A healthy stomach determines the overall positive condition of the body. Here food processing processes take place for its further absorption by other organs. Disruption of the stomach leads to both external and internal negative changes.
Gastroduodenitis is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of the lower part of the stomach and upper duodenum. Under the influence of negative factors, the functioning of the secretion regulation system is disrupted, which leads to excessive activity of gastric juice and bile entering the stomach cavity. Under the influence of these aggressive chemicals, irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs.
In the advanced phase, neighboring organs are affected: the pancreas and bile ducts. Without proper treatment, a stomach ulcer or malignancy may develop. In the system of therapeutic measures for gastroduodenitis, diet occupies a special place. Systematic proper and balanced nutrition helps to cope with the unpleasant symptoms of the disease and completely eliminates its cause - inflammation.
What is stomatitis?
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. According to statistics, about 20% of the population of our planet faces it. In adults and children, it can take the form of an independent disease or act as a symptom indicating pathologies of the body. In both cases, treatment is carried out comprehensively and under the supervision of a doctor.
What does the disease look like?
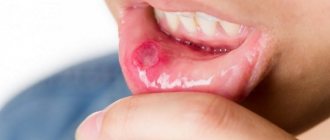
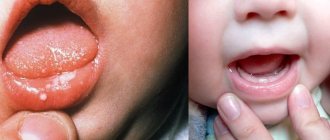
Stomatitis is not difficult to recognize. The initial stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of mild swelling of the oral mucosa. It becomes redder, drier and shiny. A plaque may appear on its surface, and at the site of future lesions the patient feels an unpleasant itching or burning sensation.
As the disease develops, small ulcers and wounds appear on the mucous membrane - painful oval or round lesions. Their location may be the inside of the lips, cheeks, palate, tonsils, or mucous membrane under the tongue. Their appearance can be seen in the photo at the end of our article.
Causes of stomatitis
The mechanism of stomatitis is not yet fully understood. But scientists are inclined to believe that the root cause of its development is the reaction of the human immune system to various irritants. At some point, the immune system ceases to recognize the potential threat of internal and external factors, which causes its atypical reaction, as a result of which “aggressive behavior” of lymphocytes is observed. The attack of lymphocytes against irritant molecules leads to lesions of the oral mucosa.
A variety of factors can provoke an atypical reaction of the immune system. The most likely of them are the following irritants:
- Pathogenic microorganisms that live in the mouth.
- Improper oral hygiene.
- Various damage to the mucous membrane, for example, burns from eating too hot food or mechanical injuries from seeds, nuts, crackers and other hard foods.
- General dehydration due to high fever, blood loss, vomiting, diarrhea, or thirst.
- Poor quality treatment of teeth and gums.
- An allergic reaction to dental structures in the mouth - braces, implants, crowns, bridges, etc.
- Long-term use of medications.
- A diet depleted of beneficial vitamins and elements.
- Smoking.
- Malignant formations of the oral cavity, respiratory organs or undergoing a course of chemotherapy.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body, for example in pregnant women or children during puberty.
- The presence of chronic diseases or allergies.
- Severe stress.
Interesting to know! Frequent stomatitis in adults can be caused by the use of toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate, a substance added to oral care products to form a thick foam. According to recent studies, it dehydrates the oral mucosa and makes it vulnerable to various types of irritants. Patient observation data confirms the fact that avoiding the use of sodium lauryl sulfate paste can reduce the risk of developing stomatitis in adults by 81%.
Causes of aphthous stomatitis
The exact cause of this disease remains unclear. It is assumed that HRAS is of an allergic nature; allergens can include: food, medicine, toothpastes, dust, worms.6,7 It is also assumed that the cause of the disease is an autoimmune reaction.8 A hereditary predisposition to this disease can be traced.
Predisposing factors:
- diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, gastric ulcer, cholecystitis, Crohn's disease)
- dysbacteriosis
- stress
- deficiency of iron, vitamins B1, B2, B6, B12, C
- chronic tonsillitis, otitis and rhinitis
Symptoms of the disease
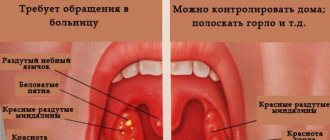
Stomatitis can occur at any age. In the early stages, its course is accompanied by swelling, redness and dryness of the oral mucosa. The main sign of the disease is the presence of one or multiple ulcers and their appearance.
