No one is immune from jaw displacement. Dislocation of the lower jaw can occur either as a result of a blow or when the mouth is suddenly opened. But there are a number of factors that provoke the occurrence of such situations. How to behave if jaw displacement occurs? How soon can it be put back in place, and where should one go if the lower jaw is dislocated? Experts answer these questions.
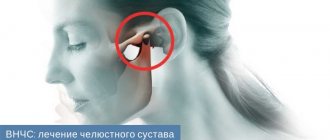
Dislocation of the lower jaw is a situation when the articular head of the temporomandibular joint is displaced. Dislocation can only affect the lower jaw, since the upper jaw is immobile. The mandible is connected to the temporal bone by the TMJ, which helps the mandible move.
Why does dislocation of the lower jaw occur?
Mandibular displacement can occur because:
- the patient suddenly opened his mouth during a conversation or yawned;
- the man dropped his jaw sharply;
- the patient suffers from certain diseases that have weakened the skeletal system and articular ligaments. Among the most common diseases that provoke dislocation of the lower jaw are osteomyelitis, rheumatism, arthritis, etc.;
- a person has a habit of opening bottles with his teeth;
- the temporomandibular joint was affected due to improper distribution of the load on the teeth (for example, if on one side there are no chewing teeth, but on the other side they are there and do more work).
Causes
The causes of displacement of the jaw joints are most often external influences. Each person has different anatomical features and the strength of fixation of the joints in the bursa. Therefore, in some people, even a minor bruise can cause subluxation. This is usually caused by weak bone tension and weakened ligaments. But also the causes of the disease are:
- rheumatism;
- epilepsy;
- arthritis (advanced stage);
- consequences of encephalitis;
- convulsions;
- joint deformation, osteomyelitis.
Factors that increase the risk of subluxation are also separately identified:
- mechanical injuries, strong impacts;
- congenital deformities, pathologies of the articular cavity;
- opening the mouth too much when biting or yawning;
- bad habits (opening bottles with teeth, habits of gnawing nuts and seeds).
How to understand that a dislocation of the lower jaw has occurred?
The symptoms of dislocation of the lower jaw are quite clear:
- it becomes impossible to open your mouth;
- pain is felt in the projection of the jaw, as well as in the area of the temporal bone;
- after dislocation of the lower jaw there may be speech impairments;
- redness may be observed in the area of the temporomandibular joint;
- the lower jaw is pushed forward or shifted to the side;
- against the background of joint dislocation, uncontrolled salivation occurs.
As a rule, a person immediately understands that something is wrong with the lower jaw. Visually, the displacement of the lower jaw is also visible. If you notice similar symptoms of dislocation, you should urgently seek help from a doctor.
First aid
Before visiting a doctor, the patient must be given first aid. All measures in this case will be aimed at minimizing the load on the joint and reducing the intensity of pain symptoms.
First of all, the affected joint is immobilized with a bandage or scarf. The jaw is fixed from top to bottom and from front to back using two flaps of fabric. At this time, the patient is prohibited from speaking and opening his mouth wide.
Options for fixing the jaw using a bandage
If a person has dislocated his jaw, his mouth will be slightly open. To prevent dirt and dust from getting into the cavity, cover it with a damp cloth. This will also reduce saliva production. For severe pain, a non-steroidal solution can be administered intramuscularly. An ice container is placed at the site of the suspected injury to reduce the severity of swelling. This event will also reduce the intensity of pain.
Which doctor should I go to if I have a problem? Jaw injuries require consultation with a surgeon. After examining the patient, the doctor decides whether to realign the joint or perform surgery. Jaw subluxations often occur in the dentist’s office, when the patient opens his mouth wide during manipulation. In this case, the specialist provides the person with qualified assistance on the spot.
If bone damage occurs at night, an ambulance is called for the person. The victim is taken to a 24-hour emergency room, where the necessary manipulations are performed. Before determining a treatment regimen, the doctor orders an x-ray to analyze the characteristics of the injury.
What types of dislocations of the lower jaw are there?
