A tongue burn is an injury that damages the mucous membrane, and in some cases even muscle tissue. This problem brings a lot of discomfort - from pain and the inability to eat or drink liquids to death. It is very important to urgently contact a specialist who, after studying the cause of the burn, will prescribe treatment. If you neglect the help of a qualified dentist, serious complications can occur, including necrotic decomposition of soft tissues and infection of the entire body.
Types of tongue burns
Depending on the cause of origin, the following types of injury are distinguished:
- Chemical burn of the tongue or oral cavity - when tissues are damaged as a result of exposure to aggressive chemical compounds;
- Thermal - when the surface was exposed to a high temperature object.
- Electrical - occurs as a result of tissue contact with electricity. For example, when performing dental procedures. Electric current affects not only the tissues of the tongue, but the entire body as a whole.
Burning tip of the tongue - causes
A burning sensation on the tip of the tongue, of course, is not a reason to panic, but a reason to pay close attention to your health.
After all, the state of this organ can be used to judge the functioning of the entire organism as a whole. Such a harmless, at first glance, symptom may be a sign of developing inflammation - glossitis. This term is usually used to describe all pathological conditions of the tongue - burning, inflammation, etc.
The danger of glossitis is not only that it causes significant discomfort - pain and swelling occur, it becomes difficult for a person to eat and speak, ulcers may appear, and abscesses may develop.
Inflammation can signal more serious systemic diseases, such as problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
The factors that cause an unpleasant burning sensation are very diverse in nature - from trauma to the mucous membrane to a specific infection or systemic pathology.
Symptoms of a tongue burn
Symptoms depend on the extent of soft tissue damage:
First degree - a burn occurs due to short-term exposure to high temperature tissue. The patient experiences slight redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. Often, a burn condition is provoked by consuming too hot food or liquid.
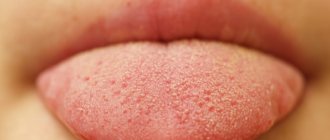
Second degree – swelling of the mucous membrane, redness, and multiple blisters on the surface are observed.
Third degree - accompanied by tissue death, large blisters, redness of the surface, the organ itself seems to “change its consistency.” As a rule, it occurs due to exposure to gases, liquids at elevated temperatures, or chemical compounds.
The fourth degree is a severe lesion when the tissues are charred. This burn condition is rarely compatible with life.
Neurological and allergic disorders
If a person is prone to an allergic reaction, then upon contact with the allergen there will be a burning sensation in the throat. In this case, the person will begin to sneeze and cough frequently, drooling will increase, and the eyes may itch and become moist. Allergies can occur to pet hair, certain foods, alcohol, pollen and household dust, chemicals, etc.
A burning sensation in the throat can occur due to pathologies of a neurological nature. In particular, with laryngeal hyperesthesia, increased sensitivity of the mucous epithelium occurs. There are many factors that provoke hyperesthesia, and when the disease worsens, a person suffers from soreness and burning. A lump appears in the throat, which can often provoke a gag reflex. The patient may swallow frequently due to increased salivation.
With pharyngeal paresthesia, a person may feel discomfort in the throat area, which can manifest itself differently each time. The throat may burn, hurt, tickle, etc. This discomfort often appears after a person becomes nervous or experiences severe stress. Paresthesia often occurs in people prone to suspiciousness or hysteria.
How to properly treat a tongue burn?
Treatment methods depend on the type of thermal injury.
What to do in case of a thermal burn of the tongue?
- rinse your mouth with cool water;
- apply ice or a cold object to the damaged area;
- treat the burn site with a disinfectant solution;
- rinse with a disinfectant to prevent bacteria from entering the oral cavity;
- use local anesthetic compounds;
- while the tongue is recovering, eat liquids, fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins C and B. Avoid spicy, pickled foods, foods that can have a mechanical effect on tissue (nuts, crackers, seeds, etc.).
- rinse the mouth thoroughly;
- neutralize aggressive chemicals. Depending on the source of the burn, a specific neutralizer is used;
- After neutralization, the burning sensation should go away. For pain relief, it is worth using anesthetics and antihistamines;
- if the mucous membrane is severely burned, with damage to the structure of the tongue and muscle tissue, it is necessary to urgently go for an examination to a doctor.
If there are bubbles on the surface of the tongue, you should urgently seek help from a dentist! Under no circumstances should you open blisters yourself! You may need hospital treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
How to treat a chemical burn of the tongue?
Note! If the oral cavity is burned with an alkaline solution, it cannot be rinsed with water, since moisture promotes more active penetration into the soft tissues of the tongue.
Therapy tactics
Treatment of burning sensation in the tongue area begins with sanitation of the oral cavity (treatment of caries, removal of tartar, hygienic cleaning of teeth, including periodontal pockets).
If you have dentures, braces and other orthodontic structures, they are checked and, if necessary, cleaned or replaced.
For stomatitis, gingivitis and other diseases of the mucous membrane, treatment is carried out. Treatment for glossalgia is prescribed only against the background of a completely healthy mouth.
Medication correction
Treatment is prescribed after the true cause of the burning sensation has been established. When the root cause is eliminated, glossitis usually goes away on its own.
The mandatory groups of drugs for the treatment of burning and other unpleasant sensations include:
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptics (Miramistin, Furacilin, Chlorhexidine aqueous);
- the use of ointments and solutions with Lidocaine, Novocaine (baby gels are suitable for teething).
If glossalgia is of a fungal nature, local medications based on active ingredients such as Clotrimazole and Nystatin are prescribed.
If the cause is bacterial, then Metrogil-denta and Metrogil gel are prescribed. If the causative agent of the burning sensation is viral agents, then it is advisable to prescribe Acyclovir, Florenal ointment, Oxolinic ointment.
