Most people aged 17-27 years old face problems caused by the appearance of a wisdom tooth (the so-called third molar or eight). Sometimes it can erupt at a later period. Almost 10% of people do not have them at all, and in a third, they remain in the jaw all their lives in the form of embryonic anlages, never appearing.
However, this process is not always accompanied by pain, discomfort and other problems. Quite often they erupt successfully and retain their chewing function for many years without showing any signs of carious lesions.
What to do if teething still causes discomfort: treat it or is it better to resort to removal? These and other questions will be discussed later in the article.
What are wisdom teeth?
Dentists and scientists call them a vestigial organ, the need for which disappeared when people learned to heat food. Eights, like all other human teeth, consist of roots, a neck and a crown, but despite this they have certain anatomical features.
Here are the main differences:
- they are only indigenous and do not come in milk;
- their eruption is often accompanied by pain;
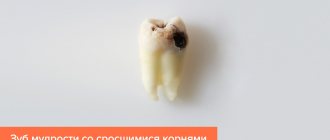
- have a larger number of roots - from 2 to 5;
- bent and twisted roots.
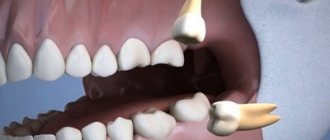
Where does the figure eight grow?
It is called so because of its late eruption. If a child’s first milk teeth appear at the age of one, and molars appear before the age of twelve, then at what age do wisdom teeth grow? They will appear when the jaw bone tissue is fully formed. This period occurs between 16 and 27 years of a person’s life. In 3% of people they may appear after many years, and in 8% they do not appear at all. These are four chewing eights on the jaw - third molars, which normally are no different from the rest. Every person has rudiments, but not everyone has them.
The process is not associated with pathology; rather, the problem is that the eighth painters are considered a rudiment that does not carry a functional load.
Common problems that can be caused by wisdom teeth
Most often, problems that arise during the period when eights emerge from the gums are due to the fact that by the time they appear, a person has already formed strong bone tissue, and there is practically no room left for them in the jaw. All this significantly complicates the process of growth and eruption.
A tooth appearing in an already formed jaw can cause the following problems:
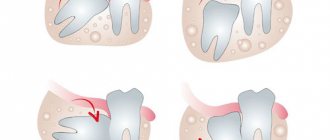
- Development of periconaritis. The peculiarity of this pathology is the formation of a “hood”. In addition to the pain that occurs when food gets on the gums and irritates the nerve endings, pathogenic bacteria accumulate in the “hood”, which can cause inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
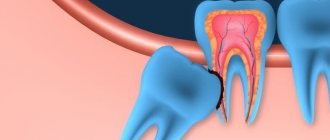
- Cyst formation. Dense gum tissue and the space constrained by the formed jaw forces the erupting tooth to grow in the direction of least resistance. Because of this, its roots can grow into the cavity of the maxillary sinus, forming cysts that become infected, inflamed and remain the cause of toothache for a long time.
- Incorrect position in a row (dystopia). As the third molar grows, it can displace teeth that have already erupted. This disrupts the bite and deforms neighboring teeth.
- Caries formation. Eights cause certain difficulties in daily care, as they are located too deep in the oral cavity. Due to poor hygiene, food particles and bacteria accumulate on their surface, creating a favorable environment for the development of infectious processes.
- Damage to the root of an adjacent tooth. During eruption, the third molar puts pressure on the adjacent tooth, thereby damaging its root. This can provoke an inflammatory process or degeneration of dental tissue.
- Incomplete eruption (retention). Impacted third molars can cause quite a lot of problems - they often cause inflammation of the gums and diseases of adjacent teeth.
If the above problems appear, the dentist may recommend resorting to their removal without waiting for the development of more serious complications.
Symptoms of physiological and pathological eruption of wisdom teeth
Tooth eruption can occur physiologically or pathologically. Discomfort occurs in any case, but if the “eight” grows without complications and other teeth do not interfere with it, inflammation usually does not occur. The complex of symptoms may vary, but most note the appearance of such phenomena as:
- engorgement and hardening of the gums;
- distension in the area of eruption;
- aching pain of varying intensity.
Important! Symptoms can vary significantly from person to person. Even one patient can experience completely different sensations when wisdom teeth erupt on the lower and upper jaws.
Severe pain, tumors, and inflammatory processes accompany pathological eruption. In this case, saving the tooth is not always advisable. If your wisdom tooth is cutting out and your gums hurt, you need to see a dentist.
Signs of pathological eruption are:
- constant, intense, aching pain;
- swelling of the gums or cheeks;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- pain when swallowing;
- temperature increase.
Are you experiencing one or more symptoms? Don't delay your visit to the doctor. Such phenomena may be a sign of pericoronitis, purulent inflammation, abscess and other pathologies. Without adequate treatment, the inflammatory process will spread to adjacent tissues, and phlegmon will form in the oral cavity. In advanced cases, the problem can only be dealt with surgically in a hospital setting. Purulent inflammation is opened through external incisions, the treatment process is accompanied by the use of antibiotics.
Even if the symptoms of wisdom tooth eruption do not cause concern, it is recommended to visit a dentist. This is necessary to exclude a pathological process.