Depending on the side of displacement of the articular head, there are:
- posterior dislocation of the lower jaw (when the jaw moves back);
- anterior dislocation of the lower jaw (when the jaw is pushed forward).
Based on the nature of the injury, we can distinguish:
- complex dislocation of the jaw, when soft and hard tissues are affected, and an open wound is visible;
- simple or closed dislocation of the lower jaw, when the displacement of the jaw bones is not visualized.
Based on the number of affected joints (and there are two of them) in articular dislocation of the lower jaw, the following are distinguished:
- bilateral dislocation of the lower jaw is a complex diagnosis in which the jaw “pops out” of both joints and is therefore pushed forward, the mouth remains slightly open, the jaw moves forward, the person is drooling, and there are problems with speech;
- unilateral articular dislocation of the lower jaw, when one temporomandibular joint is involved, while the chin shifts towards the unaffected joint.
If, when the lower jaw is dislocated, the tips of the bones do not touch each other, a complete dislocation of the lower jaw is diagnosed. If the ends of the bones partially touch, most likely the patient has articular subluxation of the lower jaw.
What it is
The lower jaw is considered the only movable part of the skull; this functional feature has its drawbacks, the most serious being an increased tendency to injury. Jaw dislocation is a pathology that is accompanied by the movement of its head from its natural anatomical position.
This happens quite often and can happen during the process of chewing and swallowing food.
How can you determine that a dislocation of the lower jaw has occurred?
As we said above, based on the symptoms, the patient immediately understands that something is wrong with his lower jaw. A doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis based on the following diagnostic steps:
- general examination;
- radiography of the jaw;
- computed tomography or MRI of the joint.
The specialist must also make sure that the dislocation or subluxation does not hide a fracture of the jaw, which is much more serious and requires surgical intervention.
It is important! If a person has a dislocation of the lower jaw as a result of injury or an accident, he should be given first aid - apply a tight bandage to the jaw and take him to a medical facility.
Jaw displacement
One of the most common types of injuries is jaw displacement. The fact is that it is very easy to get such an injury, sometimes even unnoticed by yourself, for example, when actively chewing food or yawning. To avoid complications and surgery, it is better to treat a dislocated jaw immediately.
The lower jaw is connected to the temporal bone by two joints, the heads of which fit into the articular fossae. This gives us the ability to talk, chew and perform other movements. Signs of a dislocated jaw appear instantly, so the problem is easily diagnosed. When the heads pop out of the articular sockets, the jaw “jams” in the open position. This is accompanied by pain in the temporal bone area.
Causes of jaw dislocation
Displacement of the lower jaw occurs for the following reasons:
- sudden movement of the jaw in the process of chewing food, laughing, yawning, screaming;
- physical impact, for example, from a fall, impact;
- unprofessional reduction of the joint - if the person tried to solve the problem on his own;
- diseases of the skeletal system and joints, such as arthritis, arthrosis, rheumatism;
- displacement due to constant excessive load on the jaws;
- congenital anomalies of the temporomandibular joint;
- opening hard packages with teeth.
How to understand that a shift has occurred
Jaw displacement is difficult to miss. Dislocation can be anterior, posterior, unilateral or bilateral. The degree of complexity of a dislocation depends on the type of injury and is expressed by the following signs:
- with anterior displacement (when the jaw moves forward), the mouth freezes in an open position, pain appears in the parotid area, profuse salivation begins, and the proportions of the lower part of the face are disturbed;
- if the dislocation is posterior (the jaw goes back), then in addition to sharp pain, it becomes difficult for the person to breathe and swallow saliva, and it is almost impossible to open the mouth;
With complicated dislocations, bleeding from the ears, hematomas in the parotid area and swelling in the joint area are possible.
How to diagnose a dislocation
An experienced doctor can easily diagnose jaw displacement using a general examination and palpation. But in order to exclude the possibility of a fracture and make the most accurate diagnosis, an X-ray examination is prescribed, as well as a computed tomography or MRI of the joint.
