Diseases of the ENT organs belong to the most common category of pathologies occurring in patients of any gender and age. This is due to the heavy load and vulnerability of the ear, nose and throat systems. Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the larynx and vocal cords caused by a cold or infectious disease is called laryngitis.
The inflammation has an acute or chronic course and is characterized by severe symptoms - pain, dryness, a feeling of a “lump” in the throat, bouts of “barking” cough, hoarseness or loss of voice. As the pathology develops, the mucous membrane swells, which is very dangerous in childhood due to the small lumen of the larynx. This is fraught with the development of false croup (obstruction of the upper respiratory tract) in children.
Causes of laryngitis
Inflammation of the larynx most often occurs as a complication of a viral or cold disease, or an infectious disease - scarlet fever, whooping cough, measles, tuberculosis, staphylococcal, streptococcal infections, etc. Laryngitis rarely develops in isolation; usually inflammation of the larynx occurs against the background of diseases of other ENT organs - rhinitis, pharyngitis, tracheitis or bronchitis.
Inflammation can be triggered by prolonged inhalation of polluted air, chemicals, smoking, alcohol abuse, overstrain of the vocal cords and gastroesophageal reflux, etc. The most dangerous is laryngitis of an allergic nature, as a result of which pathological swelling and destruction of the respiratory tract can occur.
Pathology can be caused by contact with infected infectious diseases, trauma or damage to the larynx, or surgical intervention on the respiratory system. Inflammation often occurs when exhaling cold air for a long time or consuming cold foods or drinks, which often happens in children and adults on hot days.
Signs of Quincke's edema
Unexpectedly for parents, the child develops swelling on the face, tongue, feet, lips and other places where there is an accumulation of subcutaneous tissue. The swelling can be large and appears in one place or another. It is painful to the touch and dense. In half of the cases, Quincke's edema occurs along with urticaria. The picture is frightening: very itchy red blisters all over the body, which merge to form bizarre patterns. But there is no need to be afraid; such manifestations do not threaten the child’s life.
But swelling of the larynx can pose a real threat. The child has difficulty breathing, has a barking cough and hoarseness of voice. The child’s facial skin turns sharply blue and then turns pale. A mild degree of laryngeal edema can last up to a day, sometimes longer.
Swelling may occur in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, tingling of the palate and tongue is observed, followed by diarrhea and vomiting. Sharp abdominal pain can occur with swelling of the loose connective tissue of the intestines. The most rare occurrence is swelling of the meninges. The child is lethargic, complains of headaches, and vomits.
General phenomena: joint pain, fever, loss of consciousness can occur even when Quincke's edema is concentrated only on the skin.
Symptoms of the disease
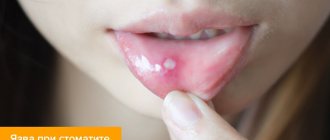
Laryngitis begins with sharp intense pain, soreness and a feeling of a “lump” in the throat. It is difficult and painful for the patient to speak, the voice becomes hoarse. Against the background of hyperemia of the larynx, difficulties with swallowing and breathing may occur. As the disease progresses, symptoms of intoxication appear - headache, fever, chills, weakness. Inflammation is accompanied by a convulsive, hysterical cough that does not bring relief, during which a large amount of sputum is released, sometimes mixed with pus.
Inhalations
To moisturize the mucous surface and eliminate unpleasant symptoms of laryngitis, inhalations are prescribed. They are carried out using traditional methods and pharmaceutical preparations.
Most often, manipulations are done with saline solution, essential oils, mucolytics, hormonal, anti-inflammatory and decongestant agents. Infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs and alkaline mineral waters are also used.
The procedure can be carried out using a special device, or in the usual way at home. Its duration should not exceed 15 minutes in one approach.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment procedures will vary depending on the cause of the disease. All patients, and especially children, are prescribed bed rest, complete rest of the vocal cords, plenty of warm drinks, gargling, and inhalations. Local medications are prescribed; for bacterial diseases, antibiotics; for allergies, antihistamines.
For severe coughs, antitussive drugs and agents that increase sputum production are recommended. If there is purulent-serous plaque on the walls of the larynx and vocal cords, the doctor will irrigate and wash the walls with medications. Physiotherapeutic procedures are very effective - ultraviolet irradiation, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, etc.
