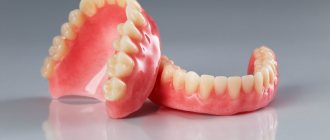
NEUTRAL ZONE – AS THE MAIN GUIDELINE FOR THE LOCATION OF THE BORDERS OF COMPLETE REMOVABLE DENTURES
Introduction.
In recent years, there has been active development of new designs of complete removable dentures and improvement of their manufacturing technology (Usmanov, I.R., 2005; Savina E.A.; 2006; Savvidi K.G.; 2007; Lebedenko I.Yu. et al. , 2008; Murray MG 1993; Wang, HY, 1993; Y. Daptrich, E. Oidmann 2007, etc.).
However, increasing the effectiveness of treatment for patients with complete absence of teeth mainly comes down to the use of dental implantation, but not all patients, for a number of reasons, can afford implantation (Markov B.P., 1988; Surov O.N., 1993; Olesova V.N. et al., 1996; Mirgazizov M.Z. et al., 2000; Kiryushin M.A., 2007; Redinov I.S., 2000; Linkow L., 1996 and others). Therefore, biophysical methods of fixation continue to occupy a central position. In the direction of improving these fixation methods, recently they have modified the methods of obtaining impressions, practiced volumetric modeling of the edges of the prosthesis, as well as the location of the edges of structures within the neutral zone [3].
The purpose of the work was to study the influence of the neutral zone on the fixation of dentures, identifying its features on the upper and lower jaws.
The concept of a neutral zone was proposed in the 1930s [5]. The concept of the neutral zone has been poorly described in the literature, and the technique itself has rarely been used in practice [6].
The neutral zone is the area in the oral cavity where, during the process, functions acting from within the pressure forces of the tongue are neutralized by external forces from the cheeks and lips [1, 6, 7]. It is also called a dead zone, a zone of stability or a zone of minimal conflict [9]. The neutral zone is the area between the mobile and immobile mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Consequently, it is located between the oral mucosa covering the alveolar process and the transitional fold. The neutral zone does not coincide with the transitional fold, but is located below it on the upper jaw, and above it on the lower jaw. This area is characterized by minimal mobility and pronounced pliability of the mucous membrane [3,7].
The oral and vestibular parts of the neutral zone are distinguished. The oral part of the neutral zone of the upper jaw coincides with the border area between the hard and soft palate. It is sharply indicated when pronouncing the sound “A” and therefore it is believed that it is located in the area of line A. It often covers the so-called vibrating zone. The vibrating zone is a section of the mucous membrane that is detected when pronouncing the sound “A”. The width of the passively mobile mucous membrane in the area of line A reaches, according to S.I. Gorodetsky (1951), 6 mm. The shape and width of the vibrating zone are of great importance in determining the distal border of the maxillary denture.
On the lower jaw, the oral part coincides with the fold formed when the tongue is raised and protruded. It usually coincides (but not always) with the maxillary-hyoid line (lineamylohyoidea).
The soft tissues surrounding the prosthesis externally and internally have a significant impact on stability
dentures and help determine the boundaries, position of teeth and the external contour of a removable denture. The use of the neutral zone concept is indicated in patients with neuromuscular disorders, tongue dysfunction, in elderly patients who have been edentulous for a long time, in cases of deformation and significant tissue deficiency [7,8,9]. The neutral zone technique is used to improve retention, fixation and stabilization of dentures.
Materials and methods.
29 patients (19 women and 10 men) aged from 61 to 74 years with complete absence of teeth in the upper and lower jaws were examined. A survey, examination, and x-ray examination were conducted. During the clinical examination, the type of jaw atrophy was determined in accordance with the Oksman classification for the upper and lower jaws and the type of mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed according to Suplee. During a complete clinical examination, the neutral zone was identified in each patient and its width was determined.
The boundaries of the neutral zone were determined as follows: using palpation, the actively mobile and immobile mucous membrane was determined in order to identify the neutral zone. The upper and lower boundaries of the neutral zone were marked with a chemical pencil or marker. Its width was measured with a micrometer [3].
Patients were given dentures with volumetrically modeled edges. Based on the data obtained, an individual tray was adjusted, which contributed to the location of the edges of the prosthesis within the neutral zone. Before obtaining a functional impression, notches were formed on the edges of the individual tray with a diamond disk to achieve mechanical retention with a silicone mass, which was applied along the edges of the tray with a strip 2 mm wide. Spidex was used to decorate the edges of individual spoons. The material was mixed in a ratio of 1:5 (cream + base mass), with the addition of a catalyst [4]. Further stages of prosthetic manufacturing were carried out using traditional methods.