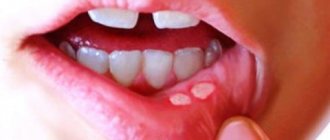
- Oval or round ulcer shape.
- Small sizes.
- Smooth edges.
- The presence of a thin grayish or white film in the central part of the ulcer.
- The ulcer is surrounded by a slightly reddish halo.
- The mucosal tissue around the lesion has a normal, healthy appearance.
The slight itching or burning sensation that the patient experienced at the beginning of the disease is replaced by pain. The ulcers hurt when eating, talking and smiling broadly. Any touch to them causes pain, which complicates hygiene measures and leads to bad breath.
On average, the disease lasts from 4 to 14 days. Its clinical picture depends on the individual characteristics of the organism, the form and type of the disease. During this period, in addition to the main signs of pathology, other symptoms of the disease may be observed.
- Increase in temperature - during the first days, until characteristic ulcers appear (in severe forms of stomatitis, the elevated temperature persists throughout the entire illness).
- General malaise and fatigue.
- Chills.
- Headache.
- Lack of appetite (especially in children).
- Enlarged lymph nodes (in rare cases).
Important to remember! Severe inflammation, toothache or high temperature for a long time indicate a severe form of stomatitis or the development of its complications. In this case, immediate medical attention is required, and if necessary, hospitalization of the patient is possible.
Can stomatitis go away on its own?
As a rule, mild forms of the disease caused by trauma to the mucous membrane, poor oral hygiene or an allergic reaction of the body can go away on their own. Severe stomatitis caused by infection requires qualified treatment. In both cases, it is better not to wait and not to self-medicate. Because the disease not only causes pain and discomfort, but can also lead to generalization of infection and serious complications.
Consequences and complications of the disease
Possible complications arise when the patient ignores treatment for stomatitis. As a result, mild and severe forms of the disease become chronic. The neglected process turns into an ulcerative-necrotic and then gangrenous form of the disease, as a result of which not only the mucous membrane is damaged, but also the soft tissues of the mouth and jaw bones.
Other serious consequences of untreated stomatitis include the following complications.
- Bleeding gums.
- Scarring of the oral mucosa, disruption of its elasticity and mobility.
- Attachment of a secondary infection.
- Tooth loss.
- Voice changes – hoarseness, hoarseness.
Important to remember! A small ulcer on the oral mucosa is a potential threat to the entire body. Infection from it can spread to other organs and systems, which will disrupt the functions of the heart, liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and respiratory organs.
Stomatitis is...
This is the name of the inflammatory process on the oral mucosa, accompanied by the formation of ulcers (ulcers). People of all ages are susceptible to the disease, but children especially. This is explained by the failure of the immune system and the fact that the child is not yet fully accustomed to personal hygiene. In adulthood, the appearance of aphthae in the mouth may signal a weakening of the body, metabolic or digestive system dysfunction.
If the diagnosis of stomatitis is established, it is necessary to urgently begin therapy. Propolis will help with stomatitis in combination with other medications.
Folk remedies
For treatment, you can use traditional medicine. The following juices, decoctions, oils and infusions have proven themselves well.
You can gently lubricate the affected areas of the mucous membrane with juices and oils. Solutions and decoctions of herbs are used for regular rinsing of the mouth.
Important! Before using traditional medicine, you should consult a doctor. Only a specialist can determine the advisability of their use without harm to health. The use of folk remedies does not cancel the main therapy, but only complements its effect.
Preventive measures with propolis
Propolis is not only a good medicine, it is also useful for prevention. If you start using it when the initial symptoms of stomatitis occur, you can quickly get rid of the disease. However, in advanced stages it is necessary to visit a doctor.
The product increases the body's resistance to infections and helps avoid stomatitis, which is a sign of weakened immunity.
Propolis products can quickly cure the initial stage of stomatitis. But some of its forms require the use of antibacterial and other drugs. In this case, traditional methods of treatment are used as an additional method. The bee bar has proven itself to be a good preventive measure for many dental diseases.
How many days does treatment last?
Correct, competent treatment of stomatitis significantly speeds up the healing process. Depending on the type of disease, it lasts for 3 to 7 days. If after 1 week of treatment the signs of the disease have not disappeared or worsening is observed, then the patient most likely has complications. The following factors may be the probable reasons for its development.
- The patient self-medicated or did not follow the doctor's instructions.
- Decreased immunity.
- The presence of chronic diseases of the body.
- Regular injury or infection of the oral mucosa.
- Undiagnosed allergy.
