From this article you will learn:
- why does flux (abscess) occur?
- abscess on the gum: treatment, antibiotics,
- opening of a gum abscess: video.
Flux on the gum is a swelling of the gums associated with the development of purulent inflammation. Dentists do not use the term gumboil or abscess (only patients say so), but use terms such as “gingival abscess” or “periostitis”.
Flux on the gum: photo
What is tooth flux?
Flux, or, in dentist's language, periostitis, is a very unpleasant pathology, which is characterized by inflammation of the periosteum and soft tissues. The causes of flux on the gums can be different: trauma, gum disease, poor-quality dental treatment - all this can lead to a complication in the form of periostitis. The localization of the disease does not depend on the area of the jaw: flux of the upper and lower teeth occurs equally often.
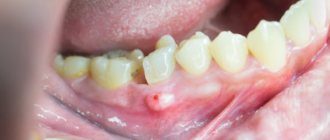
Flux under a tooth (or above a tooth, if we are talking about the upper jaw) visually resembles an inflamed sac. However, this is far from the only possible manifestation of periostitis. There is also a serous form, when the periosteum becomes inflamed as a result of trauma and damage, as well as one of the most unpleasant types - diffuse, when the infection is localized in different parts of the jaw, which requires extensive surgical intervention with the participation of a maxillofacial surgeon.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of flux is carried out by a general examination of the diseased tooth. Since this disease does not have a similar picture to other dental diseases, the dentist has no doubt that the patient has gumboil. Of course, additional research is being conducted to establish a holistic picture of the disease itself:
- X-ray of a diseased tooth to see the depth and size of the abscess.
- A blood test to identify the pathogen and stage of the disease.
go to top
Symptoms of gumboil
Flux on the gums in adults occurs much more often than in children (approximately 80-90 percent of all cases). A characteristic feature of the pathology is that it does not go unnoticed. This is one of the most unpleasant diseases, causing severe discomfort. The most striking symptoms are the classic purulent flux.
Symptoms
- Severe throbbing pain.
- Inflammation and swelling of soft tissues. At the advanced stage, the side of the face on which the flux is diagnosed swells.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Discomfort and pain when eating and talking.
- Flux of the lower tooth (in the molar area) can lead to numbness of the lip and part of the chin.
- Weakness, headache, fever.
How it proceeds
The disease progresses through several successive stages:
- Acute serous. Spreads quickly. In just two or three days, a large, painful “bump” forms, with pus inside. The cheek tissues swell.
- Acute purulent. The pain becomes more pronounced, the person feels an unpleasant pulsation. The mucous membrane in the area of the affected unit turns red and swells. Body temperature rises.
- Acute diffuse. The swelling becomes voluminous. It can go under the eye or onto the nose. The patient's appearance changes significantly for the worse.
- Chronic. The painful process fades away and is replaced by a chronic one. The patient may mistakenly think that the problem has disappeared without a trace. In fact, it only calmed down for a while. Periodically, the disease will recur.
The sooner a sick person consults a doctor, the higher his chances of a speedy recovery.
How many days does tooth flux last?
Waiting for the flux to disappear on its own is, to say the least, naive. Some patients believe that if the flux bursts and pus comes out of the wound, then further treatment may not be carried out at all. This is a big mistake, since complete removal of pus requires special drainage, as well as complex therapy and subsequent treatment in the dentist’s chair. With timely and correct treatment, the flux disappears on average in 12-14 days; rehabilitation after severe periostitis can take more than a month.
Preventive actions
To reduce the likelihood of periostitis, you need to take care of your teeth and visit the dentist at least once a year. You can't start caries. As soon as a dark spot appears on the surface of the dental crown, it needs to be treated.
After eating, it is advisable to rinse your mouth with warm water. To make hygiene as high as possible, it makes sense to use not only a brush and toothpaste, but also dental floss and irrigators. It is very important to remove tartar every year at the dentist's office.
An important place in the issue of prevention is given to diet. You should eat as much fresh fruits, vegetables, and plant foods as possible. They require more thorough chewing and thus have a positive effect on the ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth. They also provide natural cleansing of crowns from soft plaque.
If you have any questions about how to remove flux, please contact the doctors at the Line of Smile dental clinic for help. We specialize in the treatment of this disease and know how to quickly rid our patients of it.
Treatment methods
The attending physician should tell you after the examination how to treat gumboil and what measures need to be taken to achieve a successful result. The mechanism is approximately the same, but each clinical case has its own nuances. Today, several techniques are used aimed at eliminating the disease and its manifestations. As a rule, they come together.
