Visible part of the body near the mouth
"Lips" redirects here. For the band, see Lips (New Zealand band). For surname, see Lips (surname). For other uses, see Lip (disambiguation).
This article is about the front. For the cavity, see Human mouth.
| This article need additional quotes for verification . |
This article uses anatomical terminology.
| Lip | |
| Human lips | |
| Details | |
| Artery | lower labial, upper labial |
| Ven | lower labial, upper labial |
| Nerve | frontal, infraorbital |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | labia |
| MeSH | D008046 |
| TA98 | A05.1.01.005 |
| TA2 | 2775 |
| F.M.A. | 59816 |
| Anatomical terminology [edit in Wikidata] | |
Lips
are a visible part of the body in the mouths of many animals, including humans.
The lips are soft, mobile and serve as openings for eating, as well as for making sound and speech. The human lips are a tactile sensory organ and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy.
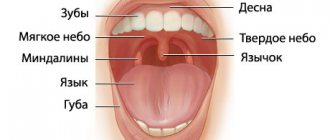
Structure
Cupid's Bow - Human Lip
The upper and lower lips are referred to as "Labium superius oris" and "Labium inferius oris" respectively.[1][2] The place where the lips meet the surrounding skin in the mouth area is the vermilion border,[3] and usually the reddish area within the borders is called the vermilion border.[4] The red border of the upper lip is known as Cupid's bow.[5] The fleshy projection located in the center of the upper lip is a tubercle known by various terms, including procheilon (also spelled prochilon
), "tuberculum labii superioris" and "labial tubercle".[6]
The vertical groove running from the procheilon to the nasal septum is called the philtrum.[7] Anatomy of the surface of the human lips
The skin of the lip, consisting of three to five cellular layers, is very thin compared to typical facial skin, which has up to 16 layers. With light skin color, the skin of the lips contains fewer melanocytes (cells that produce melanin pigment, which gives the skin its color). Because of this, blood vessels appear through the skin of the lips, resulting in a noticeable red coloration. With darker skin color, this effect is less pronounced, since in this case the skin of the lips contains more melanin and, therefore, is visually darker. The skin of the lip forms the boundary between the outer skin of the face and the inner skin. mucous membrane of the inside of the mouth.
The skin of the lips is not hairy and does not have sweat glands. Consequently, it doesn't have the usual protective layer of sweat and body oils that keep skin smooth, inhibit pathogens, and regulate heat. For these reasons, lips dry out faster and become less chapped.
The lower lip is formed from the mandibular protuberance, a branch of the first pharyngeal arch. The lower lip covers the anterior body of the lower jaw. The muscle that contracts the lower lip is reduced and the orbicularis oris borders it below.
The upper lip covers the anterior surface of the body of the upper jaw. Its upper half is normal skin color and has a depression in the center, just below the nasal septum, called the nasal septum. philtrum, which is Latin for "bottom of the nose", while its lower half is a noticeably different skin tone of red, more similar to the color of the inside of the mouth, and the term cinnabar
refers to the colored part of the upper or lower lip.
It is elevated by the levator labii superioris and is connected to the lower lip by the thin lining of the lip itself.
Thinning of the border of the upper lip and flattening of the philtrum are two facial features of fetal alcohol syndrome, lifelong disability caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
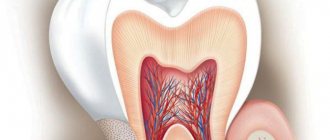
Microanatomy
The skin of the lips is stratified squamous epithelium. The mucous membrane is represented by a large area in the sensory cortex, and is therefore very sensitive. B Frenum of the lower lip
This is the frenulum of the lower lip.
B The superior frenulum of the lower lip
is the frenulum of the upper lip.
Nervous nutrition
Illustration of the lips from Gray's Anatomy
showing the inferior and superior labial arteries, labial glands, and nerves of the right side when viewed from the posterior surface after removal of the mucosa
- Trigeminal nerve The infraorbital nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve. It covers not only the upper lip, but also most of the facial skin between the upper lip and lower eyelid, with the exception of the bridge of the nose.