- Having bad habits - smoking, chewing, etc.
- Depression or frequent stress.
- Improper oral hygiene.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- The use of oral hygiene products containing sodium lauryl sulfate.
Returning to the question - can stomatitis go away on its own - it should be noted that a seemingly harmless disease can turn into serious problems for the patient. Therefore, you should remember three “don’ts” - don’t
engage in self-medication,
do not
put off visiting a specialist and
do not
ignore the recommendations of your doctor.
How to understand that stomatitis has passed?
Very simple! A complete cure is indicated by the absence of lesions in the oral mucosa. There are no small ulcers, wounds or plaque on the cheek, palate, lip, tongue or tonsil area. The mucous membrane looks healthy, is well moisturized, does not cause pain and does not create discomfort during eating, talking, smiling and performing hygiene procedures.
Types of stomatitis in adults
The clinical picture of the disease indicates that stomatitis can be mild or severe, have an acute or chronic course. To facilitate the diagnosis and treatment process, experts have developed the following classification of the disease.
- Allergy is usually a chronic disease that occurs as a result of an allergic reaction of the body to an irritant. In addition to the characteristic ulcers, it may be accompanied by the appearance of white spots, blisters and small hemorrhages on the mucous membrane.
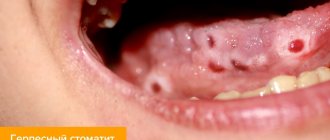
- Herpetic or herpes - the disease occurs due to the entry of the causative agent of the herpes virus into the human body. Stomatitis of this type is characterized by an acute course. Bubbles appear on the surface of the mucous membrane, which open to form erosions and crusts.
- Traumatic (bacterial) – a consequence of mechanical trauma to the oral mucosa and infection entering the wound. As a rule, the disease is mild, with symptoms characteristic of stomatitis.
- Catarrhal and catarrhal-hemorrhagic stomatitis is a mild form of stomatitis, the causes of which are poor oral hygiene, the development of candidiasis, decreased immunity or gastrointestinal pathologies. The disease is accompanied by a typical clinical picture for the disease.
- Candidal (fungal) stomatitis is an acute form of the disease, the so-called thrush, caused by the activity of bacteria of the genus Candida. It is most common in young children, the elderly, and patients who overuse antibiotics. Accompanied by the appearance of a white coating on the mucous membrane, a burning sensation and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Ulcerative is a severe form of the disease that occurs independently or as a result of a complication of the catarrhal course of stomatitis. It occurs acutely, with increased body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes. The resulting ulcers are very painful and can unite and form extensive lesions of the mucous membrane.
- Aphthous stomatitis is a severe form of the disease, occurring acutely or chronically. Accompanied by the appearance of single or multiple gray-white ulcers. The ulcers are surrounded by a red halo and are very painful.
It is important to know! By analyzing the condition of the oral mucosa, the nature of the ulcers and the patient’s complaints, specialists accurately determine the type of stomatitis and make an accurate diagnosis. Thanks to this, treatment of the disease occurs quickly and without complications.
How does propolis relieve pain and prevent infections?
Propolis contains a large amount of flavonoids - plant substances with antioxidant properties, giving it an antimicrobial effect. Caffeic acid present in propolis also has antibacterial properties. Propolis also has pronounced anesthetic and anti-inflammatory properties.
In one animal study, propolis extract demonstrated inflammation-reducing properties comparable to those of diclofenac, a pharmaceutical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Has there been a clinical study aimed at identifying the effectiveness of propolis for aphthous stomatitis?
Yes. In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study published in the journal Clinical Oral Investigations in 2007, people with canker sores were given either 500 mg of propolis per day or a placebo. The researchers noted that 60% of patients in the study group taking propolis experienced a greater than 50% reduction in the frequency of canker sores.
The team recommends the use of propolis to treat canker sores and also calls for larger studies.
Which doctor should I contact for stomatitis?
If you notice the first signs of damage to the oral mucosa, you should immediately consult a dentist. After differential diagnosis of the disease and an accurate diagnosis, it is possible to observe it with a general practitioner or other specialized specialist, for example, an allergist.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
How does propolis prevent the development of caries?
In a scientific review published in 2009 in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, analyzing numerous studies of propolis conducted from 1978 to 2008, the authors concluded that propolis extract reduces the level of streptococci (bacteria responsible for the development of dental caries) in saliva, thereby significantly preventing their adhesion to tooth enamel. The authors concluded that propolis is a promising cariostatic (caries-preventing) agent.