Treatment of acute laryngitis takes 7-10 days and does not cause complications. If adequate therapy is not available, the disease can become chronic with constant exacerbations, or lead to dangerous complications.
When the first symptoms of inflammation of the larynx appear, you should immediately seek qualified help. Otolaryngologists at the Hayde Clinic will conduct a qualified examination and prescribe effective treatment for laryngitis and its complications, which will help you quickly get rid of unpleasant and painful symptoms and return to a full life. You can make an appointment by phone: 8 (812) 322-93-07, 8 (812) 611-08-26.
Acute and chronic laryngitis
What can you do if you have a sore throat and lost your voice?
Acute and chronic laryngitis: symptoms and treatment in adults and children
Laryngitis is “ubiquitous.” It affects teachers and students, lecturers and students, singers, announcers and those whose profession is not associated with vocal strain. It appears in the cold season, when, having frozen or wet feet, the next morning you feel a telltale sore throat. Again, laryngitis and its symptoms interfere with life. Or in the summer you enjoy the coolness of the air conditioner, drink cold water and then wonder why your throat hurts and your voice has disappeared. More than 2,000,000 residents of Russia, according to official statistics, get sick every year. And almost half of them are children, in whom acute laryngitis often causes serious complications.
When to see a doctor? And when will it “go away on its own”?
Many people ignore the symptoms. Just think, your throat is sore, your voice has sunk and it’s painful to swallow. Just something to do. Type “laryngitis symptoms and treatment” into a search engine, a couple of tablets, at best, gargle, drink hot tea, and go to work.
However, with laryngitis, everything can go according to a different “scenario”. For example, when the infection spreads down the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, tracheitis begins, then bronchitis. And they take much longer and are more expensive to cure. Therefore, if your condition does not improve or worsens within a few days, consult a doctor.
Moreover, rush to talk to your doctor if a rash appears due to laryngitis, pain radiates to the ear, a severe cough bothers you and it is difficult to breathe.
If complications arise, such as false croup or laryngeal stenosis, minutes count. This often happens in children under 8 years of age. Even in the evening, the symptoms of laryngitis in children are minor, and at night patients begin to cough, turn blue and choke. You need to call an ambulance, go to the hospital to relieve the attack, treat inflammation of the larynx.
The course of the disease during a viral and bacterial process is rarely limited to the larynx. Neighboring areas are involved and pharyngitis, tracheitis, and bronchitis begin.
How to recognize acute laryngitis? Symptoms in adults and children
If:
- My throat is sore, burning, something is bothering me.
- My throat is dry.
- It became painful to swallow.
- The cough bothers me - first dry, then with phlegm.
- The voice is hoarse or has disappeared altogether.
- The temperature increased to 37.5-38°C.
- If you feel weak or have a headache, call a doctor and get treatment. “Feat of labor” and going to work in this state can cost you dearly.
Call immediately if it is very painful and difficult to swallow, or if you are coughing up blood.
Laryngitis in children, especially young children, develops faster, the temperature is higher, and the condition is more severe. And if difficulty wheezing or a “barking” cough develops, false croup may develop, and you must urgently go to the hospital.
What are the causes of acute laryngitis symptoms?
Due to the introduction of infection, swelling and inflammation of the larynx appears. The following are “to blame” for the disease:
- Influenza viruses, parainfluenza, adenovirus.
- The causative agents of “childhood” infections are measles, diphtheria, whooping cough.
- Bacteria - strepto- and staphylococci. They occur against the background of acute respiratory viral infections or chronic infections, such as tonsillitis.
Chronic laryngitis: symptoms in adults. How to understand why your voice is hoarse
If episodes of acute inflammation are repeated frequently, the process becomes chronic.
The temperature is normal, when there is no exacerbation, the general condition does not change. Patients are concerned about dryness, sore throat, hoarse voice, deep throat, and constantly want to clear their throat. When an exacerbation occurs, the symptoms of chronic laryngitis intensify.
Inflammation of the larynx rarely occurs as an independent disease. More often it accompanies other conditions. For example, it is a concern for chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, reflux disease - the reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus.
Other causes of chronic laryngitis:
- smoking and alcohol,
- air polluted with dust, smoke, industrial emissions,
- allergens,
- increased vocal load on the voice,
- specific infection - syphilis, tuberculosis.
- chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, circulatory failure, etc.)
The reasons are different, the symptoms are similar. Therefore, without eliminating the cause, searching for “how to treat chronic laryngitis at home” and then gargling with “herbs” and dissolving lozenges is, at a minimum, ineffective.
Who treats - which doctors should I contact?
First of all, if you have a sore throat, lost your voice, have a dry cough, or have other unpleasant sensations, you should make an appointment with an otolaryngologist
. However, there are situations when the participation of other specialists, for example, a gastroenterologist, is necessary in diagnosis and treatment.
How to diagnose laryngitis?
Survey
First, the specialist asks what is bothering you. Tell us in detail about your sore throat, cough, and other uncomfortable sensations. Be sure to report if you have a fever, muscle pain, weakness, or headache.
Next, the otolaryngologist will ask you how long you have had these symptoms and what you did, what medications you took to get rid of them. Be sure to let us know if you smoke, breathe dry, dusty air, have a strained voice, or have allergies.
If you have already had laryngitis, the treatment of which did not give the desired result, you have been tested - take the card and test results with you. Doctors at the Energo clinic with many years of experience take into account all the details in order to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Initial examination
During a general examination, it is noticeable that the patient’s voice has changed.
During an ENT examination of the larynx (laryngoscopy), the doctor sees redness of the laryngeal mucosa throughout, or only in the area of the vocal folds. It is not difficult for an experienced doctor to diagnose laryngitis, the signs of which are thickening, swelling and incomplete closure of the vocal folds.
With chronic inflammation, changes are of a different kind. Depending on the form of chronic laryngitis, the mucous membrane may be reddened and thickened, covered with viscous mucus, and the vocal folds may not close completely. Patients complain of soreness and discomfort in the throat, cough with sputum that is difficult to cough up. Chronic laryngitis in children, the treatment of which is a task for an experienced doctor, manifests itself in exactly this way.
In another form, the mucous membrane grows excessively, and singing “nodules” form on the vocal folds. The main complaint is loss of voice. With atrophy, the mucous membrane becomes thin, covered with crusts, and patients are bothered by a dry, painful cough.
What methods are used for diagnosis?
In most cases, a simple laryngoscopy is sufficient. If there is a suspicion of a bacterial or fungal cause of laryngitis, a smear and bacteriological culture are done.
How to treat laryngitis?
At the first stage of treatment, the doctor decides on the tactics. For acute process and chronic inflammation, treatment is different. This depends on many factors - the form of the disease, the severity of general symptoms, concomitant pathology. The doctor prescribes drugs for the treatment of laryngitis in adults: anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antiseptics, immunomodulators, physiotherapy, according to the form of the disease and concomitant pathology. For a dry, obsessive cough, medications that suppress the cough reflex are prescribed for a short course. You shouldn't prescribe them to yourself. Do you want to know how to quickly cure laryngitis? Follow these rules. During the acute period:
What to do
- Take your medications as prescribed by your doctor.
- Do alkaline (soda solution) inhalations for laryngitis.
- Avoid spicy, sour, hot foods.
- Drink enough fluids.
- Humidify the indoor air.
What not to do
- Don't talk, even in a whisper.
- Do not smoke.
- Don't drink alcohol.
In case of exacerbation of a chronic process, treatment is carried out depending on the form of the disease.
For mucosal atrophy, these are things that improve blood circulation and metabolism: physical procedures, vitamins, biostimulants. If the process is accompanied by thickening of the mucosa, anti-inflammatory drugs are needed.
For catarrhal form, antiallergic and decongestant drugs, expectorants, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory drugs and alkaline inhalations are used.
Plus, gentle mode.
If you are looking for how to treat laryngitis in children, remember: the main thing is not to waste time. All processes in a child’s body proceed much faster, and complications may arise.
At the second stage of treatment, the doctor evaluates the effect of the treatment. With a chronic process, it takes time to get the effect. Be patient and follow your doctor's recommendations.
At the third stage of treatment, after there is a positive result from the treatment, the doctor prescribes a set of measures to prevent exacerbation. Necessary:
- Treat diseases that support laryngitis: pharyngitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes, etc.
- Eliminate factors that provoke exacerbation - stop smoking, reduce contact with ARVI patients if possible, humidify the air.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor: vitamins and medications to increase general and local immunity.
