Bactericidal and modified cements
— Unitem (Vladmiva) is a universal, improved zinc-phosphate dental cement with high mechanical strength and chemical resistance. The powder consists of zinc oxide, with modifying additives, and the liquid consists of orthophosphoric acid of reduced activity.
— Unicem bactericidal (Vladmiva) is a universal improved zinc-phosphate dental cement containing the optimal amount of a bacteriostatically effective form of silver. Used in pediatric dentistry for filling temporary teeth.
— -Adhesor (Spofa Dental) – zinc-phosphate cement, Adhesorfine (Spofa Dental) – modified zinc-phosphate cement with a fine structure.
— Phosphate cement containing silver. To improve the bactericidal properties, silver (1.547%) is added to the powder composition. The material is recommended as an insulating gasket when filling molars with metal and other fillings, for filling canals, in pediatric dentistry for filling temporary teeth. Analogs: Bactericidal Unitem (Vladmiva).
— Visphat cement refers to zinc phosphate cements. Its powder contains about 3% bismuth oxide. It hardens faster, is stronger than phosphate cement, and is less soluble. It is used as an insulating lining when filling teeth with metal fillings, silicate cements, acrylic and epoxy resins.
— Dioxyvisfate Dioxidine is included in the composition of this cement. Dioxyvisfate powder is a mixture of visfate and dioxidine, the liquid is orthophosphoric acid, partially neutralized with zinc oxide and aluminum hydroxide. Cement has bactericidal properties, has high mechanical strength, is slightly soluble, and is intended for filling temporary teeth, as a therapeutic and insulating spacer, for fixing inlays, pin teeth, and bridges.
Homework to understand the topic of the lesson:
Control questions:
1. What is the chemical composition of zinc phosphate cement powder and liquid?
2. What is the chemical composition of polycarboxylate cement powder and liquid?
3. What is the purpose of zinc phosphate cements?
4. What is the purpose of polycarboxylate cements?
5. Name the materials from the group of zinc-phosphate cements of domestic and foreign production.
6. Name the materials from the group of polycarboxylate cements of domestic and foreign production.
Types of crowns
Popular materials include metal, plastic, metal ceramics, pure ceramics or glass ceramics, and zirconium dioxide.
The most affordable option is plastic. Most often it is used as a temporary option due to its low strength.
Another affordable and popular option is cermet. Ceramic is applied in layers onto a metal frame that perfectly follows the shape of the front tooth. The product is fired for special strength. This type of crown is reliable and quite aesthetic.
Among its disadvantages:
- possible allergy to metal;
- negative impact on the natural tooth and gums;
- slight external difference from natural teeth.
To avoid the last unpleasant moment, metal ceramics are placed along the entire smile line. Then the difference is not noticeable at all.
Metal crowns for the front teeth are very durable, but not aesthetically pleasing. Because of this defect, they are now almost never used.
An excellent option for front teeth is all-ceramic crowns. They are practically indistinguishable from real teeth and have maximum biological compatibility with them.
Plastic and ceramic types are used mainly for aesthetic purposes. Due to their high fragility, such crowns are installed only on the front teeth. They will not withstand the load on chewing ones.
Unitem white (50g+30ml), VladMiVa
Cement for fixing pins, crowns, bridges and inlays. Unitem has high mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
- Description
- Shipping and payment
- Reviews
Description
Unicem is a universal zinc phosphate cement formed by mixing zinc oxide powder and phosphoric acid solution.
Indications
- Fixation of crowns, bridges, pins, inlays.
- Filling teeth that are to be covered with a crown.
- Can be used as an insulating gasket when filling with silicate and silica-phosphate cements, as well as amalgams.
Characteristics
- Powder: 50 g.
- Bottle of liquid: 30 ml.
- Powder measuring cup: 1 pc.
- Dropper cap: 1 pc.
Compound
- Zinc oxide powder with modifying additives.
- Orthophosphoric acid of reduced activity.
Cement mixing process
Advantages
- High mechanical strength (90-120 MPa, depending on the ratio of powder and liquid).
- High adhesion to metal, plastic, porcelain, metal ceramics and other dental materials.
- Cement is resistant to the aggressive action of the moist environment of the oral cavity.
Instructions for use
- If the material has been stored or transported at low temperatures, it should be kept at room temperature for one hour before use.
