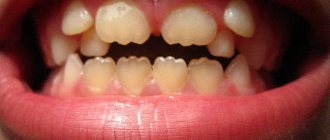
After installing a prosthesis (in most cases a crown), unpleasant symptoms can be detected. This is pain, discomfort, swelling, the sensation of a foreign body in the oral cavity, and even suppuration of the tooth. This is due to improper installation of the prosthesis or independent diseases of periodontal tissue. If the material is incorrectly selected, an allergic reaction may develop. Vulture, itching, redness, and swelling appear on the mucous membrane. The troubles don't end there.
It often happens that a removable denture is installed incorrectly by the dentist or by the patient himself after cleaning. This does not mean the doctor is unprofessional; it happens that after orthopedic treatment, the tooth is injured or the enamel cracks. The reason for this may be injuries, biting hard objects, bad habits - holding a needle or coffee bean in your teeth, thread (these are more likely professional bad habits). All this cannot go unnoticed and both the jaw itself and the installed prosthesis suffer. Any complication after prosthetics can be associated with external or internal irritants, but each time it is accompanied by minor or severe pain.
Why does inflammation begin under the prosthesis?
At the present stage of orthopedic treatment, all materials are so carefully selected that the risk of complications is reduced to a minimum. But everything has its exceptions.
Poor canal filling before prosthetics is a mistake not of the orthopedist, but of the therapist. Incomplete filling of the tooth canal leads to the entry of unfavorable microflora into it, which multiplies and provokes inflammation of periodontal tissue. The patient feels pain, swelling at the site of the installed prosthesis, and pulsation. In this case, it is extremely necessary to re-treat and reinstall the prosthesis.
Inflammation may occur under a fixed prosthesis or crown if an instrument is left in the canal during treatment or the canal wall is perforated. In any case, 95% of complications are associated with improper root canal treatment.
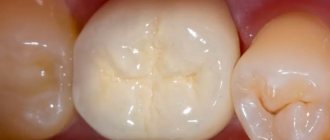
A carious cavity under the prosthesis is a complication of prosthetics and is also associated with improper preparation for prosthetics. Caries under a denture develops in two cases: incomplete removal of carious tissues and non-compliance with the rules of sealants during prosthetics. When there are holes for food debris to penetrate, it always leads to the formation of plaque and caries.
How to get used to increased salivation or dryness
Increased salivation always goes away on its own. But if you wish, you can speed up this process. There are several proven methods for this:
- — After eating, you can rinse your mouth with water pepper extract diluted in water.
- - You can rinse your mouth with a decoction of Lagochilus intoxicating.
- “Rinsing with shepherd’s purse tincture also has a positive effect.
- — Viburnum berries poured into boiling water reduce salivation. The resulting infusion can be drunk and used for rinsing.
To eliminate dry mouth, you need to drink small sips of water as often as possible. It will also be useful to increase the amount of juicy vegetables and fruits in your daily diet. Dry mouth will be relieved by periodically sucking on low-sugar candies.
Among the folk methods there are also many that will eliminate dry mouth. Decoctions of chamomile, calendula, and St. John's wort not only reduce dry mouth, but also fight pathogenic microbes, help strengthen the gums, and help with inflammation of the mucous membrane. To prepare such a decoction, dry parts of the plant are poured with boiling water and left to infuse for several hours.
How to identify complications after installation of a prosthesis?
If there are doubts about the normal state of the mucous membrane under the prosthesis, you need to pay attention to several specific manifestations.
Swelling of the gums is a sure sign of the onset of the inflammatory process. The accumulation of purulent exudate under the gum can lead to serious consequences, and in this case you need to contact a dental surgeon. Swelling or gumboil can cause not only pain, but also tooth mobility, and this will lead to the need to replace the denture.
Fistula - acute inflammation of periodontal tissues can result in gumboil. And if the acute period of the complication went unnoticed, then the appearance of a fistula cannot be missed. If the fistula closes, acute inflammation begins again.
Cyst - if adequate treatment of chronic periodontitis was not carried out before prosthetics, it will end with a cyst. The cyst contains pus and appears on an x-ray as a black spot. The symptoms of a cyst are similar to periodontitis - pain when biting, swelling in the area of the causative tooth.
