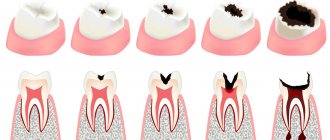
Hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues - their increased sensitivity to common physical and chemical irritants - has a fairly clear definition and designation in ICD-10© [1]. However, in the practice of a dentist, pain sensitivity is considered more broadly, as it is a symptom of a number of dental diseases [2]. The generalized form of hyperesthesia is usually associated with general causes (concomitant diseases), covers most teeth and can manifest itself without clinically visible pathological changes in them [4], the localized (non-systemic, limited) form of hyperesthesia is caused by local factors and defects in the hard tissues of teeth and manifests itself in areas of individual teeth [3]. Non-carious lesions of teeth that occur after eruption are almost always combined with hyperesthesia [2-4]. Thus, increased sensitivity of hard dental tissues with wedge-shaped defects occurs in 82-90% of cases and manifests itself most aggressively in young and middle-aged people [5]. Hyperesthesia with increased abrasion is detected in 80-90% of cases, with enamel erosion - in 80-85.6% of patients [4, 6].
The purpose of the study is to determine the features of the clinical course of increased sensitivity of hard dental tissues.
Hyperesthesia - what is it?
Name " hyperesthesia"
" comes from two Greek words meaning "increase" and "feeling". The pathology got its name from a characteristic feature - painful sensitivity of teeth to temperature, chemical, tactile (physical) influences. Hyperesthesia should not be confused with pain that occurs with carious tooth decay. Hyperesthesia often occurs with non-carious lesions of hard dental tissues and chronic periodontitis.
Manifestations of hypersensitivity in different dental pathologies are not the same. Thus, enamel erosion causes quite severe, albeit short-term pain, and with a wedge-shaped defect, the discomfort is mild, however, sometimes unpleasant sensations appear even with the slightest exposure of the neck of the tooth.
Possible complications
Dental hyperesthesia can cause a deterioration in a person’s psycho-emotional state. It is fraught with the appearance or worsening of neuropsychic diseases and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Pain often interferes with proper nutrition and forces you to give up your usual meals.
One of the most obvious complications of hypersensitivity is pulpitis - inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. Constant irritation of nerve fibers can lead to disruption of the body's compensatory capabilities. Typically, it takes six months to a year for pulpitis to develop. This is a rare complication, but its occurrence requires more complex intervention - pulp removal, endodontic treatment.
Sometimes hyperesthesia can be a harbinger or the only symptom of the development of certain dental diseases. Thus, the development of a wedge-shaped defect can begin with an increase in sensitivity. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor with this problem to find out the exact causes and prevent the development of complications.
Causes of hyperesthesia
A generally accepted classification of pathology has been developed, based on which the dentist makes a conclusion about the causes of increased tooth sensitivity. The classification systematizes predisposing factors. By comparing them with a specific case and making instrumental diagnostics, the doctor makes a conclusion about the origin of the pathology and classifies it as one of the varieties.
By localization:
- limited
- it affects one or more teeth. Usually these are ground teeth, teeth with a wedge-shaped defect; - generalized
- affects most of the dentition, sometimes the entire row. Progressive erosion of the enamel, exposure of the neck of the tooth during periodontitis, and increased tooth abrasion lead to generalized erosion.
By origin:
- caused by loss of hard dental tissues
. Its appearance is provoked by carious cavities, enamel erosion, increased abrasion, orthopedic preparation (grinding) for prosthetics; - not associated with the loss of hard dental tissues
. It occurs if the neck or root of the tooth is exposed, which can be caused by periodontal diseases, general diseases - endocrine pathologies, neuroses, gastrointestinal pathologies and others. Visually, in such cases, the enamel appears intact.
Medical errors can also be the cause. Hypersensitivity occurs if, during the finishing treatment of the filling, healthy tissue was sanded, the filling technique was violated, the enamel was over-etched, or ultrasonic teeth cleaning or whitening was performed incorrectly.
A lot of calls to clinics occur precisely because of incorrect bleaching. Hyperesthesia can occur after the procedure when it is performed without taking into account contraindications and the characteristics of the patient’s teeth.
The high incidence in women is due to hormonal and metabolic disorders, especially a decrease in estradiol. They show decreased levels of magnesium and calcium, and bone tissue shows lower density. Therefore, women undergoing dental treatment should undergo additional studies as prescribed by a dentist-therapist.
Prevention: what methods are effective
To protect yourself from such a problem as hypersensitivity of tooth enamel, it is necessary to periodically perform preventive procedures:
- Be careful about your diet.
- Use only optimally suitable care products.
- For teeth whitening, contact a trusted dentist.
- Visit your dentist at least twice a year and don't forget about professional cleaning.