Research results and discussion
All patients were satisfied with the orthopedic treatment. Excellent (in patients with types 1 and 2 atrophy), good (in patients with type 3) and satisfactory (with type 3 in the lower jaw and 4 in both jaws) were achieved. fixation of structures.
The width of the neutral zone on the upper jaw in the anterior section was 2.21 + 0.27 mm, in the area of the frenulum and lateral bands – 0.89 + 0.41 mm, in the lateral section – 2.54 + 0.16 mm, in the area line A – 5.8 + 0.23 mm. In the lower jaw, measurements were taken from the oral and vestibular surfaces. From the vestibular surface in the anterior section the width was 1.4 + 0.17 mm, in the lateral section – 1.9 + 0.15 mm, in the area of the frenulum and lateral cords – 0.31 + 0.17 mm. From the oral surface in the anterior section, the width of the neutral zone was 1.36 + 0.12 mm, in the lateral section – 1.83 + 0.18 mm, in the area of the lingual frenulum – 0.32 + 0.17 mm.
During the examination, it was revealed that a significant lengthening of the edges of the prosthesis leads to its shedding, and their shortening does not ensure the creation of a full-fledged marginal closing valve. [1, 2, 4].
Good fixation can be achieved when the boundaries of the prosthesis correspond to the topographic location of the neutral zone, which is what we observed in patients. A slight elongation of the edges within 0.48 + 0.18 mm creates increased fixation with a suction effect, due to the fact that this error corresponds to the height of the dome of the volumetrically formed edge of the prosthesis, leads to an accurate fit of the active-moving mucosa along the perimeter of the prosthetic bed and the formation of a closing valve It should be noted that when the edges of the prosthesis move to the active-moving mucosa by more than 0.8 mm, it is shed.
conclusions
For successful orthopedic treatment of patients with complete absence of teeth, it is necessary to individualize and carefully consider each stage of orthopedic treatment. However, the neutral zone is the main guide for the location of the boundaries of complete removable dentures, because achieving an effective closing valve is possible only due to the location of the boundaries of the structure in the area of this zone and maximum compliance of the internal surface of the prosthesis with the relief of the prosthetic bed.
Bibliography
1. Zholudev S.E. et al. Methods for improving the fixation of complete removable dentures by optimizing the receipt of functional impressions // Panorama of orthopedic dentistry / Part one. – 2004. – No. 2. – P. 34-39.
2. Kovaleva I. A. Comparative characteristics of methods for designing complete removable dentures: abstract. dis. Ph.D. honey. Sci. – Smolensk, 2007. – 20 p.
3. Konnov V.V., Klenkova M.I. Psychological component of orthopedic treatment of patients with complete absence of teeth // Bulletin of medical Internet conferences (ISSN 2224-6150). - 2015. - Volume 5. No. 4
4. Konnov V.V., Razakov D.Kh., Klenkova M.I., Anisimova Ya.Yu. The importance of the neutral zone when relining complete removable plate dentures //Modern problems of science and education. – 2014. – No. 5. – P.45-48.
5. Konnov V.V., Razakov D.Kh., Klenkova M.I., Anisimova Ya.Yu. A high-quality functional impression is the main component of effective orthopedic treatment of patients with complete absence of teeth // Fundamental Research. - 2014 - No. 10. - P.67-70.
6. Lebedenko I.Yu., Kalivradzhiyan E.S., Ibragimov T.I. Guide to prosthetic dentistry. Prosthetics for complete absence of teeth. – M., 2005. – 397 p.
7. Marxkors R. Complete removable dentures // New in dentistry. – 2004. – No. 7. – P. 36-49.
8. Gahan MJ, Walmsley AD The neutral zone impression revisited. Br Dent J 2005. – pp. 269-272.
9. Falmy FM, Kharat DU A study of the importance of neutral zone in complete dentures. J Prosthet Dent 1990. – pp. 459-462.
Why is missing teeth dangerous?
Losing a tooth is not just a cosmetic defect. It is capable of triggering irreversible changes in the human body that only progress over time.
