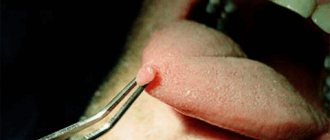
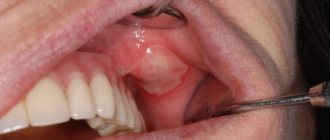
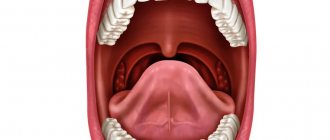
Oral papillomas are benign neoplasms in the oral cavity that grow from epithelial cells. Papillomas are discovered during a dental examination and look like separate growing seals on a small stalk, they are painless and have a white or pale pink color.
This type of neoplasm in the oral cavity is diagnosed most often. About 60% of patients are women aged forty years, about 20% are teenagers of any gender. Often, adults experience the appearance of individual papillomas, while children may experience so-called papillomatosis (multiple papillomas). In half of the cases, papillomas are localized on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
How common is the human papillomavirus?
HPV and, in particular, those forms that affect the oral cavity are a fairly common problem. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 10% of men and about 3.6% of women have signs of HPV in their mouths.
What are the causes of HPV and how is it transmitted?
HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection
In the oral cavity, HPV usually appears after oral sex or as a result of deep kissing between a healthy person and an infected person.
During oral or oral-genital contact, HPV particles travel in saliva through open cuts or sores in the infected person's mouth or throat.
In addition, HPV is transmitted from mothers to children. Most studies have shown that sometimes the human papillomavirus can be infected through contaminated utensils or medical instruments.
The body's defense system usually manages to repel invading HPV particles before infection begins. A healthy immune system typically fights off HPV infection within 1-2 years. However, in some cases, infections can bother people constantly.
Risk factors
The greatest risk of developing oral HPV comes from oral sex or mouth-to-mouth contact with someone who is infected with the virus.
Researchers have not yet determined the full list of risk factors, but it is known that this list includes the following:
- improper protection during oral sex;
- deep kisses;
- having multiple sexual partners;
- smoking cigarettes and using other tobacco products;
- onset of sexual activity at a young age;
- alcohol consumption;
- drinking drinks from the same container and using shared utensils.
Signs of a tumor in the mouth
Recognize papillomas on the inner lips
quite simple, because they all have typical manifestations. HPV growths differ from other formations provoked by fungal or bacterial flora:
- diameter – about 10 mm;
- rough surface;
- shape (round head, which connects to the mucous epithelium with a thin stalk);
- shade - from white to pale red;
- when touched, the formation is soft and painless.
The formation on the inside of the lip does not pose a threat to human life and health. However, it is located in a place that is often subject to friction (while eating, talking, etc.) and can be injured. If damaged, the formation can begin to bleed, become painful and serve as a source for the penetration of pathogens. To reduce the risk of damage to the growth, after its appearance, you should engage in complex therapy.
Symptoms and what does human papillomavirus look like in the mouth?
By using a condom during sex you can reduce your risk of developing HPV.
Many people with mild forms of HPV do not experience any obvious symptoms. There are also a number of strains, each of which causes slightly different symptoms than other strains.
When the infection manifests itself, it causes the development of formations that may have the following characteristics:
- small and hard;
- white, pink, red or flesh-colored;
- slightly elevated or flat;
- painless;
- usually slow growing;
- smooth or slightly rough;
- similar to cauliflower florets or cockscombs.
Such formations can appear in any part of the mouth, but most often they occur on the tongue, soft palate, hard palate and lips.
HPV is the leading cause of oropharyngeal or oral cavity cancer, although this complication is rare. Typically, cancer occurs as a result of infection of the tongue or the root of the tongue.
Of all the types of HPV, HPV type 16 most often causes the development of malignant tumors in the mouth.
Oral cancer tends to present with symptoms, especially as it progresses. Signs and symptoms of this condition include the following:
- tender or painful bumps that don't go away within three weeks;
- difficulty swallowing;
- discoloration of the soft tissues in the mouth to red, white or black;
- swollen and painful tonsils;
- lumps in the mouth that do not go away within three weeks;
- bumps that are felt on the outside of the neck;
- pain when chewing;
- chronic inflammation of the throat;
- hoarseness;
- chronic cough;
- numbness and tingling in the lips or tongue;
- pain in one or both ears that lasts longer than three weeks;
- salivation.
Why are papillomas on the gums dangerous?
Pain when eating The main danger of growths is that, if left untreated, there is a possibility of their degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Naturally, one cannot say that the risk of growths degenerating into cancer is high, but medical statistics show that with a strong proliferation of papillomas, there is a high probability of their transformation into a cancerous tumor.
In addition, when warts appear on the gums, the patient experiences unpleasant symptoms: it is difficult for him to eat and sometimes even speak. Symptoms are associated with the presence of nerve endings in the oral cavity that cause pain and burning.
Statistics show that today about thirty percent of women and fifteen percent of men suffer from oral papillomas.
In addition, there is a high probability of mechanical damage to papillomas located in the mouth. This can happen while talking or eating. The oral cavity has a moist environment, which contributes to the development of infection and re-infection.
If you notice the first signs of growths on your gums, you should immediately contact a medical specialist. The doctor will prescribe treatment, and if necessary, recommend surgical removal of papillomas on the gums.
Can it develop into cancer?
Growths in the oral cavity are benign neoplasms. However, these defects are considered oncogenic.
If you do not consult a specialist in time, the likelihood of malignant degeneration of small papilloma into a cancerous tumor increases significantly.
Most often, malignancy occurs when the defect is frequently damaged while eating food or palpating the growth with the hands or tongue. To protect yourself from cancer, you should immediately visit an otolaryngologist if you experience discomfort in your mouth or throat.
This is interesting: A white sore has appeared on the gum: how to treat the sore in a child and an adult
Classification of oral papillomas
Based on the number and concentration of neoplasms, oral papilloma is differentiated from papillomatosis – a massive accumulation of neoplasms in one place.
According to their origin, papillomas are divided into the following types:
- Traumatic (reactive) papilloma. May appear after traumatic effects of a mechanical, chemical or temperature nature. A distinctive and characteristic feature of reactive type oral papilloma is that their growth stops immediately after the irritant that caused them is eliminated.
- True (neoplastic) papilloma. This type of papilloma begins to develop after the mechanism of cell division, growth, and differentiation is disrupted. In most cases, this type of papillomas appears in the distal part of the cheek, in the area located behind the molars and in the area of the pterygomandibular fold.
- Viral papilloma of the oral cavity. May appear after the patient has been infected with the human papillomavirus. This type of infection occurs through direct contact with a carrier of the virus. When the integrity of the oral mucosa is compromised (for example, due to microtrauma), a path for infection appears.
Localization of papillomavirus in the mouth
Oral papilloma forms in different areas and has some distinctive features; based on these characteristics they are divided into:
- flat;
- epithelial;
- simple;
- pointed;
- threadlike.
The disease often manifests itself in the form of growths in the nasolabial triangle; less commonly, a papilloma forms on the inside of the lip. The patient needs an examination, since papilloma on the lip can only have external similarities with HPV; in reality, it can be cysts and tumors. Papilloma on the lower lip or upper lip has a rough surface. When palpated, papillomas on the oral mucosa are soft, elastic and painless.
Papilloma on the cheek in the mouth
A simple form of growth usually occurs on the cheeks. Formations on the cheeks, as well as on other parts of the oral cavity, cause discomfort when talking and chewing food.
Papilloma on the gum
New growths on the gums often have a flat shape. Their color is pink, the same as the gum itself, the surface is lumpy. The danger of formation on the gum is its degeneration, which has a high probability of occurring, since the formation is often injured by hot and cold food. The risk of cancer is high in older people and in the presence of serious infections in the body.
Papilloma on the palate
Warts on the palate are called simple or vulgar. They have a cone shape and a flat base. Treatment of papilloma in the mouth with folk remedies may not always be effective; complex therapy is more often used.