An excellent prevention of dental hyperesthesia is regular dental examinations. Despite the fact that hyperesthesia is a serious pathological process, it can be eliminated. To eliminate the pathology, you need to contact a professional and competent doctor.
Clinical picture of hyperesthesia and degree of hypersensitivity
Hyperesthesia can manifest itself in different ways. A typical sensation is intense, albeit short-term pain (about 30 seconds), a “shooting” in the jaw due to hot or cold (more often), very salty, sweet, sour foods and drinks. Sometimes severe pain occurs when inhaling cold air.
With hyperesthesia, this reaction occurs constantly, the relief is short-term and insignificant. The patient often cannot identify the tooth that is causing pain. An external examination does not reveal any difference between the teeth in the row, there is no pathological pigmentation, the enamel appears hard and smooth.
Degrees of the pathological process:
- Discomfort is caused by heat or cold exposure, the threshold values of dentin excitability are 5-8 μA.
- Discomfort is caused by heat, cold, salty, sour, sweet; the threshold values of dentin excitability are 3-5 μA.
- Pain is provoked by all irritants, including simple touch; the threshold values of dentin excitability are 1.5-3 µA.
Hypersensitivity significantly complicates oral care; even ordinary cleaning becomes a challenge, and if the process is developed and neglected, it becomes impossible. The enamel and interdental spaces gradually accumulate deposits, which can lead to caries, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
In order not to provoke the development of serious complications, the consequences of hyperesthesia, you need to contact a specialist already at the first stage of the process, with mild sensitivity.
Symptoms
The first and most common symptom is the appearance of short-term pain attacks in the teeth. More often, people complain of pain after eating cold and hot foods. Pain may occur during the process or field of brushing your teeth. In the initial stages, the pain is short-term, but over time it can intensify. Often patients experience remission, at which time the irritants stop causing pain. When a period of remission begins, patients stop thinking about the problem and do not take appropriate measures. And without proper treatment, eliminating the pathology is impossible and hyperesthesia can return with renewed vigor. To eliminate dental hyperesthesia, it is necessary to establish the causes of its development.
Diagnostics
Hyperesthesia is differentiated from other conditions that have similar symptoms:
- with inflammation of the pulp;
- with caries;
- with a cracked tooth or restoration;
- with a violation of the sealing layer.
A characteristic symptom of hypersensitivity is quickly subsiding, acute pain. To determine it, the doctor checks the condition of the nerve bundle using x-rays or electrodontometry. If the preliminary diagnosis is hypersensitivity, the dentist conducts tests to determine the degree of reaction of dental tissues to temperature, chemical, and tactile stimuli. When the degree is determined, the doctor draws up an individual treatment and prevention plan.
Why does tooth sensitivity occur (mechanisms)?
The mechanisms of short-term pain reactions with severe tooth sensitivity have not been sufficiently studied. Dentin tissues themselves are good insulators and cannot provide rapid heat conduction and quickly respond to other influences. Enamel tissues do not contain nerve endings (therefore the term enamel hyperesthesia is not correct) and cannot respond to stimuli. Therefore, it is now generally accepted that the mechanism of transmission of irritation involves dentinal tubules (tubules), which contain nerve endings penetrating from the dental pulp. Dentin tissue is penetrated by such tubes; on average, 1 sq. mm of dentin surface contains up to 20 thousand tubes, normally covered with an amorphous layer. However, if some of the tubes are open, this may provide access or influence of irritating factors.
The specific mechanisms of transmission of irritating factors that cause dental hypersensitivity are also not completely clear. The most popular is the hydrodynamic theory, according to which short-term acute pain appears due to a short-term change in the speed of movement of the fluid filling the tubules, leading to increased irritation of the nerve endings.
Therapy for hyperesthesia
Hyperesthesia is treated comprehensively, in collaboration between the doctor and the patient, because it involves clinical manipulations, specific procedures and self-care.
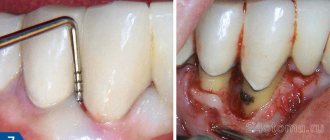
First of all, the cause of hypersensitivity is eliminated - periodontitis, periodontal disease are treated, low-quality orthopedic structures and fillings are replaced, and cervical defects are eliminated. If there are indications, microplastic correction of the gums is performed, during which it is raised to a normal level and the exposed roots are covered.
Conservative therapy should normalize hydrodynamics in dentin microchannels. Remineralization will reduce the volume of microspaces and normalize phosphorus-calcium metabolism. The patient needs to undergo a course of treatment, during which every day 10 percent calcium gluconate is applied to the surface of the teeth and the enamel is coated with a fluoride-containing preparation.
In order for the life-saving ions to better penetrate the dental tissues, electrophoresis is used. Physiotherapy makes it possible to introduce certain ions and control their concentration. Electrophoresis is absolutely safe if it is carried out by a competent specialist, and the drugs injected into the tissue are non-toxic. Physiotherapy lasts about 2 weeks, but already at the beginning there is an improvement in well-being, and by the end of the course of treatment a stable remission occurs.
