An abnormality such as bone spurs is often ignored until it actively progresses. Patients often come to the clinic late, which entails complex treatment, including surgery. Exostosis is a pathology in which hardened areas of cartilage tissue protrude above the jaw are formed. The causes of this phenomenon are mechanical damage, trauma, tooth extraction and other diseases. Chewing functions are preserved, and soft tissues are also not damaged. But as the protrusions grow, thinning of the mucous membrane and ruptures occur, causing injury to surrounding areas.
Main symptoms
Depending on the specific type, epulis can manifest itself in different ways:
- Fibrous. Doesn't hurt and grows very slowly. The shade of the neoplasm does not differ from the color of the gums. In the absence of therapy, it can reach large sizes.
- Angiomatous. Has a rich purple hue. Causes pain, for example, when chewing food. It is easy to damage during mechanical action (even when brushing your teeth). Sometimes it bleeds.
- Giant cell. The most dangerous type of epulis. Can degenerate into a cancerous tumor. Typical for adults. It has a bright red color, even the slightest palpation causes discomfort.
Based on the stage and age, the growth can be dense or soft, and can range in size from several millimeters to 10 centimeters in diameter.
Causes
Reasons for the formation of growths:
- inflammatory, infectious processes, purulent accumulations;
- mechanical impacts, injuries causing bone destruction, jaw displacement and other damage;
- deviations of row segments, formation of nodular hardenings;
- disorders of the endocrine system, hormonal levels.
One of the reasons for the development of pathology is complex tooth extraction. Often, when a wound heals, the tissue around it becomes overgrown with moving areas. If done incorrectly, compactions may appear and exostosis will gradually develop.
How to treat?
Gum treatment should begin as soon as you notice growth. In most cases, you have to resort to surgical intervention, since drug therapy in this case does not have a positive result. The growth is excised under general or local anesthesia. After removal of the epulis, it is recommended to send the biomaterial for histological examination to exclude the malignant nature of the neoplasm.
Next, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs to avoid possible complications. For speedy healing, wound healing and antiseptic agents may be prescribed.
Symptoms
The initial stage of the pathology practically does not manifest itself. Symptoms generally have a vague picture, which is why patients rarely see a doctor in a timely manner. But as the condition worsens, the following symptoms appear:
- growths with a pronounced convex shape appear on the tissues; the structure can be embossed or smooth;
- there is a feeling of a foreign object in the mouth;
- pain appears, sometimes quite severe;
- partial jaw dysfunction is observed;
- the shade of the mucous membrane changes to bright;
- capillary obstruction appears in the area of the growth.
Preventive actions
You can prevent damage to the integrity of the gums in the following ways:
- Brush your teeth more carefully, without pressing too hard on the brush.
- Use solid foods with caution.
- Clean the seeds with your hands, not your teeth.
- If there are artificial structures in the mouth, make sure that they do not cause discomfort in the form of rubbing. This mainly applies to removable dentures.
- Use orthodontic wax when wearing braces.
- Carry out dental treatment in a timely manner.
- Do not consume too hot foods or drinks to avoid burns.
- Go to the dentist twice a year to have tartar removed.
Remember that this pathology has a predisposition to relapse. Most often, such cases occur in people who do not follow basic hygiene rules. Be more attentive to the condition of your oral cavity, brush your teeth daily and use additional hygiene products. Be careful not to cause mucosal damage.
Indications and contraindications
The growth is treated surgically. Indications for using this option for removing pathology are:
- the bone growth grows quickly;
- pronounced cosmetic changes, progression of pathology;
- physical discomfort, the growth becomes too large;
- before prosthetics.
There are a number of the following contraindications to surgical intervention:
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- adrenal dysfunction;
- diabetes of any form;
- bleeding disorders.
Treatment
Before treatment, the doctor conducts an examination and prescribes a number of diagnostic measures. It is necessary to perform fluoroscopy, determine the level of blood clotting, and determine whether there are contraindications to surgery. If there are no contraindications, the doctor removes the growth:
- anesthesia is performed (for uncomplicated pathology, the operation is performed under local anesthesia);
- the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic drugs;
- an incision is made on the gum, then the mucosal tissue is dissected to open access to the bone;
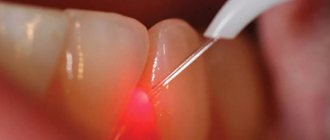
- the growth is removed using a laser beam or chisel (depending on the state of the pathology);
- the bone tissue is smoothed to an even texture, at which time cooled water is supplied to the surface;
- The tissues are sewn together and a bandage is applied.
The duration of the procedure depends on the complexity of the treatment. For mild cases, the operation takes about forty minutes; for complex pathologies, removal may take an hour and a half.
During the recovery period, the patient must follow the doctor's recommendations. For the first day, the intake of food and solid foods is limited, smoking and drinking alcohol are excluded. It is necessary to avoid physical activity, which can provoke bleeding and cause swelling.
Wisdom tooth: inflammation of the hood and its symptoms
Patients who have inflamed gums near a wisdom tooth usually complain to the doctor that their wisdom tooth is growing, their gums are swollen, and there is also an odor from the wisdom tooth. The formation of an unpleasant odor is caused by the formation of pus, which is gradually released from under the hood. Patients also complain of pain in the area of the wisdom tooth. Such symptoms correspond to only a mild form of pericoronitis.
