09.11.2020 8519
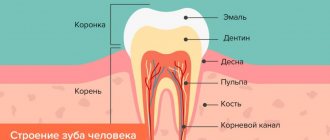
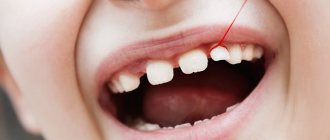
If you look closely at the structure of the jaw, you will notice a groove separating the tooth and gum. Depending on the characteristics of the patient, it has a different structure and depth.
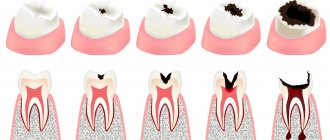
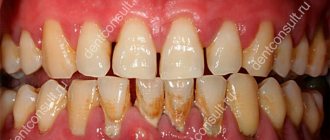
It is this groove that is called the periodontal pocket. The depth in a healthy person usually does not exceed 2 mm.
However, bacteria accumulate inside and severe inflammation gradually develops. Deepening begins, periodontitis or gingivitis develops.
The problem is that the dentist needs to remove the affected tissue to treat the patient. If this is not done, the process will only progress and the inflammation will affect larger and larger areas and begin to threaten the tooth.
The stripping process is called curettage.
About periodontal pockets and causes of inflammation
The problem does not appear by itself; there must be serious prerequisites for it.
The need for curettage is provoked by five potentially dangerous factors:
- Inflammation of the gums or periodontal tissues . Formed where soft tissue touches the tooth.
- Insufficient oral hygiene . If you brush your teeth incorrectly, food debris gets inside the groove. As they decompose, bacteria multiply.
- Serious dental plaque . Formed due to significant fossilization. Problems also begin for people who ignore the formation of tartar.
- Congenital anomalies . This leads to the pocket being deeper or having a non-standard structure. Bacteria will accumulate in it much more intensely.
- Diseases of the body . Patients with hormonal imbalances and digestive disorders are at risk. Their saliva composition changes, which can have a serious negative effect on the oral mucosa.
Curettage will be required if you have orthopedic structures installed and your metabolism is impaired.
Smokers and people who drink a lot of alcohol suffer from such problems - inflammatory processes are very common in them.
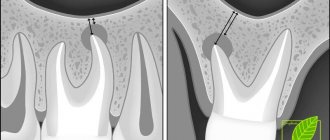
There are two types of periodontal pockets - false and true.
In the first case, the gum moves away greatly from the anatomical cell, and no damage to the deep tissues is observed.
In the second case, everything is more complicated, because periodontal tissue begins to collapse. This type of pocket can be either horizontal or vertical.
Prevention methods
It is not difficult to avoid problems associated with gum disease. The basic rule is to brush your teeth daily (at least morning and evening). Particular attention should be paid to the interdental spaces, where food debris often remains. In the future, they become a suitable environment for the appearance of bacteria. Acid produced by pathogenic organisms is the root cause of gingivitis.
Another useful rule is to rinse your mouth after every meal. In addition, it would be useful to regularly treat the oral cavity with ultrasound.
Signs of inflammation
As with many other diseases, the insidiousness of the situation is that the patient may not notice the problem for a long time. At the same time, it will constantly progress and get worse.
The disease can be noticed at an early stage if you regularly visit the dentist. The development of inflammation is indicated by 6 parameters:
- The gums change color - they turn red or darken.
- An unpleasant metallic taste appears in the mouth.
- A noticeable swelling begins to develop near the affected area.
- Severe bad breath.
- Loose teeth.
- Pain when pressing or eating food that requires chewing.
- Bleeding, which occurs, including during brushing your teeth.
Although it is not so easy to understand that there really is a problem at an early stage, it is possible.
And the sooner you can notice this, the sooner treatment can begin. This greatly affects the success of the final result.
Features of curettage
Curettage becomes the last solution resorted to if alternative methods of correcting the situation fail.
This situation occurs when the pocket deepens to 4 mm.
At this stage, attempts to solve the problem with the use of drug treatment become futile.
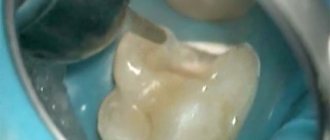
When performing curettage, tissue is scraped out or deposits and affected areas are removed by other means.
If the procedure is performed by a dentist with extensive experience and a good level of training, no problems will arise. Moreover, the efficiency in this case will also be very high.
Indications and contraindications
When a patient comes to the clinic with such a problem, they always take an x-ray.
It will show how severely the periodontal tissue is affected, what means are best to use for complex treatment, and whether surgical intervention is necessary.
There are 5 common indications:
- The appearance of severe loosening of teeth.
- Inflammation, accompanied by an increase in tissue temperature, redness, swelling, and pain.
- Large dental stones.
- Developing a deep true pocket.
