Dry throat is one of the most unpleasant symptoms indicating diseases of the nasopharynx and sluggish painful processes inside the body. This is a fairly broad symptom that accompanies many diseases - from the common cold and ARVI to an acute allergic reaction or diabetes. Despite its apparent insignificance, a dry throat can be a marker indicating the presence of serious health problems. A patient suffering from a dry throat becomes more irritable and psychologically susceptible to pathogens, provoking the appearance of increasingly painful reactions.
Dry throat - symptoms of the phenomenon
Dry throat is a rather vague formulation; the main symptoms of this painful process can be several factors from this list:
- General feeling of fatigue, weakness.
- Hoarse voice, tension in the vocal cords.
- Pain in the throat muscles, worse when talking.
- A painful dry cough during which no mucus is coughed up.
- An increase in temperature due to the body's immune response.
- Enlarged tonsils and severe redness.
In addition, dry throat is often accompanied by symptoms that accompany a cold - such as a runny nose, swollen lymph nodes, and pronounced inflammatory processes.
Doctor MOM® for the treatment of cough and sore throat
In the complex treatment of cough and sore throat, the use of herbal medicines from the Doctor MOM® line - syrup and herbal cough lozenges - is indicated. Thanks to the unique1 “FITO BRONHO formula”2 based on medicinal plant extracts, the products in the Doctor MOM® line have a complex effect, helping to both relieve unpleasant symptoms and eliminate their cause - inflammation.
The main actions of Doctor MOM® syrup and herbal cough lozenges are:
- Eliminating the cause of cough – inflammation;
- Removing infection from the body3;
- Combating unproductive and unproductive cough.
Dry throat due to bacterial infections
One of the most common causes of dry throat. Infectious diseases accompanied by fever, cough, runny nose and other unpleasant symptoms most often cause a feeling of dry mouth due to damage to the soft tissues of the oral mucosa. In this case, it is unnecessary to fight dry mouth - you need to eliminate the cause of the disease, not its symptoms. By focusing on fighting the infection with antibiotics and other medications, you will not only increase the body's resistance level, but also get rid of all unpleasant symptoms in one go.
Causes of dry mouth
Both certain physiological factors and various pathological conditions lead to subjectively felt drying of the epithelium. Natural causes of dry mouth are the consumption of pickles, herring, and other foods containing a lot of salt. Drying of the mucous membranes occurs when there is insufficient humidity in the room. Dryness of the mouth of varying intensity, associated with sympathetic release, is possible during conflicts, quarrels, fear, and chronic stress.
Sialadenitis
The most common cause of severe xerostomia is inflammation of the salivary glands. The pathological process is initially one-sided, but after a few days the inflammation spreads to the opposite side. Patients complain of swelling in the area of the salivary glands, increased body temperature, and painful opening of the mouth. Eating is difficult due to pain and dryness of the epithelium, which is caused by the cessation of secretion from the affected gland. Chronic sialadenitis is characterized by moderate pain and normal size of the salivary gland.
Other diseases of the salivary glands
Complaints of dry mouth are made by patients with mumps, a viral infection that primarily affects the parotid salivary glands in children, and less commonly, the submandibular and sublingual glands. The symptom is combined with general intoxication, pain and swelling of the glands on both sides, deforming the contours of the patient’s face. Severe xerostomia with high temperature, swelling, hyperemia in the area of inflammation are symptoms of a salivary gland abscess, complicating the course of sialadenitis and sialolithiasis.
Sjögren's disease
Dryness of the oral mucosa against the background of insufficient secretion of tear fluid, burning in the eyes, drying and peeling of the skin is typical for autoimmune damage to the glands in Sjögren's disease. The normal secretion of saliva is prevented by the infiltration of the ducts by lymphocytes and plasma cells, an autoimmune reaction with the formation of antibodies to the glandular epithelium. The parotid glands usually increase symmetrically in size; upon examination of the mouth, bright pink redness of the mucous membrane, contact bleeding, folded tongue, and multiple caries are revealed.