How to treat jaw misalignment
In most cases, dislocation is treated by manual reduction. There are several methods of treating trauma: the Hippocratic method, the Blechman method, the Popescu method and a number of others. The exact method to treat a dislocation is determined only by the doctor, depending on the specific case. The jaw realignment procedure is carried out as follows:
- The patient takes a comfortable semi-lying position so that his face is at the level of the doctor’s forearm.
- The doctor places his thumbs on the teeth and clasps the jaw from below with the rest.
- By carefully applying pressure, the specialist returns the jaw to its original position.
- As a result, the head of the joint returns to the fossa. A characteristic click occurs and the patient reflexively closes the jaw. This indicates that the problem has been resolved.
Immediately after the jaw is realigned, it is fixed with a tight bandage, which must be worn for a week. For a complete recovery and to avoid relapse, it is necessary to abstain from rough food for a while and minimize stress on the joints. As a rule, the outcome of the procedure is favorable. But in case of old or complicated injuries, surgical intervention under local anesthesia is required.
Treatment of lower jaw dislocation
To solve the problem of dislocation of the lower jaw, the jaw should be moved back into place. This should be done exclusively by an orthopedic traumatologist or orthopedic dentist. Adjusting bones yourself after a dislocation is fraught with complications - do not try to repeat the same thing at home, contact a professional.
The procedure for realigning a patient's jaw consists of 5 main steps:
Step No. 1 - the person lies down on a hard surface, takes a comfortable position;
Step No. 2 - the doctor places his thumbs on the chewing teeth of the lower jaw, the remaining fingers seem to clasp the lower part of the face;
Step No. 3 – the specialist makes movements, moving the jaw back and down, but at the same time slightly lifting the chin;
Step No. 4 - the doctor must make sure that the articular head has moved down the back of the TMJ tubercle and returned to its original position;
Step No. 5 – the doctor needs to have time to remove his fingers from the teeth so that the person does not automatically bite them, closing the jaw.
Repositioning the jaw after a dislocation takes several minutes, but must be done very carefully.
If a person’s jaw has been dislocated for a long time and for some reason he has not consulted a doctor, the bones have shifted, he is prescribed surgery under local or general anesthesia.
In case of complex dislocations, a person is recommended to have a reconstructive operation, in which the height of the articular tubercle is artificially increased, while the articular capsule is reduced. Thus, an optimal balance of the elements of the connecting apparatus is achieved, and the jaw does not move.
As a recovery after jaw realignment or surgery to correct a dislocation, the patient is recommended to wear special orthodontic appliances.
Independent actions
When a jaw is dislocated, a person should not make sudden movements. Severe pain is relieved with analgesics. In this case, the victim must know for sure that there is no allergy to the medication. Trauma is often accompanied by increased blood pressure. If the indicator increases significantly, you should take a drug that normalizes blood pressure.
Independent actions when realigning the jaw:
- Fixation of the jaw in one position using available means or a splint.
- Place a bandage in the mouth that will absorb the saliva that is produced.
- Call an ambulance. If the victim cannot speak, then he needs to ask neighbors or passersby for help (if the dislocation occurred on the street). If there is a clinic near the scene of the incident, you should go there immediately.
Before receiving qualified medical assistance, you should say as little as possible, since any movements can cause pain or complications of the dislocation. It is not advisable to adjust the joint yourself. Illiterate actions can lead to damage to the helping fingers or long-term dysfunction of the jaw apparatus in the victim.
How to behave after lower jaw reduction?
If the doctor has successfully adjusted the lower jaw, the patient is recommended to wear a thick elastic bandage for 10 to 14 days, which will securely fix the bones.
During this time, you should stop eating solid food - it is better to concentrate on liquid soups, pureed cereals, fruits and berries. It is important not to overload the jaw with chewing load, so as not to provoke re-dislocation.
With successful reduction of the lower jaw after dislocation and a professionally performed operation, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. In some cases, jaw mobility may be impaired.