Causes of complications
After installing dentures, if signs of pathological processes appear in the oral cavity, you should immediately contact your dentist to eliminate the problem. The main reasons for complications during dental prosthetics are:
- insufficiently thorough preparation for the manipulation, which consists of refusing the proposed dental treatment, sanitation of the oral cavity and elimination of caries;
- incorrectly selected size of the prosthesis, resulting in discomfort while wearing it;
- poor-quality installation of the structure, which caused the appearance of gaps and cracks, the accumulation of food debris between the teeth, as well as the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the gums;
- breakage, damage or displacement of the denture;
- decreased immunity or allergic reactions caused by dental construction materials;
- displacement of individual teeth, resulting in movement of the entire structure as a whole;
- non-compliance with the rules of oral care after installation of a denture.
What to do if there is inflammation under the prosthesis?
The first thing to do is contact your doctor or, better yet, go to a good dental clinic that will offer several treatment options.
If prosthetics involves installing a pin, treatment becomes more complicated, since removing it from the root canal is quite difficult and can result in a root fracture. After this, the tooth will have to be completely removed. The issue of repeated prosthetics is quite complicated, since a root fracture can damage the bone plate and the implant cannot be installed, just like any pin.
When the cause of a complication after installing a crown is improper treatment of the canals, again the refilling is difficult and may result in perforation.
When it is possible to unseal the canal or remove the pin, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. After this, the canals are re-filled and a new prosthesis is installed.
We can conclude that it is better to carry out painstaking preparation for prosthetics and take into account all possible complications before installing the prosthesis, rather than treating the resulting inflammation.
How to fix the situation
If the removable denture does not stay in place, you need to make an appointment with an orthopedist. You cannot adjust dentures yourself. It can be so damaged that it cannot be repaired. In addition, in the absence of special tools and skills, it is possible to create a traumatic edge and provoke prosthetic stomatitis.
The doctor will correct, adjust or reline the structure and the problem will most likely be solved.
Sometimes, the patient cannot get used to the restoration or, due to anatomical features, the denture falls off and no measures help. In such cases, implant prosthetics are recommended.
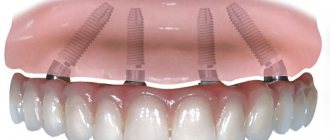
Implantation is the implantation of titanium rods into the bone tissue, which act as a tooth root. The prosthetic structure is then attached to them. This can be either a single crown or a full jaw restoration. This type of prosthetics will allow you to forget about the loss of an artificial jaw. Implantation stops bone tissue atrophy and restores normal chewing function.
An example of dental prosthetics on implants
Caring for fixed structures is easier, they are attached better and creams and gels are no longer needed. It is enough to brush them like regular teeth and undergo a preventive examination.
Fixation means
Almost all people who wear removable structures are familiar with fixation cream. Popular brands are Corega, Protefix, Fittydent, LACALUT, PresiDENT. There are also fixing pads and powders based on sodium alginate. All these products are applied to a cleaned, moistened denture, it is installed in place and glued to the gums.
Manufacturers claim that in this way, a poorly fitting structure will gain good fixation for 8-12 hours. But in practice and according to patient reviews, the action lasts only a couple of hours or even before the first meal.
“When they made an acrylic remover for me, I couldn’t use it without cream at all. Food got stuck under my gums, which was not pleasant. The clasps did not cling well to the teeth. Corrections at the dentist also did not help much. So I save myself with cream, although I still can’t chew something tough like shish kebab. And the cream has a specific taste, you need to get used to it.”
Evgeniy Nikolaevich, review from the dentistry.rf forum
Professional correction: relining, editing
Adjustment of a removable denture (relining, editing) is an adjustment of its dimensions to the changed anatomy of the prosthetic bed. Since bone atrophy does not stop when wearing such structures, and sometimes even intensifies, over time the base will not fit tightly, will begin to wobble and fall out. To increase comfort, the doctor can file down protruding areas or build up the acrylic base during the appointment - this is a clinical method. It is fast, but there is a higher risk of the patient becoming allergic to acrylic, and lower reliability.
Relocation of removable structures should be carried out according to indications. On average, every 3-6 months, depending on the rate of atrophy and the softness of the base material.
With the laboratory method, new impressions must be taken from the jaws and sent to the dental laboratory along with the prosthetic structure. The technician will modify the product in accordance with the new parameters so that it fits tightly to the atrophied areas. This method is optimal in terms of convenience and durability, plus the risk of allergies is much lower. But the adjustment will take more time - up to 5-7 days.
