an empty space appears in the dentition, the issue of prosthetics is discussed.
To eliminate partial congenital edentia, you can implant an implant or install a dental bridge. In the first case, there is no need to file adjacent teeth. The doctor, under local anesthesia, installs an artificial titanium root into the jaw tissue. When it takes root, it fixes the dental crown.
In the case of a bridge, it is necessary to depulpate and prepare the neighbors . This is not very healthy, since their service life after such manipulations is significantly reduced. Therefore, young patients who do not have separate molars are recommended by dentists to resort to implantation.
Deviations in timing and problems when changing teeth
One or another problem with the loss of baby teeth and the germination of molars occurs in at least every tenth child. Fortunately, dentists are ready to correct the bite during the growth stage, remove extra teeth, and even insert an implant if there is no point in waiting for a root one.
Let's look at the main deviations that may cause concern:
"Shark's Mouth"
Sometimes baby teeth do not have time to fall out, but the molars have already grown “second row”. The “shark’s mouth” is not worth admiring. You need to go to the dentist as soon as possible and remove unnecessary temporary teeth, otherwise your bite may be significantly damaged.
Untimely change of teeth
If the first baby teeth begin to leave the baby’s mouth before 5 years of age or after 8 years of age, then this is a deviation from the norm, which means you need to understand the reason. Trauma, caries, ecology, nutrition, congenital problems with bite or other heredity, various infectious diseases, hormonal problems (for example, thyroid disease), as well as diseases due to which the child is at risk for underdevelopment and delay may be to blame. formation of permanent dentition (diabetes, leukemia, immunodeficiency and others).
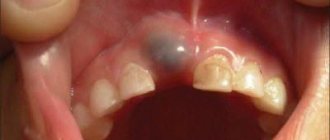
The molar does not grow in place of the lost milk tooth
There is no need to panic, but it is worth consulting with a specialist. For example, if a molar tooth does not erupt, although the baby tooth has fallen out a long time ago, the reason cannot be determined with ordinary eyes, but an x-ray will help. If there is no tooth germ in the picture, this is called adentia. This problem is extremely rare - the tooth simply has nothing to grow from. The decision will require the help of a prosthetist.
With retention, the germ of a new tooth is present, but it is directed incorrectly or is deep in the gum. All that remains is to wait for the tooth to grow. This problem occurs more often in the lower third molars, as well as in the upper incisors and canines.
With impaction, the tooth cannot come out due to the close fit of neighboring teeth. Here, too, you cannot do without the help of professionals.
We also advise you to consult a doctor if:
- molars appear darkened or grow crooked;
- the order of tooth loss and growth differs significantly from the above graphs;
- the child’s gums hurt and his cheek is swollen;
- baby tooth is corroded by caries;
- a tooth fell out, but blood from the socket does not stop oozing for more than an hour (not to be confused with ichor).
Can milk root remain in the gums?
If you carefully examine fallen children's teeth, you will not be able to see any semblance of roots. Some mothers unknowingly begin to panic - it seems to them that a significant part of the unit remains in the deep tissues of the gums.
There is no need to worry - this is how it should be. The absence of roots is the result of their gradual resorption. This process starts long before the day of loss. That is why during a natural change (when a tooth falls out without outside help), the child does not experience pain.
Anatomy of permanent teeth
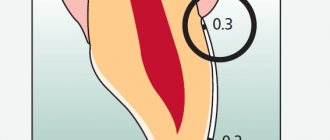
Each molar consists of certain parts:
- crown. This is the part of the tooth that protrudes from the top;
- the root, it goes deep into the alveoli. At the same time, it is attached thanks to special connective tissue bundles. There can be different numbers of roots (1-5 pieces). This moment affects the number of nerves and channels;
- neck. This part is located between the root and the crown.
Tooth tissues are distinguished by their heterogeneity. The enamel is on top and is known for its durability. Once the tooth has erupted, it is covered with a transparent thin layer. This is the cuticle, which eventually changes to the pellicle. The latter is a film that is created from what saliva produces.
Beneath the enamel is dentin, the tissue of the tooth. Dentin is similar to bone when you study how it is built. However, it is more durable because there is a high level of mineralization. In the area where the root is located, the dental tissue is covered with cement. The latter is rich in mineral compounds and is also associated with periodontium. Collagen fibers are used for this.