- Exhaustion of conservative treatment options with antibiotics and other means.
The decision that curettage can be performed is made only after a comprehensive assessment of the situation and weighing of the data obtained. The list of contraindications includes the following:
- Pronounced fibrous changes developing inside the pocket.
- Severe thinning of gum tissue.
- The pocket depth is more than 6 mm.
- Tooth mobility of the third degree.
Most contraindications are temporary. It is not recommended to carry out the procedure if, for some reason, bacteria are actively multiplying in the mouth.
In such a situation, dental intervention simply will not have an effect and you will have to find the cause of the problem and eliminate it.
Gum abscess - symptoms
A limited focus of infection in the gum most often forms during an exacerbation of existing periodontal pathologies, so signs of an abscess appear suddenly and grow rapidly. Quite pronounced local symptoms are characteristic, and due to intoxication with waste products of bacteria, the general condition also worsens.
An abscess is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the gums;
- limited tissue swelling (“flux”);
- temperature increase;
- redness and swelling of the mucous membrane;
- sometimes – tooth mobility;
- headache, weakness.
In the absence of timely treatment, a fistula can form - a canal in the gum with a hole through which pus spontaneously discharges from the lesion to the outside. After the fistula appears, the pain is relieved, but an abscess remains on the gum, treatment of which is necessary to completely relieve the infection.
Is it possible to perform curettage at the site of an extracted tooth?
Curettage of the socket of an extracted tooth - what is it? This process is similar to what is done when the tooth is still intact. After the tooth is removed, the dentist removes the affected tissue.
This process is carried out if suppuration begins at the site of the tooth, crumbs from hard tissue remain, alveolitis begins to form, or there are signs of necrosis of the walls.
The dentist performs a curettage, after which the wound is closed with a tampon. The process may often be required if, after tooth extraction, the patient behaved incorrectly and the wound did not heal as required.
Another common indication is the appearance of dry socket syndrome. It can lead to alveolitis and the fact that the area will not heal for a long time with all the ensuing dangerous consequences.
Typically, patients themselves are rarely able to determine that they have a problem. Therefore, it is important to be sure to come to the doctor on schedule in order to monitor how tissue restoration is progressing after surgery.
The process itself consists of 5 stages:
- The treatment site is anesthetized so that the patient does not feel anything. Both infiltration and conduction anesthesia are used.
- Washing the hole. All foreign matter is removed, including blood, food debris, and pus.
- Cleaning the tissue walls and the hole itself. This is a direct curettage that requires close attention from the dentist.
- Antiseptic treatment. This is necessary to prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Closing the wound. The doctor applies a bandage. This allows you to stimulate wound healing and reduce the likelihood of resumption of the inflammatory process.
Since the area is treated from all potential threats, the tissue begins to heal quite quickly, and the risk of alveolitis recedes.
Why is an abscess dangerous?
The tissues of the oral cavity are rich in blood vessels, so it is easy for infectious pathological processes to spread from one area to another. A limited abscess without treatment can lead to the following local complications:
- abscess of the adjacent area;
- phlegmon - diffuse tissue damage by infection;
- periostitis – transition of inflammation under the periosteum;
- inflammation of the bone - osteitis.
In particularly severe clinical cases, if the symptoms of an abscess are ignored for a long time, osteomyelitis can develop - melting of part of the jaw bone tissue as a result of purulent inflammation. Pathology leads to the formation of voids in the bone, jaw fractures, and tooth loss.
An abscess in the area of the retromolar fossa (near the last chewing teeth) is especially dangerous, since the infectious-inflammatory process without adequate treatment can spread to the tissues of the pharynx, and from there to the mediastinum, which leads to serious complications from vital internal organs. Another possible way for the infection to spread is into the membranes of the brain, which leads to the development of meningitis. An abscess on the gum without treatment can also be complicated by sepsis when a large number of bacteria enter the bloodstream, which is life-threatening for the patient. You should not postpone a visit to the dentist if there are signs of inflammation of any location, since self-treatment of an abscess with purulent contents leads to a worsening of the condition and serious consequences.
Open curettage technique
Treatment can be performed using various methods. And one of them is open curettage of periodontal pockets.
Dentists perform it to remove all deposits accumulated under the gums. This allows you to prevent the appearance of foci of inflammation, the development of much more serious problems, tooth loss or the need for tooth extraction.
For the procedure to be successful, it is usually accompanied by special restorative therapy.
The doctor prescribes the patient to take medications that reduce inflammatory activity in the body. In parallel, antibacterial treatment is performed.
The technique has proven itself well and allows for quick treatment of even a large number of teeth in one visit – up to seven in a row. At the same time, the use of local anesthesia makes the process much less traumatic for the patient.
It is carried out in several stages:
- Separation of the mucous membrane of the gums . It is important that it does not touch not only the bone, but also the alveolar process. This usually requires making a small, precise incision in the anatomical neck.