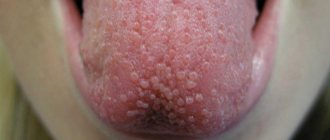
Papilloma on the tongue
The growths on the tongue may be red, pink or white. The disease is called epithelial hyperplasia. Warts cause a lot of discomfort, often break off, form bleeding wounds that become infected and begin to fester. In this case, treatment of papilloma on the tongue with folk remedies will be ineffective and surgical intervention will be required.
Papilloma on the larynx
The formation is formed in the form of a papilla, more often on the throat in women, on the larynx in men. Growths on the larynx and trachea are life-threatening because their growth impedes the flow of air.
Reasons for the formation of papillomas in the mouth and possible locations of their localization
The appearance of all types of papillomas is associated with infection of the patient with the human papillomavirus (HPV). The prevalence of this type of viral agent is very high and reaches 90% of the population in some countries. However, HPV carriage is not always accompanied by the formation of skin tumors. The virus can remain latent for a long time without manifesting itself at all. The formation of papillomas is promoted by factors such as decreased immunity, bad habits, poor nutrition and hormonal imbalance.
Science knows more than 100 types of human papillomavirus. The location of the tumor directly depends on the type of HPV. Papillomas in the mouth, covering the surface of the mucous membrane, are caused by HPV types 13 and 32, affecting various parts of the oral cavity:
- Papillomas on the tongue. The tongue most often undergoes epithelial hyperplasia, which is usually manifested by the formation of fine granularity or single tubercles of the mucous membrane of the tongue. In the first case, multiple small growths are felt as an unpleasant surface roughness, while the second type of neoplasm, being quite large, is often injured and causes its owner not only discomfort, but also pain.
Papillomas on the tongue usually appear in the tip or lateral parts of the organ. Papilloma under the tongue can also be considered a frequent occurrence. The root of the organ is least likely to suffer from such growths. The color characteristics of papilloma vary from light pink to bright red.
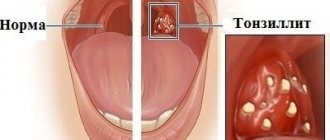
- Papilloma in the throat. Papillomas in the throat can remain undiagnosed for a long time, since they usually do not cause significant pain in the patient. Owners of such neoplasms of the mucous membrane note minor discomfort and sore throat, which is not given any importance.
If the papilloma increases in size, it can interfere with normal food intake and even change the voice of its owner, making it more muffled. The growth itself usually looks like a soft whitish or one-time bump with a rough surface. Papillomas on the tonsil are especially common.
- Laryngeal papilloma. One of the most unpleasant types of localization of neoplasms. The fact is that the formation of laryngeal papillomas interferes with the breathing process, which can lead to acute hypoxia. This phenomenon is especially typical for young children who cannot clearly formulate complaints about difficulty breathing.
- Papilloma on the lip. Such epidermal growth usually causes more trouble from an aesthetic point of view than from a physiological point of view. However, excessive growth of the tumor increases the risk of injury during eating or active facial expressions.
- Papilloma on the gum. Usually characterized by the absence of symptoms and any pain. If a papilloma on the gum has formed in a place that is invisible to the patient. It can only be detected by visiting a dentist.
Diagnosis of HPV
Currently, there are no simple solutions to diagnosing human papillomavirus. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is considered the most effective.
In PCR testing, doctors take a small piece of DNA from mucosal cells and amplify it, creating numerous identical copies. Having many copies of DNA allows doctors to detect ultra-small amounts of abnormal or viral DNA.
In rare cases where there are lesions in the mouth, HPV can only be diagnosed by a doctor based on a physical examination.
How to distinguish condyloma from papilloma
Many patients confuse papillomas with condylomas. In order not to confuse the two epithelial formations with each other, you need to know what papillomas look like and what condylomas are.
The main similarity between the two neoplasms is the cause of their occurrence – the HPV virus. The differences between papilloma and condyloma include:
| Papilloma | Condyloma |
| · caused by HPV types 1, 2, 3, 4, or 10; · almost never becomes malignant (except for the influence of certain factors); · localization site – the whole body and oral mucosa; · located singly; · capable of disappearing on their own. | · caused by HPV types 6 or 11; · capable of becoming malignant; · the main place of localization is the genitals; · located in a group with further fusion into one spot; · surgical treatment is mandatory. |
Which doctor should I contact for papillomas in the mouth?
Any diseases and defects associated with the oral cavity are primarily dealt with by an otolaryngologist. In children, this function can be performed by an ordinary pediatrician, but this is justified only if the problem has not progressed. He first examines the mucous membranes, tongue, tonsils and other organs located in this area.
Visiting an otolaryngologist for oral papilloma
When trying to understand which doctor to go to with papilloma in the mouth, it must be said that the ENT examines a person for growth, including on the vocal cords and lingual tonsil, in the nasal cavity, etc. If it is not very deep, then a visual inspection using a special mirror is usually sufficient. Otherwise, a more thorough diagnosis is required. Here can be assigned:
- Laryngoscopy . It can be indirect, performed in an outpatient setting, and direct (deep), requiring general anesthesia and placing the person in a hospital. This diagnostic technique is relevant only if there is a suspicion of a growth at the root of the tongue, on the vocal cords and in other hard-to-reach locations. This procedure for papilloma in the mouth can be carried out by the ENT specialist himself.
- Videoendoscopy . This technique involves inserting into the oral cavity, sometimes through the nose, a thin tube with a camera attached to the end to study the condition of the mucous membrane. This is an unpleasant and painful procedure, so it is prescribed only when indicated and if a biopsy is necessary. It is performed under local anesthesia.
- Radiography . As the name implies, this is nothing more than the usual “photography” of suspicious areas using special rays. If small doses of radiation are used, this procedure does not pose a health hazard, but it is still often not recommended. This method should be excluded during pregnancy, as it can negatively affect its course. A doctor with an ENT specialization does not perform this procedure for oral papilloma on his own; he refers the patient to other specialists.
If a growth is detected and malignancy is suspected, the ENT specialist must take a sample and send it for histological examination to exclude oncology.
Visiting the dentist for oral papilloma
Along with otolaryngology, this is another branch of medicine that studies diseases of the oral cavity. In other countries, especially in the United States, this specialist is also called a dentist or dentist. These doctors are not directly related to papillomas, but their consultation is relevant, for example, when growths are located near molars. This can provoke discomfort and inflammation of the gums, which is definitely within the competence of such a doctor.
If you are not yet sure which doctor to go to with papilloma in the mouth, but are going to the dentist in the near future, be sure to tell him about your problem. He, just like an ENT specialist, will conduct a visual examination of the mucous membranes for the purpose of diagnosis, but without examining the entire larynx in detail. Its task is to evaluate the surface areas and determine whether the growth is the result of any dental pathologies. For this purpose, a special mirror and x-ray can be used, and a 3D study can be carried out. The latter is the most informative and accurate in indications.
Consultation with a virologist for oral papilloma
As is clear from the specialization, the tasks of this doctor include the study of various viruses, as well as the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases that they cause. Since papillomas arise precisely as a result of HPV activity, the search for effective methods to combat them lies partly in the area of responsibility of a doctor with this profile.
This is interesting: Treatment of periodontal disease at home: the most effective folk remedies, herbs and tablets
If you want to find out which doctor treats papillomas in the mouth, you must not forget that it is the same virologist who helps determine which strain of the virus provoked its growth. He can participate in the analysis of blood and excrement to identify the causative agent of the disease. Most often, it is necessary to take referrals from him for such research.
The role of the virologist is enormous because without suppressing the activity of the papilloma virus, it is impossible to talk about the possibility of removing the formation caused by its activity. He can suggest suitable preventative measures, recommend good antiviral agents and medications for treatment.
Consultation with an oncologist for oral papilloma
Such consultation is justified if there is suspicion of a malignant process. Usually, an oncologist is contacted if there is a sudden change in the shape, color, structure of the formation, if it sharply increases in size, if there is discomfort, redness and itching, or if there is bleeding.