- The psychic nerve is a branch of the mandibular branch (via the inferior alveolar nerve). Nourishes the skin and mucous membranes of the lower lip and lips. gum (gums) in front.
Blood supply
The facial artery is one of the six non-terminal branches of the external carotid artery.
This artery supplies both lips with its superior and inferior labial branches. Each of the two branches is forked
and
anastomose
with their accompanying branch from another terminal.
Muscles
The muscles that act on the lips are considered part of the facial expression muscles. All muscles of facial expression originate from the mesoderm of the second pharyngeal arch, and are therefore supplied (motor supply) by the nerve of the second pharyngeal arch, the facial nerve (7th cranial nerve). The muscles of facial expression are all specialized members of the panniculus carnosus that attach to the dermis and therefore wrinkle or dimple the skin. Functionally, the muscles of facial expression are located in groups around the orbit, nose and mouth.
Muscles acting on the lips:
- Buccinator
- Orbicularis oris (a complex of muscles previously considered a single sphincter or ring of muscle)
- Anchor point for several Modiolus muscles
- Levator of the upper lip
- Risorius
Causes of lip cancer
Lip cancer develops for many reasons:
- From smoking;
- After a long stay in the sun;
- As a result of inflammatory processes of an infectious and non-infectious nature;
- Under the influence of high temperatures;
- In the presence of microtraumas;
- Due to prolonged exposure to chemicals.
Lip cancer often develops from smoking. Men get lip cancer much more often than women. Currently, the trend is changing, because many women suffer from tobacco addiction. Doctors believe that lip cancer develops due to smoking strong cigarettes for a long time.
The average smoker smokes at least ten cigarettes a day. In this case, the paper surface is constantly in contact with the lips. The skin here is especially delicate and sensitive. Microcracks appear on its surface. They are invisible to others and do not cause problems for the smoker. Damaged areas of the epithelium are affected by tobacco smoke. It contains a lot of harmful substances. Skin cells begin to degenerate.
The cause of mechanical trauma that causes lip cancer can be improperly made dentures, the habit of holding various objects with the lips (nails, the mouthpiece of a smoking pipe), or biting the lower lip. The mechanism of development of lip cancer is as follows: a long-term non-healing crack, wound, inflammation on the lip, papilloma develops into leukoplakia, Manganotti cheilitis, keratoacanthoma, warty form of dyskeratosis or other precancerous diseases. Against this background, lip cancer occurs.
Functions
Eating
Breastfeeding
Because they have their own muscles and adjacent muscles, the lips are easily movable. The lips are used for eating, such as holding food or putting it into the mouth. In addition, the lips serve to seal the mouth tightly, keep food and drinks inside, and protect against unwanted objects. By making a narrow funnel with the lips, suction in the mouth is enhanced. This suction is necessary for breastfeeding babies. The lips can also be used for sucking in other situations, such as when sucking on a straw to drink liquid.
Articulation
The lips are used to create different sounds—mainly labial, bilabial, and labiodental consonants, as well as rounding vowels—and are therefore an important part of the speech apparatus. The lips allow for whistling and playing wind instruments such as trumpet, clarinet, flute and saxophone. People who have hearing loss can unconsciously or consciously read lips to understand speech without having to perceive actual sounds.
Tactile organ
The lip has many nerve endings and responds as part of the tactile (touch) sense. Lips are very sensitive to touch, heat and cold. Therefore, it is an important aid for exploring unknown objects for infants and toddlers.
Erogenous zone
Lips of a young woman in red lipstick Lips of a young man
Due to the large number of nerve endings, the lips are an erogenous zone. Therefore, lips play a decisive role in kissing and other intimate relationships.
A woman's lips are also a visible expression of her fertility. In studies examining human desire, psychologists have concluded that a woman's physical and sexual attractiveness is closely related to the composition of her hormones during puberty and development. In contrast to the effects of testosterone on male facial structure, the influence of female estrogen levels serves to maintain a relatively childlike and youthful facial structure during puberty and during final maturation. It has been shown that the more estrogen a woman has, the larger her eyes and fuller her lips, which are perceived as more feminine.[8] Surveys of sexual psychologists [ WHO?