At the fourth stage of treatment, the doctor determines the frequency of follow-up examinations and studies in order to monitor your condition and notice a relapse in time.
What results can be expected from laryngitis treatment?
- Itching and dryness disappear
- Voice is restored
- The cough stops
- The general condition is normalized.
Prevention of laryngitis
Spicy
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle - eat right, don’t get nervous, get enough rest, walk in the fresh air, humidify the indoor air.
- Treat acute respiratory viral infections in a timely and correct manner, do not endure them “on your feet,” and do not allow the process to become chronic.
- Strengthen the immune system: hardening, courses of vitamins, herbal remedies.
- Eliminate factors that have a harmful effect on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract - smoking, alcohol, dust, allergens.
Chronic
- Eliminate factors causing exacerbation.
- Don't get too cold.
- Try to eliminate foci of chronic infection - treat teeth, sinusitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis in a timely manner.
If your throat is sore, hoarse, or your voice has disappeared or you have a cough, you should not wait for laryngitis to “go away on its own.”
The inflammation often spreads further, and more serious diseases will need to be treated. Making an appointment with a doctor and being treated by a specialist is easier than eliminating a chronic process or its complications. Call and schedule a visit. Or make an appointment with our otorhinolaryngologists online on the website.
Why does Quincke's edema occur?
Histamine is a special substance in the human body. It is found in mast cells of connective tissue, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow. After inflammation has occurred, mast cells are activated and release a charge of histamine into the blood. Histamine increases the permeability of vascular walls and dilates capillaries. Blood flow slows down, swelling of the skin tissue appears. For example, with Quincke's edema, the process involves the deep layers of the skin, and with urticaria, only the upper ones. In both cases, accumulations of inflammatory cells (lymphocytes and neutrophils) appear at the site of histamine action.
Quincke's edema appears as a result of non-allergic, allergic and mixed mechanisms:
- Non-allergic reactions occur most often in children. Histamine is released due to exposure to food dyes, medications, and after an insect bite.
- With the allergic mechanism, an allergen enters the body, which is accepted by the body as hostile and launches an attack of immunoglobulins (antibodies) against it. These antibodies attach to the mast cell membrane. Antibodies have a good specific memory; they know exactly what the antigen looks like. If the allergen enters the body again, it binds to the antibody and the mast cell releases histamine. Therefore, Quincke's edema develops precisely when the allergen is repeatedly exposed.
- The mixed form includes hereditary angioedema. The nature of this manifestation may be hereditary, if one of the relatives has previously experienced swelling of the larynx and other organs.
How to avoid getting laryngitis
To protect yourself as much as possible from the development of laryngitis, you need to follow simple rules:
- eliminate bad habits, especially smoking;
- exercise;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- eat a balanced diet;
- keep the premises clean, regularly ventilate, moisturize;
- do not visit crowded places during periods of epidemics;
- avoid environmentally unfavorable habitats.
Compliance with these standards will not completely protect against laryngitis, but the risk will be minimized.
How many days does the temperature last for laryngotracheitis?
Characteristic signs of laryngotracheitis include cough, change in voice (dysphonia), pain in the chest and throat, fever, general weakness, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Cough. It is characterized as dry, “barking” without sputum production. Eating or talking can trigger a coughing attack.
Dysphonia. With laryngotracheitis, the voice is hoarse, hoarse, and sometimes completely disappears.
How many days does the temperature last for laryngotracheitis? In the chronic form, the temperature remains at low-grade levels for the first three to four days.
Chest pain. Painful sensations usually intensify during coughing. The doctor will tell you during your consultation what to do during a coughing attack with laryngotracheitis and how to prevent its onset.
Possible complications are bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia (pneumonia), false croup. The most severe include: laryngeal ulcers, laryngeal ventricular prolapse, benign neoplasms.
Features of drug treatment of laryngotracheitis in adults and children
Laryngotracheitis is an inflammatory disease of the respiratory tract of viral or bacterial etiology.
Symptoms of laryngotracheitis in children: paroxysmal cough, noisy breathing, general weakness, fever. The smaller the child, the more dangerous this pathology is for him. Laryngotracheitis occurs at any age. The disease, which first affects the larynx and then the trachea, quite often develops as a complication of another disease of the respiratory system. The disease has several varieties and requires qualified treatment. In the absence of the latter, there is a high probability of developing severe complications in the form of bronchitis, pneumonia and false croup in children.
