The lips have very thin skin, so they are practically not protected from external influences. Because of this, every person has to deal with various lip diseases at least once in their life. In medicine they have common name: cheilitis
. There are about a dozen varieties of this disease.
Reasons why lip diseases develop
Human lips are very vulnerable, which often leads to redness, irritation, dryness, and even the formation of wounds and crusts. Most often, cheilitis develops under the influence of external factors.
: low temperature, wind, sun rays. Under their influence, the skin around the mouth dries out, which in itself is unpleasant. If you don't do anything about it, the problem will only get worse.
The second factor that causes lip diseases is various allergens. The culprit of the pathological reaction can be both food and cosmetics. Problems in the functioning of the internal systems of the body can also affect the face.
Most often, the delicate skin around the mouth suffers due to hormonal imbalances, fungal and viral infections. Vitamin deficiency, indigestion and general deterioration of immunity can aggravate the situation.
There are also less common causes of lip disease. They usually lead to certain types of cheilitis.
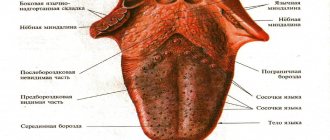
Triangle structure
If you go in order, says Tatyana Romanenko, moving from top to bottom along the arterial blood flow, then the first will be the facial artery (a. facialis). “It is a continuation of the external carotid artery (a. carotis externa). The facial artery enters the face, bending around the inner edge of the angle of the lower jaw at the level of the anterior edge of the masticatory muscle, after which it goes into the thickness of the muscles. On the face, it passes near the corner of the mouth, wing of the nose and anastomoses (connects) in the medial corner of the eye with the artery of the dorsum of the nose (a. dorsalis nasi), which is a branch of the ophthalmic artery (a. ophthalmica), belonging to the basin of the internal carotid artery (a. carotis interna),” notes Tatyana Romanenko.
The therapist also says that, having reached a place just below the corner of the mouth, the facial artery gives off a branch: the inferior labial artery (a. labialis inferior) and next to the corner of the mouth - the superior labial artery (a. labialis superior). They both hide in the thickness of the orbicularis oris muscle (m. orbicularis oris) and anastomose with the arteries of the same name on the opposite side. This creates a single anastomosis, consisting of four arteries of the lips (top and bottom), around the mouth.
Veins accompany it along the entire length of the facial artery and its branches, says the therapist. Top down:
- superior ophthalmic vein (v. ophthalmica superior).
The tributaries of the superior ophthalmic vein are:
- nasofrontal vein (v. nasofrontalis);
in the medial corner of the orbit it anastomoses with
- angular vein (v. angularis), which is the root of the facial vein;
- and the inferior ophthalmic vein (v. ophthalmica inferior); at the medial corner of the eye it flows into the angular vein.
From the medial outer corner of the orbit, the inferior ophthalmic vein goes deep into it, then divides into two trunks. One of them flows into the cavernous sinus (sinus cavernosus) or into the superior ophthalmic vein, the other passes through the inferior orbital fissure and flows into the cavernous sinus (sinus cavernosus), which lies at the base of the skull.
Marks of old age. Why does age-related pigmentation appear? More details
Types of lip diseases
Cheilitis can be divided into several categories. Here are their names:
- exfoliative;
- glandular;
- meteorological;
- actinic;
- atopic;
- eczematous;
- candida.
In addition, there are other diseases that are not related to cheilitis. Therefore, dryness, peeling, crust formation, and a red border near the lips are causes for serious concern and a reason for examining the entire body.
Atopic cheilitis
Atopic cheilitis is sometimes called allergic because it is caused by various irritants. The cause of the disease can be food or cosmetics. It turns out that the allergen affects the skin of the lips both from the inside and outside.
The disease manifests itself as inflammation of the red border of the lips. The skin becomes dry and peels. Cracks, itching and burning may occur.
Most often, children and adolescents suffer from lip allergies. Often it is the only symptom of neurodermatitis or atopic dermatitis.
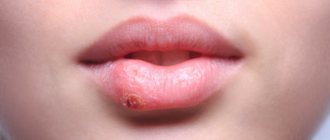
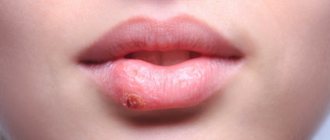
Glandular cheilitis
Glandular cheilitis is an inflammation of the salivary glands, which are located on the surface of the mucous membrane of the lips.
The disease is more common in men over 50 years of age and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- noticeable red dots appear on the lower lip;
- copious secretion of saliva from the inflamed glands, the appearance of “dew drops”;
- dryness, cracks and erosion;
- Bacteria can enter the irritated canals, leading to the formation of pus.
There are primary and secondary forms of glandular cheilitis. The primary disease develops due to genetic predisposition. Secondary lip disease can be caused by lupus, oral leukoplakia, or lichen planus.
