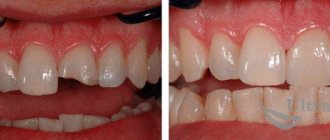
Our teeth are not only dense organic tissues covered with hard tooth enamel. Hidden inside each tooth is a complex system of blood vessels and nerve endings, which is necessary to maintain the health of the dentition. The sensitivity of soft tissues in the oral cavity is tens of times greater than the sensitivity of other organs. Therefore, any infection that gets inside the tooth causes inflammation and severe pain. Pathology is also provoked by temperature changes: burns or hypothermia. Unbearable pain forces a person to treat pulpitis and seek help from a dentist.
Will we treat him or let him live?
Often the fear of doctors forces us to make do with improvised methods. We take painkillers, fast, endure, in the hope that the sharp pain will go away on its own. Is it really possible to “wait out” an exacerbation, or is it better to get professional help in time? Let's figure it out.
To find the right method of treating a disease, you need to know the origins of its occurrence. The core of the tooth, or pulp, is responsible not only for tooth sensitivity, but also for the production of dentin. The tissue strengthens the tooth from the inside.
The anatomical features of the pulp depend on the type of teeth. In the lateral row, as a rule, there is a chamber with three dental canals. The front row and incisors each have one branch. It is logical that molars are much more difficult to treat than canines or premolars.
Pathological changes in the pulp tissue form swelling, causing unbearable pain. The pain intensifies upon contact with hot food or when pressing on the tooth.
Prerequisites
The most common cause of inflammation of the dental nerve (pulp) is the presence of caries. And in a deep stage. The infection reaches the soft tissues through the destroyed tooth tissue, provoking an inflammatory process. A similar situation occurs when a filling falls out or is damaged, when the pulp is “exposed.”
Bacteria can enter the tooth cavity from another source of infection in the body. Inflammation also occurs when a tooth is injured, minerals accumulate in the pulp, or low-quality components are used when filling canals.
Also, treatment of pulpitis may be required if the nerve overheats during preparatory procedures for prosthetics. If there is increased sensitivity, swelling of the pulp can be caused by the use of chemicals during therapy. It is also possible that an infection may accidentally enter the pulp chamber when eliminating a carious cavity.
Structure
We have already examined the structure of the tooth itself, now let’s study in more detail the structure of the pulp.
Since the main substance is a loose fibrous substance, the density of the pulp is relatively low. However, this liquid amorphous colloidal system contains a huge number of pulp cells and fibers, which are quite difficult to separate from the connective tissue. Pulp fibers are nothing more than elastin and collagen.
On the surface of the fibrous structure there are odontoblasts, cylindrical cells with long processes located in the dentinal canals. It is these processes that make dentin sensitive to all external stimuli. Next are the stellate cells. The central layer contains the largest number of nerve and collagen fibers, as well as blood vessels.
The main composition of the pulp includes the most numerous cells: fibroblasts, which produce collagen fibers and create connections between cells, macrophages, histiocytes, and mast cells. In case of damage or inflammatory processes, the structure of the dental pulp also contains plasma cells, leukocytes and lymphocytes.
Phases of the disease
Classification of any disease contributes to quick and correct diagnosis and selection of an effective treatment method for the patient. In the case of pulpitis, everything is relatively simple, there are only two subtypes - acute and chronic.
The first type of inflammation occurs with advanced forms of caries. Bacteria destroy tooth enamel and dentin, and the infection enters the pulp. The disease is accompanied by aching, sharp pain, which intensifies with mechanical or thermal effects on the tooth. Severe pain attacks may occur at night.
Interestingly, only adults are susceptible to acute pulpitis. The anatomical structure of a child’s jaw protects him from illness.
This type can be focal or diffuse. Focal inflammation is characterized by local damage to the pulp, located close to the carious cavity. Accompanied by throbbing pain around the affected tooth. Lasts approximately 2-3 days.
