Publication date: 01/11/2021
Tooth extraction is not a pleasant process. Painful sensations and swelling of the gums after extraction of a tooth are an adequate response of the body to the operation. Usually, unpleasant symptoms increase 3-4 hours after the effect of the anesthetic drug wears off. Normally, pain, swelling, redness of the mucous membrane after a conventional extraction are observed for another 2-3 days; after a complex extraction, symptoms persist for 3-5 days. If your gums hurt after tooth extraction after 7 days or longer, you need a medical examination.
Why does my gum hurt?
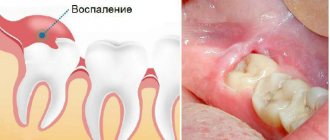
Unexpressed aching pain and slight swelling of the gums appear due to injuries to soft tissues, nerves, and jaw bone when removing a tooth from its bed. The gum tissue swells, the nerve endings are compressed, hence the pain. How much your gums hurt after tooth extraction depends on:
- Patient's pain sensitivity;
- degree of complexity of the intervention;
- features of the clinical case;
- location of the dental unit (after extraction of molars, the injury is greater, the pain lasts longer);
- state of immunity.
The body’s normal response from the development of complications is distinguished by the following properties: the pain does not intensify, pathological symptoms are present for no more than 7 days, and no other signs of deterioration in well-being are observed.
What to do after the procedure
General recommendations:
- when you arrive home, you just need to lie down and relax;
- you cannot eat or drink for 3 hours;
- for 3 days after surgery, you should not open your mouth too wide, or eat hard or hot foods;
- limit emotional and physical stress;
- hot baths, visiting the sauna, and exercising in the gym are prohibited;
- It is advisable to completely stop smoking and drinking alcohol for a week.
Remember: under no circumstances should you apply hot compresses or burn the wound with alcohol, iodine or brilliant green. It will only get worse!
A dental surgeon can prescribe applications of wound healing and antimicrobial ointments (Cholisal, Solcoseryl, Stomatofit, etc.). To strengthen general immunity, you can take immunomodulating agents and multivitamin complexes.
How long does your gum hurt after tooth extraction?
Normally, after 1-3 days, tissue swelling gradually decreases, pain goes away, and health improves. Already on the 3-4th day, the blood clot is gradually replaced by granulate, and after a week it fills the entire hole. After tooth extraction in the upper jaw, the recovery time is identical to the lower jaw, but bone regeneration in the upper dentition occurs more slowly.
In some clinical cases, the surgeon may cut the gum and drill out the jaw bone. Typically, such manipulations accompany the extraction of the outer eighth molars (wisdom teeth). Then healing takes longer than after a simple operation.
If 5-7 days after the intervention the pain does not decrease, but rather becomes more intense, you should consult a doctor. Acute, nagging, constant pain after tooth extraction can be a symptom of complications.
The tooth socket heals in approximately 2-4 weeks. Recovery time depends on the parameters of the wound and the body’s reaction to the removal procedure. Bone volume is restored approximately 6 months after the intervention.
Basic recommendations after gum incision
Implantation, tooth extraction, or opening of purulent foci is not possible without an incision in the gums. This stressful situation for the oral cavity causes considerable discomfort for a person.
Recommendations after gum incision:
- On the first day, you need maximum peace and rest;
- For 3 hours, all drinks and food should be excluded;
- In the first 3 days, hard and hot foods should be excluded, as well as excessive facial expressions;
- Any physical activity, especially those leading to blood flow to the head, should be avoided;
- Also, exclude hot relaxing baths, saunas and steam baths;
- For 7 days you need to strictly limit your intake of tobacco and alcoholic beverages;
- It is strictly forbidden to apply hot compresses to the wound or cauterize it with alcohol-containing solutions.
What to do if complications arise after gum surgery:
- Edema. Always occurs during implantation or after removal of a wisdom tooth. Small to medium edema is a normal reaction of the body. If the swelling is severe, then you need to consult your doctor to rule out the onset of alveolitis.
- Temperature. The temperature that rises a few hours after the gum incision can reach 37.5 °C, which is considered normal. However, if it goes beyond 38 °C, it may indicate the onset of the inflammatory process. In this case, you should consult a doctor to prescribe a course of antibiotics.
- Bleeding. After surgery, a blood clot usually forms to prevent bacteria from entering the socket. Bleeding occurs as a result of vascular damage or capillary fragility. To stop the bleeding, apply a thick sterile bandage to the problem area. If the bleeding does not stop, you should call a doctor.
- Pain. Natural response to surgery. The pain can be moderate or very severe. In any case, to reduce it you need to take a painkiller pill.
Dental clinic Stomatolog 11 in Moscow offers a wide range of services in orthodontics, therapeutic dentistry, and implantation. It is also popular to make an appointment with a pediatrician and for teeth whitening.
Treatment using innovative dental devices and careful attitude towards each client allows us to minimize the risks of any complications after dental interventions. You can see the work performed by a team of true professionals in the photos posted on our website and in social groups.
Choose high-quality and safe dental services in our clinic. Ensure your dental health.
Free consultation
What happens if you ignore pathological pain
The appearance of pain always signals a problem in the body. If the tooth was removed long ago, and the pain persists or increases, this is evidence of a complication. Pain may be associated with:
- Increased body temperature;
- severe swelling, redness of the mucous membrane;
- halitosis;
- purulent discharge from the socket;
- white or gray coating on the mucous membrane;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- pain while swallowing;
- restriction when opening the mouth.
In this situation, you should see a doctor immediately.
Ignoring alarming symptoms is fraught with serious problems, such as abscess and osteomyelitis. These are serious pathologies that require timely, qualified treatment.
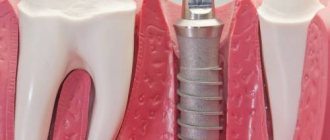
What to consider when deciding on a transplant?
