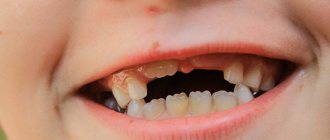
A child's teeth grow in two rows
With proper development of the jaw at the right age, permanent teeth begin to erupt and put pressure on the roots of the milk units.
Under this influence, the roots dissolve - the baby tooth becomes mobile, it wobbles and then falls out. This is a normal change in bite, the algorithm of which is known to most. But in rare cases the situation develops differently:
- when the germ of a permanent tooth and the root of the milk tooth are located in parallel planes, there is no pressure on the roots, and the permanent tooth grows in close proximity to the milk tooth;
- when the permanent one erupts quickly, and the roots of the milk unit have not yet resolved, the tooth does not fall out, and the permanent one has to bend and grow at an angle;
- when a child has a supernumerary set of teeth.
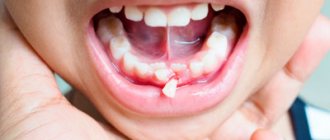
Various reasons - one result: the child’s teeth grow in the second row, threatening to ruin the permanent bite.
Types of violations
Among the types of violation of the order and timing of eruption, two forms are distinguished - early and late. If a baby is born with teeth, they are usually removed. Early teething is said to occur when children begin to develop teeth at 4 months. Late teething is said to occur if at the age of 11-12 months the baby still has a toothless mouth.
More serious disorders include the incorrect order of teeth erupting, which entails an incorrect bite and lack of space in the dentition. For example, early molars that erupted may not leave room for the 4th and 5th teeth, and the eruption of the canines simultaneously with the first molars may cause the canine to move forward or backward.
What to do when teeth grow in two rows
With “shark” jaws, the most reasonable solution seems to be the removal of excess milk units. And they did this for a long time. The result of hasty decisions showed that hasty removal of primary incisors and fangs leads to the opposite result and the formation of a malocclusion. After this, pediatric dental surgeons began to see children only as prescribed by the orthodontist - after professional consultation with a specialist.
An orthodontist is the first doctor you should go to when teeth grow in two rows. The doctor will assess the prospects for the formation of the dentition, send you for an x-ray to accurately determine the rudiments of permanent teeth and make the right decision. And this will not always be immediate removal of a baby tooth!
Based on the results of the diagnosis and examination, the orthodontist can advise:
- increase the amount of solid food in the child’s menu - provide the missing pressure on the baby tooth, causing it to loosen and fall out;
- wait for the natural change of teeth so that the permanent unit moves into its intended place under the influence of other teeth and under the pressure of the tongue muscles;
- remove primary incisors and canines to forcefully free up space.
The latter purpose is typical for parallel growing teeth and firmly standing primary units, since this is the only case when there are no natural prerequisites for root resorption and normal bite changes.
What to do if your teeth are cutting incorrectly
First of all, don't panic. When your toddler's teeth are cut out of order, balance his diet. After 5-6 months, a child, in addition to mother's milk, should receive complementary foods. It is important to measure the time of wakefulness and sleep. It is necessary to take the baby to the pediatrician for examination in a timely manner. If he prescribes a complex of vitamins, you must take them. Self-selection of medications can harm the child’s health.
The baby should be examined by a pediatric orthodontist. If there are no developmental pathologies, there is no need to worry. An objective assessment of the condition is the main criterion of health. If units emerge out of order, doctors advise observation and not skipping preventive examinations. When a one-year-old baby’s chewing organs do not grow, this is a reason for examination. This situation indicates a disturbance in metabolic processes. Violations in the order of birth of teeth should be closely monitored and reacted only if necessary.
Causes and consequences of dental pathology
Abnormal two-row growth is possible for many reasons:
- heredity;
- chronic colds and decreased immunity;
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of soft foods and purees;
- lack of vitamins and useful elements;
- premature removal of milk units;
- disturbance in the location of tooth germs.
With timely treatment, the orthodontist will easily straighten the bite and place each tooth in its proper place. If you delay visiting a doctor, the consequences can be serious:
- malocclusion;
- problems with hygiene and the development of caries;
- facial deformation due to jaw imbalances;
- ugly smile.
A sign of a potential shark jaw is the absence of gaps between the teeth in a 4-6 year old child. Insufficient space is the first prerequisite for the appearance of a second row of teeth in children and a signal for an attentive parent.
It is easy to see an incorrectly growing tooth, especially in the lower jaw. During the period of change in bite, dentists recommend monitoring the process - periodically conducting home or professional examinations and listening carefully to the baby. Complaints of discomfort in the mouth, inconvenience of chewing and pain indicate the need to visit a dentist to assess the condition of the oral cavity.
Reasons for violations
The reason for early teething is factors such as lifestyle, genetic predisposition and illness of the mother during pregnancy, endocrine disorders in the baby. The reason for the late appearance of baby teeth can be factors such as underdevelopment of the jaw or the absence of their rudiments in the baby.
If we talk about violation of the order of appearance of dental units, then the following reasons should be highlighted:
- The genotype transmitted from mother to child.
- Duration of breastfeeding.
- Toxicosis, bad habits and other concomitant illnesses of the mother during pregnancy.
- Diseases of the baby in the first year of life, including endocrine and infectious diseases.
- Deficiency in the child's diet of essential nutrients for his growth and development.
Prevention of all types of violations includes the following rules:
- Preparing for pregnancy.
- Proper nutrition for the mother.
- Treatment of diseases before and during pregnancy.
