In physiognomy, two lines of the cheeks, running from the top of the wings of the nose to the sides of the chin and covering the corners of the mouth, are called FA-LIN in Chinese. These two lines, located in positions 56 and 57, control the fate of a person in the middle years of his fifth decade of life. These years may prove critical. The “critical years” in ancient China meant that if a person had a bad life before this time, it would be much more difficult to turn failure into success in subsequent years. Below we will tell you how to determine a person’s character by their cheeks.
As a general rule, a man should have fairly noticeable cheek lines by age 30. If these lines are already expressed by the age of 20, it is clear that he matures early and is a mature person. If by the age of 30 these lines are still not defined, this is a sign of delayed maturation.
Women rarely have pronounced Fa-Ling by age 30 or even 40. However, once they embark on a competitive professional career, these lines tend to appear.
Gums and teeth
Everyone knows that teeth are the main characters in the process of chewing and grinding food. According to their roles, teeth in a person’s mouth are divided into types:
- Incisors – the front 4 teeth, play the role of biting off the largest pieces.
- Fangs - their role is to break food and separate it into pieces; they are also called “eye teeth”.
- Small and large molars play the role of chewing and grinding food.
People eat food of different origins, both plant and animal. On this basis, it was concluded that people are omnivorous creatures.
This is possible due to the arrangement of the teeth and the structure of the oral cavity, which makes humans fundamentally different from animals.
All teeth have the same structure: a soft core, dentin. The core consists of blood vessels and nerves, and the hard substance (bone) is dentin. The main function of this substance is to protect teeth from microdamage. To do this, it is “painted” with enamel, which feels absolutely nothing. In addition, enamel has no equal in strength in the human body. It consists of an alloy of minerals (phosphorus and calcium salts) saturated with organic substances. The highest concentration of calcium is observed in dentin, where nerve fibers are contained.
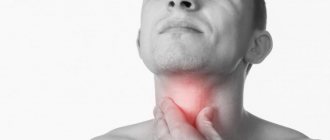
Causes of swelling on the cheek
Many people believe that only teeth can provoke swelling of the cheeks. In fact, the reasons may be different.
Dental diseases
Factors related to oral health can provoke the problem. Among them:
- Eruption of impacted wisdom teeth, especially if the patient is over 25 years old. If the growth is abnormal, it is recommended to remove the “eight”.
- Stomatitis affecting the cheek, gums, tongue. The disease is most often diagnosed in children, but it can also occur in adults. An advanced disease provokes swelling. The cheek hurts from the inside, in the corner of the mouth.
- Gum disease, in which pathogenic bacteria accumulate in dental plaque, causing inflammation. Thus, gingivitis is accompanied by bleeding gums, swelling, and bad breath. If the disease is neglected, it will develop into periodontitis, a more serious problem.
Complications in the form of swelling of the cheek can develop after endodontic treatment. If during the procedure the canals are not washed and cleaned well enough, inflammation develops in the pulp chamber. The pathogenic process spreads to the bone, gum and cheek. This is how purulent periostitis develops, which is popularly called “flux”. If the disease is not treated in time, phlegmon and sepsis may develop, which pose a health hazard.
During the recovery period after tooth extraction, swelling of the cheek may also be observed. More often the symptom appears if the intervention was performed on the lower jaw. This problem often arises after implantation. This is the body's reaction to traumatic actions. It goes away in a few days. Otherwise, you need to consult a dentist, who must confirm or rule out the presence of a complication. It can develop due to infection getting into the wound, which threatens the manifestation of peri-implantitis.
Infectious, colds and other diseases
Cheek swelling is one of the symptoms of such diseases:
- Parotitis. When the disease occurs, the salivary glands become inflamed, which explains why soft tissues swell.
- Lymphadenitis. It occurs as an independent disease or as a complication of other ailments, such as diseases of the ENT organs. With lymphadenitis, the cervical, parotid and submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged, and the cheek becomes inflamed.
- Otitis, sinusitis, sinusitis. The inflammatory process can spread to the cheek, under the eye, and the area near the nose.
Pathological processes in gingival tissues often provoke inflammation of the salivary ducts and glands. It can also be an independent disease. It is caused by stones in the ducts, cysts, tumors.
The mucous membrane also swells with inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. In this case, other symptoms appear: numbness, pain radiating to the ear, “lumbago”. Swelling is a common occurrence in diseases of internal organs. Excess fluid due to malfunction of one or another organ accumulates in soft tissues, including the facial area.
Other causative factors
Swelling can also appear as a result of injury. This symptom accompanies soft tissue bruises, joint dislocations, and jaw fractures, which can be caused by a blow or fall. Children are more often susceptible to injury due to their excessive physical activity. Swelling can occur due to an allergic reaction, when the body shows immunity to a certain product. Other reasons:
- severe burn (both thermal and chemical);
- insect bites, which also cause redness and induration;
- poor oral hygiene.
Cheek swelling can occur in pregnant women. The fact is that during this period hormonal changes occur in the body. As a result, the gums swell, which is reflected on the cheek.
