- Tooth extraction
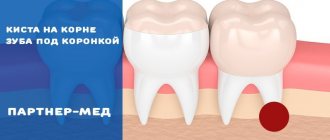
- Removal of a tooth cyst
- Bone tissue augmentation
- Resection of the apex of the tooth root
- Installation of a dental implant
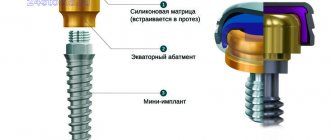
- Installation of a mini-implant
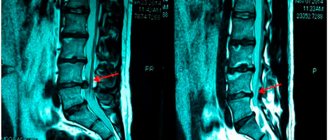
Patients have more chronic dental diseases than acute ones. Advanced caries, pulpitis, periodontitis lead to the fact that after a few months or years the patient is faced with a neoplasm on the root of the tooth or its acute inflammation. In this case, resection helps to save the tooth.
When should tooth resection not be performed?
- The main condition for successful root resection is the presence of sufficient jaw bone volume in the patient - at least 5 mm, otherwise there is a risk of jaw fracture.
- A tooth root resection operation will be ineffective if the patient has chronic periodontitis and/or periodontitis, as well as mobility of the diseased tooth.
Tooth root resection is contraindicated if:
- Large cysts or granulomas, when they reach the size of a third of the tooth root or more.
- A completely destroyed dental crown, if the tooth cannot be replaced with prosthetics.
- Close proximity of the roots of healthy teeth.
- Severe mobility of the diseased tooth.
- Some common diseases, such as diabetes, blood diseases, heart diseases, immunodeficiency conditions.
Types of bone grafting
The dentist-implantologist has several methods at his disposal to effectively restore bone volume, and their choice depends on the nature of the deficiency. In this case, we mean a vertical or horizontal tissue deficiency, that is, an expansion of the narrow alveolar process or an increase in its height to install an implant. The following innovations are recognized as the most popular among dental implantologists:
- implantation of bone tissue of biological or synthetic origin;
- expansion of the alveolar part of the bones of the upper jaw;
- targeted bone regeneration with the installation of a specific membrane;
- For bone tissue atrophy in the marginal areas of the upper jaw, a sinus lift is used.
Each of these methods has its own advantages, however, like any other intervention in the body, there are significant disadvantages of bone grafting of any kind. The most important disadvantage of this manipulation is considered to be a large time investment, that is, the process of restoring the required volume of bone tissue can reach 6-7 months. Another disadvantage of the maxillofacial reconstruction process is the cost of the procedure, and only wealthy people can afford professional dental implantation.
Do I need to do a resection or still remove the tooth?
Tooth root resection is a tooth-preserving operation. The dentist will recommend it to you when there is at least the slightest opportunity to save the tooth. If the dentist does not see this possibility, then the conversation will immediately focus on removal.
When will the tooth have to be removed?
- You have a large cyst that affects more than a third of the tooth or several teeth.
- The root of the tooth is destroyed.
- There is severe inflammation of the tissues adjacent to the diseased tooth.
- The tooth is movable.
- Subsequent prosthetic replacement of a diseased, destroyed tooth with a crown is impossible.
Indications for surgery
- Poor endodontic treatment leading to inflammation of the root apex;
- the presence of a cyst, granuloma or other neoplasm, no more than 1 cm in diameter;
- perforation of the root walls during filling;
- pin or stump inlay in the dental canal;
- obstruction of the dental canal due to a congenital developmental defect;
- a crown or bridge placed on a tooth.
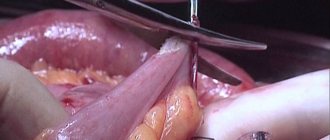
How is tooth root apex resection performed?
For the patient, resection of the apex of the tooth root is a simple operation and the procedure is tolerated quite easily.
