Enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body and a natural protective barrier for teeth. However, some people are diagnosed with its deficiency. Hypoplasia of dental enamel - as this condition is professionally called - can have different causes, but appropriate treatment methods must be used each time.
The main function of enamel in the oral cavity is to protect teeth from harmful factors: the action of bacteria, thermal and chemical irritants, as well as abrasion during chewing. Although there are proven ways to strengthen enamel, its gradual erosion is associated with various reasons. Some patients, even children, are also diagnosed with underdevelopment of this tissue. Dental hypoplasia can have many causes and each time requires appropriate treatment.
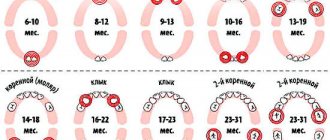
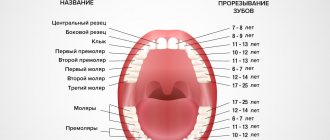
What do the deadlines depend on?
When determining why a child’s teeth do not grow, you need to take into account the following factors:
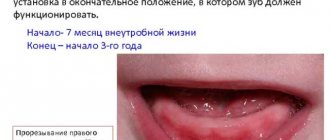
- the formation process depends on gender, girls develop teeth earlier than boys;
- The baby's growth also affects teething. So, if the baby is not tall, then teething will begin later;
- upper and lower jaws. At what stage does teething occur earlier? On the bottom.
A child’s bite has two stages – temporary and permanent. If it is temporary, then teething occurs less frequently. The location of the teeth also matters, for example, the second and third molars emerge later than the others. It is influenced by development and climate, place of residence, heredity - when the parents began to teethe, their children will begin to do so at about the same age.
If a child’s teeth are spoiling, what to do?
It is important for parents to understand that enamel is the main protection, the stability and structure of which depends on hereditary factors and on the saliva that washes the surface of the teeth. If the composition of saliva is disturbed because the child does not receive enough vital nutrients and minerals, this can lead to the formation of permanent plaque on the teeth. Even with systematic and thorough cleaning, it is impossible to get rid of such plaque forever, since it will appear again and again.
If a child’s teeth deteriorate due to the disturbed composition of saliva, then this problem can be solved by adjusting the diet. The menu should be balanced. It must contain foods rich in iron, calcium and other minerals that strengthen tooth enamel: hard cheese, sesame seeds, bran, feta cheese, milk, cottage cheese, herbs, legumes. Foods rich in phosphorus are very useful: fish, cottage cheese, cod liver, shrimp, squid, beets, carrots.
However, parents’ independent actions cannot always bring results. If your child’s teeth continue to deteriorate, then it is worth making an appointment with a pediatric dentist, who will offer effective treatment methods and help stop the destructive process.
Is late tooth growth dangerous?
If baby teeth do not grow, then in general this does not pose a danger, but it cannot be done without the intervention of a doctor. The specialist must conduct a preventive examination, talk with the parents, determining their teething characteristics, and then determine whether there is a reason for concern or not. Studies have shown that if the cause is heredity, then problems with permanent teeth are possible in the future.
What causes late eruption:
- health problems with the mother during pregnancy (for example, severe toxicosis);
- various diseases.
Incorrect placement of primary teeth affects the location of permanent teeth.
Treatment of dental hypoplasia
Symptoms are often visible already in childhood, patients complain from the first years of life. They typically require dentures well before the age of 20, making them more susceptible to tooth decay and periodontitis. The type of restorations, the material from which they are made, and the method of preparation for the restoration can have a big impact on the outcome of treatment and further prognosis. But, for example, although edge preparation provides the best edge seal, it is not as recommended as other methods for reasons such as the difficulty of further preparing the tooth.
Enamel hypoplasia can be treated in several ways. The main thing is proper and regular oral hygiene using soft bristles, toothpastes containing fluoride, dental floss and special rinses. You should exclude from your diet foods rich in sugar (which is the main environment for bacteria living in the mouth) and acids (they soften the enamel). It is recommended to consume foods that stimulate saliva production, as well as whole grain cereals, pasta and bread.
Dental treatment of enamel hypoplasia is based on several measures. The dentist can seal teeth (fissures), fluoridate them (coating the surface of the teeth with preparations containing fluoride in a certain concentration), it is also necessary to regularly remove plaque and treat caries. Children with malocclusions are also treated with orthodontic therapy.
