Every third person experiences toothache when consuming hot and cold foods (drinks), even with careful oral care. Why do teeth react painfully to temperature changes? Is it treatable? What recommendations should you follow to avoid hypersensitivity?
The reason for the high sensitivity of teeth to various irritants (temperature, acids, etc.) is enamel hyperesthesia. It can be expressed as a short-term reaction, but more often manifests itself as a systemic disease when eating cold and hot foods.
Why can teeth react to cold?
There are many reasons why discomfort and pain may occur when drinking cold or hot drinks or food. Most of them are directly related to diseases of the oral cavity, but there are also those that are not directly related to dental pathologies:
- Damage to tooth enamel.
Violation of the integrity of the outer covering of the tooth can be caused by a variety of reasons: frequent consumption of hard and dry food, which scratches the enamel during chewing; - mechanical chips;
- an incorrectly selected toothbrush (doctors recommend using medium-hard brushes for adults and soft-bristled brushes for children);
- eating foods that can negatively affect the condition of enamel (carbonated sweet drinks, sour fruits, food additives, etc.).
is one of the most common causes. The fact is that most people don't even think about the fact that they have tooth decay until a distinct black spot appears on the tooth. In fact, caries in the early stages can only be distinguished by an experienced dentist - a tiny gray dot (and this is what “young” caries looks like), if it is not examined in time and urgent measures are not taken to eliminate it, it first becomes the cause of increased sensitivity, and then acute pain.
. Untreated caries invariably leads to another, even more serious disease - pulpitis - destruction of the soft tissues of the tooth. Naturally, with pulpitis, the dental nerves are exposed, which causes acute pain when eating cold, hot, sweet or sour food.
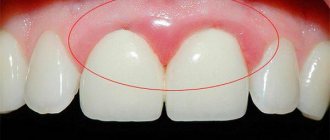
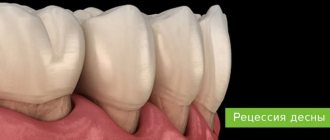
. If the gums become inflamed, in most cases the subgingival part of the tooth, the dentin, is exposed. Dentin is completely devoid of a protective layer - enamel - therefore, at the slightest contact with cold water, food, or even just cold street air, patients invariably experience discomfort and pain.
If you suspect one of the above reasons, you should not delay visiting the dentist for long - an experienced specialist will quickly identify the problem and prescribe a course of treatment.
Reasons not related to oral diseases include the following:
- any hormonal disorders
and changes in the body. As a rule, such conditions occur while taking hormonal drugs, oral contraceptives, during pregnancy or breastfeeding; - suffered nervous shocks
, life in a state of constant stress, etc.; - deficiency of vitamins
, minerals and nutrients in the body. “Seasonal” sensitivity can often occur - when in spring and autumn, due to vitamin deficiency, many patients begin to complain of a certain discomfort after taking cold or hot; - damage to the immune system
, viral diseases; - endocrine diseases
(disorder of one or more endocrine glands).
If increased tooth sensitivity is caused by these particular pathological conditions, then no special dental treatment is required - the main treatment should be aimed at eliminating the root cause.
If, after a serving of ice cream or a glass of cold juice, you suddenly feel discomfort, which smoothly turns into acute pain, it is quite acceptable to take a tablet of a pain reliever that is suitable for you - this can be Nimessil (powder for dissolving in warm water), Aertal (tablets), Ketonov , Dexalgin.
Non-systemic reasons
- Exposure to food acids. They are rich in citrus fruits, cabbage of various varieties, radishes, sweet carbonated waters;
- Non-carious lesions of hard dental tissues. Enamel wears off quickly, especially if not properly cared for;
- Development of caries. It provokes erosion of dental tissues or wedge-shaped effects (V-shaped flaw);
- Mechanical tooth destruction. Occurs during strong impacts, bleaching, grinding for subsequent installation of crowns;
- Inflammation of soft dental tissues (pulpitis). The reason is the penetration of infections, mainly bacterial.
Reaction to cold after dental procedures
Often the cause of a sudden reaction of teeth to cold or hot is recent dental procedures:
- Whitening. In order to understand how this very popular procedure today affects tooth sensitivity, let us recall that whitening (especially done at home or in a suspicious clinic by an inexperienced doctor) can cause severe thinning of tooth enamel. Needless to say, abuse of the procedure invariably leads to damage to the enamel and, accordingly, causes hyperesthesia.
By the way, frequent use of highly abrasive whitening toothpastes can lead to teeth reacting to cold or hot temperatures. If you prefer to use whitening pastes, choose gentle and gentle preparations.If increased sensitivity is the result of excessive whitening, you should first stop using abrasive pastes and contact your dentist to undergo a fluoridation or remineralization procedure.
