Throughout life, every person's teeth inevitably encounter numerous traumatic factors: too hard food, sudden temperature changes or aggressive teeth brushing. All this leads to tooth wear, enamel damage and barely noticeable chips. These defects do not cause noticeable discomfort to a person as long as they are within acceptable limits.
When dental damage develops too rapidly and its level exceeds the body’s endurance threshold, functional and aesthetic problems arise . The patient begins to worry about increased tooth sensitivity to cold or sour foods. Sometimes a person goes to the dentist with a complaint that the teeth have lost their natural whiteness, but have acquired dimples and defects on the enamel surface.
Acid erosion of enamel
After examining your teeth, an experienced dentist will quickly diagnose “non-carious dental damage . Unlike caries, the causes of this disease are not plaque bacteria, but the following factors:
• erosion, • abrasion, • abfractions (chips, wedge-shaped defects), • abrasion (grinding).
From this article you will learn about a common non-carious lesion of enamel - acid erosion of teeth .
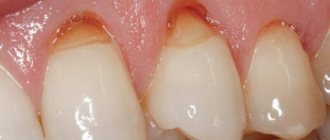
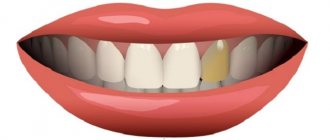
So, erosion is the progressive destruction of enamel and dentin due to exposure to various acids. A striking symptom is the appearance of saucer-shaped defects on the enamel. Due to the loss of enamel, teeth become hypersensitive to cold or sour foods. Patients look for the cause by looking at the tooth in the mirror and find a smooth yellow defect on the enamel. With a significant degree of acid damage, the tooth becomes even slightly smaller in size and acquires a yellow tint - because the enamel is completely erased down to the dentin.
Causes of acid enamel erosion
Causes of hyperesthesia
Dental hypersensitivity is caused by many factors and may indicate problems with the teeth and periodontal tissues. Hypersensitivity is one of the most common diseases in dental practice and, according to WHO, is increasing every year.
The mechanisms of the occurrence of pain syndrome due to irritating factors stimulate increased interest among both researchers and practicing dentists, prosthetists, and hygienists. This attention is explained by the fact that pain is a key symptom of most dental diseases. However, the increased susceptibility of hard tissues cannot be justified by the known pathways of nerve signal transmission. This fact prompted a series of studies to be carried out, which resulted in several theories of the development of hyperesthesia:
- odontoblastic;
- receptor;
- threshold;
- hydrodynamic.
Sufficient evidence has been collected in favor of the hydrodynamic theory. It is supported by most dental clinicians. The dentinal tubule, according to theory, is considered as a capillary tube containing fluid inside.
Exposure to air, high temperatures, etc. it shifts, the pressure in the dentin changes. This leads to increased activity of nerve endings. Penetration of irritants into the tubules is possible when dentin, the main hard tissue of the tooth, is exposed. It is exposed not only against the background of carious lesions and diseases of periodontal tissues, but also as a result of non-carious defects: hypoplasia (underdevelopment of teeth), enamel erosion, etc.
Prevention of acid erosion
All diseases - including acid erosion of enamel - can be avoided if you visit the dentist every six months to a year for a routine examination. A competent specialist is able to diagnose non-carious dental diseases in the early stages and prescribe preventive measures.
Prevention of acid erosion
To do this, the doctor will diagnose erosive tooth wear, collect a life history and ask you about possible causative factors. You need to understand that there is no special device for assessing acid erosion. These defects can only be detected by a dentist during an examination.
Erosion that is not detected in the early stages later turns into a real problem. If you ignore early symptoms and do not consult a doctor, you may end up needing a serious comprehensive restoration of damaged teeth with restoration of bite height. This includes professional oral hygiene, often treatment of dental canals, strengthening them with pin structures and total prosthetics. This is an expensive and quite long rehabilitation that can be avoided with timely prevention.
Hypersensitivity after tooth filling and preparation for dentures
Most often in dental practice, increased sensitivity is observed after filling. Patients come to the clinic with complaints of sensitivity, especially to cold, without precise localization of pain. Upon visual examination, sensitivity in the basal part is not detected. There is no evidence of open pulp or caries on the x-ray.