Antibiotics for gumboils
Antibiotic treatment is an important stage of rehabilitation. The most effective antibiotics for fighting inflammation and infection are Metronidazole, Lincomycin, Amoxiclav and their analogues. Any tablets and antibiotics for tooth flux should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor!
Physiotherapy
Used as an additional measure to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery. Recommended procedures include electrophoresis, laser and ultrasound therapy.
Therapeutic treatment
It is carried out if it is decided to save the tooth. This includes endodontic treatment and filling of root canals, as well as resection of the root apex if necessary. If the cause of the flux is periodontitis, then a series of manipulations are carried out to eliminate the accumulation of bacteria in the periodontal pockets.
Surgical procedures
This includes tooth extraction and periostotomy - the main procedure for treating flux. The doctor makes an incision into the purulent sac, and then installs a drain through which the purulent exudate comes out.
Local therapy and rinsing for tooth flux
For better release of pus, pain relief and reduction of swelling, gels and ointments are used topically: Metrogyl Denta, Levomekol, Cholisal. Many people are interested in how to rinse gumboil on the gums. Miramistin and soda solution are usually used for rinsing. As an alternative, you can use folk remedies: decoctions and tinctures of propolis, chamomile, sage or calendula. A tooth after gumboil is still very vulnerable: to minimize the risk of re-infection, these treatment and preventive procedures are very important.
Gels and ointments
Ointments are used for topical application. In particular, this is Vishnevsky’s ointment, which stops the development of the purulent process. The birch tar included in its composition increases blood circulation in tissues and accelerates their natural regeneration.
Among modern gels, it is recommended to use the drug Metrogyl Denta, which contains antibacterial components in the form of Chlorhexidine and Metronidazole.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details! Ask your doctor about contraindications and side effects.
Is a tooth removed during gumboil?
A tooth can be removed due to flux, but in modern dentistry the emphasis is on tooth-preserving manipulations. This also applies to flux. A tooth must be removed when its crown is seriously damaged and cannot be restored with a pin or inlays. If an infection occurs under the crown, then re-prosthetics are often difficult. In some cases, a tooth has to be removed because it is impossible to unfill the canals after a previous unsuccessful treatment, but this happens extremely rarely. In any case, the doctor makes the decision to remove a tooth based on the clinical picture.
Signs
You can understand that periostitis has developed by the following symptoms:
- tooth pain;
- swelling of the gums;
- an abscess at the base of the diseased unit;
- increased pain when pressing on the affected area;
- swelling of the cheek;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the lymph nodes.
If these symptoms occur, you should make an appointment with the dentist as soon as possible. In the early stages, the problem can be eliminated quite easily and quickly. Delay is fraught with health-threatening complications.
Why is tooth flux dangerous?
An inflammatory process of this type tends to develop and, as it spreads, affects deeper layers of tissue. If left untreated, flux often develops into phlegmon - a serious purulent inflammation that has no definite boundaries. The most severe forms of flux provoke the development of sepsis, which can lead to infection of the entire body and even death. It is important not only to know how to cure gumboil and visit the dentist on time, but also to follow a number of preventive measures so that the likelihood of complications developing is minimal.
- Regular and high-quality hygiene.
- Treatment of caries at the initial stage. Flux, dental cysts and other complications often arise due to untreated pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Preventative visits to the clinic to assess the condition of the oral cavity and carry out professional cleaning.
Causes
Inflammatory (infectious-inflammatory) diseases of the maxillofacial area are caused by microbial microorganisms, which are usually part of the normal microflora of the oral cavity. Microbial pathogens are staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, diplococci, gram-positive and gram-negative bacilli (intestinal, protea, etc.). In addition, during flux, fungi, mycoplasmas, treponema, and protozoa from the Trichomonas family are found in foci of odontogenic infection. According to various authors who analyzed the microbial flora in foci of odontogenic infection (flux), the microflora is represented by a monoculture of staphylococcus (aurus and epidermal) or streptococcus of groups D, F and G. Associations of the above microorganisms are often identified.