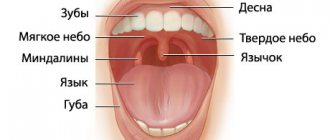
Diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx
The close location of all anatomical structures, general innervation and blood supply cause disruption of the salivary glands when various organs of the oropharynx and nasopharynx are affected. Dryness of the epithelium is observed during inflammatory processes, some rare pathological conditions - glossalgia, parotid fistula, galvanosis. Common causes of xerostomia are:
- Stomatitis
. With an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, dryness is combined with pain when eating, bad breath, and bleeding. The catarrhal form is characterized by redness and swelling; in the aphthous form, blisters and erosions form. With allergic stomatitis, hyperemia, ulcers, and erosions are determined. In older people, prosthetic stomatitis is possible. - Candidiasis
. When epithelial cells are damaged by fungi of the genus Candida, a white coating appears on the tongue and mucous membranes of the cheeks, a burning sensation and severe dry mouth are disturbing. Cracked lips are typical. The disease should be distinguished from hairy leukoplakia, which has a similar clinical picture, but affects patients with immunodeficiencies when exposed to a virus. - Hypertrophic rhinitis
. When the epithelial layer of the nasopharynx is thickened and the airways are partially blocked, patients breathe predominantly through the mouth, especially at night. This leads to severe dryness, which reaches its maximum intensity in the morning. A similar mechanism for the development of xerostomia is observed in nasopharyngeal cancer.
Infectious diseases
The appearance of dry mouth is characteristic of intestinal infections, especially those accompanied by watery diarrhea and leading to severe dehydration. Xerostomia is pathognomonic for cholera, a gastrointestinal form of salmonellosis. It is possible to identify a symptom during the febrile period of other infectious pathologies - brucellosis, psittacosis, Crimean fever. The oral mucosa dries out during the polyuric stage of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, which is caused by dehydration due to the release of up to 5 liters of urine per day.
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Xerostomia with thirst and polyuria is a specific symptom. In patients with type 1 diabetes, microangiopathies and elevated blood glucose levels are predisposing factors to dry mouth. In elderly patients with insulin-dependent diabetes, the symptom is considered a manifestation of diabetic polyneuropathy. In addition to dry mouth, the patient is concerned about constant weakness, itchy skin, rashes, pustules, and fungal skin infections. Similar symptoms occur with steroid diabetes.
Neurological dysfunction
The prerequisites for dryness of central origin are considered to be incoordination of the nervous system, disruption of connections between higher cortical structures and the vegetative nuclei of the medulla oblongata. The symptom is observed in patients with neuroses, panic attacks, and organic anxiety disorder. Drying of the oral mucosa is characteristic of peripheral autonomic failure and polyneuropathy of pregnancy. Xerostomia develops in Lambert-Eaton syndrome, an autoimmune disease that affects the presynaptic membranes of neurons.
Gastroenterological diseases
Dry mouth is a common sign of damage to the pancreas. In case of fibrosis of the organ, it is caused by secondary diabetes; in case of pancreatitis and a split pancreas, it is caused by digestive disorders. The symptom is detected in chronic gastritis and is combined with epigastric pain, stool instability, nausea and vomiting. Dryness, which is accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, often becomes a sign of hepatitis.
Urological pathology
In diseases of the urinary system, dry mouth is usually caused by two mechanisms: dehydration due to polyuria and the accumulation of toxic protein compounds in the bloodstream. With renal colic caused by obstruction of the ureter or pyelocaliceal system, the situation is aggravated by pain with a pronounced sympathoadrenal reaction. In this condition, in addition to dry mouth, unbearable pain in the lower back, nausea and vomiting, and painful tenesmus are disturbing.
Often, xerostomia is provoked by nephrosclerosis, polycystic disease, and other severe kidney diseases with increasing chronic renal failure. The combination of dryness with swelling and lower back pain is characteristic of nephritic syndrome of various etiologies. Drug-induced nephropathy is often accompanied by drug-induced xerostomia. The feeling of dry mouth is typical of paraneoplastic nephropathy, which occurs with severe metabolic and immunological disorders.