If you or your loved ones have a displacement of the lower jaw, contact dental specialists. Here, experienced doctors will help you with dislocations even in the most difficult cases.
Surgical intervention
If conservative methods of reduction are ineffective, specialists resort to surgery. The zygomatic arch is incised under general anesthesia, a small part of the lower jaw is removed and a hook is inserted into the resulting hole. It is fixed by the edge of the notch and pressed with your hand on the chin, which allows the jaw to take a normal position. Stitches are placed on top.
For chronic dislocations, prostheses are installed. This is especially true when a person does not have his own teeth. Any yawning causes the joint to pop out of its socket. Temporary or permanent structures limit the wide opening of the mouth and relieve the weakened joint from unnecessary stress.
Structure
The formation of the mandibular region is the result of the evolution of the human body. In the process of development, the entire structure became mobile and autonomous, gaining the ability to move freely and perform the basic functions necessary for a person. The temporal joint is localized in the fossa, connecting to the bony part.
When a subluxation occurs, the head of the joint partially comes out of the fossa, succumbing to the influence of external factors. As a rule, this phenomenon becomes a consequence of a general weakening of the ligaments or disturbances in the articular cavity. If you have the proper skills and practical experience, you can restore the original position of the jaw yourself, but the systematic occurrence of such a problem is the basis for complex treatment.
Group No. 3: unilateral and bilateral
Anterior dislocations are divided into unilateral and bilateral. The most common ones in clinical practice are bilateral, when the articular head pops out of its bed equally on both sides of the jaw. Symptoms of the pathology: the mouth is wide open, the face is elongated, the cheeks are flat and sunken, severe pain occurs when trying to close the mouth.
Symptoms of one-sided pathology: the mouth is half open, the chin is shifted forward, an open bite occurs (a gap is formed between the front upper and lower teeth). When trying to move the jaw, the victim usually manages to open his mouth slightly.
Classification of dislocations
Jaw dislocations are divided into types according to various characteristics. Traumatology distinguishes:
- Complete dislocation. The head appears outside the articular cavity.
- Subluxation of the jaw. Partial preservation of the connections of the articular parts is noted.
- Fracture-dislocation. During dislocation, a fracture of the condylar process occurs.
According to temporal-causal characteristics:
- Congenital. Occurs in the perinatal period of development.
- Acquired. It is a consequence of injury.
At the location of the joint displacement:
- Front. The head of the joint is located in front of the fossa.
- Rear. The head is localized behind the fossa.
- Side. The joint is localized on the side of the fossa.
In addition to the above characteristics, dislocations of the jaw joint can be unilateral or bilateral. The first group includes dislocations when the joint is displaced on one side. The second - dislocations when the jaw joint is displaced on both sides. Bilateral displacement of the head of the mandibular bone is much more common than unilateral displacement.
Dislocations of the mandibular joint can be divided into 2 groups: acute traumatic and permanent. The first type of displacement is determined by a time period of 5–15 days. Permanent dislocation - observed in patients with convulsive syndrome due to injuries that occurred more than 2 weeks ago. If the displacement of the joint is not accompanied by sprains and ruptures of the tendons, a simple dislocation is diagnosed, otherwise - a complicated one.
Habitual dislocation
In the process of yawning or sneezing, the head comes out of its usual place, forming a dislocation. Often, patients cope with the problem on their own, but subsequent joint displacements, which occur one after another, can only be prevented by surgery.
Prognosis and prevention
To prevent jaw subluxation, fracture or displacement, the amplitude of mouth opening should be controlled. This must be monitored when brushing the mouth, eating, screaming and singing. It is important to promptly eliminate risk factors and prevent injury.
When pathology has arisen, it must be promptly eliminated in the acute period. Compliance with the timing of therapy ensures a favorable outcome of the disease. In such a situation, relapses practically do not occur. If the patient has concomitant diseases, habitual displacements may recur. Loading the affected jaw bone too early often causes difficult joint mobility. Therefore, the patient must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Complete rehabilitation is the key to the effectiveness of treatment and the prevention of complications.