] also found that, in general, men rated a woman's fuller lips as more sexually attractive than less attractive ones.[
citation needed
] Thus, women's lips are sexually attractive to men because they serve as a biological indicator of a woman's health and fertility. Women's lipstick (or collagen lip augmentation) attempts to take advantage of this fact by creating the illusion that a woman has more estrogen than she actually does, and thus is more fertile and attractive.[9]
Lip size is associated with sexual desire in both men and women. Women are attracted to men with masculine lips that are larger than average, not too big or too small; they should be raw and sensual. In general, researchers have found that a small nose, large eyes, and full lips are sexually attractive to both men and women.[10] Lips may become temporarily swollen during sexual arousal due to blood flow.[ medical citation required
]
Facial expression
Lips contribute greatly to facial expression. The lips clearly express emotions, such as a smile or a frown, which is characterized by the curve of the lips forming an open or open parabola, respectively. The lips may also be pouty when whining or sassy to cause irritation.
How to get rid of unpleasant symptoms at home
It is not worth treating at home without seeing a doctor. However, there are ways that you can resort to to reduce discomfort:
- If your lips become inflamed due to the sun or cold, it is advisable that they are always covered with a protective layer of balm.
- For severe itching and burning, which occur in almost all forms of cheilitis, cold compresses will help. Before applying them, the skin is covered with a layer of balm so that the lips are treated simultaneously with the reduction of pain.
- If your lips are red and covered with cracks, sores or any other open wounds, you need to make sure that bacteria do not get into them. The surrounding skin and teeth should be treated with a cotton pad soaked in hydrogen peroxide or Miramistin. Special antiseptic ointments will have the best effect.
- If pain and itching are unbearable, painkillers can be used. Ointments with a cooling effect will have the same effect.
All methods of folk treatment for cheilitis will be useless if you resort to them thoughtlessly - without consulting a doctor. In most cases, inflammation, redness and itching of the lips are harmless. Such symptoms can go away even without therapy, but sometimes they indicate dangerous diseases, so medical help should not be neglected.
Clinical significance
| This section do not quote any sources . |
As an organ of the body, the lip can be a source of disease or exhibit symptoms of disease:
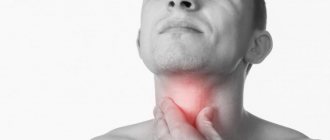
- One of the most common changes in the lips is blue coloration due to cyanosis; the blood contains less oxygen and therefore has a dark red to blue color that is visible through thin skin. Cyanosis is the reason why corpses sometimes have blue lips. Cold weather can cause cyanosis, so, especially in winter, blue lips may not be uncommon.
- Inflammation of the lips is called cheilitis. It can come in several forms, such as chapped lips (dry, flaky lips), angular cheilitis (inflammation of the corners of the mouth), herpes labialis (cold sores, a form of herpes simplex), and actinic cheilitis (lips chronically damaged by the sun).
Child with cleft lip
- A cleft lip is a type of birth defect that can be successfully treated with surgery.
- Carcinoma (malignant cancer that arises from epithelial cells) of the lips is mainly caused by tobacco use and excessive exposure to sunlight. Alcohol increases the risk of cancer associated with tobacco use. Most often, this is a diffuse and often hyperkeratinized lesion, sometimes has the form of nodules and grows infiltratively, and can also be a combination of the two types. It most often occurs on the lower lip, where it is also much more malignant. Carcinoma of the lower lip is squamous cell carcinoma, and the upper lip may also have basocellular carcinoma.
Advice from expert gynecological surgeon Ivanov A.V.
The labia can be affected by herpes, fungal diseases, HPV infection or even cancer. Therefore, when you feel itching, pain or burning in the vulva, you need to consult a gynecologist. You should also see a specialist if you notice any unusual tissue growth, ulceration, warts, nodules, or discoloration of the labia.
Regarding the size of the labia, modern plastic gynecology can solve almost any problem, so do not hesitate to contact our specialized Intimate Plastic Center in St. Petersburg with such questions.
You can see photos of labia disorders here ⇒.
