Malignant tumors can form in almost all anatomical areas. Thus, oral cancer, the symptoms of which sometimes appear only in late stages, is not a rare form of oncology.
This disease is found among heavy smokers, chewing tobacco lovers and other categories of patients. Early treatment helps minimize the effects of tumor growth in the mouth.
What is oral cancer
Regular examination by a doctor - prevention
Oncological diseases of the oral cavity are caused by malignant cell growth in various tissues of this anatomical region. Since almost the entire oral cavity is lined with epithelial tissue, the likelihood of developing cancer is quite high.
This does not mean that anyone is susceptible to this disease. For tumor growth to occur, the influence of negative factors is necessary.
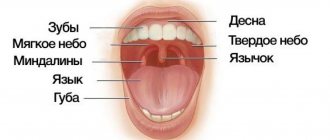
Malignant growth can affect the following parts of the oral cavity:
- Lips.
- Gums.
- Language.
- Buccal mucosa.
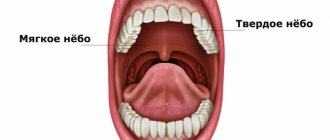
- Sky.
- Floor of the mouth.
The most common tumors are the tongue, the inner lining of the cheeks and the floor of the mouth. The clinical picture and the rate of spread of tumor cells depend on the location of the disease. When a tumor grows in the buccal area, the salivary glands may be affected.
Risk factors [5,6]
Science indicates the following reasons that can trigger the appearance of a malignant tumor of the oral cavity:
- weak immunity;
- poor nutrition;
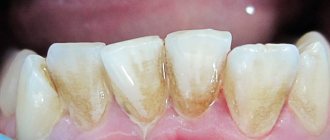
- poor oral hygiene ;
- viral infections (primarily human papillomavirus);
- precancerous diseases: Bowen's disease, lupus erythematosus, lichen planus, leukoplakia, candidiasis;
- smoking, chewing tobacco, using tobacco mixtures;
- consumption of strong alcoholic drinks;
- deficiency of vitamins A, E and C;
- chronic injuries to the mucous membrane due to the sharp edge of a tooth or filling, incorrectly selected orthopedic structures, defects in the dentition;
- bad habit of biting your tongue, cheeks, lips;
- unfavorable labor factors: heavy metal salts, acid vapors, mineral fertilizers, petroleum products.
With the development of medicine, the list is supplemented and revised. Thus, if previously tobacco and alcohol were considered the main dangers, today more and more attention is paid to neglect of oral hygiene, poor nutrition, immunodeficiency and viral infections [5].
Causes
Oral cancer
The mechanism of development of oral cancer is generally similar to the stages of formation of any malignant tumor. Healthy epithelial cells, after dividing, perform their functions and are gradually destroyed.
Cell division is regulated by genetic information and special intracellular mechanisms. Under certain conditions, the division process can be disrupted, resulting in the formation of an abnormal cell mass called a malignant tumor.
How is the process distributed?
The process is distributed in several ways:
- The path is lymphogenous. Mutated cells spread through the lymph vessels along with the lymph. This variant is observed in most carcinomas.
- The route is hematogenous. Cancer cells choose blood vessels to spread throughout the body. This is how sarcomas and kidney cancer spread.
- The implantation path. The serous membrane is the channel for the spread of the disease.
- The path is portable. Associated with mechanical spread of tumor fragments during diagnostic and surgical procedures.
Malignancy
Symptoms and signs
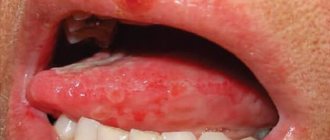
Poorly healing ulcers are a warning sign
Symptoms of any cancer can be variable. Often patients do not have any complaints until the tumor becomes large enough.
Symptoms depend on the location of the malignant growth and the individual body's response to the disease.
The most common symptoms include:
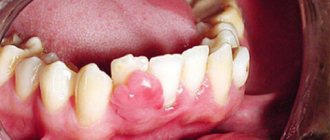
- The appearance of a lump, thickening, rough patch, or slight swelling in any area of the oral mucosa.
- Unexplained bleeding in the mouth.
- Numbness and loss of sensation in the face or neck.
- Constant appearance of sores in the mouth area.
- Painful sensations while eating food.
- Difficulties with chewing and swallowing. Speech dysfunction.
- Partial numbness of the tongue.
- Pain in the ear area.
