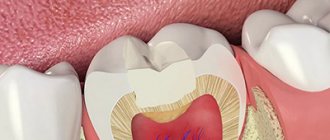
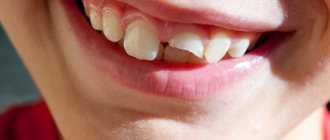
Untimely treatment of caries in children leads to the development of pulpitis - inflammation of tooth tissue, including blood vessels and nerve bundles. The lower molars are most often affected, but the disease occurs even on the anterior elements. Therefore, pulpitis in children occurs even more often than in adults. This is due to a number of factors:
- thin weak enamel;
- large volume of pulp;
- wide root canals;
- less mineralization;
- weak immunity.
In addition to caries, pulpitis can be caused by trauma, including poor treatment.
Symptoms
Inflammation occurs in acute and chronic forms. Acute occurs less frequently, but has more severe symptoms and occurs in two stages:
- serous. The inflamed pulp is filled with serous fluid. There are complaints of severe pain in the tooth, intensifying at night and when chewing. The pain, as a rule, is intermittent, appears once and subsides. Most often, the process occurs in teeth with unformed or absorbable roots. After 5–6 hours, a transition to another stage occurs;
- purulent. Pus forms in the tissues, which begins to melt cells and tissues. The severity of the condition is influenced by immunity, dental condition, and bacterial activity. If the pus has an outlet in the form of a carious cavity or fistula, then the pain is mild. In the absence of outflow, the pain syndrome is bright and long-lasting, intensifying when chewing or eating cold or hot food. The general condition may worsen and fever may appear.
Chronic pulpitis occurs after acute pulpitis or on its own and is characterized by vague symptoms. Pain can only occur under unfavorable factors - cold or hot, too sweet food. The child begins to chew on one side, an unpleasant odor appears, and a bursting and pressing sensation occurs.
The danger of this form is that it is almost asymptomatic. Because of this, inflammation affects more and more tissues. Chronic pulpitis is of three types:
- fibrous. The lightest and most common form. Fibrous tissue grows, the pulp may bleed, and episodic pain appears from mechanical and thermal contact;
- hypertrophic. Develops with severe destruction of the tooth crown. Pathological growth of pulp tissue occurs, which fills the carious cavity;
- gangrenous. The most severe form, accompanied by pulp necrosis. The tooth becomes gray and bad breath appears due to tissue decomposition.
The nuances of filling temporary teeth
Temporary teeth are prepared in much the same way as permanent teeth. When a cavity is created during cleansing of a carious lesion, it is acceptable to leave hard, dry dentin, even if it is slightly pigmented. Since this indicates low activity of the carious process. Otherwise, there is a possibility of accidental penetration into the pulp. Given the characteristics of dentin such as moisture and friability, it is necessary to completely clean the cavity.
Temporary units are filled using atraumatic chemical-mechanical methods to prepare the cavity for restoration. This affects children's ability to adequately accept dental treatment and not be afraid of going to the doctor, as was the case many years ago. The sound of the drill does not terrify the child, does not make him afraid in anticipation of painful sensations.
The use of a drill is justified in cases of large tissue damage, when it is impossible to achieve complete treatment of the cavity from a carious defect by mechanical or chemical means. An important factor in the treatment of caries is sedation. If it is possible not to use it, the doctor will not do so. But if it is necessary to numb a tooth, the dentist must, together with the anesthesiologist, select the correct dose of anesthetic.
If the treatment area is several units, a decision is made on general anesthesia or sedation, when the child is conscious, but does not experience pain and can perform the actions that the doctor tells him during the treatment process.
Children under 2 years old cannot sit in the dentist's chair for a long time, so the doctor needs to act quickly, competently, and painlessly. The child needs a pediatric dentist. An adult will not be suitable, since in pediatric dentistry special instruments and preparations are used, doctors take into account the anatomical features of the structure of the organ, as well as psychological aspects to relax the child at the doctor’s appointment.
