Molluscum contagiosum in children
Molluscum contagiosum is more common in children than in adults. Children up to one year old practically do not get sick with molluscum contagiosum. This is due to the fact that in the first year of life the child’s circle of contacts is small: the child moves in a limited space, often specially prepared for him and under the strict supervision of adults, without trying to come into contact with other children. But as soon as a child begins to actively communicate and independently explore the world, the threat of becoming infected with molluscum contagiosum increases sharply.
The peak incidence of molluscum contagiosum in children occurs between the ages of 2 and 6 years. Immunity at this age is still weak. Children become infected through toys or dirty hands. The virus penetrates the skin in the place where the integrity of the skin is damaged - through wounds, abrasions, cracks. Children's skin is delicate and sensitive, and the activity of a preschool child is great. As a result, numerous microtraumas occur, opening the way for infection. Cases of infection with molluscum contagiosum while swimming in the pool have also been described.
From 6 to 10 years, the incidence of molluscum contagiosum decreases. Instilling household hygiene skills is of great importance. The sooner your child starts taking care of clean hands, the better.
Symptoms of molluscum contagiosum
The incubation period of the disease ranges from two weeks to several months, but most often the rash appears on the 14-15th day.
At first, single rashes appear, then there are more of them. Molluscum contagiosum can affect any area of the skin except the palms and soles. In children, exposed areas of the arms and legs, as well as the face and neck are most often affected. In adults, the genital area and the inner thighs are most often affected.
In the typical form of the disease, the rashes are located only in one anatomical area; in the generalized form, they spread throughout the body.
Rash
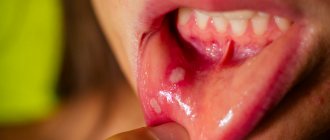
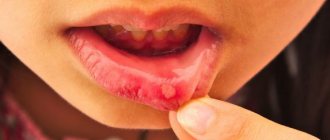
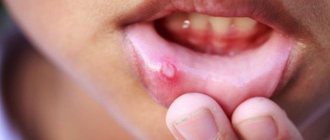
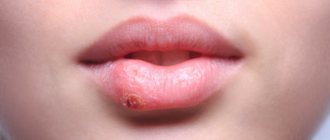
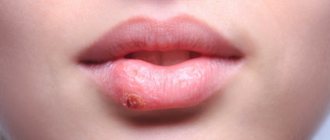
The elements of the rash look like protrusions (papules), firm and painless to the touch, pink or flesh-colored, with a pearlescent top. In the center of the papule there is a small depression, from which, when pressed, a white pasty mass is squeezed out. Papules have a round or oval shape, the size usually varies in the range of 2-5 mm, but sometimes the nodules merge, and then such formations can reach a diameter of 1 cm or more.
More about the symptom
Itching
In some cases, the rash is accompanied by itching, which intensifies when scratching. Under no circumstances should papules be scratched, as this can lead to a bacterial infection. The presence of a bacterial infection is indicated by redness of the skin around the papules, swelling, and suppuration.
More about the symptom
Hemangiomas in children
My one-and-a-half-year-old patient had a bruise under his eye.
- Where is he like that? Fell? - I asked. Unfortunately, being a pediatrician involves a certain amount of suspicion. “It’s not a bruise, he didn’t fall,” my mother answered tiredly. -Have you forgotten again? He has had this since birth, a hemangioma. I was confused. I had seen the boy once or twice before and, to be honest, had already forgotten about his peculiarity.
Taking a closer look, I was convinced that it was really not a bruise. A slightly convex, nodular formation clearly protruded above the surface of the skin. Its edges were uneven and seemed to consist of several small islands.
Infantile hemangiomas are benign vascular tumors growing from the endothelium. Hemangiomas come in various sizes - from millimeter to huge segmental ones, covering almost half of the head. The color of hemangiomas is usually red or bluish. Most often they occur on the head and neck, but can be on any part of the skin, mucous membranes and even on internal organs. Differential diagnosis must be made with other vascular formations.
There are single and multiple hemangiomas. Superficial, deep and combined hemangiomas are also distinguished.
Methods for diagnosing molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum can be confused with manifestations of other diseases, including serious ones such as syphilis or cancer. Also, the activity of the molluscum contagiosum virus increases with a decrease in immunity, so in 20% of cases molluscum contagiosum accompanies HIV infection. This means that when rashes appear that correspond to the description of molluscum contagiosum, a medical examination is required to rule out such options.