The question arises of how non-pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms trigger the initiation of an infectious-inflammatory process (flux). For the occurrence of a disease, the presence of only non-pathogenic or pathogenic microorganisms is not enough. The answer to this question is given by the so-called Arthus-Sakharov phenomenon. According to the infectious-allergic theory, its essence boils down to the following: under the influence of a foreign serum protein, which has antigenic properties, antibodies are produced, which leads to sensitization of the body. Sensitization of the body is the acquisition by the body of increased sensitivity to foreign substances (proteins) - allergens. Against this background, repeated introduction of the protein into the vascular bed causes the formation of antigen + antibody complexes, which are fixed on the membranes of blood vessels and turn into target cells. Then the cell membrane is damaged, enzymes are released, mediators (from the Latin mediator - mediator) of inflammation are released. This is accompanied by activation of the third platelet factor and can cause intravascular coagulation, which leads to impaired microcirculation and necrosis (death) of tissue. This immunopathological reaction is also involved in odontogenic infection, leading to the occurrence of gumboil. The waste products of microbes participate in the role of antigen. This explains why in many patients non-pathogenic microorganisms are found at the site of inflammation.
The dynamic balance between the focus of chronic odontogenic infection and the body is ensured by the connective tissue capsule surrounding the focus. It limits the penetration of microbes into the tissues and vascular bed adjacent to the lesion, and limits the effect of immune factors on the infectious focus. The balance is also maintained by the fact that part of the waste products of microorganisms and tissue decay through the root canal of the tooth, fistula or periodontal fissure is released from the infectious focus into the oral cavity.
An imbalance can be caused by a disruption in the outflow of exudate from the lesion through the root canal due to food masses entering the carious cavity or when filling a carious cavity by a dentist. In the infectious focus, the concentration of microbes, their toxins, and waste products, which penetrate through the connective tissue capsule into the surrounding tissues, increases. Here their direct damaging effect on tissue can occur, and upon penetration into the vascular bed, the mechanism of the Arthus-Sakharov phenomenon is triggered. Clinically, this is manifested by an exacerbation of a chronic focus of odontogenic infection and the occurrence of gumboil.
Another mechanism of imbalance between the focus of chronic infection and the human body is associated with damage to the connective tissue capsule itself. This can happen when a tooth is removed, when there is increased load on the tooth while chewing hard food, etc. Damage to the capsule leads to the spread of microorganisms (their toxins, waste products) beyond the infectious focus, which in a sensitized organism leads to the occurrence of the Arthus-Sakharov phenomenon. These are the reasons and the main mechanism of exacerbation of odontogenic infection, leading to the development of gumboil.
When does swelling of the cheek go away?
How long the swelling lasts after tooth treatment depends on the degree of damage. Swelling causes injury to tissues, ligaments, and blood vessels during surgery or root removal. After such an intervention, swelling is normal. It can last from 2 hours and last for 7 days or the first day after surgery. There are no painful sensations.
Swelling after surgery on a wisdom tooth can last 4 days longer and persists for 11 days. If the surgery was serious, a bruise may form on the cheek. Pronounced swelling, increasing every day, pain is a reason to urgently consult a dentist.
Danger of overdose
Some patients believe that by using higher doses of medication they will be able to recover faster. This is wrong. In the case of any medications, it is important to adhere to the dosage and regularity of use.
If you deliberately increase the number of tablets consumed per day, an overdose will develop. This is an insidious condition that is harmful to health. In the case of incorrect antibiotic therapy, it manifests itself:
- vomiting, nausea;
- dizziness;
- loss of strength;
- discomfort in the abdomen, exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases (if any);
- allergic rashes.
If an overdose occurs, you should immediately interrupt treatment and consult a doctor.
Rinse
They are used as an additional treatment in order to completely remove pus and ichor from an opened abscess and prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas. Soda-salt baths and rinsing with antiseptic solutions help make treatment more effective and speed up gum healing. When rinsing, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
Anti-inflammatory pills
Anti-inflammatory drugs for flux have a strong analgesic effect, relieve swelling and reduce inflammation. Some of the medications used can relieve high fever, which sometimes accompanies the symptoms of periostitis.
Nimesil
Flux tablets with a pronounced analgesic effect actively eliminate inflammation at all stages of the disease. The daily dose of the drug is 200 mg (1 tablet of 100 mg twice a day). The duration of treatment depends on the clinical picture of periostitis and the need for treatment of toothache.
Diazolin
A drug for flux from the group of antiallergic drugs. It has a strong anti-edematous effect, reduces the production of biologically active inflammatory substances at the site of abscess development. Diazolin is taken depending on the severity of swelling of the gum and cheek tissues, 1 tablet (100 mg) 1-3 times a day until the condition improves.
Diclofenac
An anti-inflammatory drug that has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect, significantly reduces toothache. To eliminate pain, use 25-50 mg 1-2 times a day.