- Sealing . Most often, after conventional therapeutic treatment of deep caries or pulpitis, patients experience increased tooth sensitivity. The reason for this is the effect on the pulp and nerve endings, after which it is not recommended to drink cold or hot for a few more days. As a rule, there is no acute pain, so the patient can easily cope with the discomfort. If it suddenly turns out that after 2-3 days the sensitivity does not disappear, the discomfort gradually turns into pain, you need to urgently consult a doctor - perhaps an inflammatory process has begun, which needs to be eliminated as soon as possible.
- Prosthetics . During the installation of fixed or removable dentures, tooth enamel can also be damaged.
It is rarely possible to avoid hypersensitivity after dental procedures, so it is recommended to minimize the consumption of cold or hot drinks, ice cream, hot food, etc.
A little anatomy
A tooth consists of a crown and root part, connected by a neck. The coronal part is covered with enamel, the root part is covered with cement. Beneath the enamel and cement there is dentin, a hard tissue. Inside there is soft tissue - the pulp; blood vessels and nerves pass through it.
Dentin is not sensitive, but consists of many tubules in which fluid circulates. The irritant causes fluid movement, which is detected by the nerve endings of the pulp. A person feels their reaction as pain.
Why does a dead tooth react to cold?
Increased tooth sensitivity is the result of irritation of nerve endings. Accordingly, after removal of the nerve, the tooth should not react in any way to cold or hot. However, in practice the opposite occurs - a “dead” tooth aches, hurts and causes the patient a lot of discomfort. There may be several reasons for this:
- In fact, one of the neighboring, “living” teeth reacts to the cold, although it may seem that it is the pulpless one that hurts. In this case, you need to contact a specialist to figure out why this healthy tooth reacts to cold (damaged enamel, caries, pulpitis, etc.).
- The “dead” tooth was poorly healed. There are times when even an extremely experienced doctor, who has the most modern equipment at his disposal, cannot completely cope with pulpitis in one go due to the banal non-standard structure of the tooth canals. As a result, the nerve is not completely removed, and when you eat cold or hot food, the tooth begins to hurt. To eliminate the sensitivity of such a tooth, it is necessary to take an x-ray and consult a dentist for complete removal of the nerve.
- It also happens that the dental nerve is completely removed, but the canals are poorly sealed - in this case, an inflammatory process begins under the filling, which causes a reaction to cold.
You should also not miss the fact that the cause of a pulpless tooth’s reaction to cold or hot may be an infectious viral disease or hormonal imbalance.
Diagnostics
If a tooth hurts from hot or cold, then this is the first sign of improper sealing of the canals. You can check the quality of your dentist's work by drinking a glass of cold water. With unfinished caries, unpleasant sensations will arise immediately, with pulpitis - after a certain period of time. If such symptoms are detected (3-4 days after treatment), you should contact your dentist again, as the discomfort will not disappear on its own. Caries and pulpitis in the complication stage lead to the loss of a unit or infection of the bone structures of the jaw.
The dentist must assess the general condition of the patient, examine the tissues of the oral cavity, determine the degree of sensitivity of the enamel to external irritants and prescribe an x-ray to the patient. If the patient reacts sharply to cold or heat, then the doctor completely removes the previously installed filling. After re-cleaning the canals, the specialist installs a new filling material.
Treatment at home
Unfortunately, getting an appointment with a good dentist can be very difficult. But what to do if you need help in the fight against increased sensitivity of teeth right now? To solve this problem, you can turn to effective folk and home remedies:
- For many years, decoctions (infusions) of herbs have been considered one of the most effective remedies. They relieve inflammation, many of them have antibacterial, soothing and healing properties. You can prepare a decoction of chamomile, oak bark, sage, oregano, calendula, and burdock. You can make an herbal cocktail - mix several dry herbs, pour boiling water and cook in a water bath for 15 minutes, cool and rinse your mouth several times a day.
- Propolis is very famous for its antibacterial properties. You can use it to prepare an alcohol tincture for mouth rinsing by pouring alcohol into a piece of propolis.
- If you are a big fan of warm milk, then the following method is created especially for you - all you need is to simply drink warm milk more often, but do not immediately swallow it, but leave it in your mouth for a while. Why does this method work? Milk contains calcium, which has a beneficial effect on tooth enamel, strengthening it, thereby reducing tooth sensitivity.
However, the surest way to get rid of increased tooth sensitivity is to use special pastes, gels and mouth rinses with fluoride. If you do get an appointment with a dentist, he will most likely suggest that you undergo a fluoridation or teeth remineralization procedure.
