Main clinical requirements
Both temporary filling materials and all of the above are subject to the same clinical requirements:
- The materials should not have a toxic effect on the hard tissues of the tooth, pulp, or mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
- Filling substances must be generally harmless to the body.
- Materials must have an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- These substances directly prevent the penetration of both pathogenic microflora and toxins into the pulp.
- The materials have an anti-caries effect.
- They are characterized by low thermal conductivity, which prevents the dissolution of materials in saliva.
- Filling materials are chemically inert. In other words, they are resistant to such aggressive agents as alkalis and acids.
- Such substances are quite hard, mechanically strong, wear-resistant, and also have good aesthetic properties.
- The materials do not change the shade of the tooth and do not lose their original color over time.
- Filling substances do not cause the appearance of galvanic currents in the oral cavity.
- The materials do not change volume and shape during the process of hardening. At the same time, they set quickly and have high adhesion to tooth tissues.
- By their nature, these substances are radiopaque.
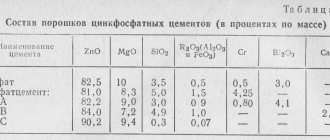
Composition and properties of PCC
The product consists of two components: powder and liquid.
The powder is converted zinc oxide with the addition of magnesium oxide. The liquid consists of a 37% water-based solution of polyacrylic acid.
Properties:
- ensuring a chemical relationship with tooth tissue;
- the formation of a strong bond with the metal, especially if it has been sandblasted;
- carboxylate has low toxicity to the pulp.
The finished working solution has the appearance of a paste-like consistency, with a smooth and shiny surface.
Carboxylate cements have their advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantages | Flaws |
| According to biological characteristics, they are highly compatible with dental tissues | Has the property of dissolving in the mouth over time |
| They do not allow acids to pass through, which are formed during the hardening of the filling. | |
| Are not an irritant to the pulp | Insufficient strength |
| Good adhesion to hard tooth surfaces |
Purposes of application
Temporary filling in dentistry is carried out for the following purposes:
- Bandages for the treatment of caries and a number of its complications.
- Control fillings for the diagnosis of pulpitis and caries.
- Insulating pads.
- Filling temporary teeth.
- Temporary fixation of orthopedic elements.
- Temporary filling of root canals for therapeutic purposes.
Accordingly, each task shows its own type of material. But universal compositions for temporary fillings are also popular in dentistry. We will get to know them all further.
About the procedure
The name of the procedure “filling” comes from the Latin plumbum - “lead”. This is the replacement of certain defects in dental tissues with artificial material. The goal is to restore the anatomical shape of the tooth and return it to functionality. Today, both permanent and temporary filling materials are used for this purpose.
You might be interested in: Do they take you into the army with braces? How to brush teeth with braces
The filling can replace not only hard dental tissues, but also protect the pulp and apical periodontium from the effects of a number of unfavorable external factors.
The success of medical interventions preceding filling in this case is assessed by the usefulness and duration of preservation of the applied filling. Today, a whole host of materials are used for the procedure, differing in structure, purpose and properties.