Definition of clasps, their classification
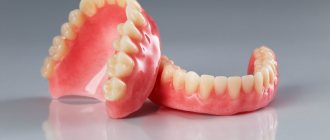
In dentistry, a clasp is a part of a removable denture that ensures reliable fixation of the entire structure in the oral cavity. The simplest option is a hook, but there are also more complex products that perform the function of fastening not only during rest, but also when talking, chewing, sneezing, coughing. The design consists of 3 parts:
- shoulder/shoulders - the part of the clasp that clasps the tooth chosen as a support and presses against the soft tissues, has high elasticity;
- body - connects two other elements, is a smooth continuation of the shoulder;
- process - a part that is almost completely immersed in the base of the prosthesis; sometimes it is attached to the arch of the clasp structure.
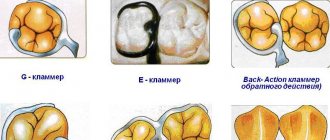
The shoulder consists of two parts - supporting and holding, the first makes up 70% of its length. The thickness does not exceed 0.5 mm. The classification of the product in question is complex, because they differ in function, shape, material used, method of covering the abutment tooth and manufacturing methods. The easiest way to navigate the types of retaining structures is by shape - there are only 4 of them: round and flat, semicircular and strip.
Types by method of connection to the base
The connection is provided in three ways:
- rigid/stable - fixedly connected to the prosthesis, there is practically no load on the gum;
- semi-labile (springy) - the body of the hook is long and has a springy property, only a minimal part of the load is applied to the coronal part;
- labile (articular) - the product has a hinge (joint) in its design, which transfers the entire load to the gum and alveolar process.
The choice of the type of connection of the fastening system to the prosthesis is made by the dentist individually, because it is necessary to take into account not only the wishes of the patient, but also the condition of his gums and alveolar process.
Types according to the degree of coverage of abutment teeth
There are three main types of this classification:
- one-armed/two-armed;
- reversible (ring-shaped);
- double.
A multi-link type of fastener is considered separately - this is a front lining on the lingual surface, which is installed in the area where the front teeth are located. It is most often used for lower row prosthetics, when it is necessary to stabilize several teeth at once.
The products in question can be made from different materials:
- titanium alloys, medical steel, nickel and cobalt alloys or any other base metals;
- palladium, gold, platinum - precious metals;
- acetal, nylon, acrylic - synthetic polymers.
All materials have sufficient strength, but have different service life - clasps made of synthetic polymers are considered the most vulnerable.
Boundary line
The choice of clasp for prosthetics directly depends on the position of the boundary line, for which there are five options:
- Location from the contact point in the defect area to the middle part of the proximal surface of the adjacent unit. In such cases, the use of Roach or Bonigrad models is recommended.
- The passage of the equator through the central part of the approximal region, with a smooth rise to the contact point of the adjacent element. Includes installation of an Acker clasp.
- The diagonal position of the equator and the passage of an extended boundary line in the area of the defective chewing surface, with a tangential intersection of the supporting element and ending on the opposite side of the tooth neck. The preferred model is the Ney clasp.
- The high position of the equator, caused by increased abrasion of the enamel coating of the dentition. In such situations, the boundary line requires covering with artificial crowns, which allow restoring the natural anatomical shape.
- Low location of the boundary line in the presence of cone-shaped elements, with the equator located at the cervical level. Involves the use of supporting structures.
Functions assigned to the fixing element
Fixing prosthetic elements must perform 3 functions simultaneously:
- Support. The clasp always rests on the tooth and transfers part of the load to it when chewing.
- Holding/fixing. The overall structure remains motionless and does not fall off during chewing or talking.
- Coverage. If the prosthesis is in the mouth without a fixing device, it will soon move to the side and cease to perform its functions.
Clasps for dentures are an essential part of the structure, without which restoration of chewing function in full is impossible.
What alternatives exist
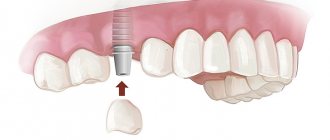
An alternative to clasp fixation are attachments (clasps) and telescopic crowns. All of these options are used for removable dentures. Dentists note that orthopedic structures on attachments are fixed better, and they themselves are completely invisible from the outside. As for telescopic crowns, this is also a very good option, but it is considered the most difficult to manufacture.
“Mom wore a clasp denture for several years. It seemed convenient, but outwardly the metal hooks on the teeth stood out. Well, she began to smile less, of course, because of this. Then the prosthesis had to be changed, and the doctor persuaded me to use attachments. “He turned out to be much better in beauty, from the outside he looks like his own teeth and no hooks are visible.”