Consultation with this doctor becomes especially important for oral papilloma caused by oncogenic types of the virus. Scientists count more than 18 such strains, some of them are less dangerous, while others pose a serious threat to health, including the oral cavity.
The oncologist’s task is, together with a virologist, to determine how serious the type of HPV that has affected a person is, and to carefully examine the formation for integrity and pathological changes. If necessary, he must select a sample and submit it for examination to exclude malignancy.
Consultation with an immunologist for oral papilloma
This specialist works with people whose papilloma is the result of problems with the immune system. A visit to him when a growth forms in the mouth is mandatory, since such failures occur in almost every person.
At the appointment, the doctor collects the patient’s medical history and refers him to the necessary tests to identify the causes of the growth. To determine the culprit for the growth of papilloma in the mouth, the immunologist gives a referral for a general and clinical blood test, sugar testing, rheumatoid tests and other studies. It is he who has the right to prescribe effective stimulants of the immune system and control the progress of treatment.
The problem is that many hospitals simply do not have an immunologist on staff. Therefore, his responsibilities are often transferred to the shoulders of the same virologist, infectious disease specialist or ordinary therapist.
Examination by a dermatologist for oral papilloma
When looking for an answer to the question of which doctor to contact for oral papilloma, do not forget that a dermatologist deals only with the diagnosis and treatment of skin-related diseases. But in recent years, his tasks have also included examining patients with complaints of growths on the mucous membranes, including in the oral cavity.
During the consultation, the doctor must examine the formation, visually assess its condition and, if necessary, scrape it. In case of papilloma in the mouth, the dermatologist is obliged to exclude violation of the integrity of the growth, its bleeding, inflammation and redness. He, like other specialists, can give directions for tests necessary to clarify the causes of the problem.
Finding such a doctor is not easy, since at the end of residency, graduates choose more universal specialties, for example, dermatologist-oncologist. It will be even better to contact him, this will reduce the time for diagnosis.
To summarize, it must be said that the easiest way would be to first contact a general practitioner or family doctor. He will be able to tell you exactly which doctor removes papillomas in the mouth and what examinations you need to undergo before this. Otherwise, there is a possibility of spending a lot of money, time and nerves, postponing the solution of the problem for a long time.
Papillomas on the oral mucosa occur against a background of weakened immunity. Such growths are single and multiple in nature.
Genital warts in the mouth
array ( 'ID' => '8732', '~ID' => '8732', 'NAME' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth', '~NAME' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth', 'IBLOCK_ID' = > '43', '~IBLOCK_ID' => '43', 'IBLOCK_SECTION_ID' => '1194', '~IBLOCK_SECTION_ID' => '1194', 'DETAIL_TEXT' => ' Genital warts in the mouth are much less common than in genitals. In adults, they are formed more often as a result of sexual transmission, and in children as a result of infection from the mother during childbirth.
Infection is possible through contact and household contact (using someone else's toothbrush). In this case, the virus enters the oral cavity through microdamages. Weakened immunity and immunodeficiency, the presence of concomitant somatic conditions contribute to the rapid onset of clinical manifestations. In the oral cavity, rashes can be on the tongue and under the tongue, on the hard palate, the inner surface of the cheeks, even spreading to the larynx. They are usually presented as large white or pinkish rounded papules, slightly raised above the mucous membranes, have a lobulated surface and a rough appearance.
You can see such formations in the photo of genital warts in the mouth .
When a secondary infection occurs, a cough may appear, which can mimic a cold. If condylomas appear in the larynx, this can lead to severe complications due to increasing respiratory failure.
A dermatovenerologist can also treat
genital warts in the mouth and under the tongue ', '~DETAIL_TEXT' => ' Genital warts in the mouth are much less common than on the genitals.
In adults, they are most often formed as a result of sexual transmission, and in children as a result of infection from the mother during childbirth. Infection through household contact (use of someone else's toothbrush) is possible.
In this case, the virus enters the oral cavity through microdamages. Weakened immunity and immunodeficiency, the presence of concomitant somatic diseases contribute to the rapid occurrence of clinical manifestations. In the oral cavity, rashes can be on the tongue and under the tongue, on the hard palate, the inner surface of the cheeks, even spreading to the larynx. They are usually presented as large white or pinkish round papules, slightly elevated above the mucous membranes, have a lobulated surface and a rough appearance. You can see such formations in the photo of genital warts in the mouth . When a secondary infection occurs, a cough may appear, which can mimic a cold. If condylomas appear in the larynx, this can lead to severe complications due to increasing respiratory failure.
A dermatovenerologist can also treat
