April 5, 2020
Neoplasms (neoplasia) is the medical name for tumors, i.e., excessive growth of any tissue in the body. Tumors are the result of uncontrolled proliferation of cells that have not yet reached maturity and therefore have lost their ability to fully perform their functions.
Tumors can occur in internal organs and on the surface of the skin. Many people, not knowing what types of skin tumors there are, when any skin tumor appears, mistakenly believe that it is cancer. In fact, this is not always the case.
According to the main classification, skin tumors are divided into benign and malignant. There are also precancerous formations - borderline between the two main types. Each type has its own subtypes and characteristics, and correct diagnosis is needed to make an accurate diagnosis.
Why do they appear?
Like warts, papillomas are not dangerous
.
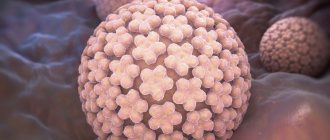
Their appearance is associated with the human papillomavirus (HPV),
which is transmitted through contact with a carrier. It is also possible to transmit HPV from an affected area of skin to a healthy one in one person. High humidity and microcracks in the skin increase susceptibility to viral particles. In this regard, you should always use personal hygiene items when visiting swimming pools, saunas and showers.
Important:
a large number of papillomas may indicate problems with the immune system.
For women in such cases, it is necessary to take a smear for HPV, since some of its types can cause cervical cancer
Depending on the clinical picture, they are usually divided into 3 types:
Benign
(atheroma, hemangioma, lymphangioma, lipoma, papilloma, mole, nevus, fibroma, neurofibroma)
They do not pose a threat to human life, but if poorly placed or large in size, they can cause disturbances in the functioning of other systems and/or organs of our body. Under external influences they can sometimes transform into malignant neoplasms.
Malignant
(basal cell carcinoma, melanoma, sarcoma, liposarcoma)
They grow quickly and aggressively, penetrating into surrounding tissues and organs, often with the formation of metastases. The prognosis of such diseases is often unfavorable, given the difficulty of curing them and the tendency for frequent relapses, and in some cases, active metastasis leads to death if vital organs are irreversibly damaged.
Borderline or precancerous skin conditions
(senile keratoma, xeroderma pigmentosum, cutaneous horn, Bowen's dermatosis)
Formations, the tissues of which, under the influence of hereditary or current causes, have changed, having the potential to degenerate into malignant tumors.
What is the best way to treat?
A large number of papillomas certainly causes inconvenience and does not look aesthetically pleasing. However, this is not a reason to use old-fashioned methods for removal with thread, pliers or a blowtorch.
For single small (1x1 mm) formations, celandine juice
- a proven folk remedy.
When there are many papillomas or they are large, this method is not suitable
, as it can last for months and lead to severe inflammation.
Removal using radio wave surgery is much more convenient and effective
The operation does not require special preparation, is practically painless, and after it you can drive a car.
Once I had the opportunity to remove about 70 papillomas from one patient at once. It is difficult to convey all the joy of a person who got rid of them, whom they tormented for several years.
Benign formations.
Atheroma.
A tumor of the sebaceous gland formed after its blockage. Most often it occurs on the scalp, neck, back, and groin area, that is, in places with a high concentration of sebaceous glands. It looks like a dense formation with clear contours, elastic and mobile upon palpation.
When suppuration occurs, redness and swelling of the tissues, pain, and increased body temperature appear. The inflamed atheroma can break out on its own, releasing purulent-sebaceous contents. This epithelial cyst has a tendency to transform into a malignant form - liposarcoma. Atheroma can only be removed through surgical excision.
Hemangioma.
A benign vascular tumor formation. Capillary hemangioma can reach large sizes, its color varies from red to bluish-black, and grows predominantly to the sides. If the heangioma is located on a complex area of the body (for example, on the face in the orbital area) or occupies a large area, it is removed beam method.
Lipoma.