Options for removable orthopedic solutions for the lower jaw
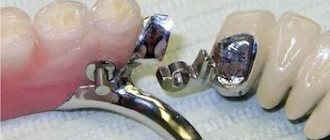
Clasp dentures
Currently, a clasp denture is one of the best solutions for partial restoration of teeth. The design involves the presence of a strong metal arch, to which a light pink base made of nylon or plastic is attached, and artificial crowns are fixed on it. There is no bulky overlap in the sublingual area, but only a thin arc that is practically not felt, and certainly does not affect comfort and taste in any way.
“So, I’ll tell you about my impressions of the clasp prosthesis. Before him, I went with nylon and it was terrible. Unlike its predecessor, the clasp version on the lower jaw is much more convenient. At first there were minor problems with diction, but these were minor things, I just had to get used to it. The denture stays firmly in the mouth, does not interfere with eating and talking, and does not emit an unpleasant odor. Excellent solution, of course, if you are not allergic to metal. By the way, I don’t feel any metallic taste either.”
Alena Shep, Moscow, review from flamp.ru
The main advantages of this type of prosthesis include increased strength and a short adaptation period. The convenient design allows you to evenly distribute the load when chewing, and is characterized by the absence of overlap in the sublingual area, which significantly increases the level of comfort. Among the disadvantages are the relative level of aesthetics due to the presence of metal fasteners, the need to prepare abutment teeth, as well as the high cost when choosing a model with attachments. In addition, this option is not suitable if we are talking about the absence of all teeth.
Clasp denture with locks
The clasp version with clasps will cost from 20 thousand rubles, while the model with micro-locks will cost significantly more - from 50 thousand. This cost usually includes payment for materials and specialist work.
Quadrotti dentures
Quadrotti is based on the soft elastic material Dental D. Thanks to its properties, it copes well with high loads, does not cause allergic reactions, and is also simple and easy to process. Dentures made from Dental D do not contain hard metal parts, which not only interfere with aesthetics, but also cause a lot of inconvenience. The material is fully validated by clinical studies conducted throughout the world over the past ten years 1 .
“In my opinion, Quadrotti is greatly overrated. No, the prosthesis is comfortable, you can’t argue with that, but I definitely haven’t had anything like that, just WOW. Before this I went with a clasp apparatus and now I don’t feel much difference. While I’m still in the period of getting used to it, it’s still a little difficult to speak, and even more so to chew. They promised that there would be no discomfort, but the artificial gum still rubs a little. Otherwise, the option is good, it looks, at least, very natural.”
Irina L., Perm, review from otzovik.com
The advantages of this model include excellent aesthetic characteristics, strength of fixation, and minimal risk of developing allergies. Such dentures are very comfortable and durable. Additionally, they can be flavored with chocolate, vanilla or citrus flavors. Among the disadvantages of Quadrotti are the high cost of the device, as well as the need for regular relocation of the prosthesis.
Quadrotti on the lower jaw
On average, the cost of manufacturing and installing a Quadrotti prosthesis for one lower jaw is 40 thousand rubles. The amount includes the cost of materials and payment for the work of specialists.
Acrylic prosthesis
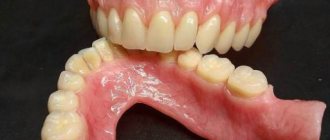
Acrylic structures for partial tooth replacement are equipped with hard clasps, which often rub and can injure soft tissues and oral mucosa. This solution cannot be called convenient, but it often becomes the best choice when the patient is financially limited. With complete edentia, these dentures are fixed quite well. Moreover, their cost is from 15 thousand rubles.
Prosthetics with complete edentia
Clasp dentures cannot be used with complete edentia, so in this case the optimal choice is the Quattro Ti design. Many experts classify this model as a clasp type, but it is based on no metal elements that could injure the enamel and gums. In addition, such a prosthesis can be used with complete edentia - it can only be fixed on the gums.
Another good option is Akri Free dentures, which meet high demands on aesthetics and durability. As for acrylic solutions, when restoring the lower row in the absence of all teeth, the fixation of the apparatus will be rather weak. As an alternative, you can resort to conditionally removable prosthetics using an acrylic device supported by implants.
Let us quote D. Jerryson, a professor at New York University College of Dentistry, who specializes in research in the field of dental prosthetics: “When choosing a specific model of removable denture, it is necessary to take into account the clinical picture as a whole. If Quadrotti is a universal option, then clasp solutions can be fixed only if there are supporting elements of the dentition. Among the less convenient but budget options, it is worth highlighting acrylic dentures, but the final choice can only be made by a qualified specialist after conducting an appropriate examination.”
Next, we will consider in detail the types of modern orthopedic systems that are most often chosen to restore both part of the teeth and the entire dentition in the lower jaw.