A person deciding whether to undergo gum transplant surgery should consider the following:
- Alternative Treatments : This may include tooth extraction if gum recession is already severe.
- Cost of surgery : If a person is considering surgery for cosmetic reasons only, they will likely have to cover the cost of the surgery out of pocket.
- Risks associated with untreated : Untreated gum recession can lead to severe gum disease and possible tooth loss. Gum disease can also cause additional problems such as heart disease and diabetes.
By maintaining good oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly for regular checkups, you can reduce your risk of developing gum disease and catch it early if it begins to develop.
How to get rid of pain at home
To eliminate postoperative pain, the dentist will prescribe analgesics and cold compresses on the side of the intervention. Additionally, you can use traditional methods - mouth baths made from tinctures or herbal decoctions. Baths with an antiseptic drug are also allowed (the solution must be held in the mouth for a while and spat out). What is strictly forbidden:
- warm the operated area;
- rinse your mouth intensively (you can wash out the blood clot);
- chew on the injured side;
- “check” the hole using your tongue, fingers, and apply medicine to it.
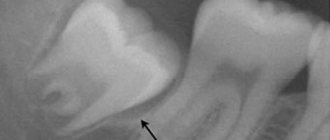
The risk of complications depends on the complexity of the operation to remove a dental unit. Simple extraction is carried out if the tooth does not have strong, intertwined roots, it is intact, and there are no associated problems (cysts, pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.).
Extraction of dystopic teeth, which are very crooked, have intertwined, crooked roots, with a destroyed coronal part, and with an inflammatory process, is considered difficult. In such cases, a more extensive operation may be necessary with a preliminary incision in the gum, sawing the tooth into elements, extracting fragments through a hole in the jaw bone, and applying sutures. Molars are usually difficult to remove. If your gums hurt for several days after the removal of a molar, but the painful symptoms are smoothed out, then the wound is healing normally.
How gums heal
After surgery, connections between tissues and cells are disrupted. The healing process is the formation of new physiological and anatomical connections between them.
Healing includes:
- Formation of a blood clot - forms within 5-10 minutes after surgery and serves as a protective barrier against infection and harmful microbes.
- Formation of granulation tissue - within 3-4 hours the production of granulation tissue (young connective tissue) begins.
- Epithelization and collagen formation lasts up to 7–10 days and is sometimes accompanied by slight itching.
- Regeneration and maturation - the wound “heals” after 2–3 weeks, but complete healing of the fibers requires several months.
Gum healing
Pain during difficult removal
The duration of pain after complex extraction (wisdom teeth, impacted or dystopic incisors) is associated with damage to a larger tissue area. Often such an operation involves making an incision in the gum, sawing out the roots, extracting tooth fragments, and draining an abscess, which increases the scope of the surgical intervention. If your ear hurts after wisdom tooth removal, this may indicate nerve damage.
In some cases, patients complain of persistent discomfort and pain for up to a week. Clinical manifestations such as swelling, swelling of the gums, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, fever, and malaise are also common.
Gum healing time
Conventionally, dentists divide the regeneration process into two stages - partial, complete. Partial epithelization is said to occur in the first 12 days after tearing out, and complete epithelialization occurs after 20-25 days. But with complex removal, leading to significant damage to bone tissue and muscles, the recovery period may increase by several more days.
Among the most common reasons causing slow epithelization:
- significant trauma to bone tissue and gums during the intervention (especially if the bone around the diseased tooth was cut out with a drill);
- the occurrence of alveolitis of the inflamed socket;
- damage to the protective clot or its unformation (“dry” hole);
- incomplete removal of bone fragments due to the doctor’s carelessness;
- mobility of the mucous membranes, which needed to be sutured, but for some reason the surgeon decided not to suture;
- refusal to use antibiotics during a severe recovery period;
- diabetes;
- reduced immunity.
When to see a dentist
A visit to the doctor should not be delayed in the following cases:
- Initially or after a couple of days, a blood clot falls out;
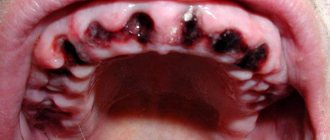
- A purulent lump appears in the area of the hole;
- The pain does not go away for a long time and inflammation appears;
- The entire jaw begins to ache, radiating to the temple and eye areas;
- There is a constant iron taste of blood in the mouth;
- Pain appears in the area of the adjacent tooth;
- Within 5 days the gums are not covered with white plaque.
If you are worried about your teeth, you will be helped at the Doctor-RAF Dental Clinic (Almaty, Muratbayev St., 101). Our highly qualified specialists will help you solve all your dental problems.
During the operation, a neighboring organ may be damaged. This will manifest itself as symptoms of pain, and perhaps the tooth will begin to loosen.
Complex removal will require additional care and the use of bactericidal drugs, but only those prescribed by the dentist. Self-prescribing antibiotics is prohibited. An exception would be local gels and ointments, which are available without a prescription and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
8 reasons why the hole does not heal after tooth extraction, ways to speed it up.
After tooth extraction, it seems that the worst is over. However, this is a surgical operation that does not exclude the possibility of complications, especially if you do not follow the doctor’s recommendations. What to do when the hole does not heal?
Causes of pain
The occurrence of pain after tooth extraction is associated with damage to nerve endings, vascular structures and soft tissues. The peak intensity of pain occurs in the first hours after the cessation of anesthesia. The symptom persists for about 12 hours.
In case of incisions in the gums or damage to the bone tissue, as well as after implantation after removal, toothache may persist for 2-3 days. Pain syndrome also occurs in the case of displacement of the dentition towards the formed void. Therefore, doctors recommend prosthetics as soon as possible after extraction.