Every person goes to the dentist at least once in his life. An unbalanced diet, genetic predisposition, lack of minerals, lack of proper hygiene, smoking and other factors negatively affect the condition of teeth, leading to rapid destruction of enamel and the appearance of caries. Only timely treatment will preserve oral health and a beautiful smile. The most common option for dental care is placing a filling on a damaged tooth. What are the materials and how is the procedure?
Requirements for filling materials
The main requirements that filling materials must meet, regardless of service life and purpose of use, are:
- Biological safety;
- Hypoallergenic;
- Easy to install and remove;
- Strength;
- Loyalty to medicines;
- Good resistance to mechanical loads and aggressive environments.
Modern dentistry has a large selection of filling materials.
In this regard, dentists quite often ask their patients questions regarding the choice of filling material, offering various types of dental fillings. To make it easier to make a decision, it is necessary to take a closer look at all types of fillings used in dentistry.
How does the procedure work?
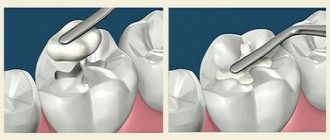
Sequence of actions when filling teeth:
- An insulating gasket is applied (if necessary);
- The tooth surface is treated with adhesive;
- The doctor carefully introduces the material into the cavity, after which he compacts it well;
- The dentist models the filling;
- For photopolymer fillings - exposure to a special lamp is carried out for rapid hardening;
- Grinding and polishing is carried out.
The filling should be comfortable and not interfere with biting. If you experience the slightest inconvenience, you should inform your doctor; adjusting the filling is a matter of a few seconds.
Temporary fillings
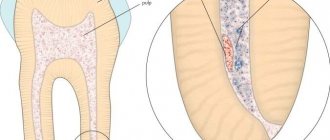
The second name for this type of dental fillings is diagnostic. Thus, caries damage can spread not only to the tooth enamel, but also to deeper tissues: dentin layers and pulp. Installing a temporary filling allows you to determine how deeply damaged the dental tissue is. In cases where we are talking about the development of pulpitis, the reaction to temporary filling material will be pronounced pain. Temporary fillings are used not only to detect pulpitis, but also as a sealing agent in case of long-term treatment, which involves the use of drugs placed in the cavity. Criteria that temporary filling materials must meet:
- Good performance in terms of tightness;
- the ability not to come into contact with drugs introduced into the cavity;
- ease of installation and removal;
- biological safety and hypoallergenicity;
- high curing rates in a short period of time.
The service life of temporary fillings ranges from several days to 3 weeks. Installing a temporary filling is similar to permanent filling and requires compliance with the same rules, namely:
- Filling is carried out after preparing (drying) the surface to be sealed;
- It is recommended to refrain from eating and drinking hot drinks for 1-2 hours.
In cases where the patient has been diagnosed with pulpitis, a temporary filling is installed in two layers. In this case, the top layer acts as a sealing gasket that isolates the pulp, and the second layer includes the drug.
It must be taken into account that temporary fillings do not have the same strength and resistance to mechanical loads as permanent filling materials. Due to this aspect, it is not recommended to brush your teeth too actively or eat solid foods until the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one. An unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth and the presence of pieces of material may indicate partial destruction of the temporary filling. The destruction of the material can occur as a result of improper care, neglect of the doctor’s recommendations, or if the installed filling was of poor quality.
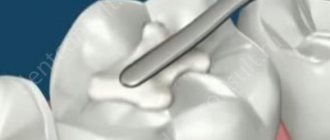
Installation steps
The process of filling a tooth has a specific algorithm, which consists of the following stages:
- First, the mouth is rinsed for additional disinfection.
- Next, the doctor must isolate the work area from exposure to saliva, which may contain bacteria.
- After this, the immediate cleansing of the affected cavity begins with the help of a special bur.
- If all foci of caries are removed, the tooth cavity is washed with a special solution and dried.
- Next, you can proceed to placing the filling.
- After it hardens, the doctor removes all excess material and grinds the surface of the filling so that it does not interfere with the patient.
This is the simplest process of installing a filling, which occurs when treating superficial caries. If we are talking about a deeper lesion, then such an algorithm can be supplemented with other stages related to the treatment of the internal tissues of the tooth.
Types of temporary fillings based on the materials used
On water dentin
Kaolin powder diluted with liquid is used as a derivative material.
From dentin paste
To create a filling, a mixture of kaolin powder and peach oil is used.
Cement based
The basis of such a filling is zinc phosphate cement, which can withstand severe loads. In this regard, this type of temporary dental fillings is used in the treatment of chewing teeth, which account for the majority of all impacts.
Made from polymer materials
Pastes made from polymers have a light-curing mechanism.
If the coating collapses prematurely
It happens that one day a person notices that the carious cavity is left without protection. No need to panic. The fact that a diseased tooth is open to invasion by pathogenic microflora is bad, but it is easy to fix. You should immediately visit your dentist to have it refilled.
If for some reason it is impossible to do this, and the visit has to be postponed by several days, you should monitor the condition of the “hole” and ensure that food debris does not collect in it. See your doctor as soon as possible.