Then the process moves to the next stage - damage to all tissues of the dental nerve. The pain syndrome changes from pulsating to constant, unpleasant sensations spread to the entire jaw. Pus forms in the tooth cavity. The phase lasts no more than two weeks. If timely treatment of pulpitis is not started, the pathology enters the chronic stage.
Eliminate cannot be deleted
A term that patients in all fields of medicine fear is chronic disease. Let's see what the consequences are in our case. Inflammation of the dental nerve with chronic pulpitis lasts from a month to several years. The pain syndrome remains, but becomes less pronounced. Seizures occur periodically. The patient can no longer chew on the side of the diseased tooth. The affected nerve begins to bleed and dentin continues to deteriorate. Chronic pulpitis is also characterized by several phases:
- Fibrous. Relatively “easy” stage. It occurs when carious tissues are not located close to the dental nerve. Unpleasant sensations occur only when you press on the tooth.
- Gangrenous. The pulp tissue is completely infected. The nerve changes color. The pain becomes more noticeable. The tooth is deeply affected by caries.
- Hypertrophic. Bacteria destroy the tooth down to the pulp chamber, connecting both cavities. A polyp grows in the vacated space, causing the nerve to bleed. The pain syndrome persists.
- Exacerbation. The final stage of the disease, when the patient is attacked by periodic attacks of pain, combined with constant aching unpleasant sensations. Pus appears in the tooth cavity, inflammation spreads to the tooth root, and periodontitis develops.
In 90% of cases, doctors treat fibrous pulpitis, less often - the second stage. In general, chronic inflammation is an irreversible process. The only solution is to remove the damaged dental nerve.
Survey
To determine an accurate diagnosis, the dentist conducts an initial examination. Because If pulpitis develops against the background of other diseases, then diagnosis includes 4-5 stages. The procedure begins with communication with the patient. It is important to understand at what stage the inflammation is, which is especially important in chronic pulpitis. Therefore, the doctor asks you to describe in detail the nature of the pain. Then a “manual” examination is carried out using medical instruments (dental mirror, etc.). Additionally, the doctor checks the sensitivity of the affected tooth for temperature changes and exposure to a weak electric current charge.
The examination is completed by an X-ray examination to assess the condition of the dental nerve and canals. After collecting information and analyzing the image, the doctor plans the pulpitis treatment process and coordinates it with the patient.
Diagnosis of pulpitis
The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on a survey and examination of the oral cavity. As a rule, pulpitis precedes developing caries, so there is a carious cavity in the causative tooth. The doctor performs probing - places an instrument into the cavity to assess its depth and reaction. Tapping is a method that also helps the doctor find out how the tooth reacts to mechanical stress. The main task of the specialist is to determine the difference between pulpitis and deep caries - treatment tactics depend on this.
An X-ray examination is necessary in order to assess the nature of the disease, as well as determine the structure of the root system - the doctor will need this information for further endodontic treatment of tooth pulpitis (treatment and filling of canals).
How to deal with the disease
At the initial stage, it is not difficult to cope with pulpitis. The nerve in the tooth is preserved, and the doctor relieves the inflammation using therapeutic procedures.
The biological treatment method eliminates inflammation through antibacterial treatment of the damaged tooth, without removing the nerve. After removing carious tissue and disinfecting the pulp chamber, the dentist applies a compress with calcium hydroxide and fixes a temporary filling.
Then, after 3-7 days, during a follow-up visit, the doctor takes an x-ray. If there is no inflammatory process, then a permanent filling is installed. However, this technique requires a highly qualified doctor, so it is rarely used. For example, with traumatic inflammation of the dental nerve.
Preserving the pulp is important because... If it is present, the tooth is constantly strengthened due to the production of dentin. Conservative therapy has age restrictions - it is carried out up to 30 years.
About the method.
Devital pulp extirpation
this is its complete removal after deprivation of viability. The method is considered quite reliable, as it prevents the spread of infection and the occurrence of periodontitis. In that case, of course, when the procedure is performed efficiently. Devital extirpation is carried out in several stages. Therefore, you will need 3 visits to the dentist's office.