The causal unit, however, can be identified. To do this, use ice, which, wrapped in a paper napkin, is applied to the cheek area or to the surface of the tongue. An area with a violation of integrity in hard tissues is a source of irritation, so severe pain occurs in the tooth. Removing all filling material will allow you to detect the break.
The reason for increased susceptibility, often to cold or too hot food, may be the appearance of microgaps between the filling and the hard tissues of the tooth due to compression of the composite material. The gap formed in the cavity near the root canals opens up space for the movement of dentinal fluid, thereby causing a response from the nerve endings of the pulp.
The area of contact of the material with the walls of the internal space of the tooth can also contribute to the formation of hypersensitivity after filling. Since filling composites have a high elasticity index, they cause stress in the contact layer “filling - hard dental tissue”. The tension in the tooth tissues is greater in cases where the surface of the restoration in contact with the walls is extensive.
After preparation (grinding) of a tooth for prosthetic structures and microprostheses, normal sensitivity is observed, which is characterized by mild pain. If there is no inflammatory process in the pulp, the pain is considered causative and disappears a few minutes after the drill stops working. If hypersensitivity persists for a long time (2 or more days after the procedure), treatment of pulpitis is required.
I have a toothache. What to do?
Each of us knows firsthand what toothache is. Aching, sharp, long-lasting, pulsating, strong - it can be different and is not always caused by caries. When we turn to an experienced specialist, he asks about the nature of the toothache. This helps the doctor find out why the tooth hurts and whether the discomfort is related to it. We will talk in detail about how to cope with toothache and why it occurs in this article.
Causes of toothache
Toothache is not always associated with tooth decay. Unpleasant sensations can occur due to inflammation of the tissues surrounding the root of the tooth, gum disease, as well as inflammation of the maxillary sinus and some neurological diseases. But since we experience severe pain when closing our teeth or while eating, we are convinced that it is they who hurt.
Based on the nature of the toothache, the dentist can determine its cause:
- 1. Caries When a cavity appears in a tooth, the pain is due to the fact that the enamel is destroyed and the process moves to dentin, which is more sensitive. The stronger the pain from sweet, cold, sour, the greater the volume of dentin has already been destroyed. At the first sign of discomfort, contact your dentist.
- 2. Pulpitis Unpleasant sensations are caused by inflammation of the soft tissues of the tooth - the pulp. Usually with pulpitis we experience aching pain, which can intensify significantly in the evening and at night.
- 3. Periodontitis Very severe pain occurs when biting and touching a tooth with your tongue; during an exacerbation it is impossible to even close your mouth. This is a sign that the tissue that surrounds the root of the tooth has become inflamed and pus is beginning to appear. In this situation, of course, it’s not the tooth that hurts.
In the early stages, caries destroys only the enamel, so we may not feel any discomfort.
What to do if your tooth hurts
Everyone understands that if a tooth hurts very badly, you should immediately seek help from a dental clinic. After a thorough examination, the specialist will determine the exact cause of the toothache and prepare a treatment plan.
When a tooth hurts, but you can’t immediately get an appointment with a dentist, you can try to temporarily relieve the pain or alleviate it. To do this you need:
- remove any remaining food pieces
- rinse the sore tooth with a solution of baking soda at room temperature
- do not chew on the sore side
- Avoid solid, hot, cold, sweet and sour foods
- do not use warm compresses, because if a tooth hurts, your cheek or gums are swollen, then such a procedure can only worsen the situation
What should you not do if you have a toothache?
At the first appearance of toothache, emergency care is required, the goal of which is to reduce its manifestations, restoring the patient’s normal well-being. Urgent measures will help to avoid complications that arise from inaction or, conversely, from excessive enthusiasm or mistakes. Immediately after the pain subsides, you need to go to the clinic for a full examination and treatment.
Useful tips for when a tooth hurts:
1. Heat is contraindicated - toothache intensifies due to local heating, especially if there is an infection at the site of the lesion. Such procedures promote the dilation of blood vessels and blood flow, which can lead to the spread of inflammation throughout the entire dentition. For patients with acute pain, cold is indicated; it is better to apply ice or a cloth soaked in cool water.