Intoxication
Xerostomia in case of exogenous poisoning and endotoxemia is provoked by disruption of all body systems, discoordination of the nervous and humoral regulation of salivary secretion processes. In case of foundry fever and other poisonings involving inhalation of aggressive substances, the situation is aggravated by the direct damaging effect of vapors on the oral mucosa. The prerequisites for dry mucous layer are:
- Bad habits.
Xerostomia is observed during hangover syndrome, which is caused by severe intoxication of the body. The symptom is also typical of nicotine addiction, in which it is caused by constant irritation of the epithelium with cigarette tar. Dry mouth in combination with convulsions and hyperthermia can be a sign of poisoning with alcohol surrogates. - Cathinone abuse
. Abuse of norepinephrine provokes an increase in the activity of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, which is manifested by dilated pupils, dry mucous membranes, and psychomotor agitation. Over time, the euphoric effects of taking the drug decrease, and encephalopathy increases.
In cancer cachexia, xerostomia occurs as a result of gross disturbances in the functioning of the body caused by endogenous intoxication by tumor metabolic products and decaying cancer cells. The condition is accompanied by dyspeptic disorders, exhaustion, severe anemia, changes in emotional and mental status, and insomnia. Dry mouth worries patients with massive intoxication of the body by tissue decay products during gangrene.
Metabolic and endocrine disorders
The secretion of saliva has not only nervous but also humoral regulation. Various deviations from normal levels of hormones and biologically active substances cause disturbances in the functioning of all organs, including the salivary glands. The appearance of dry mouth mucosa is associated with secondary fluid losses that develop due to disturbances in water-salt metabolism and homeostasis. Xerostomia is potentiated by endocrine disorders such as:
- Algodismenorrhea
. Painful menstruation can occur at different ages, but most often dysmenorrhea is diagnosed in adolescents during the period of formation of sexual function. Complaints of dry mouth are due to the increased influence of prostaglandins on the level of salivation. With algodismenorrhea, pain is accompanied by dyspeptic disorders and asthenia. - Hypercalcemic crisis
. Xerostomia in this disorder is associated with dehydration accompanied by polyuria, repeated vomiting and diarrhea. An increase in calcium levels is manifested by abdominal cramps, muscle weakness, and severe thirst. Similar symptoms occur in Burnett syndrome, a dysmetabolic pathology with hypercalcemia and metabolic alkalosis. - Hypovitaminosis
. The combination of angular cheilitis and dry lips and oral cavity is typical for pyridoxine (vitamin B6) deficiency. For hypovitaminosis, a change in the appearance of the tongue is specific - it becomes bright red with a shiny “varnish” surface due to atrophic processes in the epithelial layer. - Pheochromocytoma
. With a tumor of the adrenal medulla, dry mouth is caused by increased endocrine function with a significant increase in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the blood. These substances enhance the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, which inhibits the secretion of the salivary, gastric and intestinal glands.