First, the doctor makes an incision in the gum and bone tissue of the jaw to create access to the tumor. After which the tumor itself is removed along with the affected part of the tooth root. The entire cavity is thoroughly cleaned so that not even a small amount of infected tissue remains and is treated with an antiseptic.
Synthetic bone replacement materials are placed into the resulting space, which will take root over time and completely restore the patient’s bone.
Next, the wound is closed with a special self-absorbing membrane and the gum is sutured.
In order to protect the injured area, a bandage may be applied to the gum for up to 1 week.
After surgery, the patient may experience swelling of the gums and pain when chewing, which normally should subside within a few days.
Healing of the mucosa usually occurs in 7-10 days, the bone is restored in approximately 3-4 months.
Alternative to apicoetomy
Not in every case, surgical intervention is the only and mandatory method for eliminating granulomas and cysts. Apicoetomy is considered mandatory only in the presence of cysts measuring 1.5-2 cm or larger. The structure of the cyst shell is quite thick and dense and does not disappear completely even with the highest quality therapy.
In the presence of small pathogenic formations, dentists carry out therapeutic treatment. First, the doctor removes the source of infection from the root canals, after which he fills the canals with a special medicinal paste.
After a few months, the patient is sent for an x-ray, based on the results of which the doctor assesses how much the cyst has decreased in size. If everything is normal, then the dentist installs permanent fillings.
The disadvantage of this method is the need for multiple visits to the dentist. It should also be noted that conservative treatment does not always provide the desired effect, since the problem unit periodically becomes inflamed. Therefore, it is much easier and more expedient to eliminate the cyst by cutting off the root tip or completely removing the tooth root.
What to do after tooth root resection?
Root resection is well tolerated by patients and does not cause major problems even in the postoperative period, but it is necessary to follow a number of rules that will alleviate the condition and speed up recovery.
Typically, after surgery, patients are prescribed antibiotics and vitamin supplements. They must be taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
It is necessary to maintain gentle but regular oral hygiene and use antiseptic rinses.
You can't overwork your body. During the healing period, it is better to limit physical and emotional stress.
Do not eat hot or hard food, it should be warm and soft.
Why should you agree to resection?
Before the development of a technique for eliminating inflammation in the deep layers of bone tissue by cutting off the root tip, there were no alternatives to tooth extraction. Despite the flourishing of dental prosthetics and implantation, an artificial organ will never become a complete replacement for a natural one.
Therefore, if, after an examination, a specialist says that resection of the apex of the tooth is necessary, rest assured: this is so. Refusal to undergo surgery will certainly result in irreversible loss of the affected organ.
Preparing for tooth extraction
Removing a tooth or its roots is a rather complex surgical dental procedure, but it will not be difficult for the patient to prepare for it. If local anesthesia is planned to be used for pain relief, the patient should eat a large meal before visiting the dentist because:
- After removing a tooth or root, it is forbidden to eat for several hours;
- salivation after eating is significantly reduced, which will make the dentist’s work easier;
- after eating, blood glucose levels are normalized and the risk of loss of consciousness under the influence of local anesthesia is reduced
In the case of general anesthesia, on the contrary, it is necessary to abstain from eating for several hours before the removal procedure begins. Drinking alcohol before visiting the dentist is prohibited. Alcohol affects the structure of the blood and does not combine well with anesthetics, not to mention the negative impact on the human psyche and behavior.
Inflammatory and infectious diseases of any nature must be cured before surgery to remove a tooth or its roots. The dentist must be warned about the presence of allergies to certain medications, in particular to anesthesia drugs.
A normal pregnancy in general is not a contraindication to dental procedures. However, during this period the use of a number of drugs used in dentistry is prohibited, so information about pregnancy is entered into the patient’s dental record. Also, detailed information about the patient’s chronic diseases, especially heart pathologies, is recorded in the dental record.
What is the difference between PRJ and more complex operations?
Cholecystectomy
- Cost: 100,000 - 160,000 rubles.