The duration of remission will depend on many factors - the characteristics of a person’s hard dental tissues and the quality of self-care for teeth. If conservative therapy with saline applications does not produce a pronounced effect, the enamel is covered with filling material, but this usually occurs in advanced or clinically complex cases.
Drugs used in the treatment of hyperesthesia
All drugs for the treatment of dental hypersensitivity can be divided into 2 groups:
- Drugs that seal the dentinal canals reduce the flow rate of the cerebrospinal fluid. This group is represented by varnishes, oxalates, desensitizers, remineralizing liquids and gels. The drugs are used to carry out remineralizing therapy and fluoride teeth.
- Drugs that block nerve fiber signals that stop the transmission of pain impulses. The group is represented by local products based on potassium nitrate. They are applied in the form of gels and applications.
The named drugs (according to individual indications) are also used immediately after brushing and whitening teeth. A long-acting desensitizing gel is applied to the tooth surface. If severe pain develops, the specialist prescribes universal mouth guards with gel. The condition improves significantly after the 1st procedure.
- 1. Fluoride therapy.
The action of these drugs is determined by the reaction of fluoride ions and calcium ions. When they combine, they form calcium fluoride, an insoluble salt that clogs the dentinal canal. Different brands of fluorides work differently. To obtain a lasting, pronounced effect, the doctor must use a modern, effective drug.
- 2. Therapy with fluoridated varnishes.
Fluorinated varnishes reduce hypersensitivity for a short time. After a few hours or days, the varnish will be erased from the surface of the tooth. To make the effect of the varnish more pronounced and lasting, the varnish is applied in multi-layers. The advantage of this technique is the blockage of micropores and instant relief of the condition.
- 3. Therapy with remineralizing pastes.
Remineralizing pastes help restore the mineral balance of hard dental tissues. There are several varieties of these drugs - for use in the dentist's office and at home. Which of them and for how long to use is determined by the doctor.
- 4. Desensitizer therapy.
The name of the group of drugs comes from the English word desensitizer, which means “reducing sensitivity.” Desensitizers contain substances whose task is to seal dentinal canals by coagulating proteins. The preparations are used to restore the surface of teeth, for restoration or universally.
- 5. Oxalate therapy.
Oxalate preparations, like fluorides, are used to form insoluble salts in dentin. When using oxalates, there is no need to etch the enamel or use a photopolymerization lamp; oxalates do not irritate the gums. As a result of oxalate therapy, salt crystals tightly clog the dentinal canals, which effectively reduces hypersensitivity.
Answers on questions
When does sensitivity go away after whitening?
With proper whitening, all discomfort goes away after 3-5 days.
How to choose a toothbrush and toothpaste so as not to harm the enamel?
It is not recommended to use a hard brush or whitening paste. The selection of home hygiene products should be individual for everyone. We recommend making an appointment with a dentist.
How to get rid of sensitivity at home?
No home remedy will help eliminate this disease. Do not self-medicate: this will cause complications! It is recommended to consult a dentist so that the doctor can provide quality treatment.
Prognosis for hyperesthesia and preventive measures
If treatment is started early, the prognosis is favorable. A complex of clinical procedures plus compliance with medical recommendations leads to the onset of stable remission without pain, discomfort, or the risk of complications.
To prevent the development - initial or repeated - of hyperesthesia, it is recommended:
- bring your diet back to normal, limit your intake of foods that destroy enamel. To do this, it is necessary to exclude or limit carbonated drinks and excessively sour dishes in the diet, and use a straw when drinking juices;
- enrich your diet with foods containing calcium and phosphorus - they will help the body maintain optimal mineral balance and bone strength;
- After each meal, it is always recommended to rinse your mouth with a special mouthwash or regular warm water;
- undergo preventive examinations of the oral cavity every six months so as not to trigger the development of carious and non-carious diseases. The latter are especially dangerous, since outwardly they are invisible, and the dentist will identify them in time and provide assistance;
- monitor the condition of the stomach and the entire gastrointestinal tract, since their system directly affects the condition of the teeth.
Stages of treatment
After examination and diagnosis, the dentist determines the cause of this disease. It is from this that the treatment plan for hyperesthesia of tooth enamel will be built.
- If the disease is caused by caries, then caries treatment is carried out.
- If sensitivity occurs due to incorrectly selected home hygiene products, then the doctor individually selects a brush and paste for the patient. The enamel is also treated with a special solution - remineralizing gel.
- When a patient experiences recessions, surgical operations are performed to eliminate them.
Treatment of enamel hyperesthesia is a comprehensive approach to the problem, including examination, diagnosis, elimination of the cause and symptoms.
Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor!
Don't wait for your condition to worsen!
Sign up