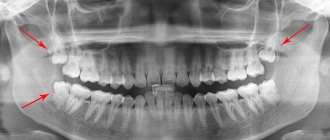
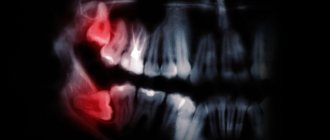
The doctor will refer you for an x-ray or computer examination. It helps determine the position of the new tooth relative to the existing ones and assess whether there is enough space for it. The photographs clearly show any deviations in the figure eight position. Based on the examination, the doctor will decide whether the wisdom tooth needs to be removed.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The main symptom indicating activation of third molar growth is pain that occurs when chewing. In the case of the formation of a cyst or “hood,” inflammation develops, which, in addition to pain, can be accompanied by an increase in body temperature, enlargement and soreness of the submandibular lymph nodes, and a headache due to the development of the inflammatory process.
A sign that wisdom teeth are growing abnormally is:
- acute pain in the temporomandibular joint;
- numbness of the jaw and aching pain. This may indicate improper growth inside the bone and possible trauma to the jaw nerve;
- inflammation and enlargement of lymph nodes. As a rule, such a sign indicates that an infectious process has begun;
- redness, swelling of the gums and pain when pressing on it;
- displacement of teeth in a row.
If you have such symptoms, you should immediately visit your dentist for diagnostic measures. Only a specialist can confirm or deny the presence of problems associated with the growth of the third molar.
Diagnosis of an impacted tooth, completely or partially hidden under the gum tissue, is carried out in several ways:
- Palpation and probing;
- Sight radiography - to determine the direction of growth and the number of roots;
- Orthopantomography;
- Computed tomography.
The diagnostic method is determined directly by the doctor; sometimes an examination in the dental chair is sufficient, and sometimes an x-ray is necessary to identify existing problems and predict the risk of their development in the future.
Why does a wisdom tooth become inflamed?
The cause of inflammation is dental plaque microorganisms. The first sign of inflammation is pain and bleeding of the gums, which usually makes good hygiene difficult. A vicious circle arises: brushing a tooth hurts, but without cleaning it becomes even worse and even more painful. Therefore, the first thing that needs to be done when inflammation occurs in the area of an erupting wisdom tooth is to improve oral hygiene and thus reduce the number of microorganisms to a minimum.
Symptoms of pericoronitis
Sometimes the onset of inflammation around a wisdom tooth can be confused with a cold and a “sore” throat. Patients report that swallowing becomes painful, and the lymph nodes in the angle of the lower jaw and near the ear become enlarged. The pain may radiate to the ear on the side of the problematic tooth. The gum above it swells, changes color to bright red, and purulent discharge may appear from under the gum. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
Symptoms of intoxication of the body are added: fever, chills, weakness, deterioration in general health, lack of appetite. With the development of inflammation, swelling can spread to the cheek and deeper cellular spaces. It becomes difficult to open the mouth, which in turn impairs the doctor’s access to the causative tooth.
Why does a wisdom tooth become inflamed?
What to do: treat a wisdom tooth or remove it?
Many people are often interested in the question: is it better to use the services of a dentist at the stage of intramaxillary development and remove a rudimentary tooth so that it does not create problems later?
However, most experts agree that preventive removal of eights is unacceptable. When the tooth has erupted correctly and does not cause any discomfort, it can be preserved. The main thing is to carefully observe the rules of hygiene and visit the dentist on a regular basis to monitor and perform hygiene procedures.
Removal is resorted to in cases where conservative treatment methods cannot achieve the desired result.
What to do if the gums above the wisdom tooth are inflamed?
- Clean thoroughly, even if it bleeds and hurts. After all, as you already know, the cause of inflammation is that plaque and food debris around the “eight” were regularly not cleaned. The plaque microbes did their job - pericoronitis occurred. To more successfully clean plaque around a wisdom tooth, it is better to purchase a brush with elongated front bristles.
Brush with extended front bristles
- Make salt baths (dissolve 1 teaspoon of salt in 1 glass of water at room temperature - never hot!). It is recommended to put the saline solution in your mouth and hold it on the side of the inflamed tooth for several minutes. Such baths are carried out every hour; it is optimal to alternate them with rinsing with chlorhexidine.
- If the swelling does not decrease within a day or two, it is better to consult a dental surgeon. Perhaps an incision (pericoronarotomy) and the prescription of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are needed. If you have a fever and it hurts to swallow, you can’t hesitate, you need to urgently go to a dental surgeon!
- If inflammation of the gums around the wisdom tooth occurs regularly and you have repeatedly visited the dentist for an incision in the gum area above the wisdom tooth, this is an indication for removing the “eight”. Surgeons recommend removing the tooth as planned, not during an exacerbation or during an active inflammatory process. Such removal will be easier for you, painless and the body will need much less time to recover.
After reading the article, did you remember your torment with the eruption of wisdom teeth? We invite you to a consultation with a dental surgeon at the KANO clinic network. Our specialists will prescribe the necessary diagnostic X-ray and tell you what to do with the problem “eight”.
The best dental clinic in Ivanteevka
Specialists at Sanident comprehensive dentistry in Ivanteevka offer a wide range of dental services: from caries treatment to prosthetics and restoration. We have innovative equipment, highly experienced staff, high-quality consumables, and at the same time quite affordable prices and promotions. We give a healthy and beautiful smile to everyone!
You can make an appointment with a dentist at our clinic by calling the phone number listed on the website or by visiting us in person at the following addresses:
- Ivanteevka, st. Novoselki, 4 (Ivanteevka railway station);
- Shchelkovo, st. Central, 80 (railway station Voronok).