- Duration: 25-30 minutes
- Hospitalization: 3 days in hospital
More details
A patient who has undergone pancreatic cancer usually does not require lifelong doses of vitamin and mineral supplements that are absolutely necessary after gastric bypass or biliopancreatic bypass. The likelihood of metabolic side effects (protein, vitamin and calcium deficiency) is also less here. PGC does not require removal of the gallbladder, although if gallstones form in the gallbladder during weight loss, this may be necessary later. At the same time, if we talk about the stability of weight loss, biliopancreatic bypass undoubtedly leads here. Due to the fact that the operation of prostate cancer is relatively young, no one can yet say how stable its results are after 5-10 or more years. Therefore, we warn all patients who are considering the option of longitudinal gastrectomy that if over time the result of PRG turns out to be insufficient, a second stage of treatment may be required - gastric bypass or biliopancreatic bypass. In this case, the second stage will be easier to complete, since the “gastric” stage of biliopancreatic bypass has actually already been completed.
Features of postoperative rehabilitation
After such surgery, the patient should refrain from any physical activity for 24 hours. Eating food is allowed only after 3 hours. Subsequently, care must be taken to ensure that the oral cavity is not exposed to thermal irritants, to limit the consumption of spicy and salty foods, as well as the use of overly aggressive means for rinsing and brushing teeth.
Swelling may persist for 1-2 days and moderate pain may be felt. To prevent the development of a purulent and inflammatory process, antibacterial agents and antiseptic solutions are prescribed, which must be used to thoroughly rinse the mouth. After 6 months you should undergo an x-ray examination.
Are postoperative complications possible? What is their probability?
It is impossible to guarantee the absence of complications with any operation. In case of prostate cancer, a staple suture is placed along the entire stomach. Although these sutures are performed using high-quality staplers and are always reinforced, there is still a small risk of postoperative bleeding, as well as failure (cutting through) of some sutures, which in rare cases may require laparoscopic or surgical revision. To prevent suture insufficiency in the first two weeks after prostate cancer, nutrition should be in liquid form, without undue stress on the gastric sutures. Since the operation takes place in the area of the splenic hilum, we always warn that if significant bleeding occurs from the spleen, it may be removed. We also warn about this during other gastric surgeries performed due to obesity.
How likely is heartburn (reflux - esophagitis) to occur after prostate cancer? How to deal with this?
Firstly, the probability of reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus largely depends on the volume of resection, i.e. the larger part of the stomach is removed and the more the stomach looks like a narrow tube, the less the danger of reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus. Secondly, reflux esophagitis can be effectively treated and prevented with the help of antiulcer drugs (omez, quamatel, ranitidine, pariet, etc.) that inhibit gastric secretion. Such treatment can be prescribed for a period of 2 - 3 months after surgery, and then only if necessary. We are not proponents of additional “anti-reflux” interventions. They are justified only when it comes to large diaphragmatic hernias.
What are the possible complications?
During the operation, damage to nearby anatomical formations is possible - blood vessels, sinus nerves, roots of neighboring teeth, therefore such operations are not performed on teeth closely adjacent to them. Due to the fact that the tooth root becomes much shorter - in the future it may become mobile; for the same reason, teeth after resection are rarely considered as a support for orthopedic structures. If after resection you still have to remove a tooth, installing an implant in this area may be difficult due to the reduced potential of the bone to heal.
The most correct decision would be to prevent the development of pulpitis and periodontitis. Treat your teeth on time!
Many patients are frightened by the phrase “gastric resection”. How justified are these fears?
Longitudinal gastrectomy is not at all the same resection that is performed for cancer or peptic ulcer disease. With PRG, the lateral part of the stomach is removed, while the important physiological valves of the stomach (cardiac sphincter and pylorus) are preserved, and thus the stomach after PRG remains physiologically quite functional. From a voluminous sac, the stomach turns into a narrow tube, where food does not stay long and quickly passes into the intestinal tract. The secretory activity of the stomach, of course, decreases, but this also plays into the hands of the goal of weight loss.