Pediatric dentistry can be considered a separate section of modern dental practice, because due to the structural features, the treatment of baby teeth is somewhat different from the treatment of permanent teeth. Unfortunately, many parents are still convinced that baby teeth do not need dental care - after all, they will soon break down and fall out anyway. Therefore, children are not taken to the dentist very often, and if they are taken to the doctor, it is with advanced diseases and multiple problems.
In fact, dental treatment should be carried out at any age, and the sooner you consult a doctor with a problem, the higher the likelihood of getting rid of it quickly and without any complications. If a child has bad baby teeth, this will inevitably affect the health of his permanent ones - this is what parents need to remember when they want to “pity” the baby and not take him to an appointment with the “evil dentist.”
Home methods for removing baby teeth are not always safe
The most common way to forcibly pull out loose baby teeth at home is with a thread tied to the tooth and wound around the door handle. Some “lucky” readers probably went through this procedure in childhood and remember how unpleasant it was. Home methods for pulling teeth are not always safe. Such removal can provoke the development of infection or inflammation of the socket of the extracted tooth, which requires serious treatment. Find out what to do if the hole becomes rotten after tooth extraction.
Using improvised means, you can remove a baby tooth at home only if it is literally “hanging by a thread.” But in order not to cause psychological trauma to the child, this procedure must be made into a game.
Treatment of baby teeth
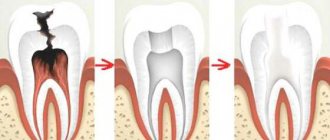
At the initial stages, caries is treated without tissue preparation - remineralization of the enamel, as well as modern Icon technology, which allows filling without drilling, easily cope with carious lesions of the enamel layer. In later stages, when the dentinal layer is affected, as well as in the case of pulpitis and periodontitis, treatment of baby teeth with tissue preparation will be required. You should not be afraid of such procedures - modern methods of anesthesia allow them to be carried out completely painlessly and comfortably for a small patient. In addition, the anesthetics used are harmless, with a minimum concentration of the active substance. And the site of the upcoming injection itself is numbed by applying a special gel or spray (application anesthesia).
Experienced dentists try to carry out treatment quickly so that the child does not have time to get tired and capricious. If a child has bad baby teeth and a large amount of work is required, it is divided into several stages. It also happens that the child does not want to contact the doctor, is too afraid of treatment, or the volume of manipulation is too large and serious - in such a situation, it is possible to carry out therapy under anesthesia or with intravenous sedation (with a preliminary examination).
In case of pulpitis, the root canals are filled with special pastes that dissolve simultaneously with the “milky” root, so there is no chance that the medicinal material will remain in the tooth socket and will prevent the new tooth from growing properly.
Little Mouse VS Tooth Fairy
Loss of baby teeth in children is associated with rituals in different countries. In Russia, back in ancient times (since the 18th century), there was a belief that a lost tooth should be put in the hole of a mouse and in return ask it for a permanent one, which will be healthy and durable.
In the West, instead of a mouse, the Tooth Fairy is popular, which exchanges a baby tooth placed under the pillow for money. This is precisely the reason why children in Russia nowadays prefer to “cooperate” with her.
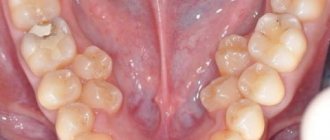
Caries, pulpitis and periodontitis of primary teeth in children
Milk teeth have thinner enamel and dentin layers than permanent teeth, they have a larger pulp chamber and, therefore, infection spreads faster to the pulp. They are more often susceptible to carious lesions - and not least because of night feeding or the habit of drinking drinks from a bottle at night (mostly sweet or sweetened - tea, juices).
In addition, caries is often provoked by plaque on baby teeth, which forms faster than in adults, and which not all parents are in a hurry to remove. Many people begin brushing their children’s teeth at a more or less conscious age, while a child should be taught hygiene and regularly remove plaque from the moment the first teeth erupt, that is, from about six months of age. Also, the cause of diseases of the dental system can be an insufficient amount of solid food in the baby’s diet, since chewing solid food helps to clean the dental surfaces themselves.