In addition, the effectiveness of propolis is being studied for its use in the treatment of severe periodontal diseases, as well as how effectively it strengthens tooth enamel.
How to distinguish stomatitis from other diseases?
The main sign of stomatitis is the presence of characteristic ulcers, the tissue around which looks healthy. The disease is rarely accompanied by systemic symptoms and, as a rule, recurs from time to time. For a competent specialist, it is not difficult to distinguish stomatitis from other ailments.
For a sore throat
When you have a sore throat, your body temperature always rises. In this case, it is not the ulcers themselves that hurt, but the throat area. Upon visual examination, the tonsils appear swollen, inflamed and red.
For herpes
The problem is that herpetic stomatitis is one of the manifestations of herpes. A viral disease is accompanied by the formation of characteristic blisters that burst and dry out. In the presence of other types of stomatitis, the nature of the ulcers is completely different.
For cancer
Ulcers due to cancer of the oral mucosa do not go away on their own even after treatment. Over time, they increase in size and may bleed and become painful.
From thrush
Candidal stomatitis is thrush caused by the activity of bacteria of the genus Candida. In all other cases, the nature of the disease will be different and can be easily distinguished from thrush by the presence of characteristic ulcers.
For syphilis
When infected with syphilis, a red spot appears on the surface of the mucous membrane. Gradually it thickens, takes the form of a dense nodule and ulcerates - a typical hard chancre is formed, which is completely different from ulcers with stomatitis.
Pharmaceutical product based on propolis
One of the most popular pharmaceutical products based on propolis is Proposol. This is an effective topical drug that fights pathogenic bacteria. The tincture also has a wound-healing and antiseptic effect.
The medicine is made from propolis, alcohol and glycerin. Proposol in aerosol form is used to treat diseases of the teeth and oral mucosa. Quickly relieves signs of stomatitis, glossitis, gingivitis.
Aerosol Proposol is used for the treatment of inflammatory processes only in patients over 12 years of age and after the drug has been approved by a doctor.
Pharmacy propolis tincture is also used to treat the disease. It is diluted in water, rinsed and wiped daily until the erosions are completely healed.
Recommendations during treatment
Treatment of stomatitis should be carried out comprehensively - local therapy, taking medications appropriate to the type of disease, and strengthening the immune system. During the treatment period, you must adhere to the following recommendations.
- Compliance with the diet - you need to exclude from the diet spicy, salty, sour, too sweet, smoked, hot, cold and any dishes that are traumatic to the mucous membranes.
- Maintaining oral hygiene . To maintain it, it is necessary to use antiseptic agents that you regularly rinse your mouth with.
- Taking vitamin-mineral complexes that strengthen the body's protective functions.
If the doctor has diagnosed the presence of candidal stomatitis, then you should not drink milk or consume fermented milk products, which activate the activity of pathogenic fungi.
Any medications should be used only as prescribed by a doctor. Especially antibiotics.
It is important to know! It is not recommended to cauterize emerging ulcers with pure alcohol solutions. The only thing that is allowed is treating the lesions with a weak solution of iodine or potassium permanganate.
Prevention
To avoid the occurrence of stomatitis and its relapses, you should adhere to the following recommendations.
- Maintain oral hygiene.
- Avoid using products containing sodium lauryl sulfate.
- Protect the oral mucosa from injury.
- To treat teeth and gums, contact experienced, qualified specialists.
- Balance your diet with healthy foods.
- Strengthen immunity.
- Be attentive to your physical health and psycho-emotional state - if necessary, seek help from specialized specialists.
And do not forget that herpes stomatitis can be transmitted from person to person - follow the rules of hygiene.
What is propolis?
Propolis, or as it is also called “bee glue,” is a resinous substance used by bees to disinfect honeycomb cells and isolate foreign objects in the hive. It consists of a sticky substance collected by bees in the spring from deciduous tree buds, beeswax, resin from coniferous trees and special bee enzymes. Propolis is a natural antibacterial agent that has been used by traditional healers and healers for thousands of years to fight infection and speed up wound healing.
Thanks to modern medical research, many beneficial properties of propolis are known today, which, in addition, is successfully used in dentistry for the treatment of stomatitis and caries.
You can learn in detail about the beneficial properties of propolis and its use here - Propolis: properties, use, contraindications.
Photo of stomatitis
Author: Elena Grunina Dentist-therapist, endodontist. Work experience more than 9 years. The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.