- On a dry glass plate, gradually mix the powder and liquid in the required proportion.
- The mixing time should not exceed 1 minute.
- Apply cement to the previously treated and dried tooth surface.
- The hardening time of the cement is 2 hours; during this period it is recommended to cover the filling with varnish or hydrophobic gel to protect it from the action of saliva.
Fixation of prostheses
- 1 scoop of powder (0.25-0.30 g) + 4 drops of liquid (0.18-0.20 g).
- The dough remains plastic on glass for 2-2.5 minutes, and hardens in the oral cavity within 8 minutes.
Dental filling
- 1 scoop of powder (0.25-0.30 g) + 3 drops of liquid (0.13-0.15 g).
- The dough remains plastic on glass for 1-1.5 minutes, and hardens in the oral cavity within 6 minutes.
Storage
- Store in a dry place, protected from direct sunlight, in a tightly closed container.
- Storage temperature: from +5°C to +25°C.
- Avoid exposure to moisture.
- Shelf life: 5 years.
The Nika Dent company is the official distributor of VladMiV products. We supply dental materials and consumables throughout Russia.
Shipping and payment
PAYMENT METHODS
| Cash to the courier upon receipt of the goods. Possible: in Moscow, Moscow region, St. Petersburg, Leningrad region. |
| By bank transfer for legal entities by account. |
TRANSFERING THE ORDER TO THE DELIVERY SERVICE
For cash payments:
the next day after receiving the order, unless a different delivery date has been agreed upon.
For non-cash payments:
the next day after receiving the money to the bank account.
Please check with your manager about the possibility of same-day delivery.
DELIVERY METHODS
Delivery by our transport is carried out in Moscow, Moscow region, St. Petersburg and Leningrad region.
To all other regions, delivery is carried out by transport companies.
Pickup of goods from the warehouse and company office is not provided.
COST OF DELIVERY
| Within the Moscow Ring Road: when ordering over 3,000 rubles - free. Up to 3,000 rubles – we temporarily do not deliver. |
| IN ST. PETERSBURG : when ordering over 3,000 rubles - free. Up to 3,000 rubles – delivery cost 350 rubles. |
| IN THE MOSCOW REGION: up to 50 km from the Moscow Ring Road: for orders over 5,000 rubles - free. Up to 5000 rubles – we temporarily do not deliver. 50-100 km from the Moscow Ring Road: for orders over 30,000 rubles - free. Up to 30,000 rubles – we temporarily do not deliver. |
| IN THE LENINGRAD REGION: up to 20 km from the Ring Road: for orders over 5,000 rubles - free. In all other cases - individually |
| TO OTHER REGIONS The minimum order amount to the regions is 3,000 rubles. Delivery is carried out by a transport company. The cost of delivery to the Moscow base of the transport company is free. Payment for the services of the transport company is at the expense of the client. We work with any Transport companies convenient for you! |
Repeated delivery due to the buyer's fault will be paid in any case!
Reviews
There are no reviews for this product yet. Be the first to leave a review!
Sealers-Endogermetics in Dentistry
No high-quality endodontics is complete without a sealer. In simple words, a sealer is a material, in this case cement, paste, that fills the space between the wall of the root canal and gutta-percha. Sealers not only provide tight sealing of the root canal, but also prevent the development of infection inside the root canal and outside its apex, so it is very important to know and understand what, why and how to use a sealer. Indeed, for each clinical case it is necessary to choose a specific chemical and physical composition of the sealer. There are many types of sealers on the dental market; in this article I will try to introduce you to some of them.
Requirements for the sealer
The requirements for the sealer are quite logical and meet the requirements of quality patient treatment. First of all, the sealer must be biologically compatible and not have a pathological effect on periodontal tissue or the general health of the patient. In addition, a high-quality sealer should not change the color of the tooth some time after filling the root canal. The next requirement for the sealer is its resistance to moisture and gingival fluid; the sealer should not dissolve in them. For a doctor, the requirements for a sealer are as follows:
- Convenient working hours;
- The material must be plastic, tightly seal the teeth canals;
- Possess adhesion to tooth dentin;
- Do not shrink;
- Do not form pores;
- Be radiopaque;
- Teeth filled with sealer should be easily refilled if necessary;
In addition, the sealer must influence the microflora of the root canal and have either a static/cidal effect in relation to microbial agents.