When contacting a dermatologist, the doctor will examine the patient, make a diagnosis and suggest a treatment method.
Inspection
In most cases, the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is made by a dermatologist based on the results of an examination of the patient.
PCR diagnostics
Since HIV often accompanies molluscum contagiosum, PCR diagnostics for HIV can be prescribed.
More information about the diagnostic method
Serological blood test
When molluscum contagiosum is detected in adults, a serological blood test is prescribed to identify sexually transmitted infections (hepatitis B and C, HIV, syphilis, etc.).
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Soon after the birth of a child, parents may notice a formation on the skin of blue, red, pink color, which can quickly grow, capturing new territories on the baby’s tiny body. Most likely, this is a benign vascular tumor, a hemangioma, with all the inherent signs of a benign tumor.
A feature of the course of vascular neoplasms - hemangiomas in young children is the unpredictability of their “behavior”. A punctate hemangioma of the cheek in a one-month-old baby can turn into an extensive and deep tumor with a complex anatomical localization and without a tendency to stop growth within 2-3 weeks. This leads to disruption of the functions of various important organs responsible for vision, hearing, breathing, etc. Due to the unpredictability of the development of hemangiomas in children under one year of age, hoping for independent resorption of large and deep hemangiomas using expectant management means voluntarily taking a conscious risk of the health and life of the baby. It is necessary to distinguish between a vascular tumor and other formations: medial spot, nevi Unna, rosacea, etc.
Therefore, if you find any spots, spots, or blood vessels on the baby’s body, immediately contact pediatric surgeons and oncologists.
Why does hemangioma appear?
It is believed that a tumor as a disease occurs as a result of the body’s reaction to harmful external and internal influences. Therefore, to prevent vascular tumors during pregnancy, simple rules must be followed: contact with harmful carcinogenic substances should be completely avoided; You should not smoke, you should not be in a room where people smoke or have smoked; Uncontrolled use of any medications is strictly prohibited. There is an opinion that the appearance of hemangiomas is associated with complex disorders of intrauterine development of the fetus, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy, when the vascular system of the unborn baby is formed. During this period, emotional and chemical stress, low-frequency electromagnetic influences, injuries, infections, hormonal disorders and any unfavorable factors of a physical or chemical nature that have embryotoxic properties are especially dangerous. Particularly dangerous factors of a physical nature include ultraviolet radiation (solariums!), ionizing radiation, mechanical injuries and elevated temperature in a pregnant woman with long-term exposure. Among the biological factors include viral and bacterial diseases, decreased immunity, and parasitic infections of the mother during pregnancy. Sometimes it is enough to dye your hair in the early stages of pregnancy and the child develops a “stork’s kiss,” as hemangiomas are often called.
Experts are still debating whether hemangiomas are true tumors or a congenital malformation of the vascular system. These tumors have the ability to self-resorb and malignant degeneration. Nowadays, hemangiomas occur in every tenth newborn. In girls it is 2-3 times more common than in boys. If a child already has one hemangioma, then during the first six months of life, 75% of such children may develop hemangiomas in other parts of the body. Recently, the number of children with multiple hemangiomas has increased to 43%. Hemangiomas can grow unevenly. Along with rapid growth, often leading to severe irreversible damage, sometimes there is a complete lack of growth, and in some rare cases even reverse development.
What complications can occur with hemangiomas?
The vast majority of hemangiomas do not have complications. However, in some cases, ulcers and ulcerations occur on them; some hemangiomas are complicated by bleeding. A feature of the course of hemangiomas in the perineum and external genitalia is their tendency to frequent ulceration. Contamination of these areas with urine and feces, friction with diapers or clothing can lead to the formation of ulcers, drip bleeding, and infection. In cases of internal hemangiomas, for example, the larynx or the inside of the nasal passage, the breathing process is complicated. Vascular tumors of the eye can cause occlusion and amblyopia. Hemangiomas of the oral mucosa and lip area disrupt the processes of sucking and digestion. With very large tumors, cardiac dysfunction may occur due to the large amount of blood that must be pumped into the excess blood vessels of the hemangioma. Angiomas adjacent to the bone can also lead to bone erosion. Children with hemangiomas may develop thrombocytopenia due to the death of platelets in the vascular tumor. There are gigantic hemangiomas of skeletal muscles, consisting of thin-walled capillaries infiltrating the entire limb.