A tumor of the fatty layer (often called a “wen”) located in the subcutaneous layer of loose connective tissue. It can penetrate deep into the body to the periosteum, seeping between vascular bundles and muscles. Most often found in areas where the fat layer is thinnest - the outer surface of the hips and shoulders, shoulder girdle, upper back. It looks like a soft formation, mobile and painless upon palpation. Lipoma grows quite slowly and is generally safe for the body, although in rare cases it can degenerate into a malignant formation - liposarcoma. At the same time, if the wen grows and begins to put pressure on surrounding tissues, surgical removal is indicated. It is better not to wait for this moment, since the larger the tumor, the more noticeable the postoperative scar will be. But small fatty deposits are easily removed using laser, radio wave or puncture-aspiration methods, after which there are practically no traces left on the skin.
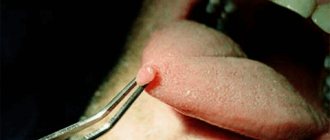
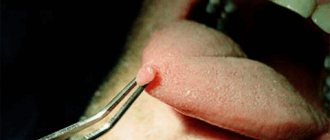
Papillomas and warts.
Formations in the form of a nodule or papilla, having a viral nature. They are caused by various strains of human papillomavirus (HPV), usually due to decreased immunity, stress and vegetative disorders. Externally they are very diverse, most often they look like growths of various shapes and sizes, coloring from light to dark brown and gray. Treatment: treatment with chemically active acids, interferon injections, cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen, electrocoagulation, radio or laser exposure, surgical excision .
Moles and nevi.
Benign skin tumors, congenital or acquired. They are a cluster of cells filled with the pigment melanin. They can have different sizes, shapes, colors and surface textures. Some of them have a high potential for degeneration into a malignant form - melanoma. For example, a pigmented border nevus, a flat nodule of dark brown or gray color with a dry, uneven surface. Such formations must be removed, and only surgically. Melanoma-dangerous moles and nevi do not require treatment, but experts recommend getting rid of those that are constantly injured or located in open areas of the body and are often exposed to sunlight in order to avoid complications. The method here is not so critical: in addition to a scalpel, a mole can be removed with a laser, cryodestruction or radio waves.
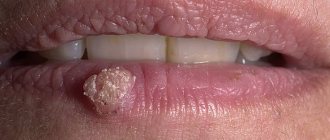
Fibroma (dermatofibroma).
Formations in connective tissue, which are most often found in women at a young and mature age. They are small in size (up to 3 cm), look like a deeply sealed nodule, spherically protruding above the surface of the skin, the color is gray to brown, sometimes blue-black, the surface is smooth, less often warty. It grows slowly, but there is a possibility of oncological complications: in rare cases, fibroma can degenerate into malignant fibrosarcoma.
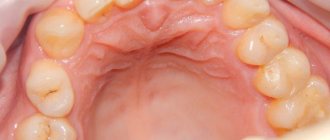
Treatment results
The photo below shows the results of removal of neck papillomas using radio wave surgery
Rarely occur again. Reappearance of papillomas is possible with high virus activity in the body. In this situation, additional treatment with immunomodulators or consultation with an immunologist may be required.
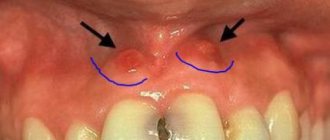
Symptoms
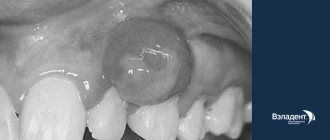
The tumor grows and develops quite slowly, so for a long time the patient may not even be aware of its presence in the mouth. Fibroma of the oral mucosa looks like a hemispherical growth rising above the plane, covered with pinkish tissue. If you press it, pain or other discomfort does not appear. The surface is smooth, there are no irregularities or roughness on it.
The appearance of ulcers with such a diagnosis is very rare. In such cases, an infection is usually associated with the subsequent development of the inflammatory process. Swelling, redness, erosion occur, and pain is felt. The pain persists even if you do not touch the pathological area.
If you do not injure the formation, it may not change its size for quite a long time and remain in a stable state. If it is exposed to constant traumatic effects, there is a high risk of malignant degeneration, which is dangerous to the life and health of the patient.
Millums (millet)
This type of bump occurs with equal frequency on the upper and lower eyelids. Millet grains can range in size from a poppy seed to a grain of rice and usually form in groups. Millums are the most harmless of all formations and cause only aesthetic discomfort. At its core, these are whiteheads localized in the eyelid area.