- Gum separation . This helps to access the bone pocket directly. The dentist will have a clear view of the affected area and will understand what is being dealt with.
- Curettage . The process uses a scaler. All solid deposits are removed. The tissue is scraped out using a curette – hence the name of the procedure.
- Antiseptic treatment . It is recommended to use special agents with a pronounced hemostatic effect - they prevent the accumulation of blood, the formation of clots and an environment for the proliferation of bacteria.
- Installation of synthetic bone . It is important that the treated fabrics are filled with something. The synthetic product helps reduce the periodontal pocket and prevents the previously eliminated problem from re-developing.
- Stitching . A suture is placed and a gum bandage is installed.
All requirements for the use of special means and antiseptic protection are observed very strictly, so regeneration takes place very quickly.
The standard period for suture removal is ten days. No further intervention will be required.
Despite the fact that the technology is well developed and shows excellent results in dental practice, doctors try to avoid its use.
This is a local surgical intervention that requires a recovery period and strict medical supervision.
Opening a gum abscess
The mainstay of treatment for most cases of gum abscess is surgery. An abscess is a source of infection, most often developing due to prolonged lack of treatment for carious complications of the corresponding tooth. A swelling that forms on one side of the gum may contain pus, exudate, dead lymphocytes and a large number of pathogenic microorganisms. Over time, the abscess becomes larger and the risk of the contents spreading into surrounding tissue increases. Therefore, for effective treatment, removal of pathological contents from it remains a prerequisite.
An abscess is opened as follows:
- the doctor examines the extent of the lesion and determines the causative tooth;
- the oral cavity is thoroughly treated with an antiseptic solution;
- an anesthetic is administered for pain relief;
- Using a scalpel, a small incision is made on the gum, which should pass through the most protruding area of the abscess;
- the cavity of the lesion is washed with drugs with antimicrobial activity, the pathological contents are removed;
- A therapeutic and protective bandage is applied, and recommendations on its contents are given.
After the operation, the acute period of the disease subsides, pain and swelling decrease. Further treatment consists of taking medications prescribed by the dentist; it is recommended to do rinses and mouth baths. In some clinical cases, an abscess can be treated only after extraction (removal) of the tooth that caused the development of the disease. After complete recovery, suitable prosthetic methods are considered. If during the diagnosis it turns out that it is possible to avoid removal and save the causative tooth, after stopping the acute processes in the area of the abscess on the gum, therapeutic treatment is carried out (preparation, cleaning of the canals).
Closed operation
In addition to open surgery, closed curettage of periodontal pockets can also be used.
Typically, dentists recommend performing it if the pocket itself is shallow and only up to 3 mm .
One of the features of this technique is that the doctor practically does not see the condition of the tissue at the time of the intervention, and against the background of this, some part of the affected tissue remains inside.
When carrying out closed-type exposure, tissues are less injured, and by reducing the affected areas, it is possible to more effectively carry out conservative treatment using a special group of medications.
Most often, this method uses ultrasound. It perfectly removes deposits and is suitable for granulation. The impact itself does not require gum detachment.
By polishing and treating the cleaned areas, plaque no longer accumulates on them, and there is no risk that the problem will manifest itself again.
Diagnostics
Any dentist can perform the diagnosis. To do this, you should study the symptoms and take an x-ray. Using the image, the doctor will see how the tooth is located, the condition of the bone tissue that surrounds it, as well as the condition of the periodontium. If the disease is chronic, then bone resorption is studied. Pericoronitis is treated by dentists in our dental center.
Alternative Methods
In addition to closed and open exposure, other types of operations can be used to clean out pockets. These include:
Laser curettage of periodontal pockets
This is one of the main techniques used in advanced dentistry today.
The advantage of the laser beam is that it heats up to high temperatures. In this case, the deposits are simply burned out and the vessels are sealed. This reduces the recovery period and eliminates the risk of re-deposition.
Another advantage is the complete elimination of the need for sutures. During the recovery period, the patient will not experience increased sensitivity due to food intake, and there will be significantly fewer restrictions.
The main thing is not to overheat or lift heavy objects on the first day after surgery. It is best to maintain a rest regime or go to bed so that the body can devote all its strength to regeneration.
Vacuum curettage
Belongs to the closed subtype. The process also uses special curettes, but they are connected to a device that can apply very low pressure.
The tissue is scraped out and immediately sucked out of the hole. The duration of the rehabilitation process is greatly reduced, and the likelihood of complications becomes significantly lower.
Chemical curettage
In this case, citric acid is actively used. It is created on the basis of various types of solutions and allows you to make deposits soft.
A balanced mixture of active substances is pumped into the pocket and actively cleanses it, gives a pronounced antiseptic effect and destroys most potentially dangerous bacteria.