Oral hygiene is another important issue for successful treatment of these patients. Long-term tooth sensitivity can interfere with proper oral hygiene, and the relief patients experience after treatment causes them to ignore the need to learn oral hygiene. Continued motivation in this regard may be critical to positive treatment outcomes for children with this problem.
Our clinic in Moscow will help you cope with the problem of enamel hypoplasia in a child. We offer affordable prices, a competent professional approach and no pain. There are experienced specialists who examine the oral cavity of children, detect symptoms and prescribe individual treatment. We guarantee excellent results for any occasion.
Recommendations for caring for a child's molars
Children's molars require careful care. Young enamel is sensitive to the external environment and bacteria that cause caries. Therefore, it is important to use hygiene products.
The best prevention is to teach your child to maintain good oral hygiene before a permanent bite has formed. To keep your teeth healthy, you need to follow a few simple steps:
- brush your teeth every day ☑️. Brush at least twice a day, use dental floss and mouthwash.
- correct diet ☑️. Sweet plaque on teeth is the best food for bacteria. After meals with a lot of carbohydrates, brush your teeth or rinse your mouth. Avoid snacking when you can't take care of your teeth.
- regular preventive examinations ☑️. You need to visit the dentist once every six months. Treat teeth immediately when problems are detected.
- strengthen teeth ☑️. Eat a balanced diet, take vitamin and mineral complexes rich in calcium.
- Visit the dentist regularly ☑️ and have your teeth professionally cleaned.
Taking care of your teeth doesn't take much time, but taking simple steps now will help you maintain beautiful, healthy teeth for life.
Treatment
Unfortunately, there are no conservative ways to solve the described problem. A small patient is indicated for surgical intervention. The doctor will administer an anesthetic, so that further actions will not cause pain. After this, the excess tooth will be carefully removed.
In some cases, doctors themselves tell parents not to rush into vomiting. The dentist's decision is influenced by factors such as:
- location of the unit in a row;
- patient's age;
- features of complaints;
- how long ago the constant change seemed;
- what condition are the temporary roots in and can we count on their rapid self-resorption.
In any case, the final decision should be made by the dentist, not the parents. Therefore, it is imperative to consult a specialist.
How can you tell if teething is delayed?
Often parents make the wrong conclusions when independently diagnosing the late eruption of the first teeth.
Particularly suspicious parents, on the day when the baby celebrates 6 months from the date of birth, examine his gums and, if the first pair of teeth have not appeared, they rush to the dentist as fast as they can. In 90% of cases, the doctor examines the baby's oral cavity and sends the parents home, saying that there is no reason to worry.
A delay is a condition in which teeth grow but do not erupt. It is easy for parents to determine this: the child becomes whiny and restless, his salivation increases, his gums turn red and swell (enlarge), he tries to put all the toys and objects in his hands into his mouth, and eats poorly.
These are classic signs of teething.
It may take 2 months from the first onset of symptoms to the appearance of the first tooth. Usually, with the problem “the gums are inflamed, but the teeth are not cutting”, parents bring children aged 9 months to a year. In this case, the doctor will examine the child’s gums and prescribe a number of diagnostic measures:
- X-ray
- Blood analysis
- Urine and stool analysis
- Ultrasound of the digestive system
- Hormone testing
If health problems are detected, the dentist prescribes an individual treatment regimen. If everything is fine and the delay is not associated with various pathologies, it will most likely be recommended to review the baby’s diet, increase the intake of vitamin D, massage the gums - in other words, promote teething in the child.
Molars in children: symptoms of eruption
In almost all children, molars appear painlessly and unnoticeably. However, there are exceptions when the growth of permanent teeth is accompanied by unpleasant sensations. A common symptom when teething is increased temperature, up to 38 ºС. The child also complains of:
- weakness and drowsiness due to decreased immunity;
- runny nose, excessive salivation;
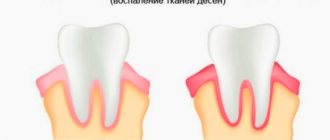
- inflammation of the gums;
- itching, pain while eating.