2. Medicines are used very carefully - there is no universal drug for toothache, since its nature can be different: from banal pulpitis to inflammation of the mandibular nerve. You should not rely on forums and sites of dubious origin offering “miracle healing.” In any case, the effect will be short-lived and soon all symptoms will return. You can even harm yourself: for example, an aspirin tablet applied to the mucous membrane can cause a burn. Only a dentist can help you get rid of pain forever by providing complete treatment.
3. Bed rest will not help - the toothache will become stronger, more painful and attack-like. This is due to the fact that in a horizontal position, blood flow to the affected area increases, so the pain becomes unbearable. It is better to try to carry it “on your feet” or in a semi-sitting position. A compromise option is to recline, leaning on a pillow. If your tooth hurts late at night, try to take a half-sitting nap in bed and go to the dentist in the morning.
4. Avoid warm rinses - for toothache, the effectiveness of traditional recipes is very doubtful. Of course, you can try decoctions, but not hot! At least this way you won't harm yourself. The cause of pain lies in nerve irritation due to infection and inflammation, which can only be eliminated by professional treatment in a dental office.
If the pain is temporary and passes quickly, there is a great temptation not to go to the dentist. Then, over time, the toothache will intensify and instead of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis will have to be treated.
What to do if your tooth hurts after treatment
When we visit a dentist, we expect to get rid of unpleasant sensations as quickly as possible. But sometimes toothache occurs after caries treatment. If it does not go away within a few days, then you need to go to the dentist again. Most likely, the treatment technology was violated or the filling was too high.
It happens that a tooth hurts after root canal filling and there is discomfort when biting. This is possible in the first days after the procedure, and there is no need to panic.
But what should you do if your tooth hurts after treatment and the discomfort does not go away, but even intensifies? Seek help from your doctor. An experienced specialist from the AktivDent clinic will conduct a full diagnosis to identify and eliminate the causes of pain.
When a child has a toothache
A child can develop toothache at any age. And if an adult experiences discomfort from unpleasant sensations, then for a child this is a real test. Parents try to calm the child, give him anesthetic syrup and look into the oral cavity to understand the cause of the toothache. At best, they will see a speck on the tooth, but usually they won’t even notice it. So why does a child have a toothache?
The causes of toothache in children can be:
- caries and its complications
- injury
- acute mucosal infections (stomatitis)
- gum disease
Wanting to help their child, parents take him to the dentist as quickly as possible. And this is the only right decision. Only an experienced specialist can determine why a child has a toothache and what to do.
A qualified doctor at the ActiveDent dental clinic will carefully examine the child’s aching tooth and oral cavity, conduct the necessary examination and help get rid of toothache.
Provoking factors for the development of dental hypersensitivity
Most often, increased sensitivity is a consequence of a violation of the integrity of the enamel or destruction of the hard tissues of the teeth, which increases the risk of irritation of the endings of the nerve fibers.
The key provocateurs are caries lesions, exposure of the necks and roots of the teeth. Hyperesthesia is diagnosed as a sign of a number of non-carious lesions - enamel defects, progressive loss of enamel and dentin with a decrease in crown height, local destruction, acid necrosis, traumatic injuries, periodontitis with an aggressive course, metabolic disorders of the body, endocrine diseases, mental disorders.
The disease can also occur when consuming large quantities of acidic foods and drinks. Under the influence of acids, the enamel softens and loosens, and erosion appears on its surface.
Increased sensitivity of teeth can be observed after removal of hard dental tissues in order to create a prosthetic space for metal-ceramic structures.
One of the provoking factors is bleaching, during which aggressive chemical bleaching agents are used.
The most common provoking factors also include:
- pulpitis, other dental diseases or pathological conditions that cause destruction of tooth enamel;
- disruptions in the body caused by uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- stress;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- malocclusion;
- incorrectly selected hygiene products (hard bristled brushes, highly abrasive paste);
- bad habits.
Prevention of tooth reaction to sour foods
The best way to get rid of an unpleasant dental problem is timely prevention, which allows you to prevent the development of factors that provoke increased tooth sensitivity to sour foods.