You should not rely entirely on folk and home remedies. They may serve as an adjunct to primary therapy rather than as the sole treatment.
Choosing toothpaste
Needless to say, you need to pay special attention to the choice of toothpaste? The first thing you need to learn is that if increased tooth sensitivity occurs, you need to give up whitening pastes (at least for a while, until this problem is finally resolved). Subsequently, such means can be used, but very carefully.
So, what to look for when choosing toothpaste for sensitive teeth:
- Choose only special toothpastes (usually manufacturers indicate this on the packaging);
- Pay attention to special medications that reduce tooth sensitivity (they are sold exclusively in pharmacies);
- It is recommended to give preference to pastes or gels with a high fluoride content - such preparations, if used regularly, restore tooth enamel, thereby coping with the problem of hypersensitivity.
Don’t forget about choosing the right toothbrush - it should be of medium hardness in order to remove food debris from the surface of the teeth without scratching the enamel.
What can you do to relieve pain?
If the pain is severe and it is impossible to get to the dentist in the next few days, hyperesthesia can be pacified for a short time. The simplest, but, alas, not always effective way is to rinse your mouth with a soda solution: 1 teaspoon of soda per glass of warm water.
Painkillers based on ketoprofen: “Ketonal”, “Flexen” and ibuprofen: “Nurofen”, “MIG” relieve symptoms of hyperesthesia well. They act quickly and allow you to completely forget about pain for 5-6 hours.
Local anesthetics in the form of gels give an even stronger effect: “Cholisal”, “Kamistad”, “Dentinox”. These drugs contain lidocaine, so they begin to act instantly. The effect, however, does not last long - for 2-3 hours, after which you can apply another drop of the product to the surface of the teeth.
Traditional medicine gives its own recipe for pain relief: rinsing the mouth with warm water with the addition of 3-4 drops of clove oil or tea tree oil.
Treatment in dentistry
Few people manage to cope with the problem of increased tooth sensitivity at home. Basically, to solve this problem, sooner or later they turn to professionals, who, in turn, offer radical methods of combating hyperesthesia:
- Fluoridation
(simple or deep). A special fluoride-containing composition is applied to the teeth, which helps strengthen the enamel. Simple fluoridation requires several procedures, while deep fluoridation is performed in one visit to the doctor, and is more effective. - Remineralization
is the treatment of teeth with special compounds that can compensate for the deficiency of minerals in the enamel. - Coating with special dental varnishes
. These preparations seal the surface of the tooth, covering it with a dense film, thereby ensuring the strength of the enamel and preventing its further destruction.
If you suddenly feel that your teeth are reacting to cold or hot, immediately contact an experienced specialist who will carry out all the necessary manipulations to solve your problem:
- Initial examination. Detection of dental diseases (caries, pulpitis, gum disease, etc.).
- Drawing up a clear treatment plan.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity, elimination of all existing foci of infection.
- Removal of plaque and tartar (professional cleaning).
- Treatment of enamel with a selected composition (fluoridation, remineralization, varnishing).
After the procedure, the doctor will recommend using only special pastes, reviewing your diet by adding more foods rich in calcium and fluoride, and, of course, visiting the dentist at least once every 6 months.
Qualified help
Professional help for hypersensitivity involves two highly effective procedures - fluoridation and remineralization. These are safe techniques that can quickly increase the strength of enamel and make it more resistant to the irritating effects of external factors.
Remineralization normalizes the structure of the upper dental layer by saturating it with phosphate , fluorides and calcium. After the session, the unit almost immediately stops reacting acutely to temperature changes.
Fluoridation consists of the use of a fluorine-containing drug. It can be repeated at intervals of several months. The procedure is especially relevant for people living in areas with a lack of phosphorus in tap water.
After treatment and preventive measures, the doctor may prescribe a special remineralizing gel to the patient. It must be used within a month. This should be followed by a long break.
How does pain occur?
People with increased tooth sensitivity know for sure that if the problem is not addressed in time, then over time it will cause a lot of trouble.
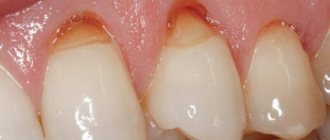
The main cause of hyperesthesia is thinning or damage to the enamel. Accordingly, the thinner this protective layer, the more often and stronger the teeth react to cold or hot. Gradually, mild discomfort turns into severe pain - after all, after the tooth enamel is destroyed, the soft tissues of the tooth, which contain the nerve endings, undergo decomposition. Irritation of the nerves invariably leads to sore teeth, it becomes painful for the patient to chew, drink, and even pain may occur when air gets into the mouth.