Acute and emergency conditions
Xerostomia in critical conditions is caused by several mechanisms: severe dehydration, disturbances of neurohumoral regulation, reflex reactions due to excessive irritation of pain receptors. These pathologies are typically characterized by a severe and extremely serious condition of the patient, dysregulation of basic vital functions. The patient requires emergency medical care. Dry mouth is caused by:
- Bleeding
. Dryness of the oral mucosa during blood loss is promoted by significant dehydration of the body. The leading signs are pale skin, tachycardia, and a drop in blood pressure. The symptom develops both with internal bleeding and as a result of external blood loss. Ruptures of aneurysms of the renal and other arteries, leading to collapse, are life-threatening. - Acute abdomen syndrome
. Xerostomia is considered one of the manifestations of catarrhal appendicitis and other surgical conditions - obstetric peritonitis, biliary peritonitis, mesadenitis. The sign is pathognomonic for the initial phase of paralytic intestinal obstruction. Dry mouth is combined with severe abdominal pain and symptoms of peritoneal irritation. - Cardiovascular pathology
. The appearance of xerostomia is associated with autonomic reactions to severe pain in the heart or severe hemodynamic disturbances. Dry mouth is observed during hypertensive crisis and angina pectoris. The symptom is accompanied by headaches, blurred vision, and disturbances of consciousness. - Traumatic shock
. Symptoms of massive soft tissue injuries and bone fractures are explained by gross changes in autonomic reactions and a collapsing state due to severe pain. Pronounced pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, xerostomia, cold sweat. Impaired consciousness and lethargy are possible. - Fainting
. The post-syncope period of syncope is characterized by dry mouth and hyperhidrosis caused by dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. A similar mechanism for the occurrence of symptoms is observed after sunstroke. In this case, in addition to dry mouth, intense headaches, flashing “spots” before the eyes, and increased breathing are observed.
Smoking
Unfortunately, despite numerous warnings from the Ministry of Health, there are still a lot of people who smoke in Russia. Over many years of addiction, they become accustomed not only to the dubious taste of tobacco, but also to the symptoms accompanying its use - a feeling of bitterness, cough, dry mouth. The complete disappearance of dry mouth in a smoking patient is almost impossible - constant inhalation of hot smoke dries out the mucous membrane and leads to the formation of dense lumps of mucus, making swallowing and breathing difficult. If the patient is not ready to give up a bad habit, but wants to get rid of an unpleasant symptom, tissue mineral therapy is carried out - the oral mucosa is moisturized and cleansed, accumulated sputum and mucus are dissolved and disinfected by medication, after which the patient experiences relief and is relieved for a while from a constant feeling of dryness in the throat.
Glossodynia - what is it?
Burning mouth syndrome, or glossodynia, is discomfort and even pain in the mouth, tongue, gums, and mucous membranes, which is accompanied by a feeling that the mouth has been scalded with boiling water or medicine. This condition may be accompanied by dry mouth (xerostomia) and loss of taste or smell. Sometimes people with a burning sensation in the mouth and tongue complain that they cannot feel anything - not even the temperature of the food [1].
This condition develops suddenly, but may begin with a slight tingling sensation in a limited area of the mouth, and then spread further or intensify only in that same area. Symptoms of this condition are described by subjective complaints; they can be combined or single:
- feeling of burned mucous membranes, burning pain. Most often, a burning sensation in the oral cavity is felt on the tongue, especially along its front edge and sides, as well as on the lips, on the inside of the cheeks, in the throat or throughout the mouth;
- a feeling of tightness, burning and dryness of the mucous membrane in the mouth, from severe to occasional;
- change in taste, up to the complete loss of this sensation;
- the appearance of an unusual taste in food and drinks, such as bitterness or metallic;
- decreased or loss of sense of smell;
- a feeling that sensitivity in the mouth has disappeared, the mouth seems to be frozen [2].
Symptoms of burning the oral mucosa can manifest themselves in different ways throughout the day over several days and even months. Sometimes they begin at a certain time of the day, for example after waking up, and by the end of the day they decrease or, conversely, intensify in order to disappear imperceptibly and return again in the morning. The subjective characteristics of pain associated with burning mouth syndrome can vary significantly. Among people with similar diseases and other life factors and conditions, the symptoms of this condition, their intensity, duration and prevalence can vary greatly [2].
Separately, it should be noted the great social and personal significance of glossopyrosis. The fact is that sensations in this state can affect the quality of life in all its aspects: nutrition, sleep, rest and restoration of physical strength, communication, reactions to some irritants. Those suffering from constant pain cannot get enough sleep or rest peacefully; they have difficulty eating and communicating. In an attempt to find the source of the problem and somehow eliminate it, they begin to pay a lot of attention to this condition. Thus, many note that with the appearance of glossopyrosis, spots have formed in their mouth, the papillae have enlarged, or the tongue has begun to look unusual. As practical observations have shown, in 50% or more cases such changes are actually normal, are in no way related to burning mouth syndrome, and the person had them before, he just didn’t notice them [2].