Under no circumstances should you close an open cavity with chewing gum, gauze, cotton wool or other improvised means. These measures will worsen the situation - they will increase the likelihood of infection entering the deep tissues of the tooth.
Permanent fillings
They are characterized by high strength and long service life. The service life of permanent fillings depends on the material of manufacture and the loads applied. In connection with the above, it is extremely necessary to compare as accurately as possible the level of expected load and the properties of the filling material.
The main purposes of installing permanent fillings are:
- The need to seal cavities formed as a result of therapeutic measures;
- reconstruction of lost or damaged areas.
In some cases, damage to teeth (chips, cracks, etc.) can be compensated for without resorting to prosthetics, but through correction (reconstruction) using filling materials. Requirements for permanent filling materials:
- Biological safety and hypoallergenicity;
- High levels of aesthetics;
- The ability to withstand mechanical loads without losing its qualities.
Types of permanent fillings for teeth
Modern types of fillings in dentistry are distinguished by great variety, which is expressed in the levels of strength and durability, hardening speed, aesthetic appeal (the possibility of the most accurate imitation of natural tooth enamel). The pricing policy for different types and types of dental fillings is built based on the qualities of the filling material, and almost always meets the price-quality criterion.
Cement fillings
This type of filling has an affordable price and fairly good resistance to mechanical loads. Medical cement has good adhesion and hardens quickly. However, it must be taken into account that cement usually has a higher density than natural tooth tissue. In this regard, one of the negative aspects of using such fillings is the possible wear of the dental tissue adjacent to the filling material, which can lead to the development of secondary caries.
Depending on the basic composition, there are two types of fillings made from medical cement: mineral and polymer.
Mineral fillings
As the name suggests, the composition of such fillings is based on minerals of natural origin:
Zinc phosphate cements
They are a powder containing oxides of zinc, magnesium, aluminum and silicon. Mixing the powder with an aqueous solution of phosphoric acid leads to the formation of a substance that does not dissolve in the oral cavity. Phosphate cement fillings are generally not used for surface sealing. The main direction of their use is filling of canals and the lower layer. The service life of fillings made from zinc phosphate cements usually does not exceed 2 years. The advantages include low cost. The disadvantages of zinc phosphates include: low strength, aesthetic unattractiveness, poor adhesion.
Silicate cement
The material contains aluminosilicates and orthophosphoric acid. A distinctive feature of this type of cement is the ability to release fluoride ions, which serve to prevent the development of secondary caries. The use of this type of filling is not advisable in cases where deep filling is necessary, since it requires the installation of a gasket that protects the dental pulp from the toxic effects of released free phosphoric acid. Silicate cement has the necessary transparency and smoothness, which allows it to be used for filling front teeth.
Silico-phosphate cements
They are a combination of silicate and zinc phosphate. This composition makes it possible to minimize the manifestation of shortcomings that occur in each of the components separately. Thus, the combined material has higher strength and better adhesion to tooth tissues.
Polymer fillings
Fillings consisting of polymeric materials are usually divided into:
Glass ionomer
They are a combination of crushed glass, fluorides and polyacrylic acid. Hardening occurs as a result of a chemical reaction. The most modern glass ionomers harden under the influence of a special lamp. The use of these types of light fillings does not imply any restrictions on food intake. You can eat and drink immediately after the filling material is installed. The advantages of GIC include: good adhesion, hydrophobicity, plasticity (usually they do not have problems with modeling), aesthetic appeal and the ability to release fluoride ions, which are a prophylactic agent. The disadvantage of this material is its fragility, leading to rapid abrasion. The service life of GIC fillings usually does not exceed 3 years.
Polycarbonate cements
They are an analogue of zinc phosphate, improved by enhancing adhesive properties, better biocompatibility and less tendency to dissolve. The main target areas are: fixation of orthodontic structures, filling of baby teeth in children. Almost all cement fillings are chemically cured materials. The main areas of use are:
- Children's dentistry;
- Temporary filling;
- As a fixative in orthodontics.
Plastic fillings
This type of filling has become quite widespread. It compares favorably with cement materials in a number of positive qualities. Advantages of plastic fillings:
- Higher plasticity rates than cement;
- Fast hardening;
- Good hardness and strength;
- Chemically resistant;
- Correctness regarding oral tissues;
- Aesthetic appeal.
Plastic fillings vary depending on the materials used. It is customary to distinguish:
Acrylic fillings
They have aesthetic appeal and, thanks to a wide range of shades, can be used even on visually visible areas of the dentition. It must be taken into account that plastic is a porous material. In this regard, it is not recommended to install acrylic fillings for deep caries damage. This is due to the fact that the porous surface of the filling can become a favorable environment for the accumulation of bacterial plaque, which can lead to a number of serious diseases. In addition to the above, such fillings are not recommended for smokers and people who regularly consume foods with large amounts of coloring substances. Exposure to coloring pigments can radically change the color scheme of the filling.