Reasons why teeth may hurt after cold weather
- General hypothermia of the body.
- Prolonged exposure to the air flow coming from the air conditioner.
- A draft can cause hypothermia.
- Inhaling frosty air through the mouth.
- Being outside in windy weather with your face open.
Forms and degrees of hyperesthesia
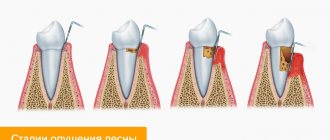
There are 3 stages of development of the problem:
- While eating cold food, the patient feels slight discomfort, which quickly passes and is forgotten. But it is important to understand that this is only the first call, which you definitely need to listen to. After all, it is obvious that there is already a violation of the integrity of the enamel, and the sooner measures are taken to restore it, the faster the problem of tooth sensitivity will be solved.
- Mild discomfort turns into pain. While this pain is quite tolerable, it does not occur immediately, gradually intensifies, but passes within a short time (provided that the irritant is eliminated - cold drink or food). Often such teeth react not only to cold, but also to hot, sweet, sour, spicy, salty, etc.
- The third stage - upon contact with cold or hot, spicy or sweet foods, the tooth immediately begins to hurt, the pain intensifies and does not stop even after the irritant is eliminated.
In addition, there are also several forms of hyperesthesia:
- Limited.
An individual tooth reacts to cold. - Generalized.
The entire dentition suffers from increased tooth sensitivity.
Despite the fact that hyperesthesia is a fairly common phenomenon and many patients treat this condition as normal, in fact, increased tooth sensitivity can cause the development of many other dental diseases. Therefore, you should not delay contacting the dentist.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
Types of hypersensitivity
If sensitivity is increased on one or more teeth, it is called limited. If for everyone - generalized.
Table 1. Types of hyperesthesia
| № | View | Reaction |
| 1. | Light | for cold, hot |
| 2. | Average | as with 1st degree plus for sour, sweet, salty |
| 3. | Expressed | as in grade 2 plus mechanical irritants (when brushing teeth, eating) |
What complications may arise?
If the disease is not treated, it will certainly cause very extensive complications. Hyperesthesia is no exception. If we take into account the fact that the reaction of teeth to cold and hot can be the result of a variety of pathologies, then this problem needs to be solved as quickly as possible, without waiting for these complications to make themselves felt.
Untreated hyperesthesia at an early stage eventually leads to severe toothaches - patients complain of the inability to eat, and feel pain when air enters the mouth. At stage 3, it is much more difficult to cope with the problem - after all, by this time the enamel is already quite badly destroyed, which is why numerous carious cavities are formed, etc., and drastic measures may be required.
Enamel is the protective layer of the tooth. When it is abraded, deformed or mechanically damaged, soft tissue becomes vulnerable to a huge number of bacteria. Therefore, you should not put off going to the dentist at the first signs of a reaction to cold or hot foods.
Toothache caused by hot and cold foods
If your teeth respond with a painful reaction when eating such dishes, this means that the problem lies in the enamel of the teeth. When the enamel is healthy, the tooth structure is reliably protected from sudden temperature changes. If your teeth respond with pain when you eat, you should immediately visit a dentist to identify the cause. Here are a few reasons that cause such pain:
- Tissue inflammation has occurred;
- The structure in the enamel is damaged;
- Non-carious lesions;
- Cracks have appeared;
- Due to severe stress, the enamel has become thinner.
By the way, it happens that such pains are caused by the endocrine system or they may be caused by a stomach disease. It is necessary to reconsider your eating habits. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of foods with too high and low temperatures, and also be careful when drinking sour juices. To do this, you should use a straw.
Prevention of tooth sensitivity
A few decades ago, it was possible to escape from increased sensitivity of teeth only with folk remedies, but today there are a lot of special drugs that help in the prevention and treatment of this pathological condition - these are toothpastes, brushes and rinses, which, when used regularly, help cope with increased sensitivity. Based on the fact that the composition of all drugs is different, experts recommend changing the medicinal paste or rinse from time to time. But it is better to avoid using whitening pastes.
In addition, there are a number of standard recommendations, the implementation of which will protect the enamel from damage:
- Regular, thorough oral hygiene (2 times a day - morning and evening, during the day it is recommended to rinse your mouth after each meal). It is advisable to use a brush of medium hardness.
- The diet should be well balanced - vitamins, minerals, nutrients. Be sure to include dairy products, fish, and meat in your menu. But it is better to limit sweets and spicy foods as much as possible. Also, to preserve the integrity of the enamel, try to avoid dry solid foods - crackers, seeds, etc., as well as carbonated drinks.