Proper production of dentures
During the manufacturing process[1], it is important to follow all the nuances of the technological process (it is different for each material). If a mistake is made at any stage, then a defect may appear in the product, and the fit will not be tight. Chewing with such “teeth” is not only inconvenient, it is impossible.
Therefore, choose experienced orthopedic doctors. Also, priority should be given to clinics that either have their own dental laboratories or have entered into an agreement with a large modern laboratory.
Correction of an incorrectly manufactured complete denture base
During the delivery of complete dentures, errors are possible, caused in some cases by incorrect determination of the central relationship of the jaws or violations in the process of laboratory production of dentures, in others - by incorrect determination of the lower third of the face or the boundaries of the prosthetic field.
However, one of the most serious and most common disadvantages of complete dentures is their poor fit. The tissues under such prostheses are often subject to mechanical trauma, which leads to pathological changes. The reasons for poor fixation of complete dentures are: shortened or elongated edges of the denture base; discrepancy between the base of the prosthesis and the relief of the hard palate or alveolar process of the lower jaw; lack of space for the torus palatinus and other bony protrusions; the tissue of the soft palate is not pressed upward with an individual spoon before and during the impression; anatomical formations on the lower jaw (sublingual and retroalveolar spaces, mandibular tubercles) are not used to hold the lower denture; the edges of the prosthesis do not correspond to the edges of the obtained functional impression; poor quality prints; the edges of the prosthesis cover the frenulum and folds; there is not enough space for the free functioning of the language, etc.
Heringer compasses
If the edges of the prosthesis are elongated, then hyperemia appears in places of increased pressure, and then pressure sores occur. In this case, during contraction of the muscles on which the edges of the prosthesis are located, the prosthesis is displaced from its bed.
Correction of the prosthesis should be made when hyperemia appears, since subsequently, when bedsores form, accompanied by pain and inflammatory infiltration of surrounding tissues, the boundaries defining the area of the elongated edge of the prosthesis are erased.
To accurately determine the elongated boundaries of the prosthesis, dentin or gypsum powder is applied to the hyperemic areas and the prosthesis is applied to the jaw. The areas marked on the prosthesis with white powder are the places of correction. If the edges of the prosthesis are shortened, they are lengthened with wax, formed in the patient’s mouth, and the wax is replaced with plastic.
Functional overload of teeth
M.A. Napadov and V.Yu. Kurlyandsky (1955) recommend correcting the base of the prosthesis and its edges directly in the patient’s mouth using quick-hardening plastic. There are other ways to reline dentures. However, using them, we did not always obtain satisfactory results.
The following method of correcting the base of the prosthesis on the lower jaw turned out to be more reliable.
Using fast-hardening plastic, areas of the prosthesis extending into the retroalveolar and sublingual spaces are supplemented, and if the base is narrowed, it is expanded from the vestibular side in the area of the lateral teeth. Excess plastic on the inner surface of the prosthesis base, which restricts the movements of the tongue, is cut off, and a recess is made between the molars and premolars on the vestibular surface of the prosthesis base for applying a retainer. After this, an orthocore plate is applied to the base of the prosthesis, the edges of which end on the vestibular and lingual surfaces. Excess orthocore is cut off in such a way as to form a smooth transition to the base of the prosthesis. Orthocor is heated in hot water, the prosthesis is placed on the lower jaw and secured with a retainer. Then the patient is asked to carry out the full range of chewing, swallowing and other functional movements, as well as to make phonetic correction of the edges of the prosthesis. In areas where the edges of the prosthesis are exposed, the latter are shortened, covered again with orthocor and reinserted into the oral cavity. Having completed the correction, the prosthesis is plastered into a ditch and the orthocor is replaced with plastic in the laboratory. The finished prosthesis is handed over to the patient and the dentition is corrected under the control of carbon paper, achieving smooth gliding of the dentition.
Anatomical articulator design and model fixation technique
If the complete upper denture is poorly fixed, then the cause of poor fixation is determined. If the posterior edge of the prosthesis is located 2-3 mm posterior to the blind foramina and overlaps them, it should be assumed that the soft palate was not pressed upward when taking a functional impression. In this case, a narrow strip of heated wax is placed on the back edge of the prosthesis, and the tissue of the soft palate is pressed out with it. As a result, the prosthesis begins to stick, which confirms the correctness of the assumption made.