Unpleasant symptoms are perfectly eliminated by means of systemic action: sea buckthorn oil, Actovegin gel, solutions of oils A or E. If respiratory disorders are noted against the background of glossalgia, it is recommended to take Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone.
All prescriptions are made by a doctor after a thorough diagnosis of the disease. In childhood, in the later stages of the disease, hospitalization may be necessary. Additionally, drugs from the group of corticosteroids may be needed.
Alternative medicine
With localized glossitis, without deterioration in general well-being, you can limit yourself to traditional methods of therapy at home.
In case of herpetic infection or the fungal nature of the disease, it is unacceptable to use alternative medicine recipes as monotherapy.
The main means for maintaining oral health include the following:
- Oak decoction.
Decoction of oak bark (rinsing or internal use). To prepare, grind 20 g of bark, place in a saucepan, add water and seal tightly with a lid. The container with the composition is boiled over a fire and infused. The finished broth is filtered and taken as a generous rinse several times a day. A fresh decoction should be prepared every day. To improve the therapeutic effect, the decoction should be warm. - Sage infusion.
Sage is a powerful natural antiseptic. Prepare the infusion as follows: place 20 grams of dry herbs in 200 ml of boiling water. The broth is infused for about 2-3 hours in a thermos or in a hermetically sealed pan, which can be wrapped in a terry towel and covered with pillows. Rinse the mouth with the prepared decoction several times a day. - Curd product. Cottage cheese is mixed with fat sour cream in a 1:1 ratio, wrapped in gauze and applied to the tongue for a long time. Sour cream softens mucous tissues, and cottage cheese acts on an absorbent principle.
- Herbal collection.
To prepare the decoction, place yarrow, chamomile, sage, aloe, and calendula in equal proportions in a bowl of boiling water and leave for an hour. After preparation, strain the mixture and rinse every 3 hours. The therapeutic effect is observed in the next 3 days. This decoction is a good addition to the main treatment. - Honey and chamomile. To prepare the product you will need a propolis tincture and a ready-made chamomile decoction. Add 15 drops of tincture to a warm herbal decoction (about 200 ml). Rinse your mouth with this mixture for 24 hours. Duration of treatment is 7-10 days. Not suitable for young children.
To achieve good therapeutic results, traditional medicine recipes should be taken adequately.
Thus, when serious diseases of internal organs or systems are manifested, as well as when dental conditions are registered, the use of chamomile decoction alone will not give the expected results. Treatment with traditional methods is often carried out only in combination with conservative therapy.
How exactly to neutralize a chemical burn in the mouth?
Carbolic acid is well neutralized by glycerol.
Baking soda and water neutralize acidic compounds.
If alkali gets into your mouth, rinse the cavity with citric acid diluted in water.
If exposed to aggressive household chemicals, the mouth should be rinsed with cool running water.
It is important! Tongue burns take a long time to heal. Unfortunately, these tissues cannot be made motionless for a certain time; the tongue is constantly in motion. On average, it can take several weeks for the tongue to recover from injury.
Treatment of a burn to the oral cavity in a child
According to statistics, a large percentage of patients who turn to a doctor for help as a result of a burn to the mouth or tongue are children. Young patients up to a year and older can unknowingly “taste” household chemicals or alcoholic drinks accidentally left on the table by their parents. Also common causes of burns are eating too hot food.
The mucous membrane of a child’s tongue is more delicate and thin, and therefore requires more delicate handling in case of a burn. For treatment, you must urgently contact a pediatric dentist.
Local reasons
In most cases, pain is associated with local irritants and diseases of the oral cavity. These include:
- allergic reactions;
- microtraumas;
- inflammatory processes in the mouth;
- fungal infections;
- neoplasms.
Tongue injuries
The most common reason why the tip of the tongue hurts, as if burned, is mechanical damage caused by eating food with sharp edges (fish bones, seeds, candies), accidental bite, incorrectly placed crown or chipped diseased teeth. With minor injuries, such microtraumas go away on their own and do not require treatment, but sometimes they can cause redness of the tongue, swelling, and pain.
Allergy
When consuming certain medications, foods, or using toothpaste, an allergy may occur, which results in burning pain in the tongue. Pain can occur after eating pineapples, kiwi, other acidic foods, as well as due to drinking alcohol or smoking. To get rid of the problem, it is necessary to identify the allergen and completely eliminate its intake.
Inflammation
Due to a weakened immune system, poor oral hygiene, long-term use of antibiotics or hormonal drugs, an inflammatory process can develop in the mouth, as a result of which a person’s tongue hurts as if it were burned. Most often, inflammation appears in the following diseases:
- Stomatitis. The pathology is characterized by swelling and hyperemia of the oral mucosa, the appearance of a whitish or yellowish coating, increased salivation, sometimes bleeding gums and bad breath. The patient often has pain in the tip of the tongue or the entire organ, and blisters and ulcers appear on the oral mucosa.
- Glossitis. The disease develops against the background of injury or the activity of pathogenic microorganisms and is accompanied by swelling of the tongue, a change in its color, and the appearance of a pale coating. The person has difficulty swallowing, chewing food and speaking.
Fungal infection
Among infections that are fungal in nature, people most often develop candidiasis. It is a consequence of the active activity of fungi of the genus Candida, which are part of the normal human microflora, but as a result of certain factors begin to multiply and cause inconvenience. In particular, pregnant women often complain that their tongue hurts, as if it was burned. This is due to changes in hormonal levels and decreased immunity.
Other causes of candidiasis include the presence of concomitant diseases (HIV, tuberculosis), prolonged use of antibacterial drugs, lack of vitamins, and use of oral contraceptives.
Tumor
The most severe pathologies that cause burning pain in the tongue include malignant or benign neoplasms, which require immediate attention to medical specialists and competent treatment.