Society and culture
Lip Piercing
Lips are often seen as a symbol of sensuality and sexuality. This has many origins; First of all, lips are a very sensitive erogenous and tactile organ. Additionally, in many cultures around the world, a woman's mouth and lips are hidden due to their representational association with the vulva and due to their role as a woman's secondary sexual organ.[11]
As part of the mouth, the lips are also associated with the symbolism of the mouth as an opening through which food is taken in. Lips are also symbolically associated with newborn psychology (see, for example, the oral stage of psychology according to Sigmund Freud).
Lip piercing or lip augmentation is sometimes performed for cosmetic reasons. Products intended for use on the lips include lipstick, lip gloss, and lip balm.
Treatment of lip cancer
How to treat lip cancer? When treating the disease, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital take into account many different factors: the patient’s age, histological type of tumor, features of the spread of the tumor. Doctors at the Oncology Clinic provide multidisciplinary treatment for lip cancer:
- Surgical interventions;
- Radiotherapy;
- Chemotherapy.
Regardless of the chosen technique, they affect the lesion or tumor, areas of regional metastasis. For grades I and II of lip cancer, radiation treatment is performed, which includes external radiotherapy and surgery.
Treatment in the initial stages
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lip is a common complex tumor process. Its treatment consists of two stages: removal of the main focus and the fight against metastases that have spread to neighboring tissues and organs. Radiation treatment can suppress the development of a tumor focus. The radiologist selects the method of radiation therapy individually, depending on the size of the tumor, stage of the disease, and age of the patient.
Removal using the Krail method
In the initial stage of the tumor, surgeons perform a wedge-shaped excision of the entire thickness of the lip under local anesthesia. In order to remove a defect on the lip, plastic surgery is performed - skin flaps are transferred from the patient's cheek. Removal of the lesion is performed using the Krail technique. The operation is performed at the first and second stages of lip cancer, when the tumor has not spread to nearby tissues. Surgical excision of carcinoma makes sense in the absence of metastases.
The decision to remove a lymph node is made by an oncologist surgeon if the primary tumor process has already been cured or if the lymph node is removed along with the removal of the main lesion. In some cases, surgeons remove the primary cancerous tumor, the affected lymph nodes and the vessels that connect them. The scope of the operation is determined collectively by the clinic's oncologists.
Due to the fact that metastasis can occur in a cross way, the lymphatic apparatus of the suprahyoid region on the left and right is removed. If the oncologist sees that there are cancer metastases in certain lymph nodes, he decides to remove them, and those that are located along the lymph outflow.
Treatment tactics for lip cancer depend on the stage of the disease:
- Preventive surgery at stages I and II of lip cancer is carried out exclusively in cases where it is not possible to control the dynamics of the disease and there are unfavorable prognoses regarding the spread of cancer;
- At stage III, in the absence of metastases, treatment is carried out using a combined effect on the lesion and adjacent areas;
- In case of spread of cancer cells and the presence of single metastases in the lymph nodes, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform combined treatment of lip cancer with subsequent surgery, plastic surgery and surgical correction of the lips;
- In stage IVC, palliative chemoradiotherapy is performed.
Candidates and doctors of medical sciences use innovative methods of treating lip cancer. The presence of modern equipment and competent medical personnel who are attentive to all the wishes of patients allows us to achieve good results in the treatment of lip cancer for many years. Lip cancer, treated in the early stages, is cured in 97-100% of cases. At stage III, 67-80% of patients can be cured. In the fourth stage of cancer and repeated relapses, complete recovery occurs in 55% of cases.
Other animals
This Asian Arowana has large, prominent antennae.
In most vertebrates, the lips are relatively unimportant folds of tissue located just behind the jaws. However, in mammals, they become more visible by being separated from the jaws by a deep cleft[ citation needed
] (A notable exception is the naked mole rat,
Heterocephalus glaber
, whose lips are closed behind the front teeth.[12]
They are also more mobile in mammals than in other groups, since only in this group do they have attached muscles. In some bony fish, the lips may be modified to bear sensitive whiskers. In birds and turtles, the lips are hard and keratinized, forming a hard beak.[13] Clevosaurids like Clevosaurus
are distinguished by the presence of bony "lips"; In these species, common to all, the serrated jaws of sphenodontians form a beak-like edge around the jaws, protecting the teeth inside.[14]
Lip cancer: treatment at Yusupov Hospital
Effective treatment of lip cancer in Moscow is carried out by doctors from the oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital. Oncologists have many years of experience in treating malignant neoplasms of the lip. Surgeons are fluent in surgical techniques. The cost of surgery is lower than in other oncology clinics in Moscow, despite the high level of qualifications of doctors and modern equipment.