If even one upper tooth is lost, its pair on the lower jaw is almost not involved in the process of chewing food. As a result, the adjacent teeth take on the load. The result is a violation of their ligamentous apparatus, due to which the risk of loss and periodontal development becomes extremely high.
The loss of several dental units increases the likelihood that the height of the bite will change. As a result, the lower third of the face becomes smaller. This not only leads to an aesthetic problem - the appearance of early wrinkles. Due to the unevenly distributed load, the temporomandibular joint suffers - inflammatory processes and degenerative changes begin.
The patient may experience pain while chewing food or talking. Improper chewing of food leads to diseases of the stomach and other gastrointestinal tract organs.
Methods of upper teeth prosthetics
Modern orthopedic dentistry uses many effective technologies for dental restoration. Various types of prostheses are used:
- bridge-like. They are a non-removable structure that is installed when 1-2 units of dentition are lost. They attach it to supporting units;
- removable plate. Inexpensive removable structures installed in place of lost teeth. They can be partial (restoring several units of the dentition) and complete (restoring the entire dentition);
- clasp (arc). They are a removable structure that uses a light metal arc. A durable, convenient solution that can restore chewing function well;
- conditionally removable. Can only be removed by a dentist. A system of locks (attachments) or a telescopic system without support from the sky can be used as fastening;
- crowns and bridges on implants. Today, the installation of implant systems is a priority method of prosthetics in European countries. Their installation is possible even with complete edentia.
The main difficulty when replacing defects in the lateral group is the proximity of the Maxillary sinus. It is extremely important that it be longer than the future implant. This is only possible if there is sufficient bone tissue. In some cases, a special operation is required in which bone tissue or a synthetic substrate is implanted.
Prosthetics for a completely toothless upper jaw
With complete edentia, it is possible to use various types of prostheses - plastic plates, lying on the oral mucosa, conditionally removable, which are fixed with implants.
Complete restoration from a functional and aesthetic point of view is possible if a minimum of four intraosseous implants are installed. The use of basal, mucosal implants is also considered acceptable, but such methods are not widespread.
Acrylic removable dentures are distinguished by their characteristics. The plate almost completely covers the hard palate. The valve area needs to be enlarged to improve fixation of the prosthesis. However, this method of prosthetics has a significant drawback - patients often note an increased gag reflex, as well as general discomfort.
However, it is worth noting that prosthetics for an edentulous upper jaw are simpler than for the lower jaw. This is due to the fact that the base of the prosthesis will not come into contact with the moving mucosa, thereby improving fixation and reducing discomfort when eating.
How are removable dentures made?
Prosthetics of the upper teeth using removable structures is a very common technique. It is carried out in several stages:
- inspection. At this stage, anamnesis is collected and a treatment plan is developed;
- taking impressions. For this, alginate material is used, as well as a standard dental instrument - a metal spoon;
- determination of jaw ratio. This is required so that the future prosthesis fits comfortably relative to the position of the jaw joint. Samples are carried out using an individual spoon;
- taking an impression. The spoon used during functional tests is used, and the doctor takes an impression. Based on it, a wax frame is made so that the patient can try it on;
- installation of a prosthesis. A prosthesis with a plastic base is placed in the oral cavity. After a few days of using it, correction is carried out.
PRESIDENT specialists have extensive experience in prosthetics of upper teeth. They will select the optimal type of prosthesis with which you will feel comfortable and can significantly improve your quality of life!
Prices
| Dental prosthetics | Price |
| Dental prosthetics using an implant: installation of a zirconium dioxide bridge supported by ASTRA-TECH implants (Sweden) | from 36,000 rub. |
| Prosthetics with partial removable plate dentures | from 28350 rub. |
| Prosthetics with partial removable lamellar dentures (immediate denture) | from 19600 rub. |
| Prosthetics with removable clasp dentures | from 49350 rub. |
| Dental prosthetics with complete removable plate dentures (immediate denture) | from 23,700 rub. |
| Dental prosthetics with complete removable plate dentures (immediate denture) in the area of the 1st tooth | from 15,000 rub. |
| Dental prosthetics with complete removable plate dentures (immediate denture) up to 3 teeth | from 12600 rub. |
| Restoring the integrity of the dentition with fixed bridges (tooth) | from 15500 rub. |
| Restoring the integrity of the dentition with fixed bridges (crown) | from 19350 rub. |
To avoid possible misunderstandings, please clarify the cost of services in clinics with the administrator or during a consultation with a doctor. Prices on the website are not a public offer.