Epoxy fillings
As the name suggests, they are made on the basis of epoxy resins. They have good strength and durability. They have a less pronounced toxic effect than acrylic materials. The main disadvantage is the tendency of such materials to darken after 2-3 years. In this regard, the main intended use of epoxy-based fillings is filling chewing teeth. Disadvantages of plastic fillings:
- Tendency to settle. Even modern materials show noticeable shrinkage after 2-3 months;
- Change in color under the influence of dyes;
- Toxicity.
Amalgam (metal) fillings
The material is an alloy of metal and mercury. Silver, copper and tin are most often used as metal components. The choice of metal is individual and different clinics may use different metals. Amalgam filling material has good strength and durability. Advantages of amalgam fillings:
- Not subject to corrosive damage;
- Has fairly high plasticity;
- Has high strength indicators;
- Virtually indestructible;
- If silver is used as a metal component, the composition has antiseptic properties.
Despite a fairly large number of positive qualities, amalgam fillings are used extremely rarely. This is due primarily to the toxicity of the mercury contained in the composition and a number of difficulties that arise during the work process.
In addition to the above, amalgam filling material has other disadvantages:
- Allergenicity;
- Unattractive appearance;
- Poor adhesion to tooth tissues;
- Low adhesion rates;
- A dark color that can give an unattractive tint to the entire tooth.
There are a number of absolute contraindications to the use of such materials:
- The patient has metal structures;
- Age restrictions;
- Individual intolerance and tendency to allergic reactions;
- Dental units located in the visual visibility zone.
The service life of amalgam fillings can be up to 10 years.
Ceramic fillings
Recognized as one of the most aesthetically attractive and reliable filling materials. Most often, ceramic fillings are installed using the inlay method, which completely follows the shape of the tooth. Such fillings have practically no disadvantages, but are used quite rarely. This is due to the high cost and rather long production time in laboratory conditions. The service life of such fillings can exceed 10 years.
Light-curing (photopolymer) fillings
The composition of the material used for the restoration of chewing teeth includes particles of silicon and zirconium. For the treatment of hard-to-reach areas, fluid-flowing composite materials are appropriate. During the work, the material is applied layer by layer until the tooth surface is completely restored. A dental ultraviolet lamp is used to harden the material. Photopolymer fillings are recognized as one of the highest quality filling materials. The advantages of light fillings include:
- Almost complete visual identity with natural teeth;
- High levels of strength and durability;
- Aesthetic appeal;
- Possibility of selecting the required shade characteristic of natural teeth;
- Almost complete biological safety of the material;
- Resistant to shrinkage and abrasion;
- Long service life from 5 to 15 years.
A relative disadvantage of light seals is their price, which significantly exceeds the cost of the previously listed materials.
Composite fillings
The material used includes plastics and inorganic fillers. This combination in the composition allows you to achieve good ductility and adhesion, expand the color range and enhance the strength characteristics of the material. It is customary to distinguish several main types of composite fillings:
Light-curing
An ultraviolet dental lamp is used to harden the material.
Chemically curable
The material contains porcelain, which extends the life of the filling and increases its strength. Composites of this type are characterized by uniform hardening and good adhesion to tooth tissues.
Gutta-percha
A material used exclusively for filling the roots of teeth. Gutta-percha is characterized by increased strength, durability, lack of shrinkage and abrasion.
Plastics and composites
An extensive group that includes:
- Acrylic-containing plastics. They are resistant to abrasion, but at the same time porous and quite toxic, so they have been used less and less in recent years.
- Composites with epoxy resins (chemically cured). Slightly better than plastic, but quite fragile and darken a few years after installation.
- Light-curing composites (photopolymers). Strong, reliable and durable. They polymerize and harden under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The composition of a photopolymer tooth filling includes porcelain, which gives the material strength and aesthetics. The most popular option today.
Criteria for choosing a filling
When choosing a filling, you need to consider the following aspects:
- The degree of expected load;
- Size of the surface to be filled and general accessibility;
- Requirements for aesthetic appeal;
- Biological safety level;
- Process depth;
- Patient's age.
Light fillings are recognized as the most popular and have virtually no negative qualities. In terms of characteristics, only ceramic fillings can surpass them. It is worth considering that the latter are significantly more expensive than all other filling materials. Filling materials used for the treatment of baby teeth deserve special attention. Most often, cement fillings are used in this direction.
This choice is due to the fact that baby teeth are subject to replacement and, as a rule, deep caries is not typical for them. Accordingly, the main negative properties of cement fillings are not important for them. Any questions you may have can be discussed with your doctor. He will also determine which material is more appropriate to use in this case.
Cost of treatment
The price consists of various factors. First of all, of course, these are the materials used. For example, ceramic will be the most expensive, and regular cement will be one of the budget options. The cost also includes the use of additional tools and equipment, the experience and qualifications of the doctor, the size of the affected area and the need for additional manipulations.
To make treatment more affordable and effective, it is better to contact a dentist when the first unpleasant symptoms appear: pain, high sensitivity, the appearance of blood, change in enamel color. It is important to undergo a preventive examination every six months.