Lina O., review from the website stomatology.rf
If we consider the best option for prosthetics in principle, then here the first place is firmly held by dentures fixed on implants - fixed or conditionally removable. They have many advantages - strong, reliable and durable fastening, highest aesthetics, comfort when chewing (they feel like your “native” teeth).
Read on the topic: conditionally removable dentures on implants - how they are attached and how they differ from others.
Requirements for clasps
When choosing a fixation structure in the patient’s mouth, you need to take into account the requirements that it must fully comply with:
- type of fixation - materials must be the same for all supporting teeth;
- the prosthesis does not tip over or rotate after it is installed in the mouth;
- when closing the jaws and chewing, no injury to the supporting units occurs;
- preserving the aesthetics of a smile - metal hooks are unlikely to retain their beauty when installed on the front teeth.
Important! The purpose of clasps is to ensure the immobility of the prosthetic structure, but the doctor must take into account that they can be installed only if the units do not have pathological mobility (do not wobble) and have the correct anatomy of the coronal part.
Advantages and disadvantages
Hook dentures, as mentioned, are one of the common ways to restore jaw functionality. The main advantages of the design are long service life, reliability, and efficiency during everyday wear.
Products are recommended for partial or complete loss of teeth. Unlike acrylic structures, the clasp system is based on a metal frame. Artificial teeth are attached to it. The structural features lead to a reduction in the weight and size of the product, which increases its significant characteristics.
The main advantages of the clasp prosthesis:
- the process of soft tissue atrophy is not as fast as when using acrylic products. When the service life of the structure expires, the patient will feel discomfort,
- The reduced size of the system increases ease of use. Instead of a polymer arc, a metal alloy is used, which improves diction, the ability to clearly distinguish tastes, and move the tongue freely. There is no risk of artificial teeth falling out,
- the metal frame increases the reliability of the system, the risk of breaking is minimal,
- The service life is much longer than that of classic products. If you perform proper hygiene and follow the doctor’s advice, dentures last 5 years instead of the usual 2.5,
- the price is affordable for different segments of the population. Although the cost is higher than acrylic structures, the benefits are worth the cost.
How clasps are made
The structures in question are made in a dental laboratory, and first you need to choose one from all the varieties. Most often, such fixing elements are made from base metals. Any type of hook is bent with pliers, tongs or round nose pliers - it is given its original shape. Then the metal element is “implanted” into the base and the prosthesis is given to the patient to try on and, if necessary, the product is adjusted.
Important! Thorough polishing of the metal in the element that is adjacent directly to the tooth is required: the material should not injure the enamel or serve as a place for plaque accumulation. But the process, on the contrary, is covered with small notches, which ensure its reliable fixation with the acrylic base.
Clasps are an integral part of a removable denture, which has an extensive classification. The choice of a specific model is made by the dentist, because it is important to take into account not only the financial capabilities of the patient, but also the condition of the supporting teeth, gums and alveolar process.
Manufacturing Basics
The production of bent-type support-holding clasps is carried out using special pliers, pliers or round-nose pliers
- Using pliers, bends one of the ends of the wire to form the shoulder of the product.
- Performs a second bend that forms the body of the clasp.
- Forms an extension of the retainer thanks to the third bend of the steel wire.
Double-armed products are made in an identical way with the formation of two elements.
Features of the production of the shoulder and contact process
When making a shoulder, the technician must follow several important rules. The element should be designed so that it meets the following requirements:
- covered the tooth from the labial or cervical area;
- did not exert pressure on the supporting element of the row;
- was carefully polished to avoid damage to the oral mucosa;
- touched the tooth surface as much as possible;
- had sufficient elasticity.
When making a contact process, the technician must use several tools: round-nose pliers to fix the shape, pliers to make a bend to the ridge.
For strong bonding with the base, the workpiece is crushed on an anvil and covered with notches.
The video shows the manufacturing process of Jackson clasps.
How much does prosthetics cost?
The cost of prostheses with hook fixation is the lowest in the segment. For example, a “butterfly” prosthesis can cost from 6,500 rubles, a removable acrylic one from 15 thousand rubles. Much here depends on the length of the orthopedic structure, the type and material of the fastening, the number of clasps, and the base material.
1Glen P. McGeevey Partial Dentures, 2006.
Your questions and answers
QUESTION Hello, tell me, which prosthesis with clasps is better to install? Irina T.
ANSWER Hello, Irina. The choice of prosthesis will depend on the condition and number of supporting teeth, as well as the capabilities of the clinic and the patient’s preferences. With clasps you can make a removable partial denture, acrylic, Acry-free, nylon, acetal, or clasp denture. Better reliability and more compact sizes are found in classic clasp frames, as well as in their modern metal-free counterparts Quattro Ti (“Quadrotti”).
Author: Chernov A. R. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)