The child's nutritional habits, lack of hygiene, and too thin enamel layer provoke a phenomenon called circular caries of baby teeth - carious lesions spread over the entire tooth surface, as if encircling the crown.
Caries quickly turns into pulpitis - an inflammatory lesion of the dental pulp. Most often, a doctor is consulted precisely at this stage of the infectious process, ignoring the initial stages of damage to dental tissues. Pulpitis, in turn, provokes periodontitis of primary teeth in children - inflammation of the periodontal tissues near the tips of the tooth roots. This condition is usually accompanied by severe pain, severe swelling of the affected area, and often an increase in body temperature.
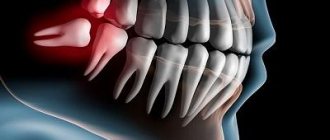
In the future, people will not have wisdom teeth
It is now recognized that wisdom teeth are vestigial. This is the most problematic group of teeth, with many painful moments associated with it. When they erupt, a person may experience severe pain, inflammation, fever, and when all wisdom teeth appear, crowding of the dentition may begin. At the same time, they play almost no role in the process of experiencing food. Evolutionary changes lead to the fact that in modern times, wisdom teeth are increasingly not erupting in adults. It can be assumed that in the future they will disappear altogether.
Restoration of baby teeth
If a child’s baby tooth breaks off or if the dental crown is severely damaged by caries, restoration is carried out. However, if for adult patients one of the most important aspects during restoration is aesthetics, then for children functionality is much more important. Therefore, restorative filling materials are always selected taking into account the patient’s age - for children, durability and impeccable aesthetics are not so important, a good marginal fit of the fillings and the preservation of dental tissues are much more important. Filling materials that are too strong can put pressure on dental tissues and contribute to their destruction, and therefore dentists choose materials that will recreate and maintain the integrity of the dental crown until the moment of natural tooth loss.
Everything has its time
One of the most frequently asked questions to our doctors from mothers is: “In what order do teeth begin to fall out?”
It usually starts at the age of 5 years. The very first teeth that undergo this process are the incisors, then the fourth and fifth teeth of the row, then the canines. To make it more clear to you, here is a diagram of the loss and eruption of baby teeth:
Don't worry if your child is over 5 years old and his teeth aren't starting to change. Each child’s body is individual, and much depends on nutrition, dental care, daily routine, and climatic conditions. In girls, the loss of baby teeth begins a little earlier than in boys. If you are still worried, then contact your dentist and conduct an unscheduled examination.
I would also like to note the timing. Complete replacement of milk teeth with molars occurs within 6-7 years. There is no need to specifically tear them out or loosen them. Everything will happen naturally.
The doctor prescribes removal only if the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, but the root tooth is already beginning to grow.
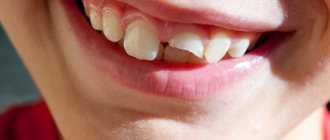
What to do if a child's baby tooth breaks off
- Is the child scared and crying? Try to calm him down. Take it in your arms, turn on your favorite cartoon or distract your baby with a game.
- If there is bleeding, apply a sterile gauze pad (do not use cotton wool - the fibers may stick to the chip).
- Try to find the tooth fragment as quickly as possible. Place it in saline solution, boiled water or wrap it in a damp cloth. This will make it easier to restore a child’s broken baby tooth.
- For pain, you can give Nurofen or paracetamol.
- If a fracture is suspected, make a circular bandage around the head, securing the lower jaw.
It is necessary to get an appointment with a dentist within the first 2-48 hours. Don't forget to take the saved tooth fragment with you.
What to do after a child’s tooth extraction?
- Make sure that the child spits out the tampon that was placed after removal after 15-20 minutes.
- After removal, a blood clot should remain in the hole, which protects it from inflammation. There is no need to clean the hole from blood, rinse the mouth, the child should not touch the removal site with hands or objects.
- If the child has been given anesthesia, explain to the child that he should not bite on the numb side until the feeling of cold and pins and needles goes away.
- Feed your baby only warm, soft food for several days.
- Maintain good hygiene; brushing your teeth is not only possible, but also necessary, with a soft toothbrush, carefully avoiding the extraction site.
- If the tooth extraction was difficult, then try to limit the child’s physical activity so as not to provoke bleeding.