Cryo method
The method is based on freezing tissue using special nitrogen-based compounds. This effectively removes deposits, kills bacteria, and significantly reduces the risk of complications.
This is one of the cowless ways to clean out a pocket.
Which method should I choose from those described?
Despite the fact that some seem to be much preferable to others, in practice everything is not so simple. The fact is that there are individual contraindications that do not allow some patients to use the most bloodless intervention options.
Only after a careful analysis of the patient’s current condition and an assessment of potential risks can one understand which method is best to use. The extensive experience of our doctors allows us to do this without errors.
Dental care for gum pockets
If a patient has gum pockets, in addition to therapy in the dental office, treatment is carried out at home. All doctor’s recommendations must be strictly followed:
- daily brushing of teeth at least 2 times a day;
- periodic use of mouth rinse to provide antiseptic treatment;
- the use of preparations for cleaning teeth to eliminate inflammation and periodontitis;
- using an irrigator to clean the interdental spaces using a jet of water with strong pressure (they additionally massage the gums, increasing blood flow, activating metabolism and regenerative processes).
Periodically rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions. For example, chamomile and calendula. They simultaneously eliminate infection and suppress inflammation.
About the duration of the rehabilitation period
As with any surgical intervention, after curettage there is a recovery phase.
It is important to understand that the procedures themselves are safe and have already been well established in practice. But the patient will be required to follow a number of recommendations in order not to provoke the development of complications.
Among the important requirements at the rehabilitation stage are the following:
- Careful oral hygiene. During the first eight hours, it is better not to brush your teeth at all and not to disturb the operated area; it is not recommended to eat food, mouthwashes - anything that can cause irritation. After this period, you also need to be more careful with cleaning until the stitches are removed.
- If there is severe pain, you can only use medications recommended by your doctor. In most cases, simply applying something cold to the sore area helps.
- The diet is worth reconsidering. In particular, until the tooth heals and stops becoming loose, you should not chew on anything too hard.
- Avoid temperature changes. You should not go into the cold without protecting your cheeks or visit the sauna.
You will also need to comply with other doctor's requirements - use special rinses, change your standard toothbrush to a soft one.
Medicines
Professional teeth cleaning removes plaque and stones. But this does not mean that the infectious process is over. To eliminate it, you need to use medications:
- Mouth rinses. Antiseptics are used to destroy pathogenic microflora. For example, Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. They are used for no more than 7-10 days, so as not to cause resistance of microorganisms.
- Gels, ointments with antimicrobial action. They eliminate the infectious process and suppress inflammation. It is recommended to use 2 times a day for 7 days.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. They are used topically in the form of an ointment or systemically in the form of tablets. They suppress swelling, pain, redness.
- Regeneration products. Use oils and ointments based on vitamins. In addition to herbal products, ointments are used that stimulate cell regeneration.
- Antibiotics. Systemic drugs are prescribed only for severe infections that affect the body systemically. They are used in the form of tablets, suspensions, injections. They are prohibited from being used together with alcohol.
Medicines are designed to complement the main treatment. They accelerate the destruction of infection and suppress the inflammatory process. With their help, the effect of professional cleaning is enhanced.
Are there complications?
The procedure is safe and is carried out in strict compliance with all technology requirements.
But there are several potential problems that may arise as a result of personal characteristics of the body or non-compliance with requirements during the rehabilitation period.
These include the following:
- Sensitivity to food temperature . It occurs in almost everyone, but goes away over time. The maximum duration of hyperesthesia is up to two months. To cope with the problem, you can use special gels, ointments, toothpastes and rinses - the dentist will advise which ones.
- Swelling and hematoma . They may not go away for up to two weeks, but do not pose a serious danger.
- Problems in the functioning of the facial muscles . You should not be afraid of such a manifestation, because it will pass in about 10 days. Some patients complain of difficulty opening the mouth, but this also resolves in no more than 12 days, more often earlier.
- Increased tooth mobility . Observed for up to three weeks. For this reason, you need to pay attention again to your diet and remove foods that are too hard.
The patient's condition is constantly monitored by an experienced dentist, so that any serious complications can be avoided.
Purulent gum abscess
At the initial stage of the disease, the inflammation may contain only serous exudate and be accompanied by moderate pain and swelling. Treatment of this condition can be conservative (medication) without surgery. Over time, as a result of pathological processes, pus appears at the site of inflammation, the pain increases and often becomes pulsating. In the area of one or two teeth, a purulent abscess forms on the gum, the treatment of which requires surgical intervention.
Accumulating pus contains interstitial fluid, dead immune cells and microorganisms. As the disease progresses, the amount of pus increases and the pressure inside the abscess increases, microcirculation disorders worsen. Under such conditions, the risk of infection spreading to surrounding tissues and the development of complications increases.