In cases where the prosthesis does not cover the blind holes, its posterior edge is lengthened. For this purpose, the wax plate is heated and folded into 2 layers so that the upper one is a continuation of the prosthesis, and the lower one extends to its surface facing the oral cavity. The wax plate is fixed to the prosthesis using a heated spatula. The prosthesis is inserted into the oral cavity and the wax part is pressed upward on the soft palate, cooled in water and reinserted into the oral cavity. If the prosthesis begins to stick, it should be assumed that its posterior edge has been shortened. If, when you press your fingers on the front teeth, the prosthesis is well fixed on the jaw, this means that its rear edge not only properly presses the soft palate upward, but also has a sufficient length.
A.I. Betelman and co-authors (1954) recommend marking the posterior border of the prosthesis on the soft palate with a blue pencil, getting a pencil imprint on the back of the prosthesis and cutting off excess wax outside the valve area. If using wax it was possible to eliminate the cause of poor fixation, the prosthesis is plastered in a ditch, the wax is replaced with plastic and the prosthesis is given to the patient.
If using the described manipulations it was not possible to improve the fixation of the prosthesis, the back side is covered with a heated strip of wax, it is strengthened and, after heating the wax strongly on an alcohol lamp, the prosthesis is inserted into the patient’s mouth. Holding the prosthesis on the jaw, the patient is asked to functionally design its edges. After clarifying the boundaries of the prosthetic field 2-3 times and cooling in water, the prosthesis should stick, as a valve will form under it. However, in some cases this does not happen, and the prosthesis, at the slightest tension of its soft tissues, begins to “slide” from the jaw. Consequently, the excessively elongated sides of the prosthesis are located much above the neutral zone on the moving soft tissues. In these cases, it can be difficult to correct the denture by shortening its sides using wax. Sometimes more serious deficiencies cannot be eliminated at all, and the prostheses must be remade.
Habituation and home care
A properly completed adaptation period and regular care are the key to making wearing an artificial “jaw” more comfortable (although getting used to it is difficult). Let's figure out what's what. In the first days (a week or two), you need to sleep with the denture in your mouth - this way adaptation will happen faster. Normally, the feeling that it is in the way, pressing, or trying to fall out should gradually disappear.
Caring for the “removers” involves removing them after every meal or any snack in order to clean and rinse the structure. In the morning and evening, thorough cleaning is carried out using a brush and paste. Once or twice a week it should be soaked in an ultrasonic bath or in a container with a disinfectant solution. And every 6 months you should visit the dentist for professional cleaning of the structure and examination of the oral cavity. A set of care procedures will help protect the denture base from tartar buildup and preserve the properties of the material - for a tight fit of the structure to the gums.
Remember what foods should not be eaten with artificial teeth - these are hard and stretchy foods. It is their fault that breakages occur and the tightness of the seal to the gums and supporting teeth is disrupted.
Preparation and full diagnostics before prosthetics
It is impossible to make comfortable dentures without a responsible approach to diagnostics before prosthetics and to the preparation of the oral cavity. In order for dentures - acrylic, nylon, clasp and others - to be comfortable, you need to undergo several studies. All of them will be useful for identifying contraindications, as well as for accurately modeling the prosthetic structure.
The first thing in diagnosis is an x-ray, panoramic image (OPTG) or CT (computed tomography) of the jaw. The second is taking impressions or impressions of the teeth. By the way, today you can make not ordinary impressions, but digital ones - using an intraoral scanner. The third is functional diagnostics, where bite parameters are assessed in dynamics, i.e. how the patient chews. This is one of the most important factors for making a prosthetic product comfortable. Otherwise, it can only be worn for beauty. Such diagnostics consists of assessing the work of the masticatory muscles, the movements of the jaw joints, and the closure of the jaws during movement.
Read on the topic: digital diagnostics before prosthetics - how modern devices help make comfortable dentures.
As part of the preparation, it is necessary to cure all identified dental diseases - eliminate caries, pulpitis, properly fill and strengthen the root canals. So that later the supports under the prosthesis do not fail, and it does not wobble, it fits tightly.
Complex on 4 OSSTEM implants with delayed loading - from RUB 170,000.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Guarantee for the doctor’s work - unlimited Call now or order a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Which removable dentures are better for the lower jaw?
Not all orthopedic solutions are equally effective for installation on both jaws, because each of them has its own distinctive features. The individual characteristics of the lower jaw largely determine the choice of a specific design model, since other dentures can cause discomfort or be poorly fixed in the oral cavity. Let us consider the features of choosing dentures for the restoration of the lower dentition.