Prevention of tooth sensitivity to acid is classic and involves a number of measures that significantly reduce the likelihood of hypertension. The best prevention is considered to be:
- Regular oral hygiene - it is recommended to clean the crop using special hygiene products (toothpaste and toothbrush) at least 2 times a day after meals. This approach prevents the accumulation and development of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity with all the ensuing consequences;
- Timely contact with the dentist - if you have any dental problems: darkening of the enamel, bleeding gums, exposure of the neck of the tooth - contact your dentist immediately. Eliminating the root cause of the problem will help avoid increased tooth sensitivity;
- Correction of the daily diet - if the diet contains a large amount of acidic foods, it is necessary to reduce the amount of them taken. Excessive consumption of acidic foods can lead not only to increased sensitivity or pain in the teeth, but also to a whole range of other problems, including gastrointestinal problems.
To avoid wondering why your teeth hurt after eating something sour, take preventive measures in advance. If this problem occurs to you periodically, consult your dentist. He will collect anamnesis and conduct an examination. It is highly likely that the problem can be prevented without dental treatment.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing dentin hypersensitivity, it should be borne in mind that it is often a symptom of a disease. Therefore, when a patient approaches, the dentist begins treatment with a survey, during which he receives answers to the following questions:
- duration and nature of the pain syndrome;
- number of units with dentin sensitivity;
- localization of increased susceptibility;
- characteristics of stimuli that cause pain.
After the examination, the patient is required to undergo probing of sensitive areas and other diagnostic tests (thermal, electrical, osmotic, evaporative), as well as percussion (tapping on individual areas of the tooth). At the same time, they find out whether the element is sensitive when biting, identify microcracks in the enamel, damage inside and around the filling, malocclusion, and signs of bruxism.
In addition, diagnostics are carried out using hardware methods and “hidden” carious lesions and periapical changes are identified if they are present.
Much attention is paid to determining the level of pain and the degree of tooth sensitivity:
- no pain;
- mild discomfort;
- medium intensity;
- severe pain or unbearable.
The patient's pain reaction may occur to a greater extent to thermal stimuli (cold, heat), tactile (tactile), evaporative (air), electrical or osmotic (solutions of weak acids).
Dentists note that the reaction most often occurs to cold, brushing teeth, heat and sweets.
The more dentin is exposed due to dental diseases and other factors contributing to enamel loss, the higher the degree of hyperesthesia. This is explained by the fact that in completely exposed dentin there are more dilated tubules with open holes.
Treatment of increased teeth reaction to sour foods
Why teeth react to acid in a particular patient can only be determined by a dentist based on the collected medical history and diagnostic examination data. Unfortunately, today the exact mechanism of the formation of hypertension is not known, but the mechanism of development of this pathology under the influence of certain factors is known.
Classic methods of treating dental reactions to acid are: physiotherapy (iontophoresis), remineralizing therapy, diet correction, changing personal hygiene products (performed taking into account the physiological characteristics of the patient), as well as the use of topical medications.
The specialized clinic "AlfaDent" in Orenburg offers high-quality dental services on favorable terms for the patient. If your tooth reacts to sour foods or there is severe pain after sour foods, make an appointment!
Initial measures to eliminate signs of hyperesthesia
To eliminate unpleasant sensations, the doctor primarily gives the patient the following recommendations:
- exclude predisposing factors;
- do not consume food acids, that is, refuse those products that contain them;
- Carry out hygienic teeth cleaning long before or after meals;
- Reduce the time you spend brushing your mouth to one minute and use a soft-bristle brush.
The patient's teeth are treated with desensitizers. They reduce the sensitivity of teeth of various etiologies by sealing the dentinal tubules. The use of special toothpastes is prescribed.
When the root and neck of a tooth are exposed, mucogingival surgery (vestibuloplasty, etc.) is used to correct gum recession. During surgery, the soft structures of the oral cavity are moved to those areas that require restoration.
For pulpitis, the doctor resorts to pulpotomy. During a dental operation, the pulp is partially amputated using a vital method. At the same time, that part of it that is located in the root canal remains viable.
If sensitivity to irritants persists, additional diagnostics are carried out to exclude chronic pain syndrome, and a more effective treatment plan is drawn up.