- Avoiding bad habits for the entire period of pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Proper nutrition of the baby, his hardening, timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
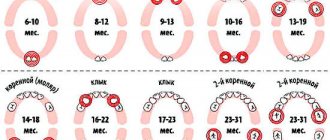
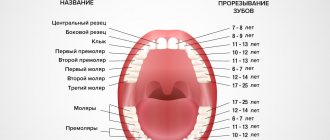
Which teeth appear first?
If the timing of the appearance of baby teeth in all children is quite individual, then the order of eruption is always the same (except in rare cases). The first to appear in the dentition are the incisors - the frontal teeth, located in the center of the jaw arch and having an elongated shape with a sharp surface intended for biting off food. The lower incisors usually appear first - they are slightly smaller than the teeth located in the upper dentition, but perform the same functions and have the same structure.
First central incisors - photo
Table No. 1. Scheme of eruption of incisors in a baby.
| Teeth position | Appearance date |
| Lower anterior incisors | 4-8 months |
| Upper frontal incisors | 6-9 months |
| Lateral lower incisors | 9-12 months |
| Upper lateral incisors | 10-16 months |
Note! During the first year of life, a child should normally erupt 8 teeth - 4 incisors on each jaw. It is possible that a child at this age has 7 teeth or even 2-4 teeth. Such a clinical picture can be considered normal if the child does not have chronic diseases of the endocrine system and other pathologies characterized by slowing or disruption of metabolic processes. If a one-year-old child has missing teeth, you should undergo an examination - this may be a symptom of rickets or a manifestation of adentia.
Baby is cutting teeth
Baby teeth in children: order of eruption
Any newborn baby has follicles of milk teeth (20 pieces) and molars (16 pieces) inside the jaws. The remaining 16 rudiments will form later.
Teething in infants begins with the lower jaw: first the central incisors appear (6-10 months of the child’s life), then the canines (10-13 months), then comes the turn of the first (14-18 months) and second (17-23 months) molars .
Emerging teeth differ from adult teeth in having low-mineralized enamel. If you do not maintain oral hygiene, caries may begin to develop. In addition to careful adherence to hygiene rules, special gels and ointments that significantly accelerate the mineralization process will help make teeth stronger and more resistant to pathogenic microorganisms.
Preventive measures
Solid foods will help the process of changing baby teeth to molars.
You can reduce the risk of dental anomalies (growth in two rows) by following the following recommendations:
- If you identify any problem in the oral cavity (including if a tooth has come out crooked or second row), you need to contact your dentist in a timely manner.
- The child's diet should include solid foods. This will help baby teeth fall out on time.
- If there are no upper respiratory tract disorders, then it is necessary to teach children to breathe through their nose. If nasopharyngeal diseases are detected, it is recommended not to delay treatment.
- From an early age, the baby should be involved in hygiene procedures to avoid the development of caries.
- It is necessary to wean the baby from putting everything in his mouth, especially sucking a finger or any objects.
- Do not let the child touch the growing incisor with his hands or constantly lick it with his tongue.
No matter how serious the problem may seem, it can be corrected quite easily if you contact a specialist in a timely manner.
Consequences
Even one molar that grows behind a baby tooth causes a lot of trouble. Ignoring the problem and lack of treatment leads to the following consequences:
- the child’s diction is impaired;
- the process of chewing food occurs poorly, the food is not crushed to the desired consistency;
- additional load on other teeth provokes displacement of healthy units, this provokes intense curvature of the bite;
- diastemas and trema (gaps) form between the chewing teeth and the front permanent teeth;
- the roots of healthy incisors and molars become bent.
Treatment
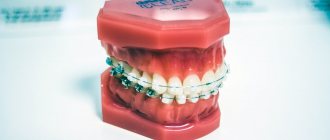
After the removal of supernumerary or baby teeth, braces are used to correct the anomaly.
Double dentition is not only a cosmetic defect, but also causes physical pain and discomfort to the child, so the problem must be solved together with specialists.
The dentist, having studied the nature and nature of the pathology, selects a suitable treatment method. In this case, the following are taken into account: the characteristics of the body, x-rays, test results, and symptoms. What to do:
- To correct the bite and free up space for the growth of the molar, the baby tooth is removed. The procedure is performed using local anesthesia. The operation should be performed immediately after the tip of the molar appears. Most often, the dentition straightens spontaneously without installing a brace system.
- to eliminate jaw underdevelopment . The main tool used is braces (removable, non-removable), which fix the correct position of the teeth as they grow. The only drawback of the method is poor quality care of the structure due to its age. As an alternative, you can use Invisalign - a transparent elastic mouthguard that is almost invisible in the child's mouth. It is removed before eating or performing hygiene procedures. The only negative is the high cost of the design.
- The treatment of overcrowding involves several stages: removal of baby teeth and fixation of molars with a bracket system that corrects the bite. If extra teeth appear in a baby under 6 months of age, they are removed immediately.
Those teeth that are located outside the dentition are subject to removal. The exception is the canine; its natural replacement occurs at 11-13 years of age. If the canine is removed early, it can lead to severe malocclusion.
The following remedies are used to eliminate symptoms:
- ointments/gels for external use (Kamistad, Kalgel, etc.) – provide an instant but short-term analgesic effect;
- antipyretic drugs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, etc.);
- the homeopathic drug Dentokind is recommended for use during the period of teeth change;
- rinsing with decoctions of chamomile, calendula and other plants that have an antiseptic effect - the procedure is indicated for children over 2 years old.