How to assess the condition of hemangioma in a child yourself?
Signs of growth, stabilization and regression:
1.Color - a fast-growing tumor is bright red, tense, bulging, the surface is shiny or peeling
2.rapid increase in tumor size: dynamic measurement of the tumor is necessary. You can transfer the contours to cellophane and get a stencil that reflects its size and area. Mark on the stencil the date and overall height of the child at the time of measuring the tumor or the length and circumference of the body part at the measurement site. After 3-4 weeks, take a repeat measurement to create a repeat stencil, observing the same position of the child’s body (standing, lying, sitting). Re-enter the date and information about the child’s height. The assessment is carried out by simple mathematical comparison. If the increase in the size of the hemangioma area in millimeters is equal to or exceeds in digital value the number of centimeters by which the child has grown, then this is an indicator of the progressive development of the neoplasm itself. Such a growing hemangioma requires immediate treatment.
A sign of stabilization of growth or the beginning of regression is its pallor, a decrease in volume, the appearance of areas of whitish coloring in the mass of the tumor - a symptom of “fly agaric”.
If there is a hemangioma, in the interests of the child, taking into account the unpredictability of its development, it is necessary to carry out therapeutic or preventive measures, and the sooner the better.
What treatment methods for hemangiomas exist?
Currently, more than 60 methods of treating hemangiomas are known: surgical, sclerosing, electrocoagulation, radiation, hormonal, laser, cryogenic, medicinal, etc. Each of the methods has certain advantages and disadvantages, and the question is which one is the most rational with in terms of simplicity, accessibility, convenience for the patient, effectiveness in terms of cosmetic and functional results. The choice of treatment method should be based on a comprehensive assessment of each case, taking into account the type, location, clinical form, size, nature of the hemangioma, and the age of the patient. Conservative and invasive methods are used to treat hemangiomas. Of the conservative methods, the most commonly used are hormone therapy, treatment with propranolol, radiation methods, and photochromotherapy. Among the invasive methods, the most popular are surgical excision, cryotherapy (cold treatment), electrocoagulation, laser therapy, sclerotherapy, and embolization of regional vessels. Unfortunately, each of these methods does not provide a guaranteed cure, but has a number of side effects. At the Oncology Research Institute in Rostov-on-Don, a non-invasive, painless method of treating hemangiomas in children was developed and patented: photochromotherapy (a treatment method in which a certain modified red light). This medical technology is protected by Russian Patent No. 2240159 for the invention “Method for treating skin tumors in children under one year of age” and has been widely and successfully used for more than 10 years.
Photochromotherapy - the use of the method is based on the ability of monochrome red light to induce photobioadaptive processes in the child’s body, leading to the activation of humoral factors regulating local blood flow and induction of reparative tissue reactions, which contributes to the stabilization of growth and regression of vascular neoplasms of the skin. This technique is non-invasive and allows it to be used for both therapeutic and preventive purposes. The developed method for treating skin tumors is suitable for children of any age - both up to one year of age and older.
Contraindications:
individual intolerance to light therapy, severe neurological symptoms, acute infectious diseases of unknown origin. Considering the simplicity, harmlessness, painlessness and high efficiency of this method, it can be actively recommended for the treatment of hemangiomas in children.
Errors in the treatment of hemangiomas
The traditional mistake is to wait and see
in the hope of spontaneous resorption. It is not possible to hope for spontaneous regression of large and deep hemangiomas due to their rapid growth or other complications.
Another common mistake is prescribing troxevasin
to the area of hemangiomas. Monitoring of children after the administration of troxevasin in the early stages showed stimulation of tumor growth in 98% of children. This also applies to Lyoton and other heparin-containing drugs. One of the erroneous prescriptions is to apply ice; after such an effect, a phase of sharp vasodilation begins, and the hemangioma grows. There is no point in using Vishnevsky's liniment, and the use of decoctions of St. John's wort, primrose, oats, bee products, acetic and sulfuric acids can significantly worsen the process, lead to dangerous bleeding and tumor growth. The obvious harm is lost time, a neglected process.
What should children with hemangiomas be wary of?