This is very important for diagnosis, because the appearance of some real clinical signs, obvious manifestations of trouble may indicate that burning mouth syndrome did not arise on its own, it is not idiopathic, but there are some problems, prerequisites for its occurrence [3].
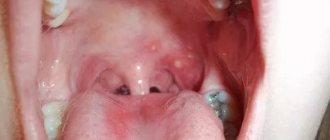
Acute tonsillitis
Tonsillitis, or tonsillitis, is an infectious disease that results in acute inflammation of the tonsils. This is not only a very unpleasant disease in terms of its course, but also a very contagious phenomenon - you can get a sore throat simply by airborne droplets from any unsuccessful contact with an infected person. Inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx lead to severe dryness in the throat. As with colds, to get rid of a dry throat with a sore throat, you should treat the cause of the disease, not its symptom.
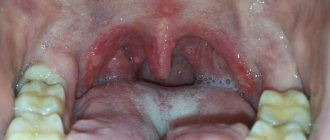
Differences from the subatrophic form
Subatrophic pharyngitis, the symptoms of which are minor, is the initial stage of atrophic pathology. There is no thinning or irreversible change in tissue yet. Subatrophic pharyngitis is dangerous because pronounced symptoms do not always appear, which is why many patients do not seek timely medical help. As a result, the start of therapy occurs at a time when the mucous membranes are already seriously damaged and cannot recover, and as a result, treatment is only supportive.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an infectious disease that is accompanied by severe damage to the oral mucosa and lymph nodes. Rarely occurs alone - most often pharyngitis is accompanied by acute inflammatory processes. A patient suffering from pharyngitis is faced not only with a dry throat, but also with an unpleasant soreness and tickling, a sensation of a foreign element in the nasopharynx, as well as a general feeling of fatigue and malaise. Most often, to eliminate the unpleasant consequences of pharyngitis, they resort to complex treatment - simultaneously with the use of medications, the patient is prescribed mineral therapy to normalize the condition of the mucous membrane in the pharynx, which is supplemented by herbal medicine (the use of medicinal herbs and infusions to irrigate the affected area of the pharynx).
Causes of sore throat
Inflammatory. The most common cause of a sore throat and dry cough is acute respiratory diseases. These are infections caused by various pathogens:
- viruses (parainfluenza, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, enterovirus);
- bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci);
- fungi (for example, yeast of the genus Candida).
Infections are transmitted mainly by airborne droplets, as well as by contact. Their maximum incidence is observed in the cold and damp seasons. An infectious agent, penetrating the body, is fixed on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, where, in response to its penetration, a protective reaction in the form of inflammation is triggered. Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane develop, leading to discomfort, pain and sore throat, causing coughing.
Non-inflammatory. A sore throat and dry cough can also occur with non-inflammatory damage to the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract:
- for allergic pharyngitis, laryngotracheitis, bronchitis;
- thermal irritation of the respiratory tract (inhalation of hot or cold air);
- irritation from chemical agents (ingress of particles and vapors of varnishes, paints, household chemicals, gasoline, etc.);
- strong vocal stress (“lecturer’s” laryngitis);
- smoking;
- injury or foreign body entering the lumen of the larynx, pharynx, trachea.
In addition to respiratory diseases, tickling and dry cough may occur:
- against the background of the use of certain medications (ACE inhibitors, diuretics);
- with heart failure;
- hypothyroidism and after surgery on the thyroid gland (damage to the laryngeal nerve leads to hoarseness, sore throat without coughing);
- diabetes mellitus;
- neuroses.