Radiotherapy is carried out using modern radiation installations from leading European and American manufacturers. In order to undergo a course of effective treatment for lip cancer at an affordable price, call the Yusupov Hospital. After the operation, surgeons at the Oncology Clinic perform lip plastic surgery using innovative surgical techniques.
Recommendations
- "Labium Superius Oris - Medical Definition." medilexicon.com
. Archived from the original on 2014-10-17. Retrieved 2011-11-12. - "Labium Inferius Oris - Medical Definition." medilexicon.com
. Archived from the original on 2014-10-17. Retrieved 2011-11-12. - "Cinnabar - Medical Definition." medilexicon.com
. Archived from the original on 2014-10-17. Retrieved 2011-11-12. - "Cinnabar Zone - Medical Definition." medilexicon.com
. Archived from the original on 2014-10-17. Retrieved 2011-11-12. - "Cupid's Bow - Medical Definition." medilexicon.com
. Archived from the original on 2014-10-17. Retrieved 2011-11-12. - “Tubercle of the upper lip - medical definition.” medilexicon.com
. Archived from the original on 2014-10-17. Retrieved 2011-11-12. - "Philtrum - medical definition." medilexicon.com
. Archived from the original on 2014-10-17. Retrieved 2011-11-12. - Law Smith, Miriam J.; Deady, Denis K.; Moore, Fhionna R.; Jones, Benedict S.; Cornwell, R. Elizabeth; Stirratt, Michael; Lawson, Jamie F.; Feinberg, David R.; Perrett, David I. (September 21, 2011). “Women’s maternal tendencies are associated with estrogen levels and facial femininity.” Hormones and behavior
.
61
(1): 12–6. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.09.005. PMID 21983237. S2CID 23542024. Fold resume. - Note, Science (2005-11-28). “Why do men find big lips and small noses so sexy? I'll draw you a picture - Commentary - Times Online." Times
. London. Archived from the original on February 22, 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-12. - “Lip size is the key to sexual attraction.” BBC News. 2003-03-04. Retrieved 2010-01-15.
- Valsiner, Jaan (2000). Culture and Human Development
. Sage Publications, Ltd. pp. 134–136. - Griffin, Ashley S. (September 23, 2008). "The Naked Mole Rat" (PDF). Current Biology
.
18
(18):R844. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2008.07.054. PMID 18812073. Retrieved November 9, 2022. - Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). Vertebrate body
. Philadelphia: Holt-Saunders International. p. 297. ISBN 978-0-03-910284-5. - Jones M. E. H. (2009). "Dentary tooth shape in Sphenodon and its fossil relatives (Diapsida: Lepidosauria: Rhynchocephalia)". In Koppe T, Meyer G, Alt KW, (eds.). Interdisciplinary dental morphology, frontiers in oral biology
(vol. 13). Greefswald, Germany; Karger. 9–15.
further reading
- Tomiyama N., Ichida T., Yamaguchi K.; Ichida; Yamaguchi (2004). “Electromyographic activity of the muscles of the lower lip during chewing of lips in contact and apart” (Abstract). Orthod corner
.
74
(1):31–6. Doi:10.1043/0003-3219 (2004) 074 2.0.CO; 2 (inactive 2020-10-19). PMID 15038488.CS1 maint: multiple names: list of authors (link) CS1 maint: DOI inactive since October 2022 (link) - Bisson M, Grobbelaar A; Grobbelaar (2004). "Aesthetic properties of lips: comparison of models and non-models" (Abstract). Orthod corner
.
74
(2): 162–6. Doi:10.1043/0003-3219 (2004) 074 2.0.CO; 2 (inactive 2020-10-19). PMID 15132441.CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of October 2022 (link) - McMinn, R. M. H.; Last, R. J. (1994). Last's anatomy, regional and applied
. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-04662-9.