Meteorological cheilitis
People have to deal with this disease all the time. Standard chapping, which more often appears in winter, is meteorological cheilitis.
The first sign of the disease is a feeling of skin tightness. In advanced cases, it turns red, dries out, and becomes covered with cracks. This lip inflammation can be treated at home. It is enough to isolate yourself from harmful factors, moisturize and nourish the skin until it is completely restored.
Eczematous cheilitis
Eczematous cheilitis is one of the manifestations of eczema - an inflammatory process of a neuroallergic nature, which most often manifests itself on the face or dry areas of the body. Usually the disease is accompanied by constant dryness and redness. In advanced cases, the skin begins to peel off and become covered with blisters.
The disease often affects the tissue around the lips, so the patient may develop a red border, as in the photo on the right. This area of skin is constantly itchy and itchy.
If the disease is chronic, the symptoms are less pronounced. But in this case, seals appear on the skin.
Actinic cheilitis
Many people believe that lips need to be protected only in winter. Therefore, it is at this time of year that people stock up on moisturizing and nourishing balms to relieve dry and itchy lips. However, delicate skin must be protected not only from frost, but also from the burning sun.
With increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation and prolonged exposure to open areas, actinic cheilitis forms. His symptoms are standard:
- dryness, flaking;
- redness and swelling;
- compaction of individual areas.
If you do nothing, your lips become crusty. This is how the body tries to somehow protect the vulnerable part of the face. This symptom appears less frequently than others.
In advanced cases, ulcers, erosions and small compactions occur around the oral cavity. This condition is precancerous.
Exfoliative cheilitis
The exfoliative form of the disease occurs due to stress and disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. Genetic predisposition plays a major role. If your parents had this disease, there is a high risk that you will develop it too.
Exfoliative cheilitis on the lips occurs in two forms: exudative and dry. In the first case, you can observe the so-called yellow lips (pictured). A dense crust of this shade forms on the skin.
The yellow crust is easy to tear off; this process does not cause much discomfort. There are no erosions or other damage under the crust.
In the dry form of the disease, a crust also forms on the lips, but not yellow, but a lighter shade. The patient is concerned about dry skin, which explains the name of the disease. There is a desire to lick your teeth, but it is better not to do this: you can cause an infection and provoke more irritation.
Candidal cheilitis
If the lips are red, inflamed and crusted with a cheesy coating of white or yellowish color, it means that the cause of these symptoms is candidiasis. If you clean off the plaque, inflamed areas of skin will be exposed. How such a lip disease manifests itself is shown in the photo.
The disease occurs due to the excessive development of the Candida fungus. The pathogen lives on the human mucous membranes constantly, but the active development of the fungus begins only under favorable conditions, which include:
- decreased immunity due to past illnesses or lack of nutrients;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- a sharp change in climate to a hotter and more humid one.
Fungal inflammation of the lips begins externally, but can spread to the internal tissues of the oral cavity, thus leading to candidal stomatitis.
Lip cancer
Many of these diseases, if not given proper attention to their treatment, lead to cancer. Perhaps this is the most terrible disease that can affect the lips and oral cavity.
At first, the symptoms of cancer are unremarkable. The lips will turn red and there will be slight inflammation. The skin may become dry and cracked. If the patient moisturizes and nourishes the affected tissues, but the lips remain sore for several weeks, he should sound the alarm and consult a specialist. Later, ulcers and lumps may appear.
Usually, if treatment is started correctly and on time, the cancer recedes completely. Only in rare cases are relapses possible.
There is another disease that is compared to cancer - Manganotti syndrome. The disease manifests itself in the form of a noticeable ulcer on the lip, which is precancerous. However, due to the fact that in most cases the syndrome still develops into a tumor, it is more often classified as oncological diseases.
Zonal risks
Such detail is extremely important to understand the potential danger of the nasolabial area. “The rich vascularization (good blood supply) of this area, anasomoses (connections) between the vessels sharply increase the risk of the spread of any infection. Hence the frightening name that this area of the face received for a reason, since the infectious process in a very short time can spread to the sinuses (sinuses), then the meninges can be involved in it, and meningitis develops,” emphasizes Tatyana Romanenko.
The therapist also notes that if the process progresses unfavorably, thrombosis may develop. “This is an extremely dangerous situation, very often leading to death. Therefore, the phrase “Don’t crush pimples!”, which everyone often heard in adolescence from their mothers and grandmothers, should be taken very seriously. Modern medicine has already learned to cope with acne, including those that form in the area of the nasolabial triangle, using effective and safe methods. The main thing is to see a doctor in time,” says Tatyana Romanenko.
Complications can also arise during cosmetic procedures, in particular contouring, says Tatyana Romanenko. “There are risks of compression or embolism of the inferior or superior labial arteries, which can lead to ischemia and/or necrosis of the tissue supplying this area,” the doctor emphasizes.