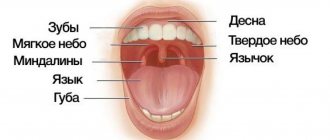
Language structure
The human tongue is a soft pink colored muscle mass on which taste buds are located. At the very top of the tongue, and along its edges, there are papillae, which are responsible for the taste of everything that comes into our mouth. It is no secret that the mouth is the first point where the initial processing of food and the adsorption of microorganisms and harmful substances begins. The tongue takes on the most important role here, accumulating on its surface all the harmful substances that form a coating known to everyone. It is imperative, for preventive purposes, to clean your tongue of plaque, which will get rid of the unpleasant odor and possible infections. At the root of the tongue, there are no papillae, there are tonsils. Which play an important role in protecting the human body, standing in the way of microbes, they do not allow them to penetrate inside.
Sky structure
The part of the oral cavity that is located on top is called the palate. The palate is made up of 2 components, hard and soft. The mucous membrane covers both parts, passing through the hard palate to the soft palate, it gradually turns into gums. The front side of the palate forms rudimentary formations (palatine alveoli), humans do not fully use them, but animals, on the contrary, use them to eat food. The palate has another role besides forming the upper part of the mouth; it is a barrier between the nose and nasopharynx. A kind of barrier wall is a small tongue that blocks access to the nasopharynx during the digestion process.
Structure of the mucous membrane
The entire human oral cavity is covered with a mucous membrane, which has a distinctive feature, regenerative ability. The mucous membrane protects the oral cavity from environmental influences. Chemical, mechanical, temperature factors cannot influence it. The structure of the mucous membrane is simple; in the lower part of the mouth - on the cheeks and lips, it forms folds; in the upper part - attached to the bones. The main roles of the mucous membrane:
- The protective role is unpleasant, but it is a fact that many viruses and bacteria accumulate in the human mouth. The mucous membrane retains, prevents reproduction and removes all harmful microorganisms from the oral cavity.
- Sensitive role - Due to the presence on its surface of many receptors responsible for sensations (taste, pain, temperature), it signals all the events that accompany food intake.
- Absorption role – Thanks to this ability, we are able to take medications “under the tongue”. The mucous membrane perfectly absorbs protein and mineral compounds.
The structure of the oral cavity and the functions of its structures
The mouth, or oral cavity, is made up of many structures that work together to help us breathe, speak, smile, eat, and digest food. Once you become familiar with these anatomical structures and how they affect your overall health, you will understand why proper and regular oral care is so important. Listed below are the elements that make up the human oral cavity and the functions they perform.
Lips and cheeks
The basis of the lips and cheeks are muscles that allow us not only to kiss, but also to express a lot of different emotions - from joy to sadness. Through open lips, air enters the mouth and then into the lungs, allowing us to breathe. The muscles of the lips and cheeks help us speak. In addition, while eating, they retain food and saliva in the mouth. Finally, these strong muscles also influence the position of our teeth.
Language
The tongue is a powerful muscle that helps us chew, swallow, speak and taste food. Thanks to the taste buds, or taste receptors, located in the tongue (as defined in the Atlas of Human Anatomy), we can enjoy the taste of food. In total, in the oral cavity - on the tongue, palate, mucous membrane of the pharynx - there are up to 2500 such receptors, with the help of which we distinguish sweet from salty, bitter from sour.
Teeth, gums and alveolar bone
Teeth have a crown covered with hard enamel and roots that are held in the jaw bone. The stability of the teeth is ensured by the alveolar bone, periodontal ligament and gums surrounding the roots, which also protects the roots of the tooth from caries. The main function of teeth is to crush and grind food so that it can be digested in the stomach. In addition, teeth support the soft tissues of the face, giving them a certain shape, help us pronounce certain sounds and make our smile attractive.
Salivary glands
Humans have six glands that produce a clear liquid called saliva. Saliva is mostly water, but also contains substances that break down food so it can be digested. In addition, saliva moistens the mouth, making it easier to speak, chew and swallow. It continually washes away bacteria from your teeth and gums, helping prevent the development of tooth decay and periodontitis. The minerals and proteins contained in saliva play an important role in protecting the enamel from carious lesions. According to information presented on the MedWeb information portal, the human body produces up to two liters of saliva per day.
Temporomandibular joint
The ability to open and close the mouth, move the lower jaw forward, backward and side to side, as well as chew, speak and swallow, we owe to the work of the temporomandibular joints (TMJ). As dentists explain, these extremely complex paired joints, located on the right and left sides of the face, are set in motion by a whole group of muscles and ligaments. The slightest desynchronization of these joints—for example, due to arthritis or teeth grinding—can cause facial pain, difficulty chewing food, and other jaw mobility problems.
Maintaining oral health
To keep all oral structures healthy, brush your teeth twice daily using fluoride toothpaste, a soft-bristled brush, mouthwash, and clean between your teeth with dental floss. Regular cleaning of the tongue with a special pad on a toothbrush or scraper will help remove plaque accumulated on its surface. Using an antimicrobial mouth rinse will reduce the number of pathogenic bacteria that cause bad breath. It is equally important to give up tobacco and limit the consumption of sugars and other carbohydrates that provoke the development of caries: this will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the body as a whole.
Don't forget to regularly undergo preventive examinations and visit a hygienist for professional teeth cleaning, which allows you to remove tartar and plaque from areas of the dentition that are inaccessible to a brush. By carefully examining the oral cavity, the dentist will also be able to notice in time the slightest signs of cancer, the early diagnosis of which is of paramount importance.
The beauty of teeth is, of course, important, but the good condition and performance of all structures of the oral cavity is even more important, because this is the key to not only dental, but also the general health of each of us.