What do the symptoms of pericoronitis look like in the video? Please note that in the video below you can see the following symptoms: redness and swelling of the hood above the upper wisdom tooth, a small amount of purulent discharge (white) from under the hood. Such symptoms correspond to a mild form of inflammation.
If pericoronitis occurs, treatment is only possible with a dental surgeon. But at the initial stage, patients try to relieve the symptoms on their own using available means: antiseptic rinses, dental drops, painkillers. In most cases, this is ineffective and the inflammation only increases. The following symptoms increase (in various combinations):
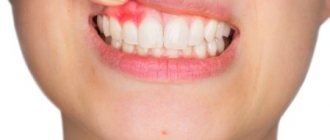
increasing pain- severe swelling and redness of the gums,
- swelling of the cheek (Fig. 4),
- purulent discharge from under the hood,
- painful swallowing
- difficulty opening the mouth,
- increase in body temperature,
- weakness,
- swelling and tenderness of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Important: if at this stage the wisdom tooth hood has not yet been removed (see below), then you should be prepared for the next development of events. Firstly, because inflammation occurs in the area of the masticatory muscles - their spasm can lead to almost complete closure of the mouth. If at this moment you decide to go to the dentist, then he will not be able to do anything for you if your mouth is not opening enough, except to refer you to the hospital.
Secondly, pus may begin to spread not into the oral cavity, but rather deep into the bone and soft tissues, which will cause the formation of an abscess or phlegmon (peripharyngeal or submandibular). The latter complications will also mean inevitable treatment in a hospital, and therefore it is better not to bring the inflammation of the wisdom tooth to a critical level.
Causes
The formation of a cyst on the gum after tooth extraction is caused by:
- tissue damage during surgery,
- using a non-sterile instrument,
- disruption of the wound healing process.
The most common cause of pathology is the patient’s failure to comply with medical recommendations. Frequent rinsing of the mouth after tooth extraction, refusal to take antibacterial drugs, poor oral hygiene are risk factors for wound infection. With the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, an inflammatory process quickly develops and a cyst with purulent contents is formed.
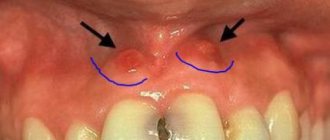
Symptoms of exostosis of the jaw
At the initial stages of development, the pathology usually goes unnoticed, as it manifests itself asymptomatically. It is often discovered when examining a patient for other dental diseases. The formation is clearly visible on an x-ray.
As the growths increase, characteristic symptoms appear. Their intensity depends on the clinical picture: location, shape, size.
By what signs can pathology be detected?
- the appearance of a tubercle or bump on the gums;
- sensation of a foreign object in the mouth, especially if the protrusion is located on the side of the tongue, at the bottom of the mouth;
- pain syndrome of varying intensity (occurs when injured by an acute growth of soft tissue);
- changes in the color of the mucous membranes in the area where the protrusion is located;
- jaw dysfunction if an osteophyte has formed near the jaw joint.
Unlike diseases of an infectious-inflammatory nature, it does not cause an increase in temperature, burning sensation, purulent abscesses, fistulas, and does not affect the tightness of the gums.
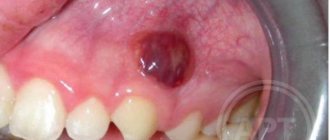
Lump on gum after tooth extraction
We would like to immediately warn you that sometimes complications after tooth extraction occur, no matter what. And it is not always the doctor or the patient himself who is to blame for complications. Although, undoubtedly, the high qualifications and experience of the doctor minimize the risk associated with complications.
If a lump forms on the gum after tooth extraction, this symptom may indicate the presence of inflammation. If the blood clot that usually forms in the hole somehow comes off or does not form at all due to frequent rinsing, then harmful bacteria can enter the wound and cause inflammation. Pieces of food that get into the wound can also inflame the gums. Therefore, dentists usually do not recommend that patients eat in the first few hours after extraction, until the bleeding stops and a blood clot forms.
If you have a lump on your gum after surgery, you should immediately see a dentist, since the inflammatory process requires immediate treatment. Before visiting a doctor, you should never warm the cheek on the side on which the abscess forms, since heat only intensifies the inflammation, making it more intense and fleeting. Cold will help relieve symptoms - you can apply ice cubes to your cheek, previously placed in a plastic bag.
You can’t try to remove a lump on your own! And that's why:
- firstly, only a doctor can correctly diagnose, and what seemed like a lump to you after tooth extraction may actually turn out to be another neoplasm;
- secondly, by removing the lump yourself, you can reinfect the wound, thereby provoking an even more acute inflammatory process!
After a careful examination of the oral cavity, the doctor will make a final conclusion about the causes. If the cause of its formation is an infection introduced into the wound and, as a consequence, an inflammatory process, then treatment will consist of anti-inflammatory therapy. First of all, the doctor will open the resulting lump to release the pus that has accumulated in it. Then rinse the gums with an antiseptic solution to prevent the lesion from spreading. After this, the doctor may also prescribe antibiotics to stop the development of the disease. As an auxiliary therapy, the doctor will recommend rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions, as well as decoctions of medicinal herbs.
It should be noted that the occurrence of inflammatory processes and lumps on the gums after tooth extraction occurs, as a rule, in those who have reduced immunity due to a previous disease. Therefore, in parallel with treatment, the doctor will definitely recommend that the patient take multivitamin complexes in order to strengthen the immune system and support a weakened body. It is necessary to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, since only their strict implementation guarantees a quick recovery.