genital warts in the mouth and under the tongue ', 'DETAIL_TEXT_TYPE' => 'html', '~DETAIL_TEXT_TYPE' => 'html', 'PREVIEW_TEXT' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth are more likely to form as a result of sexual transmission.', '~PREVIEW_TEXT' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth mouth are formed more often as a result of sexual transmission.', 'PREVIEW_TEXT_TYPE' => 'html', '~PREVIEW_TEXT_TYPE' => 'html', 'DETAIL_PICTURE' => NULL, '~DETAIL_PICTURE' => NULL, 'TIMESTAMP_X' => ' 07/02/2018 00:45', '~TIMESTAMP_X' => '07/02/2018 00:45', 'ACTIVE_FROM' => NULL, '~ACTIVE_FROM' => NULL, 'LIST_PAGE_URL' => '/forpatients/school/info /', '~LIST_PAGE_URL' => '/forpatients/school/info/', 'DETAIL_PAGE_URL' => '/forpatients/school/info/ostrokonechnye-kondilomy/ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-vo-rtu/', '~DETAIL_PAGE_URL' => '/forpatients/school/info/ostrokonechnye-kondilomy/ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-vo-rtu/', 'LANG_DIR' => '/', '~LANG_DIR' => '/', 'CODE' => 'ostrokonechnye -kondilomy-vo-rtu', '~CODE' => 'ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-vo-rtu', 'EXTERNAL_ID' => '8732', '~EXTERNAL_ID' => '8732', 'IBLOCK_TYPE_ID' => 'SERVICE ', '~IBLOCK_TYPE_ID' => 'SERVICE', 'IBLOCK_CODE' => ", '~IBLOCK_CODE' => ", 'IBLOCK_EXTERNAL_ID' => ", '~IBLOCK_EXTERNAL_ID' => ", 'LID' => 's1' , '~LID' => 's1', 'NAV_RESULT' => false, 'DISPLAY_ACTIVE_FROM' => ", 'IPROPERTY_VALUES' => array ( 'SECTION_META_KEYWORDS' => 'Acuminate condylomas, Genital warts photo, What do genital warts look like photo , Genital warts virus, Genital warts disease, Genital warts doctor, Genital warts of the skin, Genital warts to which doctor, Multiple genital warts, Are genital warts dangerous, Genital warts ICD 10, Genital warts symptoms', 'SECTION_META_DESCRIP TION' => 'Acuminate condylomas human papillomavirus: what they look like in the photo, whether it is dangerous and what are the symptoms of this disease caused by the human papillomavirus.', 'ELEMENT_META_TITLE' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth: photo in the mouth, on the tongue and under the tongue', 'ELEMENT_META_KEYWORDS' = > 'Ginital warts in the mouth, Genital warts in the mouth photo, Genital warts on the tongue, Genital warts under the tongue', 'ELEMENT_META_DESCRIPTION' => 'Ginital warts can appear on the tongue, under the tongue, and in general in the mouth. Find out more about such candylomas on our portal from medical specialists.', ), 'FIELDS' => array ( ), 'PROPERTIES' => array ( 'IMAGES' => array ( 'ID' => '240', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => '2017-11-15 09:11:27', 'IBLOCK_ID' => '43', 'NAME' => 'Photo gallery', 'ACTIVE' => 'Y', 'SORT' => '500', 'CODE' => 'IMAGES', 'DEFAULT_VALUE' => ", 'PROPERTY_TYPE' => 'F', 'ROW_COUNT' => '1', 'COL_COUNT' => '30', 'LIST_TYPE' => 'L', 'MULTIPLE' => 'Y', 'XML_ID' => ", 'FILE_TYPE' => 'jpg, gif, bmp, png, jpeg', 'MULTIPLE_CNT' => '5', 'TMP_ID ' => NULL, 'LINK_IBLOCK_ID' => '0', 'WITH_DESCRIPTION' => 'Y', 'SEARCHABLE' => 'N', 'FILTRABLE' => 'N', 'IS_REQUIRED' => 'N', 'VERSION' => '1', 'USER_TYPE' => NULL, 'USER_TYPE_SETTINGS' => NULL, 'HINT' => ", 'PROPERTY_VALUE_ID' => array ( 0 => '20787', 1 => '20788' , 2 => '20789', 3 => '20790', ), 'VALUE' => array ( 0 => '21308', 1 => '21309', 2 => '21310', 3 => '21311 ', ), 'DESCRIPTION' => array ( 0 => 'Ginital warts on the tongue | Genital warts on the tongue', 1 => 'Ginital warts under the tongue | Genital warts under the tongue', 2 => 'Ginital warts in the mouth | Genital warts in the mouth', 3 => 'Ginital warts in the mouth photo | Genital warts in the mouth photo', ), 'VALUE_ENUM' => NULL, 'VALUE_XML_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE_SORT' => NULL, '~VALUE' => array ( 0 => '21308', 1 => '21309 ', 2 => '21310', 3 => '21311', ), '~DESCRIPTION' => array ( 0 => 'Gunital warts on the tongue | Genital warts on the tongue', 1 => 'Ginital warts under the tongue | Genital warts under the tongue', 2 => 'Ginital warts in the mouth | Genital warts in the mouth', 3 => 'Ginital warts in the mouth photo | Genital warts in the mouth photo', '~NAME' => 'Photo gallery', '~DEFAULT_VALUE' => "), 'BLOCK_EXP' => array ( 'ID' => '241', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => '2017-11-15 09:11:27', 'IBLOCK_ID' => ' 43', 'NAME' => 'Sharing experience', 'ACTIVE' => 'Y', 'SORT' => '500', 'CODE' => 'BLOCK_EXP', 'DEFAULT_VALUE' => array ( 'TYPE' => 'HTML', 'TEXT' => "), 'PROPERTY_TYPE' => 'S', 'ROW_COUNT' => '1', 'COL_COUNT' => '30', 'LIST_TYPE' => 'L' , 'MULTIPLE' => 'N', 'XML_ID' => ", 'FILE_TYPE' => ", 'MULTIPLE_CNT' => '5', 'TMP_ID' => NULL, 'LINK_IBLOCK_ID' => '0', ' WITH_DESCRIPTION' => 'N', 'SEARCHABLE' => 'N', 'FILTRABLE' => 'N', 'IS_REQUIRED' => 'N', 'VERSION' => '1', 'USER_TYPE' => ' HTML', 'USER_TYPE_SETTINGS' => array ( 'height' => 400, ), 'HINT' => ", 'PROPERTY_VALUE_ID' => '20786', 'VALUE' => array ( 'TEXT' => ' Genital warts on the tongue often bring mental discomfort, feel like an unpleasant feeling of a foreign object, and can bleed when injured.', 'TYPE' => 'HTML', ), 'DESCRIPTION' => ", 'VALUE_ENUM' => NULL, 'VALUE_XML_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE_SORT' => NULL, '~VALUE' => array ( 'TEXT' => ' Genital warts on the tongue often bring mental discomfort, feel like an unpleasant feeling of a foreign object, and can bleed when injured.', 'TYPE' => 'HTML', ), '~DESCRIPTION' => ", '~NAME' => 'Sharing experience', '~DEFAULT_VALUE' => array ( 'TYPE' => 'HTML', 'TEXT' => ", ) , ), 'BLOCK_VIDEO' => array ( 'ID' => '242', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => '2017-11-15 10:20:07', 'IBLOCK_ID' => '43', 'NAME' = > 'Youtube Video', 'ACTIVE' => 'Y', 'SORT' => '500', 'CODE' => 'BLOCK_VIDEO', 'DEFAULT_VALUE' => array ( 'TEXT' => ", 'TYPE' => 'HTML', ), 'PROPERTY_TYPE' => 'S', 'ROW_COUNT' => '1', 'COL_COUNT' => '50', 'LIST_TYPE' => 'L', 'MULTIPLE' => ' N', 'XML_ID' => ", 'FILE_TYPE' => ", 'MULTIPLE_CNT' => '5', 'TMP_ID' => NULL, 'LINK_IBLOCK_ID' => '0', 'WITH_DESCRIPTION' => 'N' , 'SEARCHABLE' => 'N', 'FILTRABLE' => 'N', 'IS_REQUIRED' => 'N', 'VERSION' => '1', 'USER_TYPE' => 'HTML', 'USER_TYPE_SETTINGS' = > array ( 'height' => 200, ), 'HINT' => ", 'PROPERTY_VALUE_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE' => ", 'DESCRIPTION' => ", 'VALUE_ENUM' => NULL, 'VALUE_XML_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE_SORT' => NULL, '~VALUE' => ", '~DESCRIPTION' => ", '~NAME' => 'Youtube Video', '~DEFAULT_VALUE' => array ( 'TEXT' = > ", 'TYPE' => 'HTML', ), ), 'BLOCK_VIDEO_DESC' => array ( 'ID' => '243', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => '2017-11-15 09:11:27', 'IBLOCK_ID' => '43', 'NAME' => 'Video Description', 'ACTIVE' => 'Y', 'SORT' => '500', 'CODE' => 'BLOCK_VIDEO_DESC', 'DEFAULT_VALUE' = > array ( 'TYPE' => 'HTML', 'TEXT' => "), 'PROPERTY_TYPE' => 'S', 'ROW_COUNT' => '1', 'COL_COUNT' => '30', 'LIST_TYPE ' => 'L', 'MULTIPLE' => 'N', 'XML_ID' => ", 'FILE_TYPE' => ", 'MULTIPLE_CNT' => '5', 'TMP_ID' => NULL, 'LINK_IBLOCK_ID' = > '0', 'WITH_DESCRIPTION' => 'N', 'SEARCHABLE' => 'N', 'FILTRABLE' => 'N', 'IS_REQUIRED' => 'N', 'VERSION' => '1', 'USER_TYPE' => 'HTML', 'USER_TYPE_SETTINGS' => array ( 'height' => 400, ), 'HINT' => ", 'PROPERTY_VALUE_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE' => ", 'DESCRIPTION' = > ", 'VALUE_ENUM' => NULL, 