Tooth sensitivity (hyperesthesia)
Encyclopedia of Health / Encyclopedia of Diseases
In general, there is nothing wrong with excessive sensitivity - but only if it is a property of your character, and not of your tooth enamel. If teeth react painfully to cold, sour and sweet foods, this can and should be dealt with.
What exactly hurts?
The pain with hyperesthesia of tooth enamel is short, no longer than 30 seconds, but at the same time stinging and sharp, like the blow of a dagger.
| WHAT IF THIS IS INFLAMMATION? Sensitivity to hot and cold may persist for some time after dental treatment. The reason is mild inflammation of the pulp, which usually goes away after a few weeks. But sometimes such sensitivity signals a serious inflammatory process in the tooth. Here are the signs for which you should definitely consult a doctor :
|
If more than a quarter of all teeth have excessive sensitivity, they speak of generalized hyperesthesia; if less, we are talking about a localized form.
Where does this pain come from? It is not the tooth enamel that is highly sensitive, but the looser layer underneath it, the dentin. Enamel, like strong armor, protects this vulnerable tissue from the aggressive effects of various factors. However, for a variety of reasons, tooth enamel can become thinner and even destroyed, and then the dentin remains defenseless.
However, destruction of tooth enamel alone is not enough for the development of hyperesthesia. Inside the dentin there are thin microtubules through which nerve endings pass. As long as these tubes are closed, the teeth are in relative order (even if there are enamel defects, nothing hurts). But when the dentinal tubules open, exposing the nerve endings, a sharp piercing pain occurs in response to any irritant.
Nature's mistakes and our own
Nervous and endocrine diseases, as well as special hormonal conditions (menopause, pregnancy), in which disturbances of mineral metabolism occur in the body, can make teeth too sensitive. Therefore, it is extremely important to determine your overall health before starting dental treatment. This is the key to not only more effective, but also safer treatment. The fact is that formulations containing fluorides, which are used to combat hyperesthesia, especially in high concentrations, can lead to hypofunction of the thyroid gland if the condition of this organ was not normal. So if you have sensitive teeth and your mouth is full, before visiting the dentist you should also visit an endocrinologist.
Other causes of hypersensitivity often include various dental problems: caries, erosion and cracks of enamel, wedge-shaped defects and bruxism (teeth grinding during sleep). Also, teeth can “become sensitive” if gum atrophy has occurred and their neck is exposed - then the roots of the teeth remain not covered with enamel. This happens due to periodontitis, as well as the characteristics of the bite.
Sometimes we ourselves are to blame for hyperesthesia: for example, if we really like sour foods and carbonated drinks that destroy tooth enamel. The habit of eating very cold and hot foods, as well as improper oral hygiene, also lead to cracks in the enamel. Moreover, the enamel can suffer not only from poor or irregular brushing of teeth, but also from excessive zeal in this matter.
Do not press the brush too hard on your teeth, and do not use brushes with hard bristles or toothpastes that contain a high percentage of abrasiveness.
For prevention
- Pay attention to your diet. The diet must be balanced so that the body does not lack minerals. By the way, one of the causes of hyperesthesia is a deficiency of vitamin A. Therefore, if you have sensitive teeth, it is important to have enough of it (it is found in carrots, eggs, and liver). Avoid carbonated drinks that contain acids - colas, forfeits, sour juices, as well as any acidic foods. After eating (especially if you ate something sweet or sour), you need to brush your teeth or at least rinse your mouth with boiled water;
- Brush your teeth with a soft-bristled brush. Movements should be smooth, vertical, not horizontal. It is better to start not with the incisors, but with the distant teeth.
- Buy pastes with a low degree of abrasiveness (better, special ones for sensitive teeth, for example, Sensodyne, Lakalut, Rembrandt). They may contain potassium salts (nitrate or chloride), fluorides, citrate, strontium. The most common and effective are potassium compounds: they reduce the diameter of the dilated dentinal tubules of sensitive teeth, reduce the flow of fluid inside them and reduce the reaction of teeth to irritants. The effect of using such pastes will be noticeable within a few days. True, after switching to regular paste, everything will return to normal.
- Fluoridated mouth rinses are useful, but they must be prescribed by a doctor, as such products cannot be used regularly.