Massaging your gums will help relieve discomfort in your mouth. To relieve inflammation, use dental gel. Important: Disinfect your hands or wear sterile gloves before applying.
Consult your dentist before purchasing medications. Severe inflammation is a signal that teeth are not growing properly. Without treatment, the child's bite may become deformed.
Complications during teething
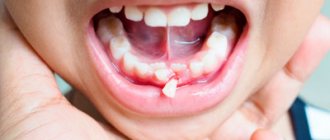
- bite defects. Molars are larger in size than baby teeth; there may not be enough space in a narrow jaw. The bite changes if the baby teeth do not fall out, but new ones begin to grow.
- hyperdentia – teeth grow in a second row. This happens for various reasons, most often - the baby tooth holds tightly and the root one looks for other ways.
- teeth don't grow. If the milk one falls out, but the permanent one is delayed for six months, you need to consult a doctor. Poor dental growth is one of the signs of problems with the immune system in children.
- caries and pulpitis. The first sign of enamel destruction is the child’s complaints of a sore throat, sweet and hot foods “getting” into the tooth. If pulpitis affects the molars, children’s body temperature rises and severe pain appears. Then treatment of pulpitis is urgently needed without delay.
Content:
- Reasons for violation
- What are shark teeth
- Consequences of a shark smile
- When is urgent dental care indicated?
- Treatment
If a baby tooth falls out, but the root remains, the situation is clear - it is necessary to remove bone fragments from the soft tissue so that they do not cause an inflammatory process.
There is no need to be afraid of the treatment procedure, since it is performed under local anesthesia, which means it will not cause acute pain in the little patient. It is more difficult for parents to make a decision if the molar has come out, but the milk tooth has not fallen out. How to act correctly? After all, for obvious reasons, loving mothers and fathers don’t really want to take their baby to an appointment with a dental surgeon. There is always hope that a complete change of the primary milk unit will occur naturally. We propose to look into this problem in detail.
When is urgent dental care indicated?
Doctors assume that the patient can walk with double units for two to three months. Watchful waiting is suitable if the disorder does not bother the baby and does not cause him significant discomfort. But there are times when it is unacceptable to hesitate. So, it is necessary to get to a dental clinic as soon as possible if:
- There was an unpleasant odor from the mouth. It indicates that the inflammatory process is progressing, and pathogenic microorganisms are actively multiplying in the interdental zone.
- The gums often become inflamed and painful. This occurs due to the pressure exerted by food debris on the delicate mucosal tissues. If the problem is not dealt with in time, inflammation can spread to the roots, and this is very dangerous.
- Pus began to ooze from the problem area. This is an indication for emergency removal of the unit. You cannot wait a day for it to fall out on its own if pus has begun to separate.
- The child cannot eat normally. The unpleasant sensations that occur when food gets into the free space negatively affect the baby’s physical condition and reduce appetite. Without receiving the necessary nutrients, the child becomes lethargic, moody, and loses weight. These sacrifices are not justified. There is an urgent need for dental surgery to remove it.
Also, the wait-and-see scenario is not suitable if the baby is prone to malocclusion (for example, one of his parents wore braces in childhood). Removing the unit will be a good prevention of the development of dental anomalies in adulthood.
What types of delayed eruption are there?
Currently, doctors talk about two main types of delayed eruption.
The first is retention. Pathology is diagnosed in 1-7% of cases, and retention can be associated with both baby teeth and permanent teeth. The essence of the disorder is that the teeth have already formed, but have not yet erupted. The pathology can be caused by various anomalies: improper formation of buds, inflammatory processes, hematomas. In many children, the canines of the upper jaw are susceptible to retention.
The causes of adentia are not fully understood
The second type is edentulous. This is a more dangerous pathology in which the absence of teeth (complete or partial) is detected. The absence of all teeth is extremely rare, and the reasons for such an anomaly are not fully understood. Usually we are talking about problems with the formation of tooth germs in the prenatal period, and this, in turn, is provoked by various external factors (infections and inflammations, poor lifestyle of the mother, complicated pregnancy, deficiency of nutrients). In case of edentia, an x-ray is prescribed, during which it is determined whether there are any rudiments of milk teeth in the jaw. If they are present, the reason why teeth are not erupting is determined.