- Consult your doctor and choose the appropriate course of vitamins and minerals for yourself.
- Don't forget to visit your dentist regularly - for a routine examination you need to make an appointment at least once every six months.
If, despite all preventive measures, your teeth react to cold or hot, be sure to consult a doctor - perhaps the problem lies deeper and only an experienced specialist can identify its cause.
Author: Elena Grunina Dentist-therapist, endodontist. Work experience more than 9 years. The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
What is periostitis and how does it develop?
Periostitis (flux) is an inflammation of the periosteum - the tissue covering the bones of the upper and lower jaw. The inflammatory process in this case usually proceeds very intensely: a large amount of pus is formed, the patient’s well-being is disturbed, and a significant rise in body temperature may be observed.
- The pain in this case is intense and can be bursting, throbbing or tearing.
- Upon examination, the gums of the diseased tooth are inflamed, swollen, and painful when pressed. The swelling extends to the cheek and can be so severe that the face becomes asymmetrical.
- On the mucous membrane of the cheek in the immediate vicinity of the diseased tooth there may be a swelling with a hole for the release of pus. If there are no ways for the outflow of pus to the outside, then it can break into the soft tissues of the cheek and neck, posing a threat to the health and life of the patient.
If your tooth hurts after filling
So, why does a tooth hurt after filling? Any installation of a filling is an intervention in the tissue, so pain during and after treatment may well occur. On the other hand, one pain is a natural stage in the recovery of the body after treatment, and the other is a sign of incipient complications or injury. So when should you sound the alarm? Experts distinguish different types of toothache: according to duration, nature of manifestation and correlation with various types of manipulations.
How to rinse your teeth when they hurt?
Rinsing cannot replace full treatment, but it will help alleviate the patient’s condition for a short period of time. For rinsing you can use:
- furatsilin solution, which can be slightly warmed before use;
- a solution of baking soda, to which you can add a pinch of table salt;
- if there is severe inflammation of the gums, you can (in the absence of other means for rinsing) use an alcohol solution or vodka.
To prevent toothache from taking you by surprise, visit the dentist on time.
General rules for oral care when it is not possible to immediately visit a dentist
If toothache appears at the most inopportune time and in the most inopportune place, then you should use the available means to alleviate your condition:
- You can apply ice to the sore side or suck an ice cube like a candy;
- Do not heat a sore tooth, this can lead to activation of the inflammatory process and increased pain;
- if there is a carious cavity, food debris should be removed from it, and gum pockets, if any, should also be cleaned;
- in case of severe pain, you can take any painkiller, but you should not get carried away with them; taking analgesics does not replace a visit to the dentist.
When pain is normal
There are very frequent cases when the procedure for treating caries and pulpitis is carried out according to all the rules, but pain still occurs.
In this case, the cause of the pain is hyperesthesia.
Excessive sensitivity of dental tissues to various irritants is hyperesthesia.
Symptoms intensify if there are small cracks in the enamel of the teeth. Various factors contribute to the appearance of such cracks:
- Damage to the enamel from mechanical impact (hard bristles of a toothbrush, during the whitening process, due to impact or scratch with cutlery, etc.).
- Exposure of enamel tissue to aggressive nutrients (for example, citric acid).
Installing a filling after caries treatment as a problem of discomfort
Caries has two degrees of progression: chronic and acute. There are also several forms of dental damage by this pathology: deep, medium and initial.
The dentist treats deep and medium forms of lesions by mechanical treatment of the affected area, followed by installation of a filling.
If during the treatment of the tooth part of the tissue affected by caries was left behind, this may become the root cause of pain when exposed to cold.
In some dental offices, doctors use a special liquid that stains the affected part of the dental tissue with a certain color. This is very convenient, since the dentist can clearly see which area needs to be removed. But not all doctors use this drug.
In a filled tooth, pain can also be caused by other reasons, for example, improper filling procedures for deep caries. The chronic course of caries will be expressed by dense pigmented dentin, in which case the procedure for removing the affected tissue can be stopped, followed by the installation of a filling.
If the dentin is soft, the dentist may decide to strengthen it with a lining containing calcium. In this case, it does not open the tooth cavity. The infection contained in the affected bottom of the cavity gradually penetrates into the dental cavity through the dentinal canals.
Inflammation of the neurovascular bundle, accompanied by pain, is a response to infection.
The occurrence of pulpitis can be provoked by incorrect tactics of the procedure, when in the process of removing tissues affected by caries, sufficient air-water cooling of the tooth tissues was not applied. The consequence of this is heating of the pulp tissue, which provokes the occurrence and development of pulpitis.