'VALUE_XML_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE_SORT' => NULL, '~VALUE' => ", '~DESCRIPTION' => ", '~NAME' => 'Video description' , '~DEFAULT_VALUE' => array ( 'TYPE' => 'HTML', 'TEXT' => " ), ), 'BLOCK_TEXT_BOTTOM' => array ( 'ID' => '244', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => '2017-11-15 09:11:27', 'IBLOCK_ID' => '43', 'NAME' => 'Text block at the bottom of the page', 'ACTIVE' => 'Y', 'SORT' => '500 ', 'CODE' => 'BLOCK_TEXT_BOTTOM', 'DEFAULT_VALUE' => array ( 'TYPE' => 'HTML', 'TEXT' => "), 'PROPERTY_TYPE' => 'S', 'ROW_COUNT' => '1', 'COL_COUNT' => '30', 'LIST_TYPE' => 'L', 'MULTIPLE' => 'N', 'XML_ID' => ", 'FILE_TYPE' => ", 'MULTIPLE_CNT' => '5', 'TMP_ID' => NULL, 'LINK_IBLOCK_ID' => '0', 'WITH_DESCRIPTION' => 'N', 'SEARCHABLE' => 'N', 'FILTRABLE' => 'N', 'IS_REQUIRED' => 'N', 'VERSION' => '1', 'USER_TYPE' => 'HTML', 'USER_TYPE_SETTINGS' => array ( 'height' => 400, ), 'HINT' => ", 'PROPERTY_VALUE_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE' => ", 'DESCRIPTION' => ", 'VALUE_ENUM' => NULL, 'VALUE_XML_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE_SORT' => NULL, '~VALUE' => ", '~DESCRIPTION ' => ", '~NAME' => 'Text block at the bottom of the page', '~DEFAULT_VALUE' => array ( 'TYPE' => 'HTML', 'TEXT' => "), ), 'AMP' = > array ( 'ID' => '305', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => '2021-03-01 22:23:44', 'IBLOCK_ID' => '43', 'NAME' => 'AMP', 'ACTIVE ' => 'Y', 'SORT' => '500', 'CODE' => 'AMP', 'DEFAULT_VALUE' => ", 'PROPERTY_TYPE' => 'S', 'ROW_COUNT' => '1', 'COL_COUNT' => '30', 'LIST_TYPE' => 'L', 'MULTIPLE' => 'N', 'XML_ID' => ", 'FILE_TYPE' => ", 'MULTIPLE_CNT' => '5', 'TMP_ID' => NULL, 'LINK_IBLOCK_ID' => '0', 'WITH_DESCRIPTION' => 'N', 'SEARCHABLE' => 'N', 'FILTRABLE' => 'N', 'IS_REQUIRED' => 'N ', 'VERSION' => '1', 'USER_TYPE' => NULL, 'USER_TYPE_SETTINGS' => NULL, 'HINT' => ", 'PROPERTY_VALUE_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE' => ", 'DESCRIPTION' = > ", 'VALUE_ENUM' => NULL, 'VALUE_XML_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE_SORT' => NULL, '~VALUE' => ", '~DESCRIPTION' => ", '~NAME' => 'AMP', '~DEFAULT_VALUE' => ", ), 'DISPLAY_PROPERTIES' => array ( 'BLOCK_EXP' => array ( 'ID' => '241', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => '2017-11-15 09:11: 27', 'IBLOCK_ID' => '43', 'NAME' => 'Sharing experience', 'ACTIVE' => 'Y', 'SORT' => '500', 'CODE' => 'BLOCK_EXP', ' DEFAULT_VALUE' => array ( 'TYPE' => 'HTML', 'TEXT' => "), 'PROPERTY_TYPE' => 'S', 'ROW_COUNT' => '1', 'COL_COUNT' => '30' , 'LIST_TYPE' => 'L', 'MULTIPLE' => 'N', 'XML_ID' => ", 'FILE_TYPE' => ", 'MULTIPLE_CNT' => '5', 'TMP_ID' => NULL, ' LINK_IBLOCK_ID' => '0', 'WITH_DESCRIPTION' => 'N', 'SEARCHABLE' => 'N', 'FILTRABLE' => 'N', 'IS_REQUIRED' => 'N', 'VERSION' => ' 1', 'USER_TYPE' => 'HTML', 'USER_TYPE_SETTINGS' => array ( 'height' => 400, ), 'HINT' => ", 'PROPERTY_VALUE_ID' => '20786', 'VALUE' => array ( 'TEXT' => ' Genital warts on the tongue often bring mental discomfort, feel like an unpleasant feeling of a foreign object, and can bleed if injured.', 'TYPE' => 'HTML', ), 'DESCRIPTION' => ", 'VALUE_ENUM' => NULL, 'VALUE_XML_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE_SORT' => NULL, '~VALUE' => array ( 'TEXT' => ' Genital warts on the tongue often bring mental discomfort, feel like an unpleasant feeling of a foreign object, and if injured they can bleed.', 'TYPE' => 'HTML', ), '~DESCRIPTION' => ", '~NAME' => 'Sharing experience', '~DEFAULT_VALUE' => array ( 'TYPE' => 'HTML' , 'TEXT' => "), 'DISPLAY_VALUE' => ' Genital warts on the tongue often bring mental discomfort, feel like an unpleasant feeling of a foreign object, and can bleed when injured.', ), 'IMAGES' => array ( 'ID' => '240', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => '2017-11-15 09:11:27', 'IBLOCK_ID' => '43', 'NAME' => 'Photo gallery', 'ACTIVE' => 'Y' , 'SORT' => '500', 'CODE' => 'IMAGES', 'DEFAULT_VALUE' => ", 'PROPERTY_TYPE' => 'F', 'ROW_COUNT' => '1', 'COL_COUNT' => ' 30', 'LIST_TYPE' => 'L', 'MULTIPLE' => 'Y', 'XML_ID' => ", 'FILE_TYPE' => 'jpg, gif, bmp, png, jpeg', 'MULTIPLE_CNT' => '5', 'TMP_ID' => NULL, 'LINK_IBLOCK_ID' => '0', 'WITH_DESCRIPTION' => 'Y', 'SEARCHABLE' => 'N', 'FILTRABLE' => 'N', 'IS_REQUIRED' => 'N', 'VERSION' => '1', 'USER_TYPE' => NULL, 'USER_TYPE_SETTINGS' => NULL, 'HINT' => ", 'PROPERTY_VALUE_ID' => array ( 0 => '20787', 1 => '20788', 2 => '20789', 3 => '20790', ), 'VALUE' => array ( 0 => '21308', 1 => '21309', 2 => '21310' , 3 => '21311', ), 'DESCRIPTION' => array ( 0 => 'Acuminate condylomas on the tongue | Genital warts on the tongue', 1 => 'Ginital warts under the tongue | Genital warts under the tongue', 2 => 'Ginital warts in the mouth | Genital warts in the mouth', 3 => 'Ginital warts in the mouth photo | Genital warts in the mouth photo', ), 'VALUE_ENUM' => NULL, 'VALUE_XML_ID' => NULL, 'VALUE_SORT' => NULL, '~VALUE' => array ( 0 => '21308', 1 => '21309 ', 2 => '21310', 3 => '21311', ), '~DESCRIPTION' => array ( 0 => 'Gunital warts on the tongue | Genital warts on the tongue', 1 => 'Ginital warts under the tongue | Genital warts under the tongue', 2 => 'Ginital warts in the mouth | Genital warts in the mouth', 3 => 'Ginital warts in the mouth photo | Genital warts in the mouth photo', '~NAME' => 'Photo gallery', '~DEFAULT_VALUE' => ", 'DISPLAY_VALUE' => array ( 0 => 'Download', 1 => 'Download', 2 => 'Download', 3 => 'Download', ), 'FILE_VALUE' => array ( 0 => array ( 'ID' => '21308', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => Bitrix\Main\Type\DateTime::__set_state(array( 'value' => DateTime::__set_state(array( 'date' = > '2018-07-02 00:45:33.000000', 'timezone_type' => 3, 'timezone' => 'Europe/Moscow', )), )), 'MODULE_ID' => 'iblock', 'HEIGHT' => '220', 'WIDTH' => '250', 'FILE_SIZE' => '21153', 'CONTENT_TYPE' => 'image/jpeg', 'SUBDIR' => 'iblock/9cc', 'FILE_NAME' = > 'ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_na_yazyke.jpg', 'ORIGINAL_NAME' => 'Ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-na-yazyke.jpg', 'DESCRIPTION' => 'Acuminate condylomas on the tongue | Genital warts on the tongue', 'HANDLER_ID' => NULL, 'EXTERNAL_ID' => '8819841073890ee638a5733e8e417a81', '~src' => false, 'SRC' => '/upload/iblock/9cc/ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_na_yazyke.jpg', ), 1 => array ( 'ID' => '21309', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => Bitrix\Main\Type\DateTime::__set_state(array( 'value' => DateTime::__set_state(array( 'date' => ' 2018-07-02 00:45:33.000000', 'timezone_type' => 3, 'timezone' => 