The therapist also says that one of the most formidable and dangerous complications is blindness as a result of embolism of the ophthalmic artery (a. ophthalmica). “Embolization of this artery can occur due to the introduction of an embolus in any part of the facial artery. If it gets into the bed of the facial artery and some of its branches, the embolus with blood flow can be delivered to the place of blood supply to the eyeball through the ophthalmic artery. Such cases are rare, but the existing risks cannot be underestimated. Remember that the face is our beauty and a high-danger zone, so all manipulations should be performed only by professionals, and cleanliness and proper care will help you avoid health problems,” notes Tatyana Romanenko.
Sew a young face. How is the popular thread lift applied? More details
Features of cheilitis in children
Lips suffer due to minimal protection. In children it is even weaker, so cheilitis worries them somewhat more often. In addition to children, the risk group includes the elderly and pregnant women.
The main causes of cheilitis in childhood:
- allergic reaction to food;
- use of products for the care of the skin of the lips and around them, not intended for children;
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious and fungal infections;
- weather.
Typically, infantile cheilitis does not develop until critical stages. When children's lips turn red, parents immediately begin to treat them. After all, people pay more attention to the health of the younger generation than to their own. If cheilitis in children still requires treatment, therapy should not be delayed longer than a few weeks. The main thing is to remove all allergens from the children's diet and balance the diet.
How to treat lips with cheilitis
The most important thing in treating cheilitis is to identify its cause, which is difficult to do without professional help. You'll have to contact a specialist. First, it is better to go to a therapist, and he will then refer you to a specialist doctor.
Typically, treatment for diseases of the lips and skin around the mouth is based on eliminating not the symptoms, but the root cause. It includes lifestyle changes, proper nutrition, and medication.
If the cause of inflammation is an infectious or fungal infection, local drugs are included in the therapy. Typically, patients are prescribed various medicinal ointments for external use, which must be applied to damaged skin several times a day:
- anti-inflammatory – Tetracycline, Erythromycin;
- antifungal – Clotrimazole;
- hormonal – Prednisolone.
To cure lips, you need to influence them not only from the outside, but also from the inside. The skin around the mouth often suffers from a lack of B vitamins, so they are often prescribed in the treatment of lips.
Introduction
So, a dangerous triangle of the face. We can describe this zone in this way: the apex of the triangle is located in the glabella area, its legs enclose the nasolabial folds and reach the base, which is located under the lower lip [Fig. 1].
Rice. 1. Dangerous triangle of the face.
The area within this zone is often corrected with filler: just think about glabellar lines, nasal hump correction, nasolabial folds and lip remodeling. The anatomical feature, or originality of this zone, which makes it so “insidious”, lies in its blood supply and especially in the topography of the arteries.
How to get rid of unpleasant symptoms at home
It is not worth treating at home without seeing a doctor. However, there are ways that you can resort to to reduce discomfort:
- If your lips become inflamed due to the sun or cold, it is advisable that they are always covered with a protective layer of balm.
- For severe itching and burning, which occur in almost all forms of cheilitis, cold compresses will help. Before applying them, the skin is covered with a layer of balm so that the lips are treated simultaneously with the reduction of pain.
- If your lips are red and covered with cracks, sores or any other open wounds, you need to make sure that bacteria do not get into them. The surrounding skin and teeth should be treated with a cotton pad soaked in hydrogen peroxide or Miramistin. Special antiseptic ointments will have the best effect.
- If pain and itching are unbearable, painkillers can be used. Ointments with a cooling effect will have the same effect.
All methods of folk treatment for cheilitis will be useless if you resort to them thoughtlessly - without consulting a doctor. In most cases, inflammation, redness and itching of the lips are harmless. Such symptoms can go away even without therapy, but sometimes they indicate dangerous diseases, so medical help should not be neglected.
Causes of cyanosis
Whether constant cyanosis is characteristic of a particular disease or is transient in nature depends on the cause of its occurrence.
If after examination the cause of cyanosis of the skin cannot be determined, then it is called primary, or idiopathic.
Cyanosis may not have a pathological basis, but in order to protect the patient, it is necessary to undergo an examination and exclude organic pathology. Secondary cyanosis occurs as a result of some disease.
Central cyanosis most often occurs in respiratory failure, when there is high pressure in the pulmonary arteries, pathology of the bronchi, lungs, or if the patient has a congenital defect of the interventricular or interatrial septum. The most intense cyanosis will be in those areas where the skin is the thinnest; for example, cyanosis of the lips will be characterized by an almost purple color. A characteristic sign is also cyanosis of the nails.
Peripheral cyanosis is more often observed in patients with heart failure, as the speed of blood flow is significantly reduced. Areas of the body that are exposed to low temperatures have a bluish color.