Treat caries or remove a tooth?
Here, the recommendations of pediatric dentists agree: teeth need to be treated, although this is often associated with inconvenience. True, it is now much easier to persuade a child to calmly undergo treatment than it was before, when quality dentistry was unavailable. In a modern clinic, a calm and friendly atmosphere is important in a pediatric dentist's office. The doctor will first show the instruments, explain what he will do, and establish contact with the child. And drugs for pain relief will help carry out the treatment so that there are no negative impressions left from it.
Dental treatment is not scary! Especially if it doesn't hurt
It is best to treat tooth decay in its early stages. Then you can do without drilling at all - it will be enough to clean the surface of the tooth and apply a remineralizing composition. Small areas of caries can also be treated using a special device that uses a laser beam.
But even if a large carious cavity has already formed in the tooth, it is still recommended to install a filling. In some cases, crowns are even placed to save the tooth, which will last until the tooth falls out naturally. All this is justified in order to preserve the functionality of the tooth, which is extremely important for the formation of a correct permanent bite in a child.
Crowns can be installed to save teeth
How to go to the dentist, remove a baby tooth and not scare your baby?
It is recommended that a child’s baby teeth be removed by pediatric dentists: it will be painless, safe and timely. For everything to go smoothly, a visit to the dentist should be associated with something pleasant and calm. Modern dentistry has a friendly atmosphere, new painkillers have appeared, and instruments (especially in children's offices) do not inspire fear.
Finally, our advice: don’t worry and don’t let your child worry. The calmer you are about going to the dentist, the calmer your baby will behave. Stay nearby in the dentist's office, because parental support is extremely important to him.
Possible treatment options
The method of preserving a damaged baby tooth depends on the degree of damage. Sometimes the dentist suggests taking an x-ray to diagnose damage to adjacent crowns, tooth dislocation and assess the condition of surrounding tissues. Before restoring a tooth, the dentist performs hygienic treatment of the oral cavity.
Treatment methods for a chipped baby tooth
- Enamel chipped - polishing the sharp edges of the crown.
- A baby tooth has broken off within the dentin - building it up with photocomposite material or covering the chip with a crown fragment.
- Fracture exposing the dental nerve - reconstruction using a tooth fragment.
- Mobility, displacement of teeth - applying a splint to the damaged tooth and two adjacent crowns (one on the right and on the left) under local anesthesia.
- A child has a cracked baby tooth in the root zone - sealing the damage and strengthening the crown with an onlay.
Thanks to the precise selection of the color of the composite material, the restored baby tooth does not differ from healthy crowns. The child will not experience psychological discomfort, but the teeth must be treated with care to avoid repeated chipping.
Physiological features of the development of baby teeth
The front, or frontal, teeth are located very tightly to each other and only when the child reaches the age of four, diastemas become visible between them - physiological gaps that increase after a year or two against the background of jaw growth. If there are no diastemas at the age of six, this indicates insufficient jaw growth, leads to crowding and requires correction of the bite in children. Physiological abrasion of surfaces, which contributes to the timely development of the masticatory apparatus, begins at three years of age.
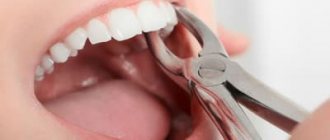
How temporary teeth are removed
Like any other medical procedure, tooth extraction has a clearly developed scheme and is carried out in several stages:
- Local anesthesia is the most common form of anesthesia. Specialists turn to more serious methods (general anesthesia) only in extreme cases: pathologies of the child’s psyche, purulent processes in the oral cavity, an allergic reaction and a history of individual intolerance to local anesthetics;
- Application of forceps to the crown;
- Rocking baby tooth;
- Its removal from the hole;
- Removal of fragments and granulations remaining in the socket;
- Packing the wound surface.
In order for both the doctor and the little patient to feel comfortable, parents must prepare the child and explain to him the importance of this procedure. Mental preparation is an important aspect of treatment.
How to protect baby teeth from caries?
