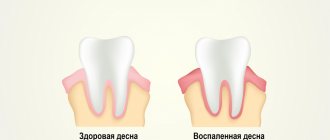
The gum has a pale pink color; normally it is not felt at all. The gums in the area of the tooth can be fixed or mobile. Between the teeth, the gum grows into the interdental spaces, filling them, thereby preventing food from getting stuck between the teeth.
For what reasons can gums hurt:
- due to the eruption of wisdom teeth
- due to food getting between teeth
- due to gum mobility
- due to gum injury
- due to gum suppuration
- due to tooth extraction
When a wisdom tooth erupts, the gum covering this tooth begins to thin out, often food gets between the gum, tooth and cheek and this also causes pain in the gum. In the oral cavity, the gum becomes red, swollen, and when touched it hurts terribly.
Why do ulcers appear on the gums, and is it always dangerous?
There are many possible reasons. To understand how dangerous the appearance of certain lesions on the gums is, you need to look at additional accompanying symptoms:
- in case it is trivial mechanical damage. The gums can be damaged by hard food, a toothbrush, or a foreign object. These lesions may resolve in 3-5 days. If a person does not brush his teeth, then infection is added to these damages, and healing may take several weeks.
- Sometimes ulcers can appear as a result of wearing orthodontic structures, braces or removable dentures.
Types of gum injuries
- Mechanical injury. The most common type of damage. The cause is usually external physical influence. Most often such injuries occur during a fall or from an external blow.
It is possible that injuries may occur during sports activities in strength martial arts - boxing, freestyle wrestling, judo, karate and other sports. Mechanical injuries are easier to diagnose, since in most cases they are accompanied by external injuries, such as bruises, bruises, and even skin tears.
- Chemical injury. Such gum injury may be the result of exposure to chemically active drugs. For an inattentive or in a hurry person, it is quite acceptable that he can confuse externally similar liquids, for example, vinegar and water, or a concentrated solution of manganese and currant juice. After such an impact, the gums receive extensive trauma.
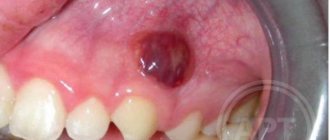
The most common diseases of the oral cavity in which ulcers appear
- ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis. The cause of this disease is bacteria that multiply when immunity decreases. Extensive ulcers appear on the gums, regional lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise
- chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Up to 4-5 white spots first appear in the mouth, which later turn into ulcers. There is no temperature or other problems related to well-being. If such symptoms appear 1-2 times a year in small quantities, then there should be no cause for concern. Frequent occurrence is associated with weakened immunity and possible intestinal diseases, as well as allergies.
- acute herpetic stomatitis. Herpetic stomatitis occurs in a child when he first encounters the herpes virus. Many bubbles appear on the gums, which, after bursting, turn into ulcers that merge with each other. The gums are always bright red, and the ulcers themselves are very painful, the temperature may rise
Surgical techniques
In advanced situations, plaque removal alone is not enough. Then there may be a need for open or closed curettage. It is indicated if the gums are very severely detached from the dental neck and the bone structure is changed.
The dentist-surgeon treats the lesion with an antiseptic, makes a small incision and removes purulent deposits and affected tissue . Then the gum is sutured. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. This means that the patient is conscious and can communicate with the doctor, but does not feel pain.
For a speedy recovery after curettage, antibiotics and mouth rinsing with an anti-inflammatory solution are prescribed. If the pain after surgery is very severe, the patient can use painkillers.
First aid
If the temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic drug. In the future, before visiting a doctor, nothing should be done. Do not take antibiotics yourself or try to get into the ulcer with any object.
How to relieve symptoms of ulcers
- do not eat sour and salty foods
- food should be warm, no hot dishes or drinks
- Care should be taken to ensure that the child does not put dirty hands in his mouth
- teeth should be brushed, but make sure that the bristles do not touch the gums with ulcers
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal solutions (oak bark, chamomile) 3-4 times a day
You should be careful when using antibacterial solutions. They must be prescribed by a doctor. If such solutions are used incorrectly, they can provoke the development of thrush. The antibacterial agent will “kill” the beneficial microflora, which can result in a fungal infection.
Prevention of ulcers
- professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year
- Regularly replacing your toothbrush
- Proper brushing of teeth at least 2 times a day
- using additional hygiene techniques such as irrigators, dental floss, and tongue scrapers
- Children should be monitored for bad habits such as putting dirty fingers and other objects into their mouths
- It is important to treat your teeth in a timely manner. Microbes that are found in carious teeth and rotten roots can serve as a source of infection for ulcers
If you have problems in the oral cavity, contact the specialists of the Center for Family Dentistry!
How is the treatment carried out?