'Europe/Moscow', )), )), 'MODULE_ID' => 'iblock', 'HEIGHT' => '160', 'WIDTH' => '550', 'FILE_SIZE' => '79092', 'CONTENT_TYPE' => 'image/jpeg', 'SUBDIR' => 'iblock/131', 'FILE_NAME' => ' ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_pod_yazykom.jpg', 'ORIGINAL_NAME' => 'Ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-pod-yazykom.jpg', 'DESCRIPTION' => 'Gunital warts under the tongue | Genital warts under the tongue', 'HANDLER_ID' => NULL, 'EXTERNAL_ID' = > '26edc886f2182066a45b17acc001b08f', '~src' => false, 'SRC' => '/upload/iblock/131/ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_pod_yazykom.jpg', 2 => array ( 'ID' => '21310', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => Bitrix\Main\Type\DateTime::__set_state(array( 'value' => DateTime::__set_state(array( 'date' => '2018-07-02 00:45:33.000000', 'timezone_type' => 3, 'timezone' => 'Europe/Moscow', )), )), 'MODULE_ID' => 'iblock', 'HEIGHT' => '267', 'WIDTH' => '300', 'FILE_SIZE' = > '11959', 'CONTENT_TYPE' => 'image/jpeg', 'SUBDIR' => 'iblock/4be', 'FILE_NAME' => 'ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_vo_rtu.jpeg', 'ORIGINAL_NAME' => 'Ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-vo- rtu.jpeg', 'DESCRIPTION' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth | Genital warts in the mouth', 'HANDLER_ID' => NULL, 'EXTERNAL_ID' => '8e10b9c72bc8d9c1057e9b4d98a839ed', '~src' => false, 'SRC' => '/upload/iblock/4be/ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_vo_rtu.jpeg', ), 3 => array ( 'ID' => '21311', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => Bitrix\Main\Type\DateTime::__set_state(array( 'value' => DateTime::__set_state(array( 'date' => ' 2018-07-02 00:45:33.000000', 'timezone_type' => 3, 'timezone' => 'Europe/Moscow', )), )), 'MODULE_ID' => 'iblock', 'HEIGHT' => '330', 'WIDTH' => '600', 'FILE_SIZE' => '29938', 'CONTENT_TYPE' => 'image/jpeg', 'SUBDIR' => 'iblock/036', 'FILE_NAME' => ' ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_vo_rtu_foto.jpg', 'ORIGINAL_NAME' => 'Ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-vo-rtu-foto.jpg', 'DESCRIPTION' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth photo | Genital warts in the mouth photo', 'HANDLER_ID' => NULL, 'EXTERNAL_ID' => '5b2c3f469d8e127f355a12c9b59fc646', '~src' => false, 'SRC' => '/upload/iblock/036/ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_vo_rtu_foto.jpg', ), ), ), 'IBLOCK' => array ( 'ID' => '43', '~ID' => '43', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => '10/10/2021 23:51', '~TIMESTAMP_X' => '10/10/2021 23:51', 'IBLOCK_TYPE_ID ' => 'SERVICE', '~IBLOCK_TYPE_ID' => 'SERVICE', 'LID' => 's1', '~LID' => 's1', 'CODE' => ", '~CODE' => " , 'API_CODE' => NULL, '~API_CODE' => NULL, 'NAME' => 'Information for patients', '~NAME' => 'Information for patients', 'ACTIVE' => 'Y', '~ ACTIVE' => 'Y', 'SORT' => '500', '~SORT' => '500', 'LIST_PAGE_URL' => '/forpatients/school/info/', '~LIST_PAGE_URL' => '/ forpatients/school/info/', 'DETAIL_PAGE_URL' => '#SITE_DIR#/forpatients/school/info/#SECTION_CODE_PATH#/#ELEMENT_CODE#/', '~DETAIL_PAGE_URL' => '#SITE_DIR#/forpatients/school/info /#SECTION_CODE_PATH#/#ELEMENT_CODE#/', 'SECTION_PAGE_URL' => '#SITE_DIR#/forpatients/school/info/#SECTION_CODE_PATH#/', '~SECTION_PAGE_URL' => '#SITE_DIR#/forpatients/school/info/ #SECTION_CODE_PATH#/', 'PICTURE' => NULL, '~PICTURE' => NULL, 'DESCRIPTION' => ", '~DESCRIPTION' => ", 'DESCRIPTION_TYPE' => 'text', '~DESCRIPTION_TYPE' = > 'text', 'RSS_TTL' => '24', '~RSS_TTL' => '24', 'RSS_ACTIVE' => 'Y', '~RSS_ACTIVE' => 'Y', 'RSS_FILE_ACTIVE' => 'N ', '~RSS_FILE_ACTIVE' => 'N', 'RSS_FILE_LIMIT' => NULL, '~RSS_FILE_LIMIT' => NULL, 'RSS_FILE_DAYS' => NULL, '~RSS_FILE_DAYS' => NULL, 'RSS_YANDEX_ACTIVE' => 'N' , '~RSS_YANDEX_ACTIVE' => 'N', 'XML_ID' => ", '~XML_ID' => ", 'TMP_ID' => '9ab202583d0e34f2de1d81c689f407f2', '~TMP_ID' => '9ab202583d0e34f2de1d81c689f407f2', 'INDEX_ELEMENT' => 'Y', '~INDEX_ELEMENT' => 'Y', 'INDEX_SECTION' => 'Y', '~INDEX_SECTION' => 'Y', 'WORKFLOW' => 'N', '~WORKFLOW' => 'N ', 'BIZPROC' => 'N', '~BIZPROC' => 'N', 'SECTION_CHOOSER' => 'L', '~SECTION_CHOOSER' => 'L', 'LIST_MODE' => ", '~LIST_MODE ' => ", 'RIGHTS_MODE' => 'S', '~RIGHTS_MODE' => 'S', 'SECTION_PROPERTY' => 'N', '~SECTION_PROPERTY' => 'N', 'PROPERTY_INDEX' => 'N ', '~PROPERTY_INDEX' => 'N', 'VERSION' => '1', '~VERSION' => '1', 'LAST_CONV_ELEMENT' => '0', '~LAST_CONV_ELEMENT' => '0', 'SOCNET_GROUP_ID' => NULL, '~SOCNET_GROUP_ID' => NULL, 'EDIT_FILE_BEFORE' => ", '~EDIT_FILE_BEFORE' => ", 'EDIT_FILE_AFTER' => ", '~EDIT_FILE_AFTER' => ", 'SECTIONS_NAME' => 'Sections', '~SECTIONS_NAME' => 'Sections', 'SECTION_NAME' => 'Section', '~SECTION_NAME' => 'Section', 'ELEMENTS_NAME' => 'Elements', '~ELEMENTS_NAME' => 'Elements ', 'ELEMENT_NAME' => 'Element', '~ELEMENT_NAME' => 'Element', 'CANONICAL_PAGE_URL' => ", '~CANONICAL_PAGE_URL' => ", 'EXTERNAL_ID' => ", '~EXTERNAL_ID' => " , 'LANG_DIR' => '/', '~LANG_DIR' => '/', 'SERVER_NAME' => 'logoderm.ru', '~SERVER_NAME' => 'logoderm.ru', ), 'SECTION' => array ( 'PATH' => array ( 0 => array ( 'ID' => '1194', '~ID' => '1194', 'CODE' => 'ostrokonechnye-kondilomy', '~CODE' => 'ostrokonechnye-kondilomy', 'XML_ID' => ", '~XML_ID' => ", 'EXTERNAL_ID' => ", '~EXTERNAL_ID' => ", 'IBLOCK_ID' => '43', '~IBLOCK_ID' = > '43', 'IBLOCK_SECTION_ID' => NULL, '~IBLOCK_SECTION_ID' => NULL, 'SORT' => '500', '~SORT' => '500', 'NAME' => 'Genetary warts', ' ~NAME' => 'Condylomata acuminata', 'ACTIVE' => 'Y', '~ACTIVE' => 'Y', 'DEPTH_LEVEL' => '1', '~DEPTH_LEVEL' => '1', 'SECTION_PAGE_URL ' => '/forpatients/school/info/ostrokonechnye-kondilomy/', '~SECTION_PAGE_URL' => '/forpatients/school/info/ostrokonechnye-kondilomy/', 'IBLOCK_TYPE_ID' => 'SERVICE', '~IBLOCK_TYPE_ID' => 'SERVICE', 'IBLOCK_CODE' => ", '~IBLOCK_CODE' => ", 'IBLOCK_EXTERNAL_ID' => ", '~IBLOCK_EXTERNAL_ID' => ", 'GLOBAL_ACTIVE' => 'Y', '~GLOBAL_ACTIVE' = > 'Y', 'iproperty_values' => array (' secation_meta_keywords' => 'gangster condylomas, pointed condylomas photos, pointed condylomas how the photos look, pointed condylomas virus, pointed condylomas of the disease, gloomy condylomas of the skin, pointed confectionery, spicy confectionery K. which doctor, Multiple genital warts, Are genital warts dangerous, ICD 10 genital warts, Symptoms of genital warts', 'SECTION_META_DESCRIPTION' => 'Gined warts human papillomavirus: what they look like in the photo, are they dangerous and what are the symptoms of this disease caused by the papillomavirus person.', ), ), ), 'SECTION_URL' => '/forpatients/school/info/ostrokonechnye-kondilomy/', 