What materials are used (which fillings are best placed on baby teeth)
Filling materials for baby teeth,
suitable especially for children, used if conservative treatment does not help. It may also be that it is ineffective at this stage of the disease. It is important for parents to understand what fillings are used, whether there is a difference between them, the cost of the material, its effectiveness, and what reviews the formulations used have received.
On the dental portal you can see children's dental clinics, reviews of doctors, and videos about filling mammary units. To understand the compositions currently used in pediatric dentistry, let’s look at them.
Composite photopolymers
This material hardens in the cavity under the influence of a light lamp. They aesthetically match the color of the patient’s enamel, protect against the spread of caries, and are an expensive technique. Installed in the smile area to achieve the cosmetic effect of invisibility of the filling. Widely used on anterior units to achieve a cosmetic defect. Produced on the basis of silicon dioxide. They have some toxic effects on pulp tissue, so they are used with caution for pulpitis.
In terms of service life - they have great strength, they last until the change of the milk permanent bite. The disadvantage of their use is the need for anesthesia. Not used if the patient does not maintain hygiene, does not brush his teeth well, and there is acute caries in the cavity. The disadvantages of use are also the weak shrinkage.
It is established when the patient can sit quietly in a chair and allows the doctor to carry out manipulations to thoroughly clean the cavity from caries. For this reason, children under 2 years of age are not suitable patients for installation of this type of filling.
Glass ionomer cement
It consists of powdered glass and polyacrylic acid, which hardens when the components react acidically with each other. Glass ionomer cement for filling baby teeth
widely used on the chewing surface. The composition includes fluoride ions that work to remineralize the enamel. This type of material does not have strong strength, but it will last for several years until the bite changes. A child does not have such a strong chewing load as an adult, so the use of glass ionomer cement is justified. They differ in composition in some components, in their area of application - for strengthening fabrics and for aesthetics.
It has good adhesion to the tissues of the organ itself and other materials used for filling, protection, and strengthening of walls. Protects against the spread of caries and bacteria. Reviews from dentists who use glass ionomer material confirm the good properties of this cement: it does not stain when it comes into contact with coloring products, and its strength is sufficient for the entire time until the bite changes.
Colored compomers
Colored compomers are a great way to correct a tooth defect and involve your child in the process. The cooperation of a young patient with a dentist leads to positive results: the child is not afraid to have his teeth treated and visit the doctor, the doctor does his job efficiently, without making the child nervous. A colored filling gives the child the opportunity to take his mind off the unpleasant process, participate in choosing the color, make his own decision, feel responsible and allow the doctor to finish the job.
Colored fillings require chemical preparation of the cavity before installation. The doctor does everything quickly: cleans the cavity, etches it with 35% orthophosphoric acid for a minute, applies a compomer, then polymerizes and polishes it. The whole process takes about 15-20 minutes. During this time, the child will not get tired, and will be motivated to come to the appointment next time and choose a different color of filling if the need for treatment arises.
Colored compomers are placed on the chewing surface. The material is characterized by high plasticity, fills the entire space in the cavity, has the property of releasing fluoride to the enamel, as well as accumulating it from products. The low price allows you to economically treat caries in a child. Today the material is presented in the following colors: blue, gold, yellow, green, silver, orange, pink.
Preventive measures
The well-known phrase that preventing a disease is cheaper, better, more convenient than treating it afterwards also applies to teeth. Preventative measures are ways to care for the oral cavity and take care of the health of the milk units. This will ensure a healthy permanent bite. Taking care of your baby's dental health begins with the mother's health during pregnancy.
- While breastfeeding, you need to maintain your health and take minerals to strengthen your enamel.
- Child’s oral hygiene after feeding, use of cleansing wipes and fingertips for the smallest children, special toothbrushes and pastes.
- It is important for adults to remember: you should not lick a child’s spoon, caries develops due to the presence of bacteria, and they are transmitted from adult to child.
- A balanced diet, the presence of dairy products and fish, a minimum content of carbohydrates and sweets.