Prevention is the best way to cope with any disease. Therefore, those parents who care about the health of their children should definitely think about caries prevention. How to protect baby teeth from caries? The recommendations of experts in this matter are as follows:
- The correct diet for the mother during pregnancy is with a sufficient amount of foods containing calcium, fluorine and phosphorus: cottage cheese, beef and beef liver, sea fish, nuts, fruits and vegetables, cereal porridges.
- Compliance with hygiene standards: daily brushing from the moment the first teeth appear, first with a cotton or gauze swab with boiled water, then with special baby brushes and pastes. Plaque on baby teeth should be removed promptly and thoroughly.
- A healthy diet for a child: as little fast carbohydrates, carbonated drinks, sweets as possible, more fruits and vegetables, cereals, and dairy products.
- Timely visits to the dentist for preventive examinations (at least once every six months).
It is important that parents develop a conscious attitude towards the health of their children's teeth and oral cavity in general. A timely visit to the dentist in case of any identified problems, as well as for regular medical examinations, will help maintain the health of the child’s dental system – and therefore the digestive system too.
Why shouldn't you remove baby teeth yourself?
Removal of a baby tooth is considered premature if more than a year remains before a new one appears. This period is difficult to predict accurately, but you can roughly estimate it using a graph with average indicators.
Premature removal of a baby tooth is dangerous because its neighbors will try to take the vacant space. The roots of permanent teeth that are about to emerge will become crowded. The bite will change, which will take a long time to correct. Moreover, there are several strict contraindications for extracting baby teeth:
- Acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
- Inflammatory diseases of the throat (ARVI, sore throat, etc.).
- It is not recommended to remove teeth for pathologies of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, central nervous system, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency and nutritional dystrophy.
So when your child's first baby teeth start to loosen, don't disturb them and let them fall out naturally. The child's body knows its business.
When a tooth is already loose, it needs to be cleaned very carefully so as not to rush things. If your child is still in kindergarten and his motor skills are not well developed, help him: take ASEPTA® Baby dental wet wipes and wipe the tooth (as well as its neighbors) from the top and sides.
When should a pediatric dentist remove a baby tooth?
There are cases when a baby tooth needs to be removed without waiting for natural loss.
If the tooth is not loose, it CANNOT be removed at home; this can ONLY be done by a pediatric dentist. Temporary teeth have long roots, underneath them there are the rudiments of permanent teeth that can be damaged, and baby teeth themselves are fragile and easy to break. Tooth extraction is a mini-operation, for which you need to contact a specialist.
In what cases does a baby tooth need to be removed?
- The tooth is damaged by 50% or more by caries and cannot be restored.
- Serious complications of caries have led to the fact that the tooth is a source of infection that cannot be cured - periodontitis, periostitis, phlegmon.
- A fistula has formed on the gum next to the tooth.
- A cyst was found on the root of a baby tooth.
- The tooth is injured (severely chipped, twisted by a blow, broken and scratches the mucous membrane)
- The tooth wobbles for a long time, but holds tightly and cannot fall out on its own, which prevents the child from eating.
- The loose tooth became infected and inflammation began.
- A permanent tooth has already erupted next to the milk one, but the milk tooth is not going to fall out.
- If, according to the timing, the baby tooth should have fallen out a long time ago and a permanent one should have grown in its place, but nothing happens. This indicates a delay in root resorption. In order to understand how to proceed, an X-ray diagnosis of the presence of a permanent tooth germ is needed. If there is a germ, then it is better to remove the baby tooth to cause the growth of a permanent one.
- Sometimes a tooth needs to be removed for orthodontic reasons.
Anatomy of different types of temporary teeth
- Incisors.
- Fangs.
- Molars.
Eight temporary incisors have the same structure - a fairly flat crown and 1 root. The incisors of the upper dentition, like the rest of the teeth, are larger than the lower ones. In the center, the incisors have one canal, and in 93% of cases, the lateral ones have two.
The four temporary canines are distinguished by a slightly sharp crown on all sides and the longest root. The crown of the canine preceding the permanent one is shorter and convex. The root has a rounded shape in cross-section and a slightly curved apex towards the buccal direction.
Each of the eight teeth of this type has a multi-cusped chewing surface and ends in several root canals. These are the largest teeth in childhood. The second molars are always larger than the first, which cannot be said about similar molars.