- Gradual decrease in body weight.
The listed signs are not specific to oncology and may indicate a variety of diseases of the oral cavity. However, if such symptoms are detected, you should consult a doctor for a detailed diagnosis.
Metastases - what is it?
This term is quite scary for any person. Indeed, metastases are secondary, often distant, malignant lesions of any tissue in the body. The cancerous tumor itself can be localized in any part of the body, sometimes located very far from the area affected by metastases.
Metastases - what is it?
The presence of metastases significantly complicates the treatment of the underlying cancer, which often turns out to be completely powerless. These abnormal cells quickly and easily spread throughout the body without control. True, this happens only at a certain stage in the course of the underlying pathology.
Metastases to the spine
Metastases can also appear in the spine. Here they often affect the vertebrae themselves and structures close to them. They are usually detected in such parts of the spine as the lumbar, thoracic, and rarely in the cervical. Regarding the human skeleton, this is the most common malignant pathology.
Cancer metastasis
On a note! Most often, this type of secondary formations in the spine is found in lung cancer, malignant neoplasms of the prostate or mammary glands. Their “donors” are the kidneys, lungs, digestive organs, thyroid gland, etc. Metastasis of the spinal region often accompanies myelomas, sarcomas and lymphomas.
Table. Types of metastases in the spine.
| Type | Description |
| Osteoclastic or osteolytic | In this case, the so-called osteoclasts are activated, causing the destruction of individual bone elements. The vertebrae decrease in height, which can be clearly seen on x-rays. |
| Osteoblastic or osteosclerotic | In this case, the cells of the spinal tissue begin to grow uncontrollably, and the density of the bone substance increases. The shape and size of the affected area changes, which is clearly visible in the photographs. Almost all elements of the vertebra are affected. |
Osteoblastic metastases
Diagnostic methods
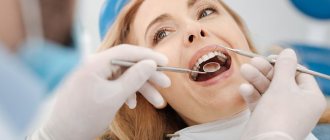
If you suspect a disease, you should contact an oncologist. During your appointment, your doctor will ask about your complaints, take a medical history, and examine your mouth to look for signs of malignant growth.
Any abnormality of the epithelial mucosa may be suspected, including areas of irritation, ulcers and white spots. To exclude other diseases and confirm oncology, instrumental and laboratory research methods will be required.
Special research methods:
- Sampling of a section of the oral mucosa followed by histological examination. A biopsy is the most accurate method for diagnosing cancer and identifying the type of malignant tumor. Also, the results of the method may indicate precancerous changes in the epithelium, which increase the risk of cancer.
- Endoscopic examination. During the procedure, a small flexible tube equipped with a camera and a light source is placed down the patient's throat. The nasal cavity is examined in the same way. Endoscopy is necessary to detect the primary area of tumor spread if oral cancer is a secondary formation.
- Visualization. To obtain high-precision images of certain tissues and organs, doctors prescribe radiography, as well as computer or magnetic resonance imaging. These methods are useful for assessing tumor size and finding the primary site of malignant tissue spread.
Screening diagnostic methods aimed at detecting the early stages of oncology are also important. If a patient has certain risk factors, regular examinations are necessary.
What symptoms to look out for
To recognize a tumor at an early stage, dentists advise being guided by your own feelings. The first symptoms that raise suspicion may be:
- slight bleeding of the gums that occurs as a result of gentle pressure on the gums;
- change in the color of the gum tissue and the appearance of swelling, which is often perceived as gingivitis;
- the appearance of neoplasms on the gums that have a pronounced red color, as well as light-colored ulcers and inclusions.
There is no need to panic if your gums are bleeding. This can be the cause of a number of diseases that are not related to cancer (periodontal disease, gingivitis, periodontitis). But plaques and ulcers should alert you and be the reason for an immediate trip to the dental clinic. At this stage, the disease can still be defeated and the likelihood of causing harm to the body can be reduced.
- Admin
- Oncology,
- Dentistry
Forecast
The survival period directly depends on the type of tumor and the stage of spread. During the first stage, when malignant cells remain on the surface of the mucous membrane, surgery helps to completely get rid of the problem.
A poor prognosis is typical for late stages, when tumor cells have spread to the deep cervical lymph nodes. In this case, survival rarely reaches two years.
Thus, oral cancer, whose symptoms may be nonspecific, is best treated in its early stages of growth. Screening diagnostics help detect precancerous changes and prevent tumor growth.