'META_TAGS' => array ( 'TITLE' => 'Acuminate condylomas in the mouth', 'ELEMENT_CHAIN' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth', 'BROWSER_TITLE' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth: photos in the mouth, on the tongue and under the tongue', 'KEYWORDS' => 'Ginital warts in the mouth, Genital warts in the mouth photo , Genital warts on the tongue, Genital warts under the tongue', 'DESCRIPTION' => 'Ginital warts can appear on the tongue, under the tongue, and generally in the mouth. Find out more about such candylomas on our portal from medical specialists.', ), 'GALLARY_INFO' => array ( 21308 => array ( 'ID' => '21308', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => Bitrix\Main\Type\ DateTime::__set_state(array( 'value' => DateTime::__set_state(array( 'date' => '2018-07-02 00:45:33.000000', 'timezone_type' => 3, 'timezone' => ' Europe/Moscow', )), )), 'MODULE_ID' => 'iblock', 'HEIGHT' => '220', 'WIDTH' => '250', 'FILE_SIZE' => '21153', 'CONTENT_TYPE' => 'image/jpeg', 'SUBDIR' => 'iblock/9cc', 'FILE_NAME' => 'ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_na_yazyke.jpg', 'ORIGINAL_NAME' => 'Ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-na-yazyke.jpg', 'DESCRIPTION' => 'Guminatum on the tongue | Genital warts on the tongue', 'HANDLER_ID' => NULL, 'EXTERNAL_ID' => '8819841073890ee638a5733e8e417a81', '~src' => false, 'SRC' => '/upload/iblock/9cc /ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_na_yazyke.jpg', 'NAME' => 'Acuminate condylomas on the tongue', 'ALT' => 'Acuminate condylomas on the tongue', 21309 => array ( 'ID' => '21309', 'TIMESTAMP_X' = > Bitrix\Main\Type\DateTime::__set_state(array( 'value' => DateTime::__set_state(array( 'date' => '2018-07-02 00:45:33.000000', 'timezone_type' => 3 , 'timezone' => 'Europe/Moscow', )), )), 'MODULE_ID' => 'iblock', 'HEIGHT' => '160', 'WIDTH' => '550', 'FILE_SIZE' => '79092', 'CONTENT_TYPE' => 'image/jpeg', 'SUBDIR' => 'iblock/131', 'FILE_NAME' => 'ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_pod_yazykom.jpg', 'ORIGINAL_NAME' => 'Ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-pod-yazykom .jpg', 'DESCRIPTION' => 'Gunital warts under the tongue | Sitty condylomas under the tongue ',' Handler_ID '=> NULL,' EXTERNAL_ID '=>' 26EDC8866F218206A45B17ACC001B08F ',' ~ SRC '=> FALSE,' SRC '=>'/Upload/Iblock/131/Ostrokonechnye_ ONDILOMY_POD_YAZYKOM.JPG ',' NAME ' => 'Guminatum under the tongue', 'ALT' => 'Guminatum under the tongue', ), 21310 => array ( 'ID' => '21310', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => Bitrix\Main\Type\DateTime ::__set_state(array( 'value' => DateTime::__set_state(array( 'date' => '2018-07-02 00:45:33.000000', 'timezone_type' => 3, 'timezone' => 'Europe /Moscow', )), )), 'MODULE_ID' => 'iblock', 'HEIGHT' => '267', 'WIDTH' => '300', 'FILE_SIZE' => '11959', 'CONTENT_TYPE' = > 'image/jpeg', 'SUBDIR' => 'iblock/4be', 'FILE_NAME' => 'ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_vo_rtu.jpeg', 'ORIGINAL_NAME' => 'Ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-vo-rtu.jpeg', 'DESCRIPTION' = > 'Guminatum in the mouth | Genital warts in the mouth', 'HANDLER_ID' => NULL, 'EXTERNAL_ID' => '8e10b9c72bc8d9c1057e9b4d98a839ed', '~src' => false, 'SRC' => '/upload/iblock/4be/ ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_vo_rtu.jpeg', 'NAME' => 'Acuminatum in the mouth', 'ALT' => 'Acuminata in the mouth', 21311 => array ( 'ID' => '21311', 'TIMESTAMP_X' => Bitrix\Main\Type\DateTime::__set_state(array( 'value' => DateTime::__set_state(array( 'date' => '2018-07-02 00:45:33.000000', 'timezone_type' => 3, 'timezone' => 'Europe/Moscow', )), )), 'MODULE_ID' => 'iblock', 'HEIGHT' => '330', 'WIDTH' => '600', 'FILE_SIZE' => ' 29938', 'CONTENT_TYPE' => 'image/jpeg', 'SUBDIR' => 'iblock/036', 'FILE_NAME' => 'ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_vo_rtu_foto.jpg', 'ORIGINAL_NAME' => 'Ostrokonechnye-kondilomy-vo-rtu- foto.jpg', 'DESCRIPTION' => 'Guninal warts in the mouth photo | Genital warts in the mouth photo', 'HANDLER_ID' => NULL, 'EXTERNAL_ID' => '5b2c3f469d8e127f355a12c9b59fc646', '~src' => false, 'SRC' => '/upload/iblock/036/ostrokonechnye_kondilomy_vo_rtu_foto.jpg ', ' NAME' => 'Ginate condylomata in the mouth photo', 'ALT' => 'Ginate warts in the mouth photo', ), ), )
Papillomas on the gums of a child
The reasons for the formation of benign growths on the gums in children are the same as in adults. Children aged 6-12 years are at risk of contracting HPV. This is due to extreme curiosity, poor hygiene, lack of stress tolerance and reduced immunity.
The places where papillomas form in childhood are as follows:
- gum;
- language;
- red border of lips;
- larynx;
- throat.
Complaints in a child with HPV may indicate pain and discomfort during eating and breathing. The clinical picture is similar to the course of the disease in an adult.
What treatments are available?
Modern medicine is not able to offer treatment for human papillomavirus. Doctors can't even slow down the infection.
Scientists have tried a number of topical medications to slow the progression of HPV, but these attempts have not been successful. At the moment, the only treatment for HPV formations is surgical removal. Some doctors also use cryotherapy, which involves freezing the lesions with liquid nitrogen and then removing them.
If a person has been diagnosed with human papillomavirus, they will then need to be tested for HPV every 8-12 months until the infection clears or is no longer detectable in DNA samples.
Drug treatment
Initially, the patient is prescribed sanitation of the oral cavity: treatment of caries and inflammation of the gums, removal of stones and plaque from the teeth.
After all oral problems have been treated, the dentist will recommend effective supportive hygiene procedures to the patient.
The growths on the gums are surgically removed, and the foci of infection are lubricated with antiviral gels and ointments (only a doctor can recommend effective medications, based on the clinical picture of the disease).
To strengthen the immune system, the patient is prescribed a therapeutic diet and vitamins.
For severe immune disorders, the doctor may prescribe immunomodulatory drugs. For treatment to be effective, it is very important to maintain the patient’s immunity. Only with strong immunity the virus will not appear again.
Surgical
The main component of the course of treatment is the excision of the growths themselves, since papillomas are cells changed under the influence of the virus.