Partial and complete nerve removal
Partial extraction of the pulp is also acceptable if the coronal component of the nerve is separated from the root. To prescribe surgery, there must be a large volume of intact periodontal tissue.
The procedure is performed under anesthesia for patients under 45 years of age.
In practice, pulpitis is treated surgically. The nerve is completely removed, which saves the patient from relapse and re-treatment.
Pulp removal occurs in two ways:
- Extraction of living nerve.
- Preliminary killing of the pulp (devitalization) with further removal.
In the first option, all work is carried out in one session. The dentist removes the affected tooth tissue, thoroughly disinfects the cavity, and then removes the inflamed nerve. At the final stage, a filling is installed.
If it is not possible to remove the living nerve from the tooth, it is treated with medical paste made from arsenic or paraformaldehyde. After 1-2 days, the pulp dies and is painlessly removed. Patients cannot always visit the doctor the next day; in this case, the dentist fixes a less concentrated composition for up to two weeks. A temporary filling is placed on top. During the next visit, the doctor treats the canals with an antiseptic and fills the tooth. Important: this method of treating pulpitis is not applicable in the presence of pus and dead tissue in the pulp.
Treatment of pulpitis
To avoid complications of pulpitis, it is important to start treatment in a timely manner. In rare cases, this allows you to save the pulp and avoid its extraction from the canal, but partial or complete removal of the neurovascular bundle is still more often practiced, and here’s why.
Removing the pulp allows you to completely eliminate the source of inflammation, which means preventing the spread of pathogenic microorganisms into the tissue surrounding the tooth. This is the basic principle of preserving the tooth and tissues from possible complications.
How is therapy carried out?
The process of extracting the dental nerve may require 2-3 visits, depending on the number of roots in the tooth. The time interval between sessions is prescribed by the doctor, in accordance with the diagnosis.
Traditionally, treatment of pulpitis consists of 4 stages:
- Application of local anesthesia. Nerve endings are very sensitive to any impact, so painkillers are indispensable.
- If caries is present, the affected tooth tissues are first removed. Sometimes it is necessary to remove a healthy part of the tooth to gain access to the pulp.
- Using a special tool, a pulp extractor, the dental nerve is extracted. Depending on the stage of the disease, the pulp is pre-treated with arsenic or extracted alive.
- The dental canals are measured and thoroughly disinfected.
After treatment, the tooth is filled: first the root canals, then the upper, coronal part of the tooth. In difficult cases, for example, with chronic pulpitis, the doctor fixes filling materials only in the canals in order to track a possible relapse of the disease. If inflammation reappears, then intermediate therapy is prescribed using antibiotics.
After installation of a permanent filling, the patient may experience pain. This usually lasts no more than 2-3 days, with a reaction to cold foods and drinks. If the discomfort continues, then the inflammatory process has resumed, and you need to visit the dental office as soon as possible.
What it is
The tooth consists of two parts - the root, located in the gum, and the crown, rising above it. The outside of the tooth is covered with a dense layer of enamel, which prevents food, bacteria and other irritants from reaching the sensitive layers. True, enamel is not so durable, since it is constantly exposed to physical stress, resulting in the formation of microcracks. Infections and food debris get into them, destroying the upper protective layer over time.
Beneath the enamel is dentin. This tissue is much softer than enamel and is destroyed more quickly by foreign substances, but it still serves as an obstacle to the path of external irritants to the nerve. Under the dentin layer there is soft tissue containing all the nerve endings and blood vessels of the tooth, running from the jaw through the apical foramen along the root canal. This is the pulp of the tooth; it is a nutrient medium that provides access to mineral substances to its walls, which allows the tooth to remain viable, grow, recover and maintain its original appearance.
In essence, pulp is fibrous, loose connective tissue that fills the internal space of the tooth.
Dental pulp also has a protective function: it is a kind of barrier that delays the penetration of pathogenic bacteria that have entered through dentin, through the root canal into the periodontium and further beyond the boundaries of the tooth itself.