Informative video about oral cancer - in the video:
Process speed: what affects it?
The speed with which metastases spread throughout the body largely depends on the type of disease, its stage, location, and molecular genetic characteristics.
Clinical practice shows that tumors with low differentiation give metastases earlier than tumors with high differentiation. The quality of blood supply to the affected organ also plays an important role.
In many cases, tumor foci appear in the bones, lungs, liver, and brain.
The development of secondary tumor foci makes it impossible to defeat the disease, but with the help of palliative treatment it is possible to stop the progression of the pathology, improve the patient’s condition, and prolong his life.
In cancer patients, millions of mutated cells move through the bloodstream every day. Not all of them are capable of starting the process of metastasis. There is a dependence on a number of factors: histology of the neoplasm, stage of the disease, cellular differentiation.
Is it possible to get implants after cancer treatment?
In addition to disrupting the aesthetics of a smile, the absence of teeth entails chewing dysfunction. After all, complete chewing of food is necessary for recovery. Previously, the installation of implants was not available to patients with severe bone atrophy due to cancer. After all, radiation and chemotherapy can make the bone brittle.
After oncology, it is impossible to carry out bone augmentation, so titanium implants cannot be used. The solution to this problem was a new material that replaces titanium and surpasses it in osseointegration properties.
Biopolymer Polyether ether ketone (PEEK, Polyether ether ketone) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic. This is a dense material that is resistant to any environment and is actively used in the space and aviation industries. Based on it, the Perso-B and Perso-C implants were created, which can be installed when the bone is thinned. They are recommended by European and American clinics.
Polyetheretherketone has the following properties:
- Isoelasticity. The elasticity of PEEK-OPTIMA implants is almost identical to the elasticity of bone. It is possible to reduce stress concentrations that lead to bone resorption, change or displacement.
- Reinforcement or replacement of bone to support soft tissue. The polymer can serve as a basis for installing implants into bone. Its elasticity prevents fractures of the implant.
- The polymer provokes the formation of bone tissue. Implants based on PEEK-OPTIMA do not inhibit, but stimulate regenerative properties.
- The material is biocompatible and has good osseointegration.
- The biopolymer is biologically and chemically inert, so allergies and inflammation cannot develop, which is important for patients with allergies to titanium (4% of the total).
- The implants have good adaptability.
- Light weight and small thickness.
The polymer can be used after previous or current oncological diseases (Perso-B implantation system). In case of severe bone atrophy, implants do not increase the risk of bone damage; on the contrary, they stimulate growth. Implants are installed in one stage. Immediate loading of the prosthesis is allowed. Implantation of polymer rods does not lead to side effects or contraindications.
Polymer-based implants can be placed:
- smoking patients;
- patients with gum disease;
- with significant bone atrophy;
- to restore the alveolar ridge;
- to restore deficiencies of the facial skeleton;
- to avoid bone augmentation surgery.
There are opinions that polymer material can replace zirconium dioxide, the most advanced material in dentistry.
- Complete restoration of the dentition in just 4 days!
more detailsRoott Pterygoid Implants Sinus lift is no longer needed!
more details
Once and for life! Express implantation in 4 days with a permanent ReSmile prosthesis
more details
All-on-4, All-on-6, ReSmile, Zygomatic implantation We use all modern methods of dentition restoration
more details
What is the danger of metastases?
The process of development of a secondary tumor focus is of great importance in the course of the disease: having spread throughout the body in large numbers, mutated cells lead to organ failure and death of the patient.
Clinical practice shows that the process of formation of a secondary tumor focus is detected in almost 70% of patients at the diagnostic stage. Even in the absence of metastases at the time of cancer diagnosis, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment in order to prevent progression.
Oncology as a contraindication to dental implantation
Oncology requires priority serious treatment; any concomitant treatment during this period is impossible. Implantation is no exception. The question of implantation of dental implants can be raised after achieving stable remission.
Received radiation and chemotherapy threatens to develop consequences that will make the implantation procedure impossible.
Irradiation causes the following complications:
- local reaction;
- radiation osteopenia;
- necrosis of bone structures;
- secondary osteoporosis;
- reduced ability of bone to recover (regenerate);
- bone demineralization;
- suppression of bone marrow functions;
- general intoxication.
Significant toxic effects and metabolic disorders after irradiation can be stopped no earlier than six months after treatment.