Some people think that they can be cured with regular rinses. Unfortunately, it is not. The first step is to make an appointment with a dental hygienist. The doctor removes soft and hard deposits from the surface of the crowns and subgingival area in one session.
The following methods are used to remove stone:
- Instrumental. Involves the use of special scrapers that remove deposits. It is considered outdated and is extremely rarely used by doctors, as it is traumatic.
- Ultrasonic. Using an ultrasonic scaler, the doctor crushes the stones into tiny particles. This equipment produces waves of the required frequency, which easily destroy dental plaque.
- Sandblasting. It is the most modern and safe. The doctor delivers the cleaning solution under high pressure. Abrasive particles wash away deposits from crowns and effectively flush out existing pockets. The advantage of the technique is to achieve the effect of teeth whitening by one or two shades.
If the hygiene procedure does not help and the problem is serious, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment.
Summary -
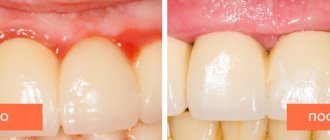
In this article, we briefly listed the main stages of treatment necessary to quickly relieve inflammation. Removing dental deposits from teeth and anti-inflammatory therapy will relieve redness, swelling, bleeding of the gums, the gums will become denser, pale pink in color, and bad breath will disappear. However, the treatment of a disease such as periodontitis does not end there.
In the case of deep periodontal pockets, and when the gums move away from the teeth, it can be assumed with a high degree of probability that splinting of mobile teeth will be required, as well as one of the surgical methods for treating periodontitis (for example, flap surgery or open curettage of the gums). During flap surgery, a thin strip of marginal gum is removed, which is loose and not attached to the teeth and, accordingly, this reduces the depth of periodontal pockets, as well as the rate of progression of periodontitis.
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a periodontist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. American Academy of Periodontology (USA), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry. Textbook" (Borovsky E.V.).
Additional treatments
Considering that gums become inflamed for various reasons, it is important to try to find out the provoking factor. Then the risk of relapse of dental pathology can be reduced to a minimum.
If the doctor determines that the disorder is related to hormonal levels, it is necessary to select hormonal therapy . In case of malocclusion, consultation with an orthodontist is indicated. If the diet is unbalanced, the patient is told what the diet should be like after recovery.
Often, when fighting gum that has receded from a tooth, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, glucocorticosteroids, and antiseptics are used. It is very important that the patient strictly follows all medical prescriptions and does not engage in amateur activities. An integrated and responsible approach to treating recession is a guarantee of a speedy recovery.
If the tissues become so inflamed that the teeth begin to loosen, splinting may be required. If there is a deficiency of bone tissue, their deficiency is compensated with special compounds.
Why does the gum move away from the tooth?
A prerequisite for the destruction of the periodontal attachment is the presence around the necks of the teeth - soft microbial plaque or supragingival tartar. The formation of dental plaque occurs due to irregular oral hygiene. In some patients with periodontitis, tartar may not be visually visible, because... when the attachment of the gum to the tooth is destroyed, it can already be localized below the level of the gum (then it is called “subgingival”).
But usually the destruction of the attachment of the gums to the teeth is always preceded by a long period of chronic inflammation of the gums, during which the patient is only bothered by periodic bleeding of the gums, possibly bad breath, redness or cyanosis of the gingival margin, as well as swelling of the gingival papillae. These symptoms are characteristic of gingivitis, an inflammatory disease of the gums in which the attachment of the gum to the tooth is not yet broken.
The lack of professional treatment for gingivitis (usually patients during this period self-medicate using antiseptic rinses and toothpastes for bleeding gums) leads to destruction of the attachment of the gums to the teeth. As a result, so-called periodontal pockets (gingival pockets) are formed between the teeth and gums, and patients in this case may complain that their gums have moved away from their teeth.
Stages of gum inflammation (gingivitis and periodontitis) –
Conclusions: Figure 10 shows the differences between gingivitis and periodontitis, and that with periodontitis, the gums are not attached to the teeth to the full depth of the periodontal pockets (from 3 to 6 mm or more). Therefore, if your gum has moved away from a tooth, there is simply no point in delaying a visit to the dentist, unless, of course, your goal is to remove these teeth in the near future. And in this case, there is no method of self-medication (magic rinses or ointments for gums) that would allow you to save the situation without going to the dentist.
In the absence of professional treatment of gums by a dentist, such teeth will first become mobile, then they will begin to fan-shaped and shift in different directions (under the forces of chewing pressure). In Fig. 11-13 you can see advanced forms of periodontitis in patients who, unfortunately, turned to the dentist too late. The teeth in these photographs have a very high degree of mobility and many of them only need to be removed.
Consequences of lack of treatment -