- Accustom your child to self-hygiene, ensure that he does it efficiently and regularly, and achieve automaticity of a useful habit. In the morning and evening - brush your teeth, rinse your mouth - in the afternoon after meals.
Regular preventative visits to the dentist will help avoid a big problem. In the early stages, caries responds well to mechanical impact on the enamel, which does not leave a mark on the enamel tissue and stops the pathological process. The tissue does not need to be prepared. Preservation technique in the early stages will allow baby teeth to remain in the jaw all the time until they are due to be replaced by permanent ones.
How to recognize the problem and is emergency treatment required?
Due to the reduced sensitivity of the pulp, pain during inflammation may be mild and not cause severe discomfort. In this case, the process of tissue destruction occurs rapidly. It is important to visit the dentist regularly and not ignore your child’s complaints of pain when chewing or when eating cold and hot foods.
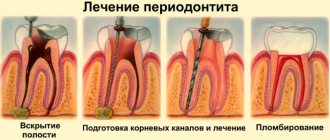
Treatment for pulpitis should be immediate. The disease is dangerous due to complications - periodontitis or periostitis. It can also spread to a permanent tooth that has not yet erupted and destroy it.
Treatment of permanent teeth at the stage of root canal formation
In this case, instrumental preparation is carried out similarly to the previous option. The specialist cleans the walls of the root canals with large H-files that have a safe tip. As in the treatment of temporary teeth, the internal cavity does not need to be given a conical shape, since at the stage of active formation the dentin layer remains very thin. In the process of removing infected tissue, the dentist needs to guide the instrument in such a way as to ensure the highest quality cleaning of the root canal, which expands towards the top.
Treatment methods
The treatment of primary teeth in general does not differ from the treatment of permanent elements. If the child’s condition is serious, there is a threat of infection spreading throughout the body, amputation is performed. In most cases, the tooth is preserved to prevent malocclusion. Therapy is carried out in different ways:
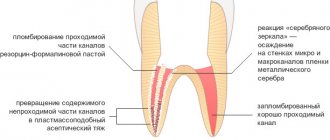
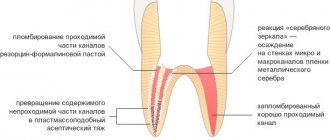
- traditional. Involves treatment in three visits. During the first one, the nerve is opened, a devitalizing paste with arsenic is applied for 24-48 hours or without it for a period of up to 7 days. On the second visit, a pulp mummification mixture based on resorcinol-formalin is placed into the canals. At the last visit, a permanent filling is installed;
- modern. It takes place in 1 – 2 visits. If the child can sit quietly for a long time at the doctor and the roots of the tooth are formed, extraction is performed. The nerve is removed either on the first visit or after applying the paste. Next, the canals are carefully processed, infected tissue is removed, an anti-inflammatory paste (for example, zinc eugenol) is applied and closed with a filling. The composition will gradually dissolve along with the roots when changing teeth;
- partial vital amputation. The doctor removes the upper portion of the nerve and applies an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory medication that seals the remaining living pulp.
When treating teeth with immature roots, a different approach is chosen. This is due to several reasons:
- the apex of the roots has not yet closed and there is a risk of infection of the permanent tooth germ;
- the roots are short and the channels are wide;
- trauma to the upper zone of the root can lead to disturbances in its formation;
- It is impossible to remove the entire pulp and perform a complete canal treatment.
Most often, they choose amputation of the pulp by any method or biological treatment, when the tooth is cleaned of the affected tissue and a paste with calcium hydroxide is applied for several days. After this, a filling is installed.