- Avoid procedures that are risky for sensitive teeth. For example, chemical and mechanical bleaching is contraindicated for you - it is better to resort to ultrasound. This is the most gentle method, in which a low concentration of the active substance is used (5-15% instead of 35-40%), and the exposure time of peroxide on the teeth is minimal - only 12 minutes. There is no heating or injury to dental tissues during the session, so the patient does not experience any unpleasant sensations either before, during, or after the procedure. This method can be used in combination with laser whitening. Before and after the procedure, desensitizing pastes should be used for some time.
Treatment for excess feelingsSUBTLE NATURES Over the past 10 years alone, in Western European countries, the number of visits to the doctor for enamel hyperesthesia has increased by 35%. More than half of the world's population suffers from various forms of tooth sensitivity. Most often women complain about it.
To treat hyperesthesia, dentists use either special varnishes, which close micropores in tooth enamel and empty spaces in dentinal tubules, or remineralizing preparations (usually containing fluoride). Thanks to the latter, the threshold of excitability of nerve fibers increases, and the hard tissues of the teeth are saturated with the missing calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. To make the strengthening substances penetrate the dental tissues more easily, iontophoresis is used (the drugs reach their destination using a weak electric current). So that the patient can continue treatment on his own, there are special mouthguards for home use, which contain desensitizing substances.
Treatment methods for tooth sensitivity
For treatment, medications, combination therapy, complex therapy and physical methods are used.
Algorithm of the doctor’s actions in the treatment of dentin sensitivity:
- decreased excitability of the neuroreceptor apparatus of the dental pulp;
- decreased dentin permeability;
- blocking the entrances and obstructing the lumens of the dentinal tubules;
- mineralization of hard tooth tissue.
Based on the clinical picture, complex therapy may be prescribed, including obturation of the lumens of the dentinal tubules and electrophoresis with sodium fluoride solutions. The entrances of the tubules are closed with resin-containing or salt-containing desensitizers.
Laser therapy, a procedure for reducing pores using remineralizing gels, restoring gums in case of receding gums, filling teeth in places where the protective layer is thinning, and coating the enamel with fluoride varnish can also be used.
At home, the patient is recommended to use pastes containing strontium chloride, potassium nitrate, and sodium citrate for hygienic care.
Medication treatment at home
Dentists consider the use of special gels, rinses, and toothpastes with or without very mild abrasives to be effective treatment at home.
When treating hypersensitivity, potassium nitrate is recognized as the most effective remedy. The therapeutic effect when using hygiene products that contain it occurs as a result of the penetration of potassium ions into the dentinal tubules, where they accumulate, surround the nerves in the pulp areas of the tubules and block their activity, thereby reducing the excitability of the nerve endings.
To achieve the effect, it is recommended to maintain a high concentration of potassium nitrate on the surface of the causative tooth or group of teeth. Potassium nitrate can be used as a solution, gel, paste, or other oral hygiene products.
When using toothpastes containing potassium nitrate or chloride and sodium monofluorophosphate, as when using potassium nitrate alone, hypersensitivity to tactile stimuli and cold air is reduced.
If, after two weeks of daily use in the morning and evening, the therapeutic effect of brushing teeth and applying products containing the substance is not observed, then the patient is recommended to wear mouth guards. They are filled with the same compositions and worn at night. Symptoms of hyperesthesia disappear after two weeks.
Also, positive dynamics in home therapy for hypersensitivity are shown by hygiene products that contain fluorides, strontium salts (chloride or acetate), calcium glycerophosphate or hydroxyapatite.
Sources used in writing the article:
- “Modern aspects of pain and local anesthesia in dentistry” (2003), Duiseeva G. Sh., Ruzuddinov S. R.
- “Dentistry: a textbook for universities” (2008), ed. N.N. Bazhanova.
- "Occlusion and Clinical Practice" (2008), Jaeger Klinenberg
Please rate this article
Stanislav Mezheritsky
Chief physician, surgeon, orthopedist
The author of the article is Stanislav Mezheritsky, a practicing dentist with 19 years of experience, chief physician and one of the founders of the Matisse Dent clinic. The main focus is orthopedic and surgical dentistry. Author of numerous publications, regular participant in specialized seminars.