Allergic reaction
An allergic reaction of varying severity is also often the cause of an unpleasant feeling of dryness in the throat. Associated symptoms include difficulty breathing, severe pain when swallowing or breathing, and many other signs. Since at this stage of development of medicine, allergies cannot be treated, but are chronic and haunt the patient throughout life, there are several ways to avoid dry mouth:
- Using antiallergic drugs to relieve allergic reactions.
- Integrated use of mineral therapy and herbal medicine to restore normal functioning of the throat.
- Exotic treatment methods for the restoration of mucous membranes in especially critical cases - laser therapy (in this case, a photosensitive gel is applied to the damaged tissues of the throat, which, under the influence of a laser, releases oxygen and saturates the soft tissues with it, promoting their regeneration and destroying pathogenic bacteria), ultrasound and other treatment methods .
Diagnostics
The main methods for diagnosing the disease are collecting anamnesis and performing pharyngoscopy. However, such a diagnosis is not enough to determine the cause of the pathology. After the diagnosis is made, the doctor refers the patient for examinations in order to identify the factors that led to the pathology. If you look at a photo of a sore throat with atrophied mucous membrane, it will help even a non-specialist to visually recognize the pathology in life.
Without fail, a person is sent for a consultation with a gastroenterologist, since it has been precisely proven that most of the atrophic pathologies of the pharyngeal mucosa develop due to the reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus. Sometimes the patient himself does not notice this problem, and only a specialist can determine it.
If no disorders of the gastrointestinal tract are established, a blood test for hormones and a smear to identify pathogenic microflora are indicated. In addition, a referral may be given for an allergy test.
When there is concern that the patient has begun to develop cancer, a biopsy of throat tissue is performed. It can be performed independently or in parallel with pharyngoscopy. Thanks to the procedure, a malignant process can often be detected at an early stage, when therapy is still possible.
Dry throat due to vascular pathologies
Diseases of the circulatory system and vascular pathologies are almost always accompanied by a painful feeling of dryness in the throat. In this case, the most acute symptom of the pathology is treated first. As soon as the danger to human life and health has disappeared, the attending physician can begin to get rid of dry throat. Most often, lymphotropic or capillary therapy is used for this. The essence of these methods is to normalize the functioning of capillaries that provide circulation of blood, lymph and nutrients in the damaged area of the throat. The body is saturated with useful substances, releasing large amounts of oxygen and ozone, which are destructive to most harmful bacteria. At the same time, the therapy is also of a general strengthening nature - it not only relieves the patient of the feeling of dry throat, but also prevents the appearance of similar symptoms for a long time, protecting soft mucous tissues from damage.
Disease prevention
Despite the fact that dry throat itself is not an independent disease (it is just a symptom), it can and should be avoided by promptly implementing a set of preventive measures to maintain the health of the oral mucosa. You can do this as follows:
- Do not neglect daily oral hygiene. When brushing your teeth and gargling, a person easily gets rid of many pathogenic bacteria, which can cause complications and even an infectious disease if not treated properly.
- Monitor the condition of the throat mucosa. If you observe the first signs of dryness or pain, immediately consult your doctor.
- Avoid unhealthy habits, particularly smoking. Stay outdoors more often; if you need to stay indoors for a long time with dry air, use a humidifier.
- Gargle regularly.
- Conduct herbal medicine at home - prepare plant decoctions and natural teas. They have a beneficial effect on the condition of the oral cavity, relieving a person of dry throat even in the bud of the disease.
Which doctor should I contact?
Dry throat is a fairly common symptom, so there is no clear answer to this question. It all depends on your individual clinical picture. However, if you are seriously concerned about a growing symptom and feel severe dryness in your throat, you should immediately visit an otolaryngologist, or ENT specialist - this is the specialist who deals with the treatment of the throat and will be able to advise you both on the treatment of dryness and on further medical specialist .
Dry throat is a dangerous symptom, without proper attention to which a person is recommended to face significant complications. At the first signs of dry throat, we recommend that you immediately consult your doctor to receive qualified medical care.
Call our contact center at 8 (495) 230 03 09 and we will help you make an appointment with a specialist!