Preventive measures
Obviously, it is better to prevent a dental problem than to subject the child to treatment and, accordingly, stress. But for this it is necessary to take care of prevention, and for this purpose, parents should take note of the following recommendations:
- The sooner you start taking care of the condition of your child’s teeth and oral cavity, the better. Even during pregnancy, the expectant mother should eat properly and also enrich her diet with foods high in calcium and fluoride. At the same time, you should start carrying out daily hygiene procedures even before the first teeth appear - you can clean your gums from bacterial plaque using special napkins or fingertips,
The photo shows oral hygiene in a baby using a special napkin. - As soon as the child reaches the age when he can brush his teeth on his own, he needs to be taught daily hygiene. At the same time, he must learn how to clean correctly, and a pediatric dentist will help you with this,
The future smile depends on the health of baby teeth - You should limit your child’s consumption of sweets, including sweet mixtures for little ones. Excess sweets in the diet is one of the most common causes of dental caries in childhood.
- Regular preventive examinations at the dentist’s office will allow you to detect the problem in time, and therefore quickly deal with it. At the same time, it is better to show the baby to a specialist as soon as his first teeth appear.
Parents need to understand that treatment of baby teeth is an extremely important condition for the health of permanent teeth. Therefore, if caries or any other dental diseases develop, the child should be immediately shown to a specialist. And in order to prevent problems from arising, it is necessary to take your child to the dentist for preventive examinations 3-4 times a year.
Is it possible not to treat pulpitis if the teeth are baby?
There is a common opinion that it is not necessary to treat baby teeth, because they will soon fall out. This is the biggest mistake parents make. Untreated pulpitis leads to irreparable consequences and even affects permanent teeth:
- purulent abscess, periodontitis, life-threatening condition;
- deep infection affecting the germ of a permanent tooth;
- malocclusion due to early tooth extraction due to untimely treatment;
- pain interferes with normal chewing of food, uneven load on the teeth leads to accelerated destruction of other elements.
Prevention
The main method of preventing dental and oral diseases is regular visits to the dentist and treatment of caries in the early stages. It is important to teach a child hygiene and the rules of brushing teeth from the first years of life. Parents should control the diet, which should contain all the necessary substances, limit sweets and allow only water to drink at night.
Doctors at the VIMONTALE clinic treat pulpitis of primary teeth in children of any age. Specialists not only master modern painless techniques, but also know how to find contact with a child, know how to reduce anxiety and win the favor of the youngest patients.
Expert of the article you are reading:
Lozinskaya Alla Nikolaevna
Pediatric dentist, general dentist.
You may also be interested in:
Children's orthodontist Dental treatment for children Correction of bite in children Features of the treatment of childhood caries Removal of baby teeth Prevention of childhood caries Silvering of teeth in children
Show more
What materials are used
Many parents are interested in what is currently used to fill children’s teeth. Not so long ago, the choice of materials used to fill children's teeth was not as diverse as it is today. At one time, dentists more often resorted to using amalgam, but this composition cannot be called completely safe and harmless to the body, especially when it comes to a child. Later they began to use glass ionomer cement, but it also has its disadvantages. For example, it takes quite a long time for the material to harden, which is not always convenient if there is a baby in the dental chair.
On a note! Often, special pastes are used to fill the root canals of baby teeth. Such compositions are not able to provide perfect tightness if used to fill a vertical cavity. In addition, after some time they dissolve, and therefore are not intended for permanent filling.
This is how a child’s teeth are filled with reflective composites.
To date, the situation has changed a little, and today pediatric dentists increasingly prefer fillings made of light-curing composite, as well as compositions that are a combination of a hybrid composite and glass ionomer cement. These materials are characterized by increased strength, are easy to polish and have a high degree of adhesion.
Our patients
Patient recommendations
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Alekseeva O.V.
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Zolotareva S.V.
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Vera
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Mikhail Ivanovich
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Collapse
Features of machine treatment of dental canals in children
Regardless of the technique used, the dental specialist should consider the following points:
- Curved canals should be treated with a pre-curved tool.
- After removal, the reamers and files need to be cleaned and checked for damage.
- Rinsing the treated area should be done using an endodontic syringe equipped with a special needle.
Particular attention should be paid to medicinal treatment of the canals using EDTA and other drugs. It should be carried out at all stages of instrumental preparation, from the initial opening of the cavity to the final washing out before filling.