As for the part of the tooth that is inside, this is the crown and root canal. They are filled with pulp. This is loose connective tissue; it contains nerve endings and blood vessels.
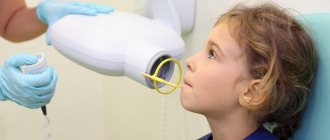
When does radiography come to the rescue?
Very rarely, but still situations occur in dental practice when even the doctor doubts which tooth he has to work with - a child’s or a molar. In this case, the capabilities of radiography are used. In the photographs you can see:
- length and structural features of the roots;
- presence/absence of radical primordia;
- the location of the unerupted unit and the direction of growth of its incisal edge.
If you need to find out exactly what the situation is with a change in bite in a child, contact your dentist. He will tell you the number of units that should fall out in the near future, and tell you whether it is worth interfering with this process.
It doesn't hurt at all
Many parents put off their child’s meeting with the dentist for a completely obvious reason: adults have a fear of this office since childhood. But today dentistry is completely different. And a visit to the dentist becomes more of an exciting game for a child. In the doctor's office there are beautiful toys, sketchbooks, and favorite children's cartoons - the child can watch them even during the examination. In some clinics, the baby is allowed to “participate” in the treatment, for example, choose a filling of the color he likes.
ON A NOTE. In order for a child to never be afraid of the dentist, it is important to set it up correctly even before visiting the doctor. Never frighten a child with a dentist, do not mention your unsuccessful examples of visiting a doctor in front of your child, if you yourself are very worried, try not to show your emotions, children very easily feel the mood of their parents. Many children's dental clinics have specially designated areas for children's games; try to keep your child busy with games while waiting for their turn. If you have been prescribed a very long course of treatment, you can divide it into several stages so that the child does not get tired.
A child can remember the first feeling of pain in a dental office for the rest of his life. To prevent this from happening, doctors use local or general anesthesia and even pre-treat the injection site with an anesthetic spray or gel. Thus, dental treatment does not cause any unpleasant sensations in the child. To treat children's teeth, other instruments, materials and medications are used that are not used to treat permanent teeth. When choosing a pediatric dentist for your child, you can rely on reviews from other patients. In a good children's dental clinic, the rooms are equipped with the most modern technology, which allows you to treat children's teeth silently and painlessly.
If the disease is not advanced and caries has affected only the surface layer, the teeth are simply silvered - this is an old and well-tested method of treating teeth without a drill. But it has a significant drawback: the black silver salts that fall out during the reaction leave dark spots on the enamel. Therefore, silvering is currently giving way to remineralizing therapy. In this case, the teeth are coated with a special composition that saturates them with fluoride, closes the affected crystal lattice of the enamel and allows you to stop the process. The natural color of the enamel is not lost.
If the destruction goes deeper, a filling is placed. Treatment is carried out under general anesthesia. When the caries damage is so large that a simple filling cannot withstand the load, the doctor uses metal or plastic crowns as a temporary measure. Their main task is to preserve the baby tooth until it is replaced with a permanent one.
The saddest verdict of the dentist: the tooth needs to be removed. The measure is necessary in two cases: when the tooth is severely damaged or when the milk tooth goes out of the natural loss schedule and prevents the permanent tooth from erupting.
After removal, a special plate is installed under general anesthesia, which compensates for the defect in the dentition and prevents further deformation and malocclusion.
Of course, removing baby teeth is a last resort, as this can lead to serious problems. Firstly, to improper development and deformation of the jaw, which in the future is fraught with bite pathology. Secondly, the absence of a tooth disrupts the process of chewing food and diction. Timely prevention and proper dental care will help you avoid serious problems. Therefore, it is recommended to show the baby to a specialist at least once every four months.
Adults also have milk “long-livers”
Yes, this is indeed possible. Milk teeth, which have a different structure and difference from permanent ones, may well be preserved in the bite of an adult. Whether to remove them, save them or replace them with prosthetics - this must be decided by the doctor depending on the clinical situation. For example, if they do not have the rudiments of permanent units under them, then you can simply improve the shape and aesthetics of the crown part so that they do not stand out in size against the background of their full-fledged “neighbors.” Read more about this phenomenon in the feature article on the website.