Millet removal should only be done by a cosmetologist. Since they do not carry the risk of complications, they are not considered an ophthalmological disease, but fall within the competence of a dermatologist-cosmetologist.
Prevention of millums includes caring for the eyelids, timely removal of dead epidermal cells, ensuring the cleanliness of the ducts of the sebaceous glands and pores of the skin around the eyes, as well as a balanced diet that excludes excessive consumption of fatty foods.
Diagnosis of fibroids of the upper and lower jaw
The doctor will not prescribe treatment until he is sure that the diagnosis is correct. To do this, diagnostic procedures are carried out, the results of which will confirm or refute the fears of doctors.
First, the patient is asked to describe the symptoms. The dentist examines and palpates the tumor. However, this is not enough to develop therapeutic tactics, since it is extremely important to determine the depth of tumor growth into soft tissue. For this purpose, an ultrasound examination is performed.
In difficult cases (ulcers, development of an inflammatory process in a pathological area of the gum, etc.), a biopsy is indicated. After surgical removal of the tumor, fragments are necessarily sent for histological analysis.
The examination is necessary not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to identify the factors that provoked the disease. A full dental examination is carried out to confirm the presence of inflammation. In addition, one cannot do without radiography, orthopantomogram and other images in different projections.
If a person has dentures, a consultation with an orthopedic dentist may be necessary. This is necessary to eliminate the possible traumatic effects of artificial elements on the mucous membranes.
Differential diagnosis
Biopsy remains one of the most informative methods for distinguishing fibroids from other benign neoplasms. The study is indicated for suspected papilloma, lipoma, epulis of various structures, neurofibroma, cyst, squamous cell carcinoma, wart, etc.
If the growth is localized on the tongue or sublingual part, it is extremely important to differentiate it from all existing seals. Timely diagnostic measures make it possible to detect cancer at the earliest stages and provide high-quality therapy with a short recovery period.
Chalazion
Cones of this type are quite common. They develop from a sebaceous gland whose duct is blocked. This formation is also called a “grading lump” or “cold barley.” The continued production of sebaceous gland secretion leads to the accumulation of a viscous mass in the capsule, which stretches and thickens, taking the form of a dense lump. On palpation, the contents under the skin feel like a moving ball.
Cold barley develops at a slow pace, so it does not cause pain. Only a formed hard capsule can cause pain when squeezed. If a chalazion is not treated, it can develop into a cyst. As the lump develops, the risk of complications increases: inflammation, formation of a purulent fistula, granulation.
Barley
Styes are more common than chalazions. This type of lump on the lower or upper eyelid is caused by inflammation of the follicle (bulb) of the eyelash. This also clogs the sebaceous gland duct. Styes develop over several days or even hours and can occur in both adults and children. More often, the systematic appearance of barley is observed in people with weakened immune systems or who have changed their place of residence to an area with a more severe climate, as well as in people exposed to constant stress factors.
Based on their origin, there are two types of barley. Inflammation can be external (when the sebaceous gland suppurates) and internal (when the source of inflammation is located in the membolic gland).
The development of external styes is characterized by subjective sensations similar to a foreign body entering the eye. The initial stage may also be accompanied by stabbing pain. External stye visually manifests itself as redness and swelling of the eyelid. The internal one is usually not so noticeable, but it causes even more discomfort and pain.
Without treatment, barley develops within a few days into an abscess, which opens with the release of purulent contents. This brings relief, but an open wound is dangerous due to the possibility of re-infection.
It is better to start treating barley without waiting for the abscess to spontaneously break through. This allows you to get rid of the painful lump faster and with less risk of complications. If you still don’t have the courage or time to visit an ophthalmologist, you should remember that prolonged suppuration of the eyelid is very dangerous. If the stye does not open for more than two weeks, surgical treatment is necessary. An ophthalmic surgeon will remove the abscess under local anesthesia and give recommendations for further treatment of the eyelid. Most often, therapy for developing or already opened barley includes drops and ointments that contain antibiotics (albucid, gentamicin, erythromycin, tetracycline ointment).