Among other things, pulp is also a stimulator of regeneration of replacement dentin, which is formed during caries and prevents its growth and penetration deep into the tooth. However, in about twenty percent of cases out of a hundred, the pulp does not cope with its functions, which is why inflammatory processes begin inside the tooth, one of which is pulpitis.
If left untreated, this disease threatens to develop into a more serious disease, namely apical periodontitis. It, in turn, leads to the spread of infection outside the tooth cavity and the formation of such unpleasant diseases as gingivitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis, purulent abscess and many others, often amenable to only one treatment - removal of the source of infection, i.e. sick tooth.
Children's horror stories
The phases of disease progression at a young age are approximately the same. But unlike adults, children's pulpitis develops many times faster. A small hole in the tooth is enough for the infection to cause inflammation in the pulp chamber. Accelerated pathological processes can lead to infection of the soft tissues around the tooth, which can lead to problems with the growth of molars. Therefore, if a child complains of toothache, it is important to consult a doctor immediately.
The question often arises: is it possible to treat pulpitis or is it still necessary to remove the dental nerve in children? An experienced dentist always strives to preserve both the baby tooth and the pulp. Because the absence of teeth in a row can affect the location of neighboring teeth, change the bite, and even diction.
In the case of baby teeth, the dentist uses special filling materials that dissolve over time and do not interfere with the growth of the permanent dentition.
Gentle drugs that are hypoallergenic and safe for babies are used as pain relievers.
Indications during pregnancy
There is a myth that it is impossible to treat teeth while expecting a baby. This misconception can have serious consequences. Infection, for example in the form of caries, through blood vessels can spread throughout the body.
It is also a mistaken belief that x-rays harm the development of the fetus. It has been proven that modern equipment has a minimal radiation dose that does not affect the body. It is much more dangerous to bring the inflammatory process to a chronic state. Therefore, you should not delay treatment of pulpitis or caries when symptoms appear.
The process of bearing a child is associated with a decrease in immunity, and as a result, with increased sensitivity to bacteria and infections. Tooth enamel in pregnant women is not as strong, because... All nutrients are aimed at the growth of the baby. Therefore, the appearance of pulpitis and deterioration in the condition of the dentition is a normal phenomenon.
The second trimester is considered the optimal period for receiving dental care. During this period, the child is protected by the placenta from harmful substances. However, if an inflammatory process occurs in the dental nerve, it is not recommended to delay treatment so as not to expose the baby to unnecessary risk.
During pregnancy, the doctor chooses a gentle treatment method, when the filling is fixed only in the dental canals. If possible, without the use of anesthesia. After childbirth, the patient is given a permanent filling. X-ray examination is carried out only in emergency cases.
Inflammation of the nerve in the wisdom tooth
Eights have their own specifics, and the doctor often chooses to remove the tooth. The complexity of therapy is due to the anatomical features of the third molars. Curved roots, lack of access to the tooth, partial overlap of the gums equates the treatment of pulpitis in figure eights to jewelry work. And it requires experience and high qualifications of a doctor.
An inflamed nerve in a wisdom tooth can be treated by filling the canals. Provided that there is access to the root and the dental canals have good patency. It makes sense to preserve a tooth in the presence of an antagonist tooth, if the tooth is involved in the chewing process and is used when installing a prosthesis.
Cost of pulpitis treatment
The cost of treating pulpitis is determined by several factors, including the geography of the clinic. In a good clinic, the price already includes anesthesia, canal treatment, fillings and other materials.
The total amount is added up taking into account the number of root canals, their anatomical features, the degree of destruction of the crown and the method of its restoration, if we are talking about caries. You can find out the exact cost during a consultation with a dentist-therapist at the Dentist-K clinic.
It is important to remember that you can avoid expensive treatment by consulting a doctor in a timely manner. It is necessary to maintain hygiene and undergo professional teeth cleaning on time - this will avoid the need for pulpitis treatment.