Causes of the disease laryngotracheitis:
- ARVI, adenoviral infection;
- parainfluenza;
- rubella, chickenpox;
- mycoplasmosis, staphylococcal and streptococcal infections;
- chlamydia.
The disease most often occurs in people with weakened immune systems. The body's resistance is reduced by chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, duodenitis, gastroenteritis), endocrine system, respiratory tract and diseases of the central nervous system.
On our website Dobrobut.com you will find more information, including on the treatment of laryngotracheitis in adults. Let us recall that the acute form of the disease is more often diagnosed in children, and chronic laryngotracheitis - in adults.
First aid for Quincke's edema
At the first signs of Quincke's edema, you should call a doctor. But before the ambulance arrives, you need to take some measures:
- Stop contact with the allergen, lay the baby down and elevate the limbs.
- If the swelling is caused by an insect bite, a cold compress is applied to the bite site.
- The child needs to be given plenty of fluids to improve microcirculation and remove the allergen from the body. Children over three years old can be offered alkaline drink, Narzan or Borjomi.
- You can give absorbent drugs, such as activated carbon, smecta or enterosgel.
Antiallergic and antihistamine drugs can be given to a child only after consultation with a doctor.
If allergic reactions occur frequently and the child has already had angioedema, ask the doctor to show what drug should be administered to the child and where the medicine should be administered.
It is better to hospitalize the child so that in a hospital setting the reasons that led to Quincke's edema can be identified.
Causes of Quincke's edema
There are many medications that can cause hives or swelling. These may be anticonvulsants, acetylsalicylic acid, antibiotics, iodine preparations, B vitamins, medicinal serums, sulfites, corticosteroids, eye medications, bronchodilators.
Anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs increase skin sensitivity to histamine. This group of drugs is very dangerous for children prone to allergies. Atopic dermatitis and bronchial asthma will increase the risk of developing Quincke's edema.
Many food products, or rather the additives contained in them, also cause an allergic reaction. Such allergenic additives include monosodium glutamate, sulfites, tartrazine dye, etc. Allergies can be caused by Chinese dishes; of course, children are not given seafood, but cases of angioedema caused by the smell of fish have been observed.
Fish, strawberries, lemons, egg whites, bananas, and chocolate contain substances that release intracellular histamine. This is why these foods should not be given to children under three years of age. Some foods themselves contain large amounts of histamine: sausages, sauerkraut, cheese. Hereditary complications, gastrointestinal diseases, allergic reactions in the mother during pregnancy increase the possibility of angioedema.
Quincke's edema can appear from plant pollen. Children from three to nine years old can develop hay fever, an allergic disease caused by hypersensitivity to plant pollen. According to statistics, in 11% of children who suffer from hay fever, the disease is complicated by Quincke's edema.
Insect bites can also cause angioedema. Insect saliva contains histamine and other substances. If parents were allergic to insect bites, then it is better to protect children from this.
Complications
Most often, the pathogen can spread to other organs. This can often lead to heart complications. It is difficult to restore normal functioning of the cardiovascular system after this type of complication.
Often, the consequences can affect other parts of the upper respiratory tract or even spread to the lungs, thereby greatly complicating symptoms and treatment.
It is a mistake to believe that this disease can go away on its own. Also, you should not turn to alternative medicine, which can harm your health if not agreed with a specialist. Self-medication is not the best, since the cause of the disease can be various microorganisms, as well as medications that helped in one situation, but in another can even worsen the disease.
Remember: frequent colds or cases of laryngitis may be the first symptom of immunodeficiency!
Acute form
With an exacerbation of the disease, the symptoms also worsen: the cough becomes even drier and debilitating, enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes with irradiation of pain in the ear can be a concomitant disease with sore throat and scarlet fever.
Chronic form
It occurs when not only the upper and lower respiratory tracts are affected, but also other organs. It has the greatest effect on the heart, so disturbances on its part are possible - tachycardia, arrhythmia. This may be due to direct damage to the organ, or may cause incorrect innervation of the vagus nerve, which provides a conduction system not only to the heart, but also to the diaphragm and intestines. Accordingly, various gastrointestinal disorders associated with its poor, inactive functioning are possible.