1. Injuries . Danger of bleeding in case of injury - call an ambulance if there is bleeding. It is necessary to apply a hemostatic sponge and press firmly. Cold compress - ice cubes, preferably made from a decoction of oak bark, but you can keep it for no more than 10-15 minutes, then remove it for 15 minutes and repeat the procedure. Hydrogen peroxide 1-2% and antiseptic disinfectants (miramistin or chlorhexidine) are used.
2. Sun. _ You should be wary of direct sunlight. You should take a walk in the summer until 10 a.m. and from 6 p.m. From 11 a.m. to 5 p.m., direct sunlight causes irreparable damage to the skin. Before a walk in the sun, give your baby salted water or tea with lemon. Use sunscreen.
Sunscreens for babies: AVEN: sunscreen for babies spf 50+, Garnier AMBRE SOLER: sunscreen milk-screen baby spf 50, spray, sunscreen color, control for babies, spf30, Vichy Capital Soleil, baby sunscreen spray, spf 50, sunscreen hypoallergenic baby cream, spf 30. La Roche Pose antiheliosdermoKIDs: milk (for babies), spf 50. Mustella sunscreen milk for babies spf 50+, sunscreen spray for children, spf 30. Uriage baby sunscreen milk for hypersensitive skin spf50 spf 30. Floresan, sunscreen milk for babies spf25. Bübchen sunscreen spray for children spf 30, sunscreen milk for children spf 20, sunscreen foam for children spf 15 and 25. Nivea sun sunscreen spray color for children spf 30, children's sunscreen lotion spf 50+. Oriflame children's sunscreen spf 40, spray spf30."Our Mother" Russia children's sunscreen cream spf 15, children's sunscreen mousse with a water-repellent effect, spf 20, children's sunscreen milk spf15."Our Sun", Russia children's sunscreen cream spf 20.1. You need to choose the right protection product: creams are useful for children For those with dry skin, sprays are most convenient.2. Check safety: apply the cream behind the ear, on the elbow and knee bends, observe the skin and the child’s reaction to the smell for 24 hours. 3. Apply the product half an hour before going outside. 4. Distribute correctly over the entire surface of the skin - colored sprays are convenient. 5.Storage sunscreen in the refrigerator for a maximum of six months.
3. Bathing . It is not recommended to bathe in hot water up to 37 degrees, do not bathe in a manganese solution, use neutral soap on the hemangioma area once every 10 days.
4. Before recovery, it is not recommended to do routine preventive vaccinations, since the possibility of provoking the rapid growth of hemangiomas in children after vaccination cannot be ruled out.
Photochromotherapy.
This is a type of treatment with visible electromagnetic radiation (light quanta) with a certain wavelength. The clinical use of red light with a wavelength of 0.67 microns allows for a therapeutic effect due to the photolytic breakdown of biomolecules, which leads to the growth of free forms with high biological activity. This medical technology is protected by RF patent No. 2240159 for the invention “Method for treating skin tumors in children under one year of age.” The technique is non-invasive, which allows it to be used in the treatment of early infants with hemangiomas of critical locations (head and neck, genitals, mammary glands, places of natural skin folds, articular surfaces. The high efficiency of the FCT method lies not only in achieving a local therapeutic result (photo-induced regression of the vascular tumor itself), but also in increasing the overall protective and compensatory potential of the child, achieving an immunostimulating and anti-stress effect on his body.
Treatment methods for molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum should be treated by a doctor. You should not try to remove papules yourself - this can lead to bacterial infection.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum depends on a number of factors, primarily on the stage of development of the disease, the severity of symptoms and the state of the patient’s immunity. The following methods can be used:
Instrumental removal
Papules can be removed instrumentally, followed by treating the wound with antibacterial agents.
Credestruction
Cryodestruction is the removal of papules using exposure to low temperatures. Papules are treated with liquid nitrogen. Tissues treated in this way freeze and die.
Radio wave removal
Molluscum contagiosum papules can be removed using the radio wave method (using the Surgitron apparatus) and using a laser.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is the effect of high-frequency current on papules. It is popularly described as “cauterization with electricity.” At the moment of discharge, a local strong thermal effect occurs, the tissues coagulate, which virtually eliminates the risk of infection at the treatment site.
Conservative treatment
The course of treatment for molluscum contagiosum may include conservative treatment with ointments and creams, as well as taking antiviral drugs (if the affected area is large).
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating