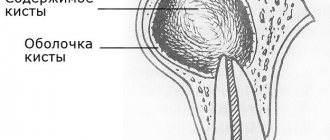
The structure of the formations, their size and type of contents vary, depending on the location and duration of the onset of the pathological process. They are true (inside lined with epithelial cells) and false (without lining). Based on the type of appearance, neoplasms are divided into:
- retention (usually formed due to a disruption in the process of outflow of secretions in tissues and organs, occurring in the mammary glands, uterus, cervix, ovary, etc.);
- ramolitic (usually found in the ovaries, brain and spinal cord, can form in areas of tissue necrosis, for example after a stroke);
- parasitic (appears in different organs, is the shell of the parasite);
- traumatic (due to bruises);
- dysontogenetic (usually congenital, include different tissues of the embryo);
- tumor (formed due to metabolic disorders, have cavities filled with physiological fluids).
Cysts in women and men: symptoms and treatment
In the initial stages of development, cystic elements do not have symptoms. When they grow and suppurate, they manifest themselves differently, depending on the etiology, location, composition of the contents and size. For example, when the ovary is damaged, women complain of a feeling of heaviness and compression of the lower abdomen, pain during menstruation, cycle disruption, etc. With kidney pathology, the lower back hurts and aches, it is difficult to empty the bladder, and jumps in blood pressure are noted.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods depend on the location of cystic formations. Most often this is an ultrasound, but MRI, CT, and radiography can also be prescribed. Laboratory tests are also carried out - blood and urine.
Surgery
The intervention tactics are determined by the doctor based on the location, size of the cystic formation and the patient’s complaints. The classic technique is scalpel excision of the tumor along with adjacent tissues. Today, such an operation is performed mainly laparoscopically using an endoscope. Laparoscopy of a cyst is less traumatic, the patient’s recovery lasts one day. You can also choose the method of aspiration (suction) of the contents with further cauterization of the capsule with a laser, liquid nitrogen, radio wave or a special drug for sclerosis of the walls. The removed lesion must be sent for histological examination.
Is surgery necessary?
When making such a diagnosis, many patients wonder whether the cyst needs to be removed. Some tumors, if they are small and do not bother the person, can remain under observation. Others, such as cervical cysts, can have consequences: bacteria accumulate in them, which sooner or later will lead to inflammation or suppuration. The need for removal should be discussed with your doctor.
Healing properties of burdock
Burdock, also known as burdock, contains groups of useful elements that suppress the growth of tumor-like formations. These include.
- Fisterine is an alkaloid with a strong oncoprotective effect.
- Essential oils, saponins and amino acids together normalize the function of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Microelements necessary for the correction of metabolic processes
- Inulin is a polysaccharide, a sugar substitute. Reduces serum cholesterol concentration.
These components are also contained in burdock root. Considering the ease of preparation, it is recommended to use the juice of this plant at home.
To extract juice, take a burdock leaf, cut it, put it through a juicer, then strain and store it in a container inside the refrigerator for up to two days.
The juice is dosed in teaspoons. On the sixth and seventh days of the menstrual cycle - one spoon before breakfast and dinner. On the third and fourth days after menstruation, another spoon is added to lunch. From the fifth to the first day of the next menstruation, the juice is consumed in tablespoons.
When using herbal medicine to combat cancer, notify your doctor. A competent gynecologist analyzes the condition of his patients and selects appropriate therapy to completely get rid of pathological cysts.
The main types of cystic formations
Ovarian
This is a fluid-filled bladder that causes the ovary to enlarge, leading to pain and sometimes infertility. The main reason for its appearance is hormonal imbalance. The disease often occurs without symptoms; when the formation is large, the cycle is disrupted, pain is felt in the lower abdomen, a false urge to urinate occurs, and bleeding occurs outside of menstruation. Methods of surgical treatment: oophorectomy (complete removal of the ovary), laparoscopic cystectomy (excision of the cyst), adenxectomy (surgery to remove the uterine appendages). In most cases, the choice is not classical surgery, but gentle endoscopic removal of the cyst while preserving the patient’s reproductive function.
Read more about ovarian cyst removal
Coccygeal
Most often occurs in men aged 15-30 years. It is an opening in the area of the gluteal fold, approximately 10 cm from the anus. Externally it looks like a fistula. It can be congenital or acquired - due to too much hair in this area. It manifests itself as pain when walking, sitting, redness of the tailbone, a feeling of discomfort and the presence of a foreign body in the area where it is located. At a later stage, pus is released from the hole.
Read more about the treatment of coccygeal cyst
Bartholin gland
Appears due to blockage of the gland duct due to infection or chronic inflammation. The formation has a capsule and is filled with secretion, which gradually gels. If it is large, it interferes with walking and sitting, makes intimate intimacy inaccessible, and can become infected and lead to an abscess. Usually reaches 2 cm, but there are formations up to 9 cm. The main causes are chronic bartholinitis, candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, decreased local immunity.
Where and how to remove a Bartholin gland cyst
Eye
A hollow formation filled with non-inflammatory fluid - products of the activity of the cornea or conjunctiva. May originate from the cornea, iris, conjunctiva and other eye membranes. Causes: inflammation and trauma, congenital anomalies. The disease is manifested by pain, a feeling of fullness, blurred vision, and the presence of translucent dots in the field of vision.
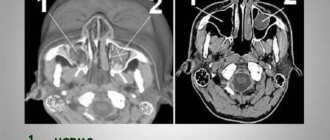
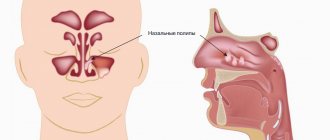
Maxillary sinus
A cavity containing fluid and having a membrane attached to the wall (usually the lower) of the maxillary sinus. A cystic formation can be true (its walls consist of mucous membrane) or pseudocyst (the mucous membrane is split and fluid accumulates in it). It manifests itself as headache, difficulty breathing through the nose, a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the eye and cheek area, mucus discharge from the nose and its flow down the wall of the pharynx, discharge of yellow transparent fluid from the nose, frequent sinusitis with suppuration. It is formed due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the nose, blockage of the excretory duct of the glands of the maxillary sinus, inflammation of the teeth, spreading to the roots.
Read more about the treatment of abscesses and cysts of the ENT organs
Mammary gland
A cavity bounded by a capsule of connective tissue and filled with fluid is formed in the ducts and can be single or multiple. It is formed due to an increase in the duct of the mammary gland, the accumulation of secretions in it. The lesion may be round, oval, or irregular in shape. The disease is asymptomatic for a long time; over time, pain and burning appear in the mammary gland, and may be accompanied by suppuration and inflammation. One of the varieties is a fatty cystic formation that occurs when the sebaceous gland of the skin is blocked and filled with secretions. The main provoking factors are mastitis, thyroid disease, inflammation of the genital organs, and ovarian dysfunction.
Learn more about symptoms and treatments
Uterus and cervix
These are dilated and clogged glands, inside of which secretions (mucus) accumulate. The disease occurs against the background of endocervitis, cervitis. Provoking factors: abortion, childbirth, infections, menopause, hormonal imbalance, use of an intrauterine device, infections. Nabothian cystic formations are localized in the vaginal area of the uterus and are not removed until they reach a certain size. Retention occurs due to an excessive amount of secretion in the gland duct. The disease is often asymptomatic; its indirect signs are frequent inflammation.
Read more about surgical treatment of uterine and cervical cysts
Brain
A cystic formation is an accumulation of fluid in the substance or membranes of the brain. When large in size, it entails intracranial hypertension and puts pressure on the surrounding brain structures. Can form at any age. Depending on the location, cerebral (intracerebral) and arachnoid formations are distinguished. The first are found in the internal structures of the brain, in areas of necrosis. The second ones are in the meninges. Provoking factors: inflammatory diseases, trauma, including birth, cerebrovascular accident, parasites, complications after surgery. They manifest themselves as nausea, a feeling of pressure on the eyes, decreased performance, sleep disturbances, pulsation or noise in the head, and visual impairment.
Thyroid gland
Small formations (up to 5 mm) may not have pronounced symptoms. If the thyroid cyst has dense inclusions and a complicated structure, then special studies (for example, ultrasound), tests and biopsy are needed, because such a condition may be a sign of malignant degeneration.
Read more about surgical treatment of thyroid cysts
Larynx
Cysts of the larynx can be located in any part of the larynx. They do not grow into the mucous membrane, but grow towards the lumen of the larynx and thereby narrow it. The cause of retention cysts is blockage of the excretory ducts of the laryngeal glands. There are cysts of the vocal cords that arise due to constant irritation.
More information about surgical treatment of laryngeal cyst (laryngocele)
You can find out the prices for cyst removal endoscopically or by another method, as well as the cost of preoperative diagnostics on our website or by calling honey. +7 (812) 435 55 55.
Prevention
The best prevention for the development of ovarian cysts is periodic examinations by a gynecologist and a transvaginal ultrasound to assess the condition of all organs of the female reproductive system. Every six months, every woman needs to visit a gynecologist to avoid the development of not only cysts, but also other diseases, including cancer.
Timely consultation with a doctor helps to identify the disease at the earliest stages and begin treatment immediately.
In addition, a woman should avoid excessive stress and sports activities, which disable the hormonal system and can trigger the development of ovarian cysts. Take care of your health, and if unpleasant symptoms appear, trust a specialist.
Gynecologists at MC “Health” are ready to help patients with any problems in maintaining women’s health. An ovarian cyst of any kind is not a death sentence. Our specialists will conduct a full examination, determine the type of cyst and prescribe appropriate treatment as soon as possible.
Diagnostics
The first stage of diagnosing cysts is an examination by a gynecologist in a chair; the doctor may detect unilateral (less often bilateral) enlargement of the ovary; with large cysts, pain is sometimes noted during the examination.
To diagnose ovarian cysts, ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is widely used, which makes it possible to determine the type of cyst, since all the formations described above have their own distinctive features.
In some cases, to make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct repeated ultrasound examinations during one or more menstrual cycles. In case of controversial issues, the doctor may additionally recommend an MRI of the pelvic organs.
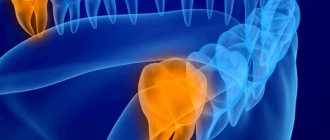
Why does a dental cyst appear?
What is the prerequisite for the appearance of such an unpleasant disease - dental cyst:
- physical trauma;
- periodontitis, peritonitis, pulpitis - inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth;
- residual effects after diseases of the nasopharynx - ARVI, complications after influenza;
- decreased immunity;
- advanced caries process;
- poor oral hygiene;
- development of infection in the root canal;
- poorly placed crown, poor quality filling;
- the appearance of problems with the wisdom tooth.
Prevalence of ovarian cysts
According to various authors, the incidence of ovarian tumors among all gynecological diseases ranges from 8 to 19%.
Foreign researchers claim that more than 80% of women of the reproductive period had a history of an ovarian cyst at least once. However, only 1/4 of them had any clinical manifestations.
In postmenopausal women, the incidence of ovarian tumors ranges from 3 to 18%, but it is at this age that they need to pay special attention due to the high risk of malignancy.