Unfortunately, most sealers are not 100% insensitive to moisture or gingival fluid. As a result, the formation of microspaces, micropores, microleakages at the border of gutta-percha and the wall of the root canal. And any space is filled with pathogenic microbes, which causes the development of a pathological process.
The course of the hardening reaction
Ion formation , dissolution stage. The acid reacts with the upper glass particles, forming calcium, fluorine, aluminum and sodium cations;
Primary gelation , hardening - polyacid molecules quickly cross-link with each other and with aluminum and calcium ions. At this stage, the pH of the cement increases markedly, and the polyacid molecules turn into a gel;
Final hardening - strong ionic cross-links are formed, mainly from fluorine and aluminum polyalkenate. This stage lasts about a day. It also completely stops the formation of silica gel on glass particles.
Due to the fact that aluminum is a trivalent element, a very high degree of cross-linking is ensured, which ultimately makes the cement extremely strong.
When cement hardens completely, it is structurally composed of glass particles surrounded by silica gel. All particles are located in a matrix created from cross-linked polyacid molecules, along with insoluble phosphate and fluorine salts.
Basinetzin
Active ingredients
: bacitracin (in the form of bacitracin zinc* - 0.00416 g) - 250 IU, neomycin (in the form of neomycin sulfate * - 0.00746 g) - 5000 IU.
Excipient
: corn starch – 0.987 g.
* Quantitative content in grams depends on the initial activity of the active ingredients. The content of active ingredients in grams is indicated based on activity:
— 60 IU/mg bacitracin in terms of bacitracin zinc;
— 670 IU/mg neomycin calculated as neomycin sulfate.
Description
Fine powder of white or yellowish color.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
ATX code
: D06AX.
Pharmacodynamics
The drug is a combined antibacterial drug intended for external use.
Adhesor Fine, Carbofine (Fine, Carbofine): instructions
Adhesor Fine is a modified cement with a fixing action.
It is based on zinc phosphate with a fine-grained structure. Thanks to its fine grain, it can be laid in an ultra-thin layer (no more than 25 microns). The manufacturer is the company Spofa Dental. Adhesor Carbofine is a cushioning material that does not have a toxic effect on the dental pulp. It is a radiopaque material, excellent for isolating a preparation based on calcium hydroxide and permanent filling material.
The cement is packaged in two containers. Powder (80 g) is placed in one, liquid (55 g) in the other.
Adhesor Fine
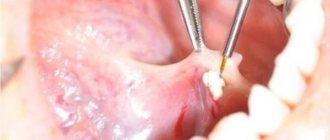
How is the operation performed?
Under local anesthesia, a resection of the apex of the tooth is performed; the doctor peels off a flap of gum from the jaw and removes the apex of the tooth root. The required shape is given as soon as a flat and smooth surface remains. Mandatory treatment with an antiseptic is also necessary, sometimes this must be done twice. Then, the air is dried and etched out, and treated with adsorbents. After the necessary preparation, the filling material is inserted and covered with a dry swab until polymerization occurs. Then the cavity is again treated with an antiseptic, and the excess filling material is removed. The gum flap is sewn into place.
The stitches are usually removed after an average of a week. It is recommended to remove the ichor throughout this time, and radiotherapy is sometimes prescribed for successful rehabilitation. During the postoperative period after surgery, you must maintain careful oral hygiene and follow all the doctor’s instructions. The recovery program for each patient is individual; it includes taking antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunostimulating and some other drugs. If all instructions are strictly followed, the possibility of any postoperative complications is reduced to a minimum.
vote
Article rating
ISO requirements
Requirements for dental cements are established by international standards ISO 9917-2-95 and 9917-91. The regulated parameters depend on the purpose of the cement. So compositions for filling dental canals should have:
- working time , max., min. – no more than 20;
- hardening time , hour – no more than 72;
- fluidity , min., mm – not less than 20;
- solubility ,% – no more than 3;
- film thickness , microns – no more than 50.
Restoration mixtures must meet the following requirements:
- compressive strength , MPa – not less than 130;
- erosion , mm per hour – no more than 0.05;
- hardening time , min – 2-6.
General requirements for dental cements include biocompatibility with the human body and tissues, uniform distribution of pigments, absence of foreign impurities, homogeneity of consistency and some others.