Growths on the gums very rarely go away on their own, but, unfortunately, they often degenerate into malignant tumors. Therefore, they must be removed.
The main methods for removing papillomas on the gums:
- radio waves;
- laser.
Both of these methods are not traumatic, and damaged surrounding tissues are restored quite quickly.
When removing warts using radio waves, the doctor may send the material for a biopsy to ensure that the cells are benign.
Traditional methods
You can alternate compresses with other treatment methods.
Alternative medicine methods have their place. They are not as effective as pharmaceutical drugs, but allergic reactions to them are extremely rare. There are such methods:
- crushed garlic mixed with Vaseline is applied to the affected area overnight;
- pickled lemon is fixed to the skin with a band-aid and waited for several hours;
- mashed potatoes with egg yolk are applied as a compress;
- lubricate the affected area with essential oils of juniper, orange, and tea tree.
Traditional methods are used for at least two weeks to achieve results. This makes it impossible to say that they are effective. To treat a viral disease, it is better to immediately consult a specialist.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C supports the immune system, helps fight viruses and recover from illnesses. Sodium ascorbate is the best form of vitamin C. The powder is inexpensive and does not contain harmful impurities. To be effective, you must complete the full course of treatment. The recommended dose is no more than 15 mg/kg body weight per day.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is necessary for the immune system to effectively fight viruses. Every person gets enough of it by spending 20-30 minutes in the sun. Those who, due to circumstances, are deficient in vitamin D should take care of a balanced diet high in vitamin D.
This is interesting: The neck of the tooth is exposed: what to do to quickly fix the problem
It should be borne in mind that with excessive consumption of the vitamin, intoxication may develop . The daily dose of the vitamin should not exceed 2.5 mcg.
Herbal remedies
- Spicy mouthwash. To prepare, mix equal parts cayenne pepper, turmeric powder, crushed cloves and elm bark. Brew 1/4 teaspoon of the mixture with 50 ml of water, leave for 10 minutes. You should rinse your mouth with the infusion 2 times a day. The product may taste bitter the first time you use it, but after getting used to it the unpleasant feeling will go away. After rinsing the mouth, the infusion should not be swallowed.
- Fresh coconut oil has excellent antiviral properties. It can be taken orally, 2 large spoons in the morning on an empty stomach, to act on the virus in the body. The second option is to lubricate a separate papilloma in the oral cavity. The oil soothes and heals ulcers and microcracks.
- Bay leaf will help get rid of papillomas in just 3-4 weeks. Pour 3-5 leaves of the plant with boiling water (100 ml) in an enamel container. Simmer the product over low heat for about 10-15 minutes. Moisten a bandage in the cooled broth and treat the affected areas of the oral cavity. The procedure must be carried out 3-4 times a day until complete recovery.
Ammonia
Treatment of papillomas with ammonia is the cheapest and simplest method. Treatment with this method lasts from several days to 2 weeks. It is not suitable for treating the oral mucosa, but the outer part of the lips can be treated.
Sea buckthorn oil
The use of sea buckthorn oil in the treatment of papillomas relieves inflammation and suppresses HPV activity.
Walnut tincture
An infusion is prepared over 2 weeks from 70% medical alcohol and leaves or green walnut shells. Formations in the mouth are treated in the morning and evening.
Egg
As soon as a growth in the mouth begins to appear, it is recommended to lubricate it with chicken protein.
Garlic and onion
It is effective to rub the formations in your mouth with a clove of garlic and onion several times a day or drip their juice onto the warts. Onions and garlic are effective natural antibiotics that help fight many viruses.
Castor oil
A cotton pad soaked in castor oil is applied to the growth in the mouth.
Potato juice
The wart in the mouth is treated with starch juice several times a day. The course of treatment is 1 month.
Essential oils of cedar and tea tree
These oils are considered effective natural antiseptics; moreover, they do not cause harm or sting when they come into contact with healthy areas of the skin. Treatment of papillomas in the mouth can be carried out several times a day.
Sanitation of the oral cavity
Sanitation of the oral cavity is a mandatory stage in the treatment of papillomas.
Sanitation is a comprehensive measure aimed at removing concomitant diseases that affect the growth of the tumor or interfere with its treatment. It includes:
- treatment of inflammation;
- removal of plaque and tartar, treatment of caries and filling, installation of crowns, etc.;
- cleaning dentures;
- cleaning the braces (usually surgery, if necessary, is carried out after they are removed).
Sanitation of the oral cavity is necessary to reduce the risk of relapse. If they are not carried out, then the probability of re-growth increases by 2-3 times. After completing comprehensive oral therapy, the doctor prescribes special antibacterial tablets and rinsing with medical solutions for disinfection and healing.
Treatment of oral papillomas
Diagnosis of this disease includes a collection of the patient’s medical history, as well as a thorough histological examination of removed papillomas.
Treatment of papillomas is only surgical. The neoplasm is excised down to the borders of healthy tissue. Techniques such as electrocoagulation, cryosurgery, sclerotherapy and others are rarely used, since as a result of their implementation it is impossible to conduct a histological analysis of the papilloma removed to the base.
If a large accumulation of papillomatous neoplasms is detected, a combined technique is used: a scalpel is used to dissect the largest number of papillomas accumulated in one place, and single papillomas are removed using electrocoagulation.
If oral papillomas have a viral etiology, antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy is prescribed along with surgical intervention to prevent relapses.
Depending on the etiology of the disease, relapses may occur with greater or lesser probability. So, if there is a human papillomavirus in the body, the risk of papillomas returning after surgery is quite high.
Complications
In the absence of adequate treatment, the pathology can progress rapidly, which will cause the formation of new lesions. In addition, the risk of developing the following complications increases:
- Hoarse voice.
- Deterioration of speech function.
- Inability to use dentures .
- Impaired respiratory (if papillomas have spread from the gums to the tonsils, larynx).
- Painful discomfort while eating.
- Bleeding .
Removal of tooth granuloma
- In addition, the risk of damage to the tumor increases, which causes the development of cancer.
If papilloma appears on the gum, you must immediately contact a dentist, who, after conducting research, will refer the patient to an oncologist or dermatologist.
HPV prevention
Vaccination is the main method of preventing human papillomavirus
One of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of contracting the human papillomavirus is vaccination. The popular vaccine Gardasil 9 provides almost 100% protection against strains of HPV that are associated with cancer. Specifically, people can protect themselves against the strains of HPV 6, HPV 11, HPV 16, HPV 18, HPV 31, HPV 33, HPV 45, HPV 52, and HPV 58.
Doctors recommend getting the HPV vaccine for all men ages 11 to 21 and all women ages 11 to 26.
Girls and boys aged 11-12 years usually receive two doses over a period of no more than six months. Boys and girls who get their first dose at age 15 or later usually need three doses.
In addition to vaccination, people can reduce their risk of developing HPV by doing the following:
- protect yourself during vaginal, anal and oral sex with condoms and dental dams;
- avoid sexual relations with multiple partners;
- avoid oral sex and deep kissing if there are open wounds or inflammations in the partner’s mouth;
- be regularly screened for sexually transmitted infections when engaging in sexual activity;
- avoid oral sex with a new partner;
- Visit the hospital regularly for dental checkups;
- inform sexual partners about the presence of sexually transmitted infections;
- monthly check for unusual changes and formations in the language;
- Consult a doctor if you notice inflammation or formations in the mouth and tongue that do not go away within two to three weeks.
Causes of papilloma in the mouth
The most common cause of this type of tumor is the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Factors that provoke the appearance of papillomas in the oral cavity are, for example, constant microdamage to the cheeks and tongue. A relatively small damage is enough for viral particles to penetrate inside and trigger the formation of papilloma. In children, the provoking factor is a too short frenulum of the tongue - the lower incisors injure it, creating a gateway for infection.
When analyzing papilloma under a microscope, it can be noted that this neoplasm is a tumor, which consists of many layers of epithelial tissue, which in some places has become significantly keratinized. In some areas, traces of the appearance of a focus of inflammatory infection can be noted.